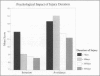
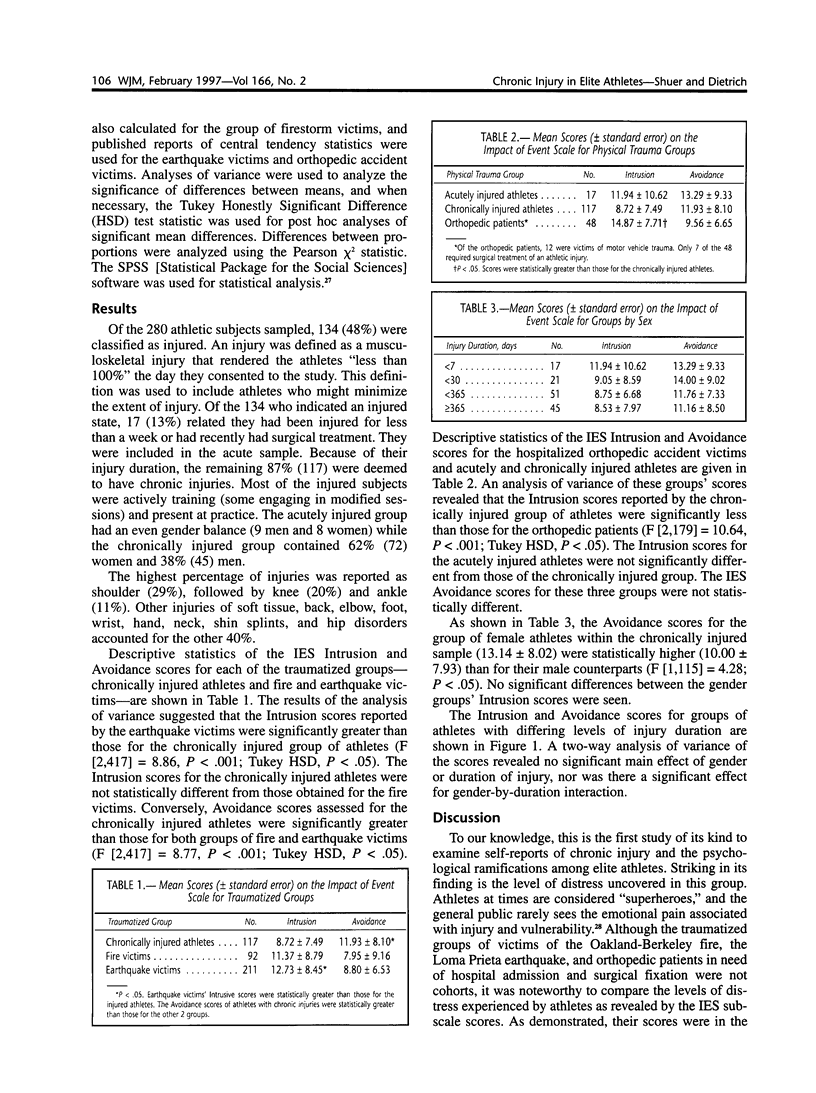
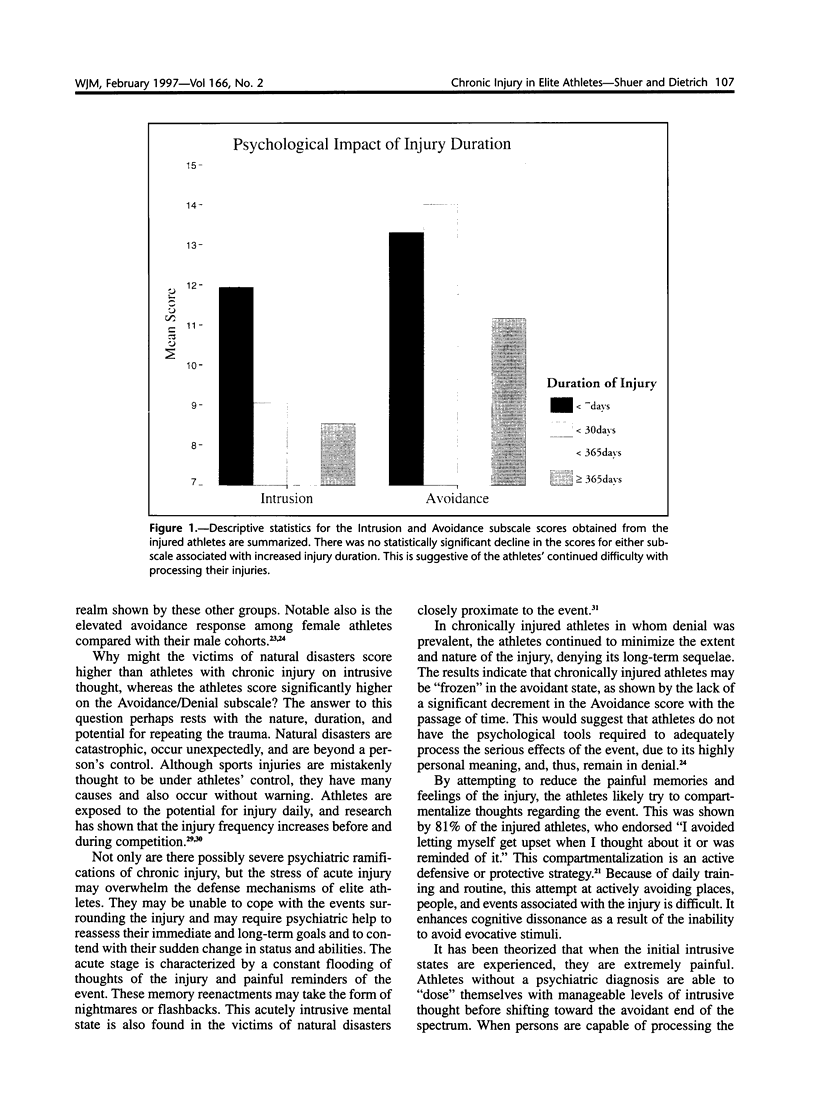
Abstract
Many athletes train in a constant state of pain or injury while meeting the demands of an elite level program. It is hypothesized that the emotional distress experienced by athletes with chronic injuries is not inconsequential. A self-report battery, the Impact of Event Scale, was administered to 280 inter-collegiate athletes at a division I institution in an attempt to examine their response to chronic injury. Of the 280, 134 (48%) had been injured by study definition, with 117 (42%) meeting the criteria for chronic injury. Athletes with chronic injury scored on the Intrusion subscale of the Impact of Event Scale in the range of those who had experienced natural disasters, but scored higher (P < .05) on the Avoidance/Denial subscale. Their Avoidance subscale scores were similar to those of a group of orthopedic patients who required hospital admission with surgical fixation. Female athletes' Avoidance scores were significantly higher than those of their male peers (P < .05), but no gender differences were seen in intrusive thoughts. Subsets of athletes defined by the duration of injury showed no significant differences on subscale scores. It appears extraordinary that athletes should score in the realm of groups traumatized by natural disasters in intrusive thought and higher in avoidance thought when referring to their chronic injury. Although some attention has been focused on psychiatric intervention for acutely injured athletes or those who have undergone surgical treatment, the psychological needs of athletes struggling with chronic "minor" injuries also appear to merit consideration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almekinders L. C., Almekinders S. V. Outcome in the treatment of chronic overuse sports injuries: a retrospective study. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1994 Mar;19(3):157–161. doi: 10.2519/jospt.1994.19.3.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. W. Self-identity and specific vulnerability to depressed mood. J Pers. 1993 Sep;61(3):343–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.1993.tb00284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein A., Dolan R. Predictors of post-traumatic stress disorder following physical trauma: an examination of the stressor criterion. Psychol Med. 1991 Feb;21(1):85–91. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700014689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick J. G., Requa R. K. Injuries in high school sports. Pediatrics. 1978 Mar;61(3):465–469. doi: 10.1542/peds.61.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Hanrahan S. J., Stewart R. M. Attributions for rapid or slow recovery from sports injuries. Can J Sport Sci. 1990 Jun;15(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M. J. Stress-response syndromes: a review of posttraumatic and adjustment disorders. Hosp Community Psychiatry. 1986 Mar;37(3):241–249. doi: 10.1176/ps.37.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M. J., Wilner N., Kaltreider N., Alvarez W. Signs and symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980 Jan;37(1):85–92. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1980.01780140087010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Wilner N., Alvarez W. Impact of Event Scale: a measure of subjective stress. Psychosom Med. 1979 May;41(3):209–218. doi: 10.1097/00006842-197905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaasa S., Malt U., Hagen S., Wist E., Moum T., Kvikstad A. Psychological distress in cancer patients with advanced disease. Radiother Oncol. 1993 Jun;27(3):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(93)90073-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman C., Classen C., Cardeña E., Spiegel D. When disaster strikes, acute stress disorder may follow. J Trauma Stress. 1995 Jan;8(1):29–46. doi: 10.1007/BF02105405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman C., Classen C., Spiegel D. Predictors of posttraumatic stress symptoms among survivors of the Oakland/Berkeley, Calif., firestorm. Am J Psychiatry. 1994 Jun;151(6):888–894. doi: 10.1176/ajp.151.6.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leddy M. H., Lambert M. J., Ogles B. M. Psychological consequences of athletic injury among high-level competitors. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1994 Dec;65(4):347–354. doi: 10.1080/02701367.1994.10607639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. C. Avoidance and intrusion in posttraumatic stress disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1992 Jul;180(7):439–445. doi: 10.1097/00005053-199207000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeuwisse W. H., Fowler P. J. Frequency and predictability of sports injuries in intercollegiate athletes. Can J Sport Sci. 1988 Mar;13(1):35–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pen L. J., Fisher C. A. Athletes and pain tolerance. Sports Med. 1994 Nov;18(5):319–329. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199418050-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie T. A. Psychosocial antecedents of athletic injury: the effects of life stress and social support on female collegiate gymnasts. Behav Med. 1992 Fall;18(3):127–138. doi: 10.1080/08964289.1992.9936963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rynearson E. K., McCreery J. M. Bereavement after homicide: a synergism of trauma and loss. Am J Psychiatry. 1993 Feb;150(2):258–261. doi: 10.1176/ajp.150.2.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. M., Scott S. G., O'Fallon W. M., Young M. L. Emotional responses of athletes to injury. Mayo Clin Proc. 1990 Jan;65(1):38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. M., Stuart M. J., Wiese-Bjornstal D. M., Milliner E. K., O'Fallon W. M., Crowson C. S. Competitive athletes: preinjury and postinjury mood state and self-esteem. Mayo Clin Proc. 1993 Oct;68(10):939–947. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson T. L., Hershman E. B., Nicholas J. A. Rehabilitation of the injured athlete. Pediatrician. 1990;17(4):262–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberg N. J., Weiss D. S., Horowitz M. J. Impact of Event Scale: a cross-validation study and some empirical evidence supporting a conceptual model of stress response syndromes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1982 Jun;50(3):407–414. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.50.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]