Abstract
Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging technology has undergone many technologic advances over the past few years. Many of these advances were stimulated by the wealth of information emerging from nuclear magnetic resonance research in the areas of new and optimal scanning methods and radio-frequency coil design. Other changes arose from the desire to improve image quality, ease siting restrictions and generally facilitate the clinical use of MR equipment. Many questions, however, remain unanswered. Perhaps the most controversial technologic question involves the optimal field strength required for imaging or spectroscopic applications or both. Other issues include safety and clinical efficacy. Technologic issues affect all aspects of MR use including the choice of equipment, examination procedure and image interpretation. Thus, an understanding of recent changes and their theoretic basis is necessary.
Full text
PDF
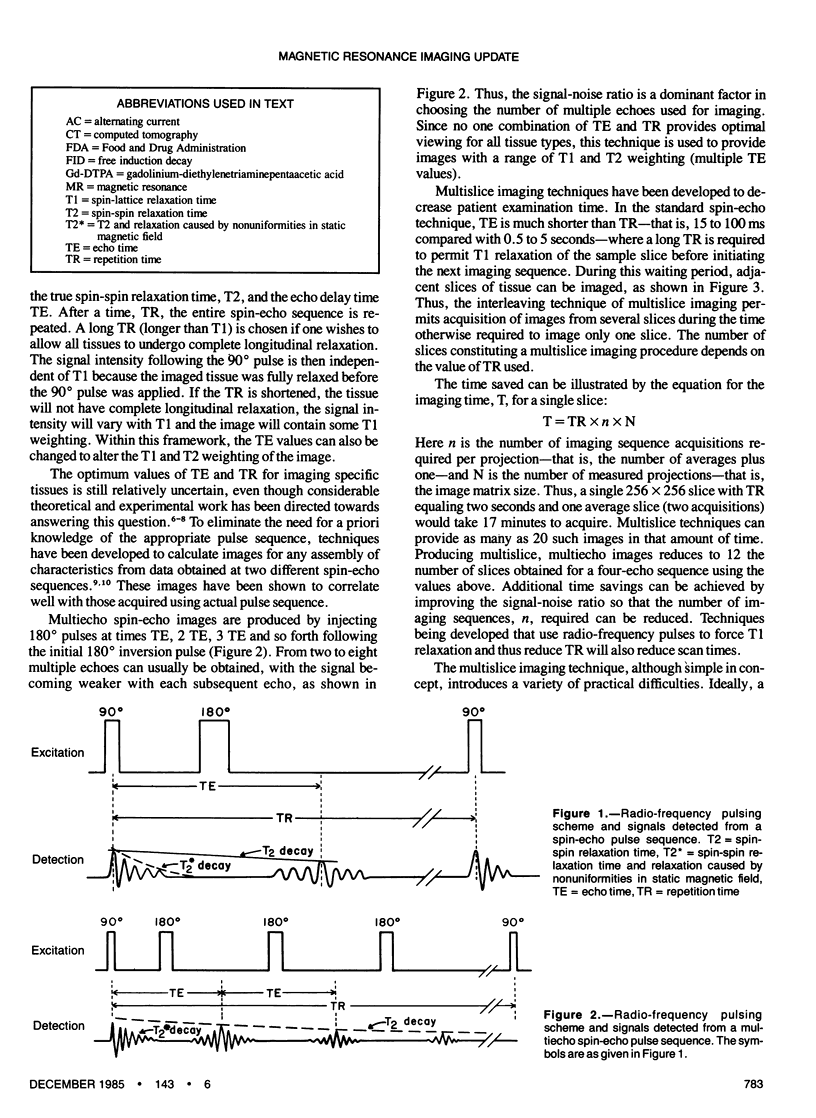
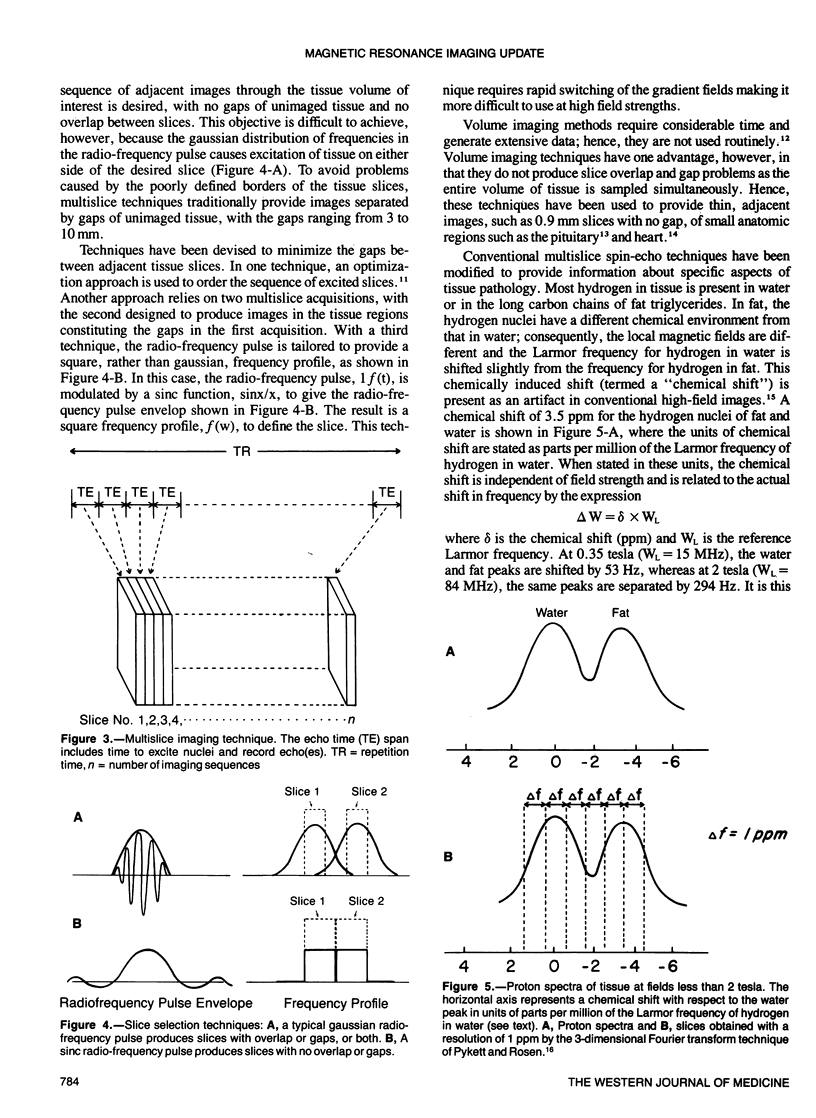
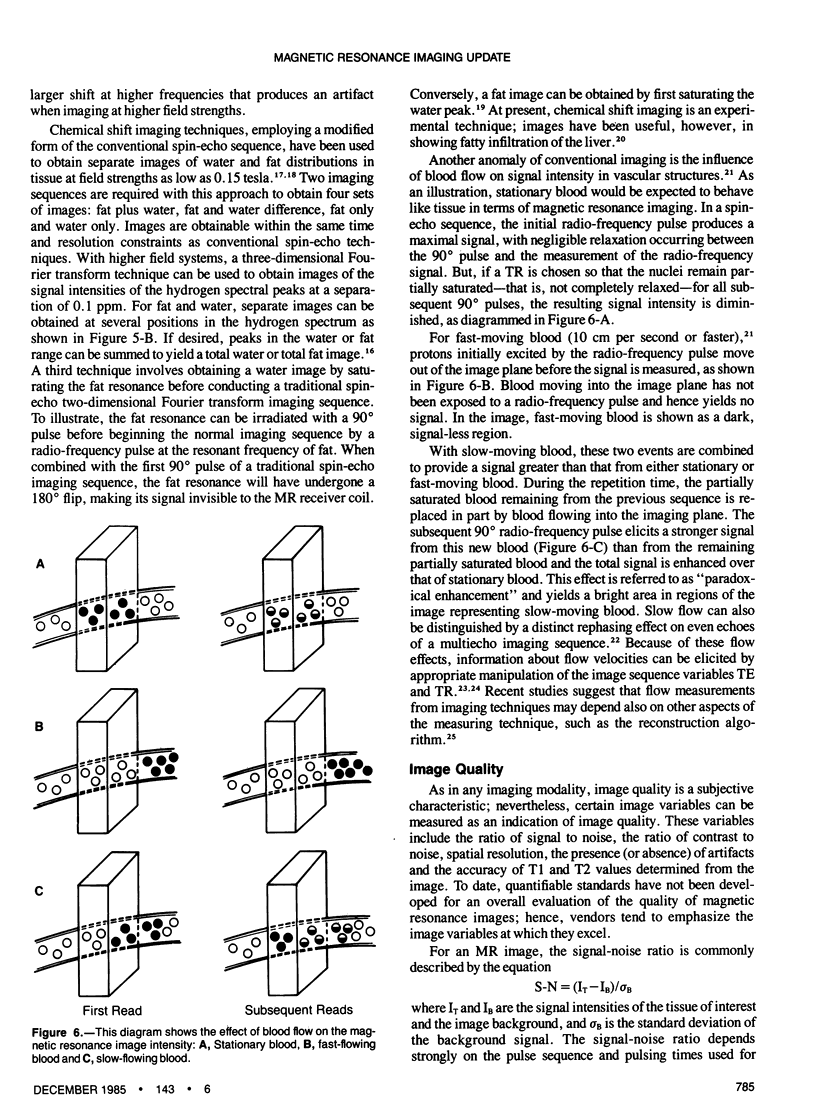

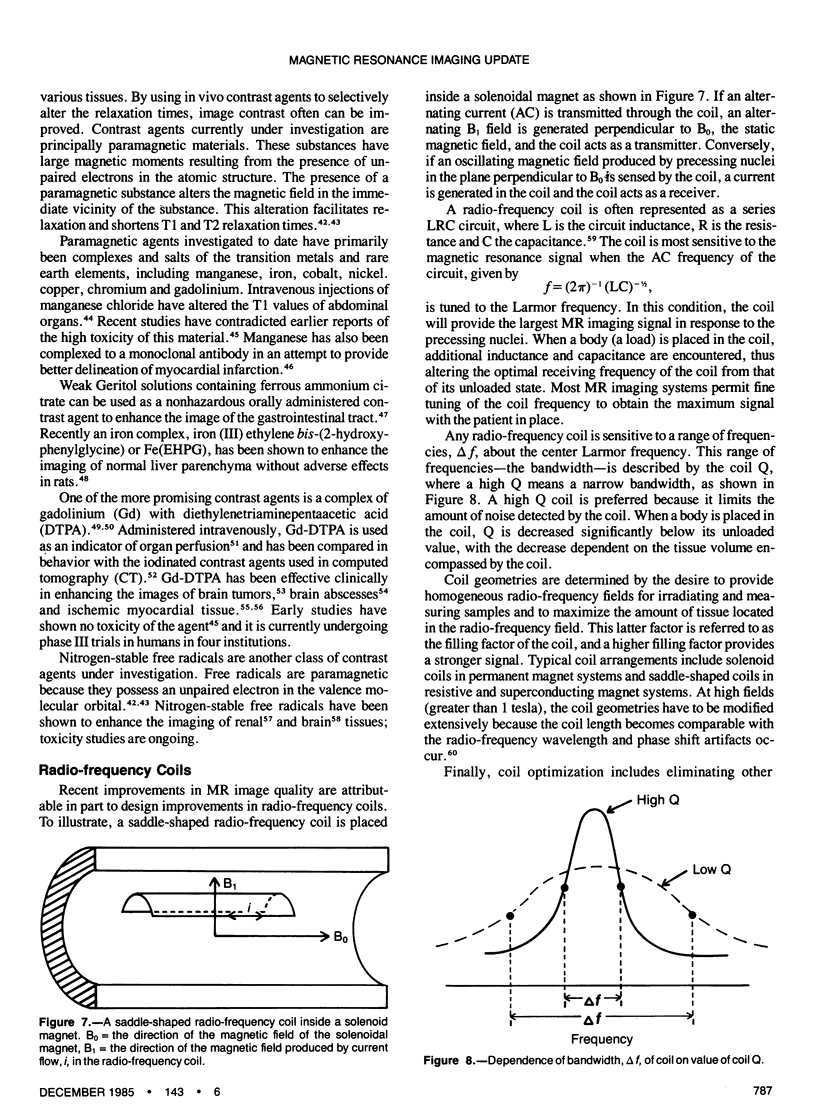



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman J. J., Grove T. H., Wong G. G., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Mapping of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):167–170. doi: 10.1038/283167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araki T., Inouye T., Suzuki H., Machida T., Iio M. Magnetic resonance imaging of brain tumors: measurement of T1. Work in progress. Radiology. 1984 Jan;150(1):95–98. doi: 10.1148/radiology.150.1.6689793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardino M. E., Small W., Goldstein J., Sewell C. W., Sones P. J., Gedgaudas-McClees K., Galambos J. T., Wenger J., Casarella W. J. Multiple NMR T2 relaxation values in human liver tissue. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Dec;141(6):1203–1208. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley P. A., Hart H. R., Jr, Edelstein W. A., Schenck J. F., Smith L. S., Leue W. M., Mueller O. M., Redington R. W. Anatomy and metabolism of the normal human brain studied by magnetic resonance at 1.5 Tesla. Radiology. 1984 Feb;150(2):441–446. doi: 10.1148/radiology.150.2.6691099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G., Jr, Waluch V. Blood flow: magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1985 Feb;154(2):443–450. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.2.3966131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brant-Zawadzki M., Norman D., Newton T. H., Kelly W. M., Kjos B., Mills C. M., Dillon W., Sobel D., Crooks L. E. Magnetic resonance of the brain: the optimal screening technique. Radiology. 1984 Jul;152(1):71–77. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.1.6729138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch R. C., London D. A., Wesbey G. E., Tozer T. N., Nitecki D. E., Williams R. D., Doemeny J., Tuck L. D., Lallemand D. P. Work in progress: nuclear magnetic resonance study of a paramagnetic nitroxide contrast agent for enhancement of renal structures in experimental animals. Radiology. 1983 Jun;147(3):773–779. doi: 10.1148/radiology.147.3.6844613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch R. C., Nitecki D. E., Brant-Zawadzki M., Enzmann D. R., Wesbey G. E., Tozer T. N., Tuck L. D., Cann C. E., Fike J. R., Sheldon P. Brain nuclear magnetic resonance imaging enhanced by a paramagnetic nitroxide contrast agent: preliminary report. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Nov;141(5):1019–1023. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.5.1019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch R. C. Work in progress: methods of contrast enhancement for NMR imaging and potential applications. A subject review. Radiology. 1983 Jun;147(3):781–788. doi: 10.1148/radiology.147.3.6342034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr D. H., Brown J., Bydder G. M., Steiner R. E., Weinmann H. J., Speck U., Hall A. S., Young I. R. Gadolinium-DTPA as a contrast agent in MRI: initial clinical experience in 20 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Aug;143(2):215–224. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooks L. E., Arakawa M., Hoenninger J., McCarten B., Watts J., Kaufman L. Magnetic resonance imaging: effects of magnetic field strength. Radiology. 1984 Apr;151(1):127–133. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.1.6701302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooks L. E., Barker B., Chang H., Feinberg D., Hoenninger J. C., Watts J. C., Arakawa M., Kaufman L., Sheldon P. E., Botvinick E. Magnetic resonance imaging strategies for heart studies. Radiology. 1984 Nov;153(2):459–465. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.2.6484178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crooks L. E., Watts J., Hoenninger J., Arakawa M., Kaufman L., Guenther H., Feinberg D. Thin-section definition in magnetic resonance imaging. Technical concepts and their implementation. Radiology. 1985 Feb;154(2):463–467. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.2.3966133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damadian R. Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance. Science. 1971 Mar 19;171(3976):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. L., Crooks L., Arakawa M., McRee R., Kaufman L., Margulis A. R. Potential hazards in NMR imaging: heating effects of changing magnetic fields and RF fields on small metallic implants. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Oct;137(4):857–860. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.4.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore R. E., Wismer G. L., Levine R. A., Okada R. D., Brady T. J. Magnetic resonance imaging of the heart: positioning and gradient angle selection for optimal imaging planes. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Dec;143(6):1135–1142. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.6.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon W. T. Simple proton spectroscopic imaging. Radiology. 1984 Oct;153(1):189–194. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.1.6089263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiglin D. H., George C. R., MacIntyre W. J., O'Donnell J. K., Go R. T., Pavlicek W., Meaney T. F. Gated cardiac magnetic resonance structural imaging: optimization by electronic axial rotation. Radiology. 1985 Jan;154(1):129–132. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.1.3155478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimmons J. R., Thomas R. G., Mancuso A. A. Proton imaging with surface coils on a 0.15-T resistive system. Magn Reson Med. 1985 Apr;2(2):180–185. doi: 10.1002/mrm.1910020209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullerton G. D., Cameron I. L., Ord V. A. Frequency dependence of magnetic resonance spin-lattice relaxation of protons in biological materials. Radiology. 1984 Apr;151(1):135–138. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.1.6322223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadian D. G., Payne J. A., Bryant D. J., Young I. R., Carr D. H., Bydder G. M. Gadolinium-DTPA as a contrast agent in MR imaging--theoretical projections and practical observations. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 Mar-Apr;9(2):242–251. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geard C. R., Osmak R. S., Hall E. J., Simon H. E., Maudsley A. A., Hilal S. K. Magnetic resonance and ionizing radiation: a comparative evaluation in vitro of oncogenic and genotoxic potential. Radiology. 1984 Jul;152(1):199–202. doi: 10.1148/radiology.152.1.6729111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman R. I., Wolf G., Biery D., McGrath J., Kundel H., Aronchick J., Zimmerman R. A., Goldberg H. I., Bilaniuk L. T. Gadolinium enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance images of experimental brain abscess. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Apr;8(2):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart H. R., Jr, Bottomley P. A., Edelstein W. A., Karr S. G., Leue W. M., Mueller O., Redington R. W., Schenck J. F., Smith L. S., Vatis D. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging: contrast-to-noise ratio as a function of strength of magnetic field. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Dec;141(6):1195–1201. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.6.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendee W. R., Morgan C. J. Magnetic resonance imaging. Part I--physical principles. West J Med. 1984 Oct;141(4):491–500. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick R. E., Nelson T. R., Hendee W. R. Optimizing tissue contrast in magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 1984;2(3):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(84)90005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. P., Partain C. L., Mitchell M. R., Patton J. A., Stephens W. H., Price R. R., Kulkarni M. V., James A. E., Jr Principles of magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Annu. 1985:71–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffer R. B., Greif W. L., Stark D. D., Vincent A. C., Saini S., Wedeen V. J., Brady T. J. Iron-EHPG as an hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: initial imaging and biodistribution studies. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985 May-Jun;9(3):431–438. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. K., Dixon W. T., Ling D., Levitt R. G., Murphy W. A., Jr Fatty infiltration of the liver: demonstration by proton spectroscopic imaging. Preliminary observations. Radiology. 1984 Oct;153(1):195–201. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.1.6089264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. S. Accuracy of proton T1 calculated by approximations from image signals. J Nucl Med. 1985 Jan;26(1):54–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley A. A., Hilal S. K., Simon H. E., Wittekoek S. In vivo MR spectroscopic imaging with P-31. Work in progress. Radiology. 1984 Dec;153(3):745–750. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.3.6494470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara M. T., Higgins C. B., Ehman R. L., Revel D., Sievers R., Brasch R. C. Acute myocardial ischemia: magnetic resonance contrast enhancement with gadolinium-DTPA. Radiology. 1984 Oct;153(1):157–163. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.1.6473777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mechlin M., Thickman D., Kressel H. Y., Gefter W., Joseph P. Magnetic resonance imaging of postoperative patients with metallic implants. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Dec;143(6):1281–1284. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.6.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills C. M., Crooks L. E., Kaufman L., Brant-Zawadzki M. Cerebral abnormalities: use of calculated T1 and T2 magnetic resonance images for diagnosis. Radiology. 1984 Jan;150(1):87–94. doi: 10.1148/radiology.150.1.6689792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P. R., Moran R. A., Karstaedt N. Verification and evaluation of internal flow and motion. True magnetic resonance imaging by the phase gradient modulation method. Radiology. 1985 Feb;154(2):433–441. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.2.3966130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. A., Gutierrez F. R., Levitt R. G., Glazer H. S., Lee J. K. Oblique views of the heart by magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1985 Jan;154(1):225–226. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.1.3964939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New P. F., Rosen B. R., Brady T. J., Buonanno F. S., Kistler J. P., Burt C. T., Hinshaw W. S., Newhouse J. H., Pohost G. M., Taveras J. M. Potential hazards and artifacts of ferromagnetic and nonferromagnetic surgical and dental materials and devices in nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1983 Apr;147(1):139–148. doi: 10.1148/radiology.147.1.6828719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. NMR blood flow imaging using multiecho, phase contrast sequences. Med Phys. 1985 Jan-Feb;12(1):59–64. doi: 10.1118/1.595736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortendahl D. A., Hylton N., Kaufman L., Watts J. C., Crooks L. E., Mills C. M., Stark D. D. Analytical tools for magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1984 Nov;153(2):479–488. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.2.6091173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavlicek W., Geisinger M., Castle L., Borkowski G. P., Meaney T. F., Bream B. L., Gallagher J. H. The effects of nuclear magnetic resonance on patients with cardiac pacemakers. Radiology. 1983 Apr;147(1):149–153. doi: 10.1148/radiology.147.1.6828720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykett I. L. NMR imaging in medicine. Sci Am. 1982 May;246(5):78–88. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0582-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pykett I. L., Rosen B. R. Nuclear magnetic resonance: in vivo proton chemical shift imaging. Work in progress. Radiology. 1983 Oct;149(1):197–201. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.1.6310682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riederer S. J., Suddarth S. A., Bobman S. A., Lee J. N., Wang H. Z., MacFall J. R. Automated MR image synthesis: feasibility studies. Radiology. 1984 Oct;153(1):203–206. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.1.6089265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen B. R., Pykett I. L., Brady T. J. Spin lattice relaxation time measurements in two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance imaging: corrections for plane selection and pulse sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1984 Apr;8(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge V. M., Clanton J. A., Lukehart C. M., Partain C. L., James A. E., Jr Paramagnetic agents for contrast-enhanced NMR imaging: a review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Dec;141(6):1209–1215. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.6.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge V. M., Clanton J. A., Partain C. L., James A. E., Jr Respiratory gating in magnetic resonance imaging at 0.5 Tesla. Radiology. 1984 May;151(2):521–523. doi: 10.1148/radiology.151.2.6709928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. R., Crooks L. E. Nuclear magnetic resonance blood flow measurements in the human brain. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):654–656. doi: 10.1126/science.6867733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutsky R. A., Peterson T., Strich G., Brown J. J. Hemodynamic effects of rapid and slow infusions of manganese chloride and gadolinium-DTPA in dogs. Radiology. 1985 Mar;154(3):733–735. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.3.3969479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soila K. P., Viamonte M., Jr, Starewicz P. M. Chemical shift misregistration effect in magnetic resonance imaging. Radiology. 1984 Dec;153(3):819–820. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.3.6494479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich G., Hagan P. L., Gerber K. H., Slutsky R. A. Tissue distribution and magnetic resonance spin lattice relaxation effects of gadolinium-DTPA. Radiology. 1985 Mar;154(3):723–726. doi: 10.1148/radiology.154.3.3969477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli F. W., MacFall J. R., Glover G. H., Grigsby N., Haughton V., Johanson J. The dependence of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) image contrast on intrinsic and pulse sequence timing parameters. Magn Reson Imaging. 1984;2(1):3–16. doi: 10.1016/0730-725x(84)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmann H. J., Brasch R. C., Press W. R., Wesbey G. E. Characteristics of gadolinium-DTPA complex: a potential NMR contrast agent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Mar;142(3):619–624. doi: 10.2214/ajr.142.3.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreb J. C., Maravilla K. R., Peshock R., Payne J. Magnetic resonance imaging: improving patient tolerance and safety. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1984 Dec;143(6):1285–1287. doi: 10.2214/ajr.143.6.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesbey G. E., Brasch R. C., Engelstad B. L., Moss A. A., Crooks L. E., Brito A. C. Nuclear magnetic resonance contrast enhancement study of the gastrointestinal tract of rats and a human volunteer using nontoxic oral iron solutions. Radiology. 1983 Oct;149(1):175–180. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.1.6611926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wesbey G. E., Higgins C. B., McNamara M. T., Engelstad B. L., Lipton M. J., Sievers R., Ehman R. L., Lovin J., Brasch R. C. Effect of gadolinium-DTPA on the magnetic relaxation times of normal and infarcted myocardium. Radiology. 1984 Oct;153(1):165–169. doi: 10.1148/radiology.153.1.6473778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G. L., Baum L. Cardiovascular toxicity and tissue proton T1 response to manganese injection in the dog and rabbit. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1983 Jul;141(1):193–197. doi: 10.2214/ajr.141.1.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf G. L., Burnett K. R., Goldstein E. J., Joseph P. M. Contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Annu. 1985:231–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S., James T. L., Young G. B., Margulis A. R., Bodycote J., Afzal V. Magnetic resonance imaging: absence of in vitro cytogenetic damage. Radiology. 1985 Apr;155(1):163–165. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.1.4038809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



