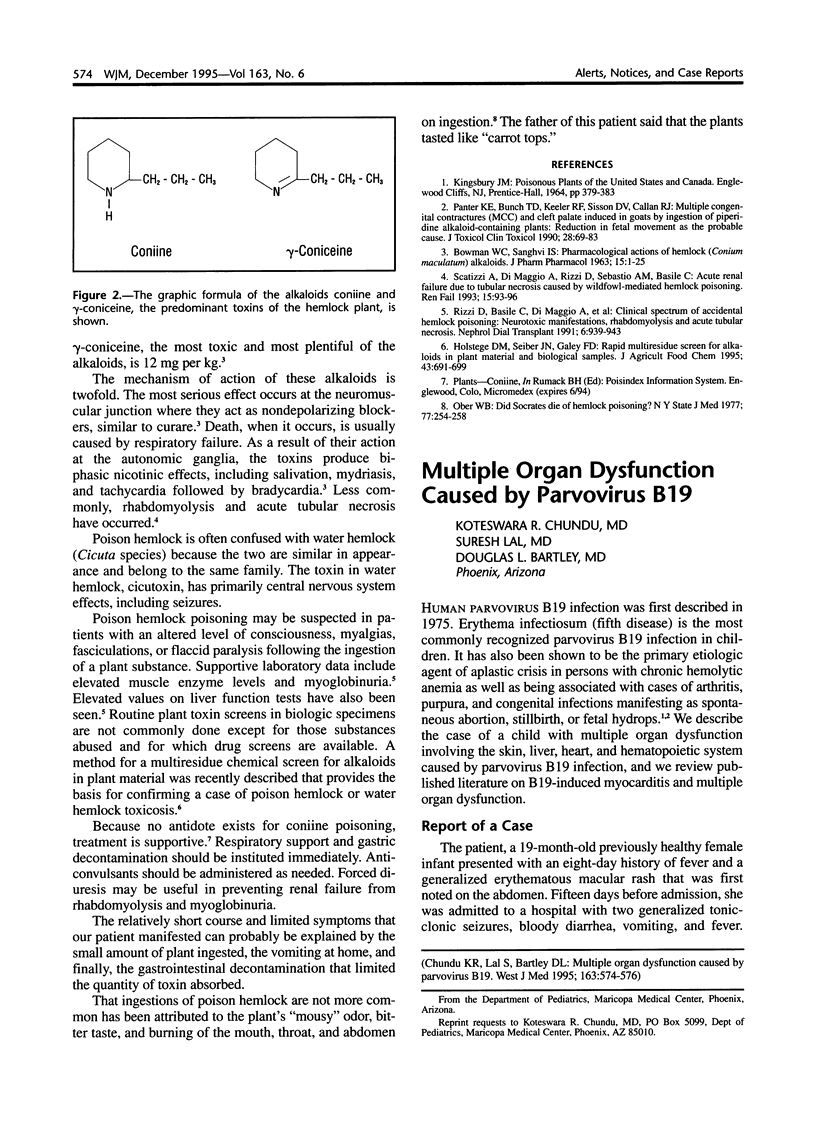
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOWMAN W. C., SANGHVI I. S. Pharmacological actions of hemlock (Conium maculatum) alkaloids. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1963 Jan;15:1–25. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1963.tb12738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ober W. B. Did Socrates die of hemlock poisoning? N Y State J Med. 1977 Feb;77(2):254–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panter K. E., Bunch T. D., Keeler R. F., Sisson D. V., Callan R. J. Multiple congenital contractures (MCC) and cleft palate induced in goats by ingestion of piperidine alkaloid-containing plants: reduction in fetal movement as the probable cause. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1990;28(1):69–83. doi: 10.3109/15563659008993477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi D., Basile C., Di Maggio A., Sebastio A., Introna F., Jr, Rizzi R., Scatizzi A., De Marco S., Smialek J. E. Clinical spectrum of accidental hemlock poisoning: neurotoxic manifestations, rhabdomyolysis and acute tubular necrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1991;6(12):939–943. doi: 10.1093/ndt/6.12.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scatizzi A., Di Maggio A., Rizzi D., Sebastio A. M., Basile C. Acute renal failure due to tubular necrosis caused by wildfowl-mediated hemlock poisoning. Ren Fail. 1993;15(1):93–96. doi: 10.3109/08860229309065580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



