Abstract
Achalasia, diffuse esophageal spasm, and nutcracker esophagus constitute the main primary esophageal motility disorders. During the past decade major progress has been made in understanding their pathophysiology and in the ability to establish a precise diagnosis. In addition, minimally invasive surgical intervention has radically changed the therapeutic approach, and thoracoscopic or laparoscopic myotomy is probably the best treatment for most patients.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abid S., Champion G., Richter J. E., McElvein R., Slaughter R. L., Koehler R. E. Treatment of achalasia: the best of both worlds. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Jul;89(7):979–985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achem S. R., Kolts B. E., Wears R., Burton L., Richter J. E. Chest pain associated with nutcracker esophagus: a preliminary study of the role of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1993 Feb;88(2):187–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggestrup S., Uddman R., Sundler F., Fahrenkrug J., Håkanson R., Sørensen H. R., Hambraeus G. Lack of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide nerves in esophageal achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1983 May;84(5 Pt 1):924–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ancona E., Anselmino M., Zaninotto G., Costantini M., Rossi M., Bonavina L., Boccu C., Buin F., Peracchia A. Esophageal achalasia: laparoscopic versus conventional open Heller-Dor operation. Am J Surg. 1995 Sep;170(3):265–270. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(05)80012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benini L., Sembenini C., Castellani G., Bardelli E., Brentegani M. T., Giorgetti P., Vantini I. Pathological esophageal acidification and pneumatic dilitation in achalasic patients. Too much or not enough? Dig Dis Sci. 1996 Feb;41(2):365–371. doi: 10.1007/BF02093830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonavina L., Nosadini A., Bardini R., Baessato M., Peracchia A. Primary treatment of esophageal achalasia. Long-term results of myotomy and Dor fundoplication. Arch Surg. 1992 Feb;127(2):222–227. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420020112016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castell D. O., Katzka D. A. Botulinum toxin for achalasia: to be or not to be? Gastroenterology. 1996 May;110(5):1650–1652. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.agast961650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Braghetto I., Henríquez A., Cortés C. Late results of a prospective randomised study comparing forceful dilatation and oesophagomyotomy in patients with achalasia. Gut. 1989 Mar;30(3):299–304. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies H. A., Lewis M. J., Rhodes J., Henderson A. H. Trial of nifedipine for prevention of oesophageal spasm. Digestion. 1987;36(2):81–83. doi: 10.1159/000199403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., O'Sullivan G. C., Bermudez G., Midell A. I., Cimochowski G. E., O'Drobinak J. Esophageal function in patients with angina-type chest pain and normal coronary angiograms. Ann Surg. 1982 Oct;196(4):488–498. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198210000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr Esophagomyotomy for noncardiac chest pain resulting from diffuse esophageal spasm and related disorders. Am J Med. 1992 May 27;92(5A):129S–131S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr, Gibb S. P., Crozier R. E. Esophagomyotomy for achalasia of the esophagus. Ann Surg. 1980 Aug;192(2):157–161. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198008000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis F. H., Jr Oesophagomyotomy for achalasia: a 22-year experience. Br J Surg. 1993 Jul;80(7):882–885. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. K. Achalasia: current evaluation and therapy. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991 Aug;52(2):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(91)91373-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. D., Ryder D., Marryatt G. Extended esophageal myotomy and short total fundoplication hernia repair in diffuse esophageal spasm: five-year review in 34 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1987 Jan;43(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)60161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaakkola A., Reinikainen P., Ovaska J., Isolauri J. Barrett's esophagus after cardiomyotomy for esophageal achalasia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1994 Feb;89(2):165–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy K. S., Grider J. R., Jin J. G., Makhlouf G. M. Interplay of VIP and nitric oxide in the regulation of neuromuscular activity in the gut. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1995 Jan-Feb;329(1):27–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okike N., Payne W. S., Neufeld D. M., Bernatz P. E., Pairolero P. C., Sanderson D. R. Esophagomyotomy versus forceful dilation for achalasia of the esophagus: results in 899 patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 1979 Aug;28(2):119–125. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)63767-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Rai R., Ravich W. J., Hendrix T. R., Kalloo A. N. Botulinum toxin for achalasia: long-term outcome and predictors of response. Gastroenterology. 1996 May;110(5):1410–1415. doi: 10.1053/gast.1996.v110.pm8613045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasricha P. J., Ravich W. J., Hendrix T. R., Sostre S., Jones B., Kalloo A. N. Intrasphincteric botulinum toxin for the treatment of achalasia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Mar 23;332(12):774–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199503233321203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patti M. G., Pellegrini C. A., Arcerito M., Tong J., Mulvihill S. J., Way L. W. Comparison of medical and minimally invasive surgical therapy for primary esophageal motility disorders. Arch Surg. 1995 Jun;130(6):609–616. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430060047009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
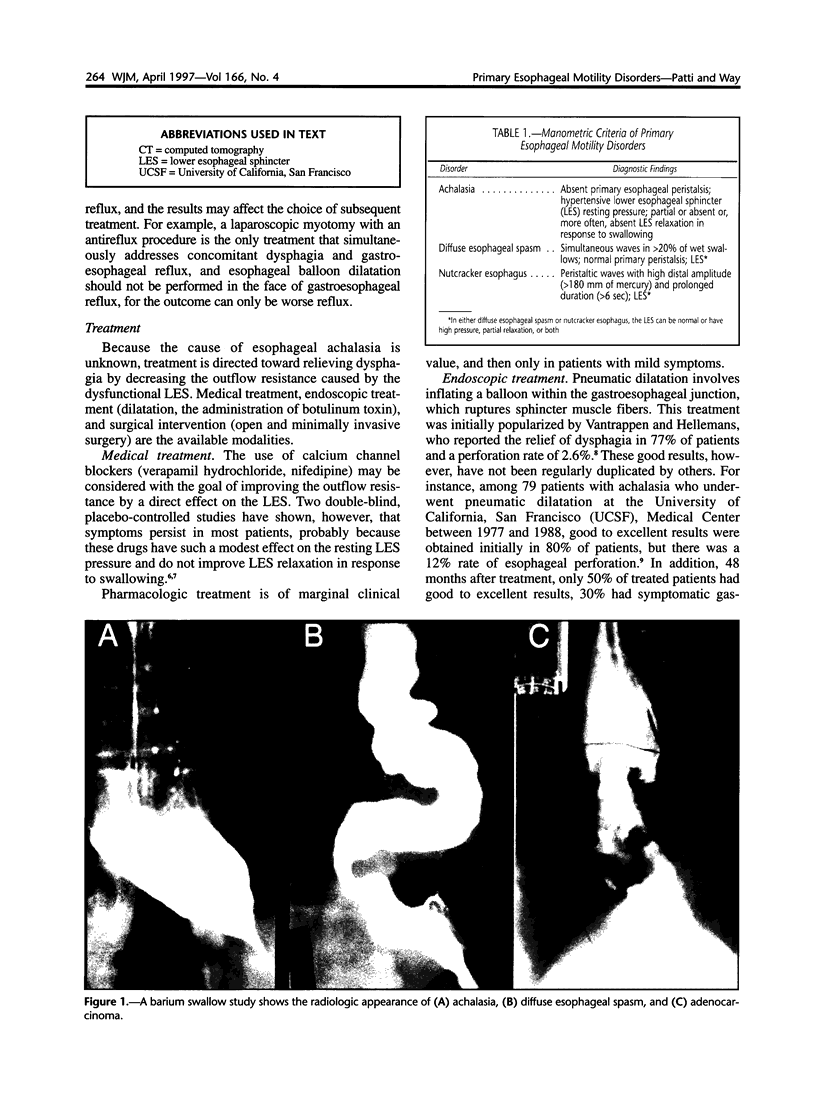
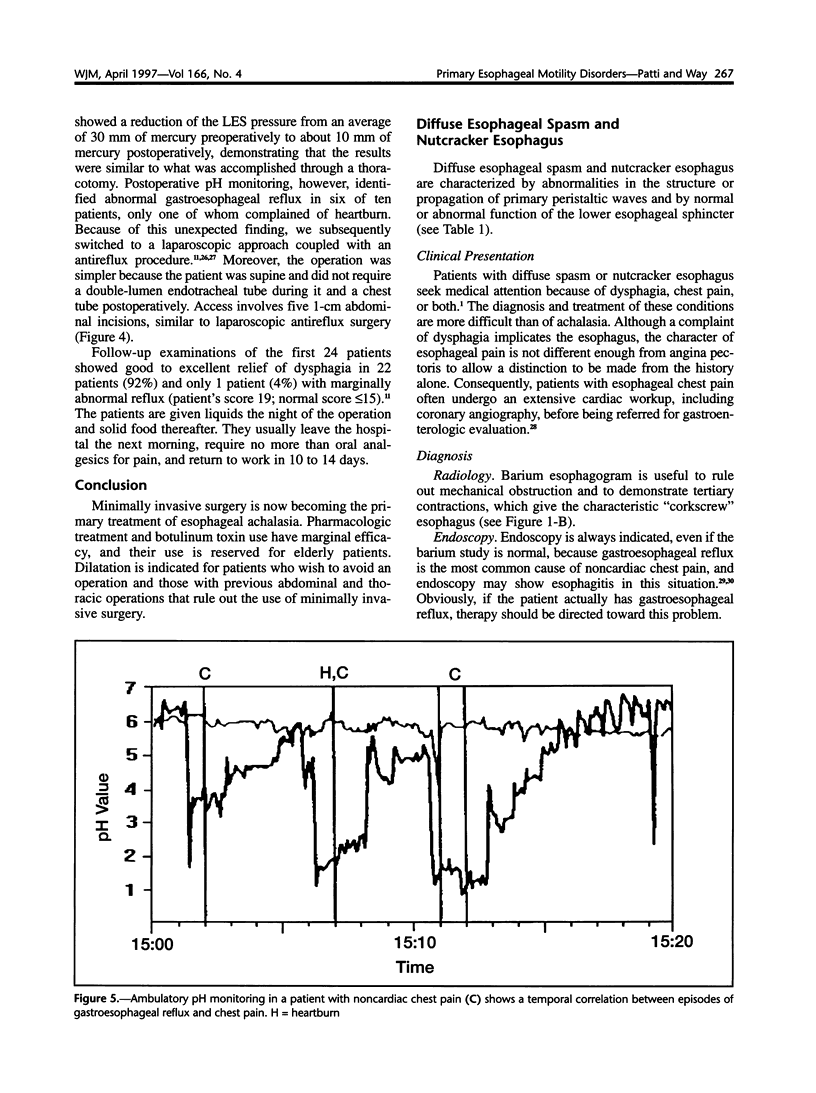
- Patti M. G., Pellegrini C. A. Endoscopic surgical treatment of primary oesophageal motility disorders. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1996 Jun;41(3):137–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini C., Wetter L. A., Patti M., Leichter R., Mussan G., Mori T., Bernstein G., Way L. Thoracoscopic esophagomyotomy. Initial experience with a new approach for the treatment of achalasia. Ann Surg. 1992 Sep;216(3):291–299. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199209000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. E., Dalton C. B., Bradley L. A., Castell D. O. Oral nifedipine in the treatment of noncardiac chest pain in patients with the nutcracker esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter J. E., Dalton C. B., Buice R. G., Castell D. O. Nifedipine: a potent inhibitor of contractions in the body of the human esophagus. Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with the nutcracker esophagus. Gastroenterology. 1985 Sep;89(3):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer L., Pellegrini C. A., Way L. W. The treatment of achalasia. A current perspective. Arch Surg. 1989 Aug;124(8):929–932. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410080061009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoenut J. P., Micflikier A. B., Yaffe C. S., Den Boer B., Teskey J. M. Reflux in untreated achalasia patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1995 Jan;20(1):6–11. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199501000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streitz J. M., Jr, Ellis F. H., Jr, Williamson W. A., Glick M. E., Aas J. A., Tilden R. L. Objective assessment of gastroesophageal reflux after short esophagomyotomy for achalasia with the use of manometry and pH monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1996 Jan;111(1):107–113. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5223(96)70406-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom L. L., Pennings J. Laparoscopic esophagomyotomy for achalasia. Surg Endosc. 1995 Mar;9(3):286–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00187770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traube M., Dubovik S., Lange R. C., McCallum R. W. The role of nifedipine therapy in achalasia: results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;84(10):1259–1262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadafilopoulos G., Aaronson M., Sackel S., Burakoff R. Medical treatment of esophageal achalasia. Double-blind crossover study with oral nifedipine, verapamil, and placebo. Dig Dis Sci. 1991 Mar;36(3):260–267. doi: 10.1007/BF01318193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vantrappen G., Hellemans J. Treatment of achalasia and related motor disorders. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jul;79(1):144–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrmann T., Jacobi V., Jung M., Lembcke B., Caspary W. F. Pneumatic dilation in achalasia with a low-compliance balloon: results of a 5-year prospective evaluation. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995 Jul;42(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(95)70239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



