Abstract
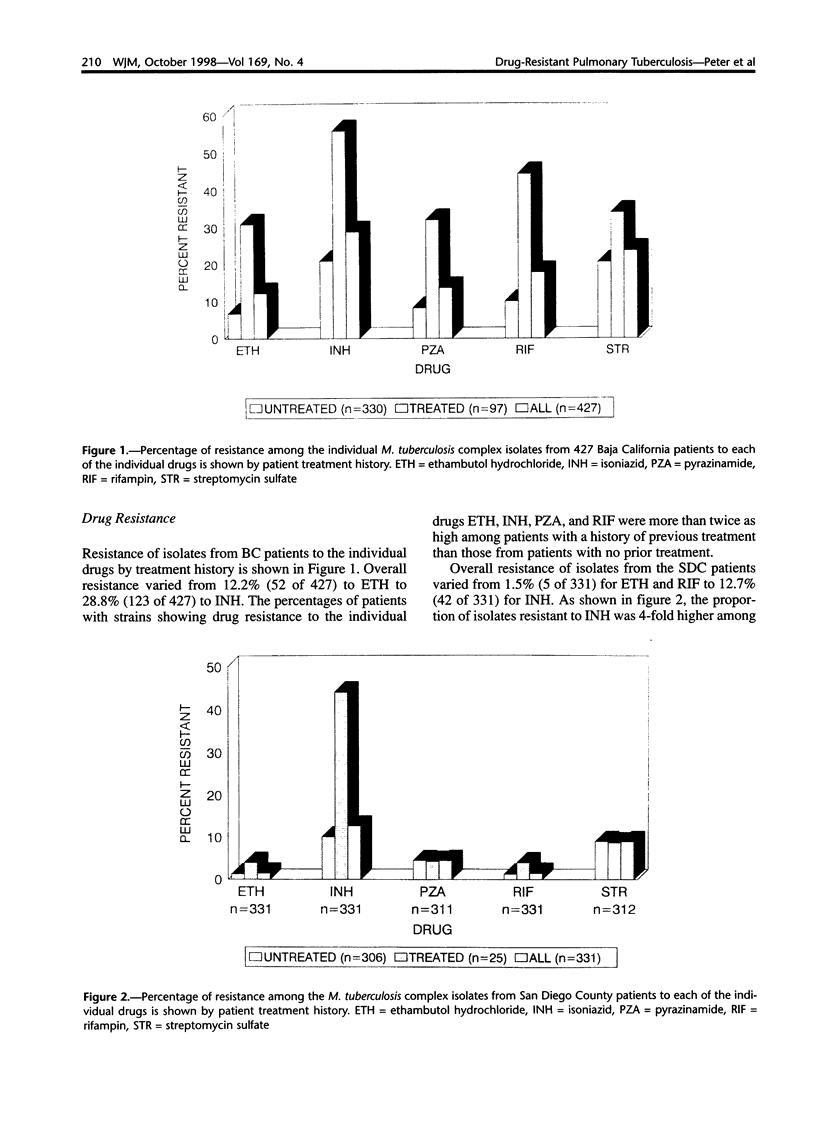
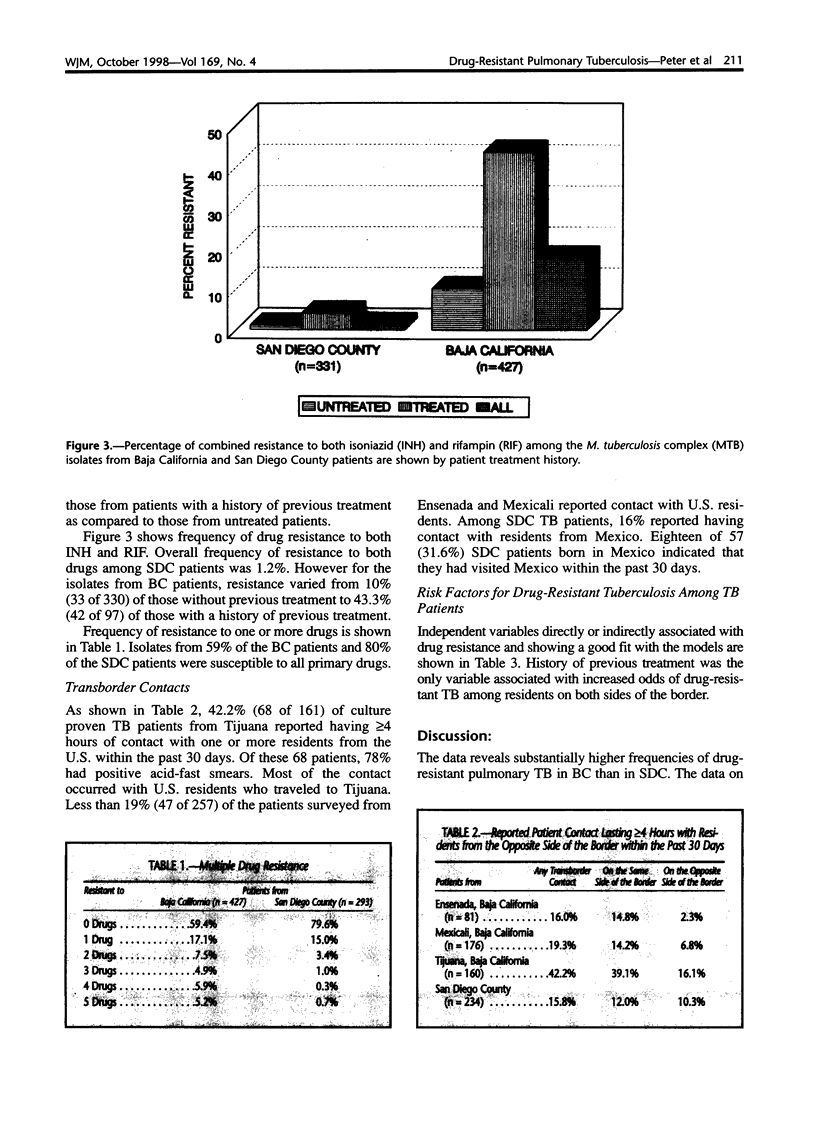
A study was conducted to determine the frequency of, and risk factors for, drug-resistant pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) among Baja California (BC) and San Diego County (SDC) residents. Another purpose was to document the amount of contact between pulmonary TB patients and residents of the opposite side of the the border. During the period from February 1995 to May 1996, pulmonary TB patients from BC (n = 427) and SDC (n = 331) were evaluated with cultures, drug susceptibility tests, and questionnaires. Drug resistance was found in 41% of the BC Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTB) isolates and 20% of the SDC isolates. Resistance to both isoniazid (INH) and rifampin (RIF) varied from 1% of isolates from SDC patients to 17% of isolates from BC patients. Patients with a history of previous treatment had increased odds of drug-resistant disease. Older BC patients were more likely to have INH- or RIF-resistant TB. Although 42% of Tijuana TB patients reported recent contact with residents from SDC, travel to Mexico and contact with residents from Mexico were not significant risk factors for drug-resistant TB among SDC residents. However, the demonstrated contact between TB patients and residents on opposite sides of the border indicates the importance of coordinating efforts internationally to control TB.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Gordillo G. C., Halperin-Frisch D., Blancarte-Melendres L., Vázquez-Castellanos J. L. Factores de riesgo para resistencia a drogas antifímicas en Chiapas, México. Salud Publica Mex. 1995 Sep-Oct;37(5):408–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arévalo M., Solera J., Cebrian D., Bartolomé J., Robles P. Risk factors associated with drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Castilla-la-Mancha (Spain) Eur Respir J. 1996 Feb;9(2):274–278. doi: 10.1183/09031936.96.09020274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dankner W. M., Waecker N. J., Essey M. A., Moser K., Thompson M., Davis C. E. Mycobacterium bovis infections in San Diego: a clinicoepidemiologic study of 73 patients and a historical review of a forgotten pathogen. Medicine (Baltimore) 1993 Jan;72(1):11–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandes G., Lopez-de-Munain J., Diaz T., Rullan J. V. Drug-resistant tuberculosis in Puerto Rico, 1987-1990. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jul;148(1):6–9. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/148.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent J. H. The epidemiology of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in the United States. Med Clin North Am. 1993 Nov;77(6):1391–1409. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30200-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza M. T., Gonzaga A. J., Roa C., Velmonte M. A., Jorge M., Montoya J. C., Tan Torres T., Ong M., Barez M. Y., Ang C. F. Nature of drug resistance and predictors of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis among patients seen at the Philippine General Hospital, Manila, Philippines. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1997 Feb;1(1):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Onorato I. M., McCray E., Castro K. G. Trends in drug-resistant tuberculosis in the United States, 1993-1996. JAMA. 1997 Sep 10;278(10):833–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Arathoon E., Loverde V. D. The epidemiologic patterns of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections: a community-based study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1282–1285. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon N., Perlman D. C., DePalo V. A., Kolokathis A., Wilets I. Drug-resistant tuberculosis: factors associated with rise in resistance in an HIV-infected urban population. Mt Sinai J Med. 1994 Sep;61(4):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sifuentes-Osornio J., Ponce-de-León L. A., Camacho-Mezquita F. E., Bobadilla-del-Valle J. M., Infante-Suárez M. L., Ramírez-Fernández N., Hernández-Gómez L., Nelson A. M. Resistencia de Mycobacterium tuberculosis en pacientes mexicanos. I. Características clínicas y factores de riesgo. Rev Invest Clin. 1995 Jul-Aug;47(4):273–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


