Abstract
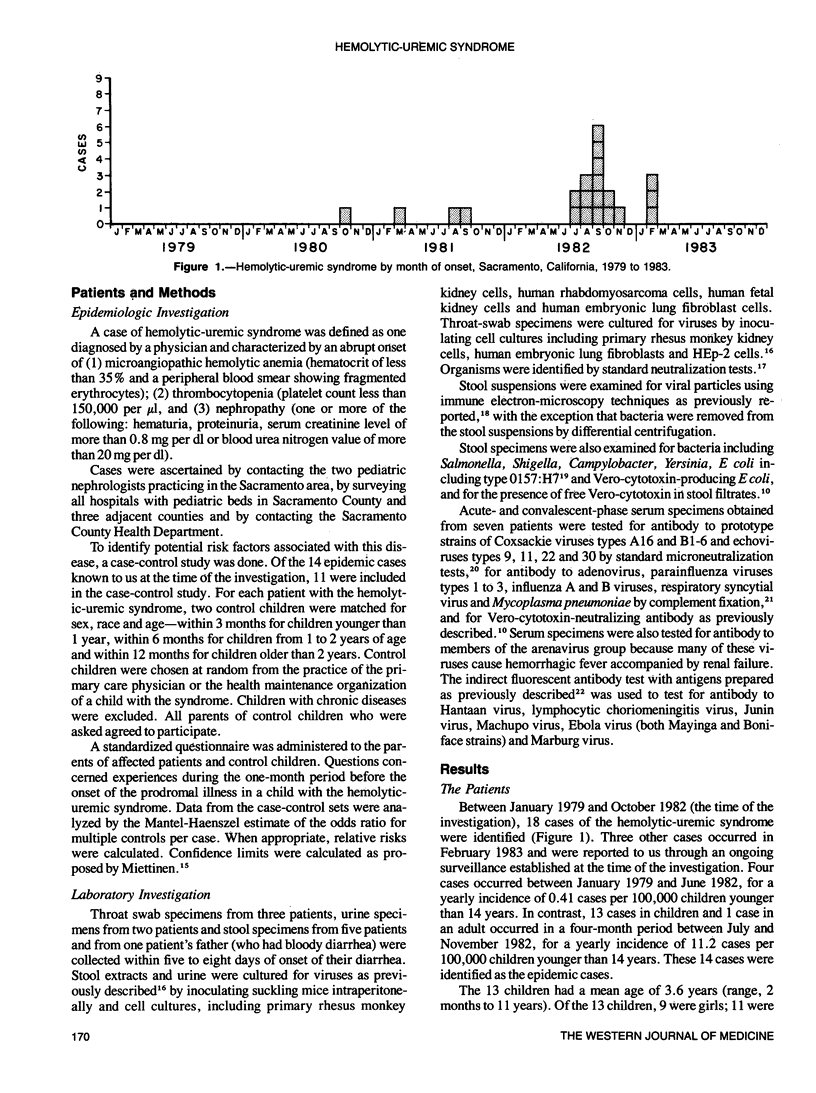
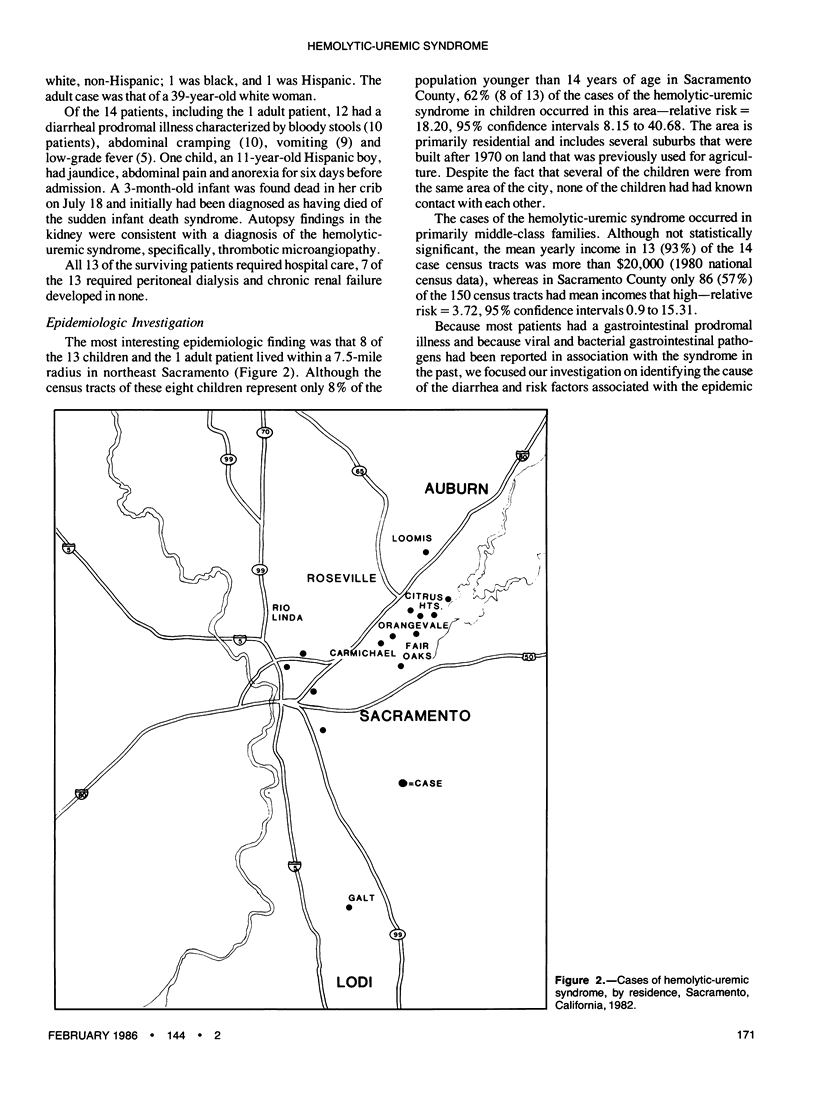
Between July and November 1982, 14 cases of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome occurred in the Sacramento, California, metropolitan area; 9 of the 14 patients lived within a 7.5-mile radius in northeast Sacramento, 10 were female, 12 were white non-Hispanic and 13 were children with a mean age of 3.6 years. Of the 14 patients, 13 were admitted to hospital; 7 required peritoneal dialysis. The 14th child, a 3-month-old white female infant, was found dead in her crib and had renal histopathologic findings consistent with the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Of the 13 nonfatal cases, 12 patients had diarrhea before being admitted to hospital. A case-control study involving 11 cases and 22 controls did not show any significant differences in exposure to a variety of possible risk factors including restaurants, specific foods and water supply. Stool specimens were negative for enteric bacterial pathogens by culture and for viruses by tissue culture assay, suckling mouse inoculation and immune electron microscopy; no serologic evidence was found for infection due to enteroviruses, respiratory viruses or arenaviruses. Two of four children tested, however, showed serologic evidence of infection by Vero-cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli. These 14 cases represent one of the largest reported outbreaks of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome in the United States.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamovitz B. N., Hartstein A. I., Alexander S. R., Terry A. B., Short P., Katon R. Campylobacter jejuni-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome in a mother and daughter. Pediatrics. 1983 Feb;71(2):253–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolin R., Reichman R. C., Roessner K. D., Tralka T. S., Schooley R. T., Gary W., Morens D. Detection by immune electron microscopy of the Snow Mountain agent of acute viral gastroenteritis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):184–189. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolislager D., Tune B. The hemolytic-uremic syndrome: spectrum of severity and significance of prodrome. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Jan;132(1):55–58. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120260057014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIANANTONIO C., VITACCO M., MENDILAHARZU F., RUTTY A., MENDILAHARZU J. THE HEMOLYTIC-UREMIC SYNDROME. J Pediatr. 1964 Apr;64:478–491. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. M., Elliott L. H., Heymann D. L. Preparation of polyvalent viral immunofluorescent intracellular antigens and use in human serosurveys. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(5):527–529. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.5.527-529.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan B. S., Thomson P. D., de Chadarévian J. P. The hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1976 Nov;23(4):761–777. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)33359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karmali M. A., Steele B. T., Petric M., Lim C. Sporadic cases of haemolytic-uraemic syndrome associated with faecal cytotoxin and cytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli in stools. Lancet. 1983 Mar 19;1(8325):619–620. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91795-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibel M. A., Barnard P. J. The haemolytic-uraemic syndrome: a survey in Southern Africa. S Afr Med J. 1968 Jul 13;42(27):692–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F., Levin J., Walker L., Tung K. S., Gilman R. H., Rahaman M. M., Majid M. A., Islam S., Williams R. C., Jr Hemolytic-uremic syndrome after shigellosis. Relation to endotoxemia and circulating immune complexes. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 27;298(17):927–933. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804272981702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean M. M., Jones C. H., Sutherland D. A. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. A report of an outbreak. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Feb;41(215):76–81. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.215.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettler N. E. Isolation of a microtatobiote from patients with hemolytic-uremic syndrome and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and from mites in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1969 Nov 6;281(19):1023–1027. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196911062811901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen O. Estimability and estimation in case-referent studies. Am J Epidemiol. 1976 Feb;103(2):226–235. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M., Baron R. C., Filstein M. R., Lofgren J. P., Rowley D. L., Schonberger L. B., Hatch M. H. Aseptic meningitis and high school football players. 1978 and 1980. JAMA. 1983 Apr 15;249(15):2039–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Regan S., Robitaille P., Mongeau J. G., McLaughlin B. The hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with ECHO 22 infection. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1980 Feb;19(2):125–127. doi: 10.1177/000992288001900207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prober C. G., Tune B., Hoder L. Yersinia pseudotuberculosis septicemia. Am J Dis Child. 1979 Jun;133(6):623–624. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1979.02130060063013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBAUM M. J., PHILLIPS I. A., SULLIVAN E. J., EDWARDS E. A., MILLER L. F. A simplified method for virus-tissue culture procedures in microtitration plates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 May;113:224–229. doi: 10.3181/00379727-113-28325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray C. G., Tucker V. L., Harris D. J., Cuppage F. E., Chin T. D. Enteroviruses associated with the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Pediatrics. 1970 Sep;46(3):378–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrenti L. Y., Lewy P. R. The hemolytic-uremic syndrome: experience at a center in the Midwest. Am J Dis Child. 1978 Jan;132(1):59–62. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1978.02120260061015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele B. T., Murphy N., Arbus G. S., Rance C. P. An outbreak of hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with ingestion of fresh apple juice. J Pediatr. 1982 Dec;101(6):963–965. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Wachsmuth I. K., Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Sokolow R., Morris G. K. Laboratory investigation of hemorrhagic colitis outbreaks associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Sep;18(3):512–520. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.3.512-520.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wieringen P. M., Monnens L. A., Schretlen E. D. Haemolytic-uraemic syndrome. Epidemiological and clinical study. Arch Dis Child. 1974 Jun;49(6):432–437. doi: 10.1136/adc.49.6.432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



