Abstract
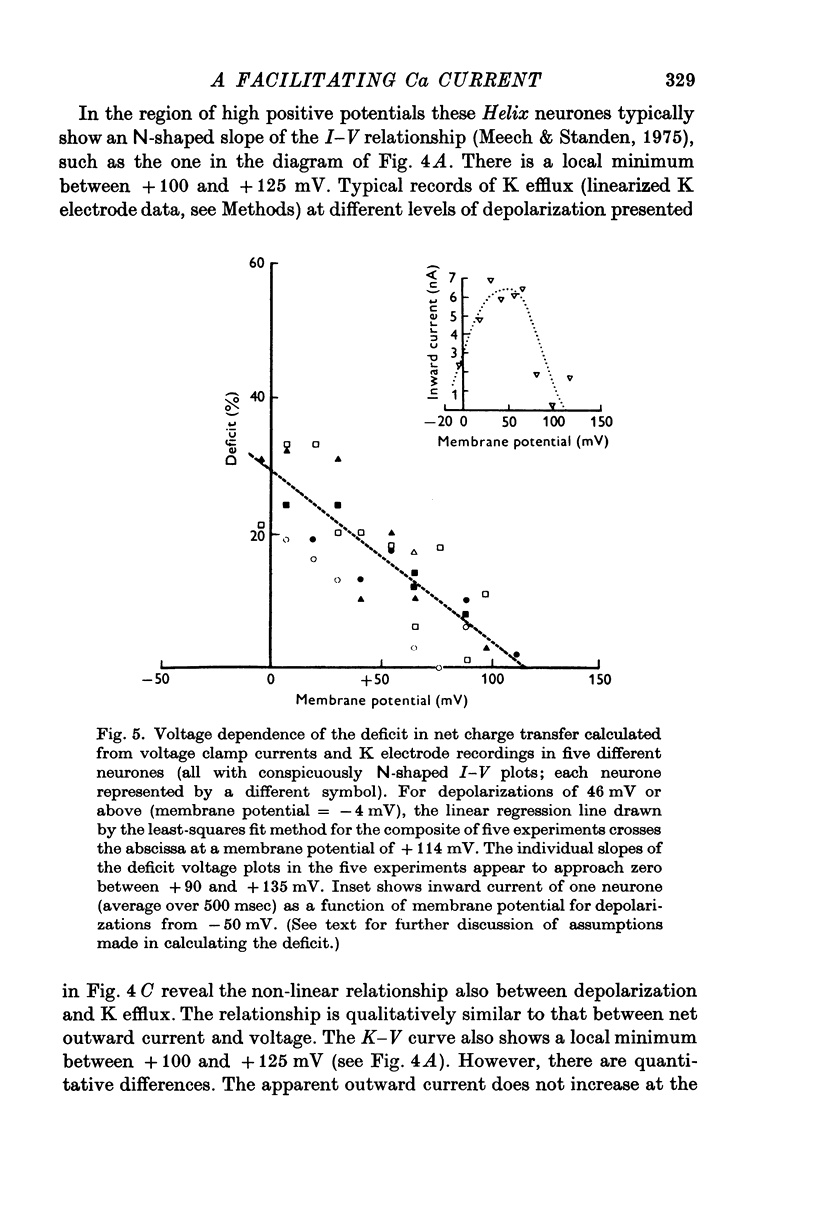
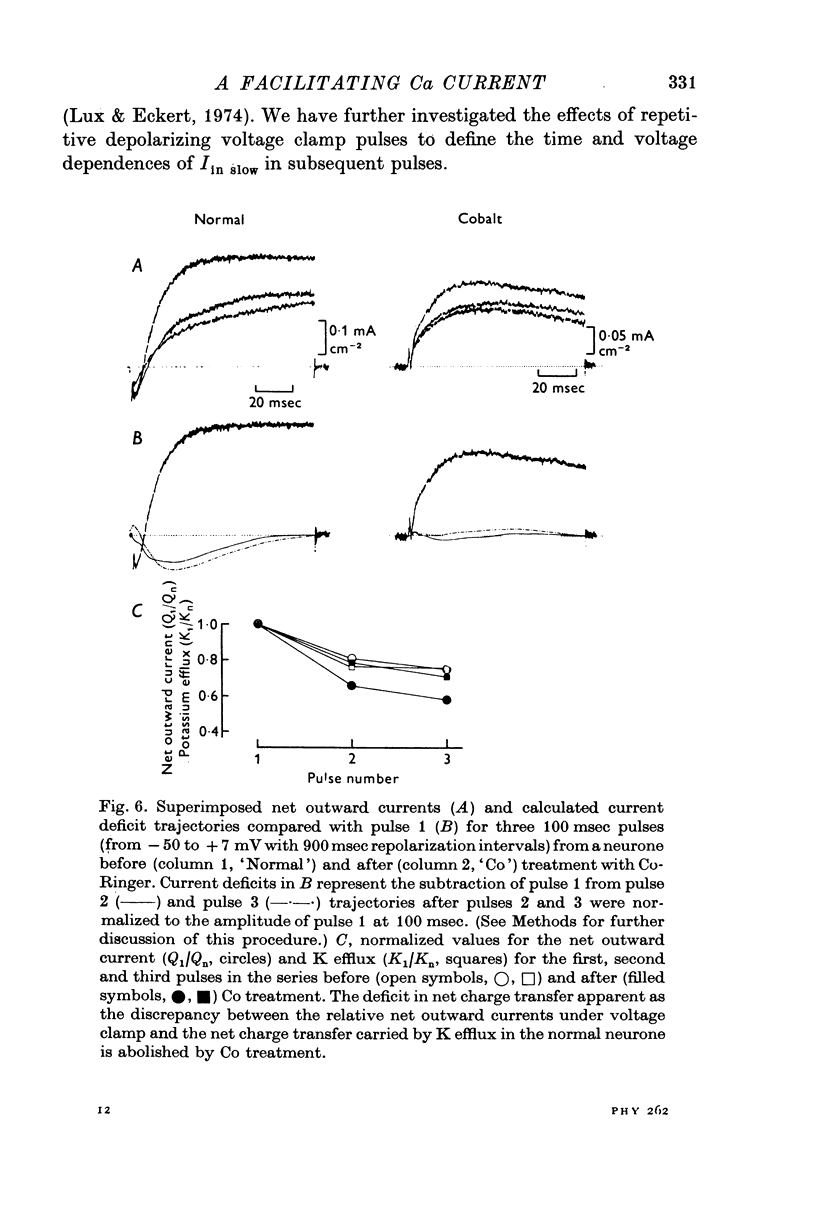
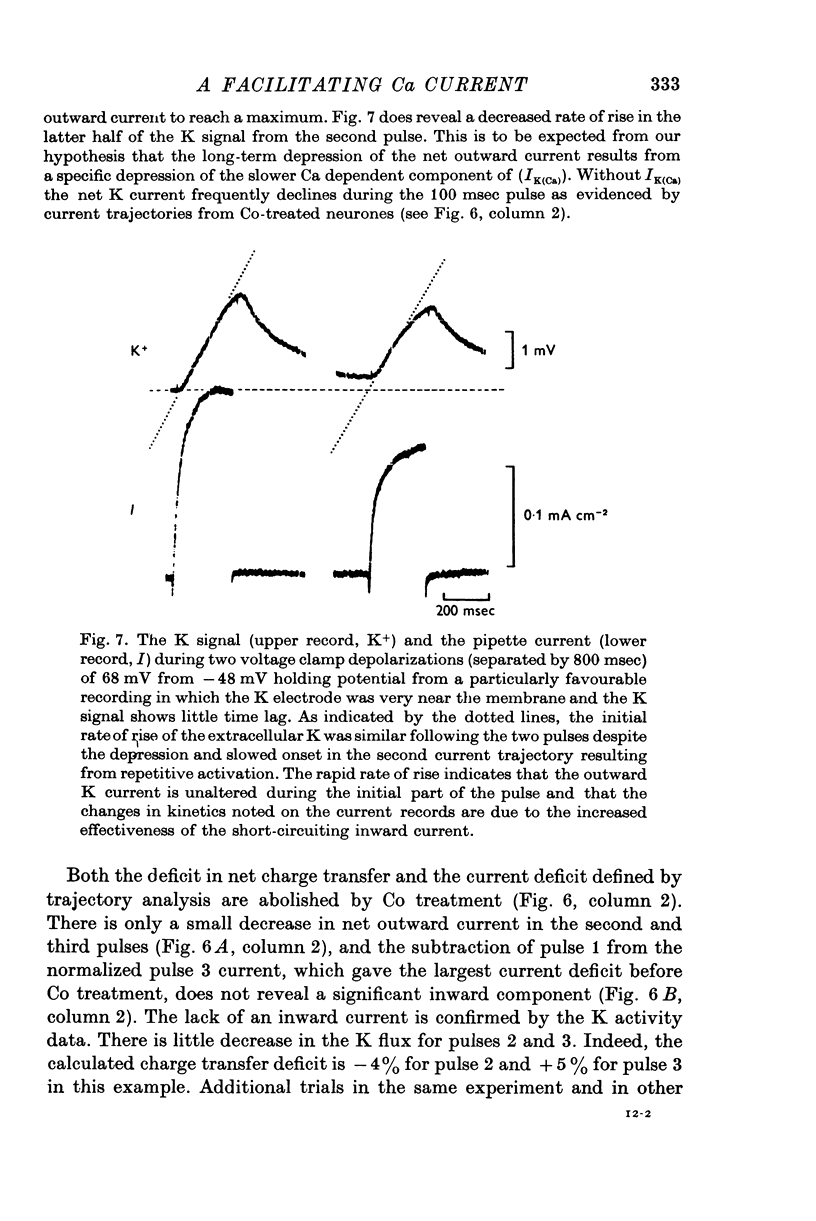
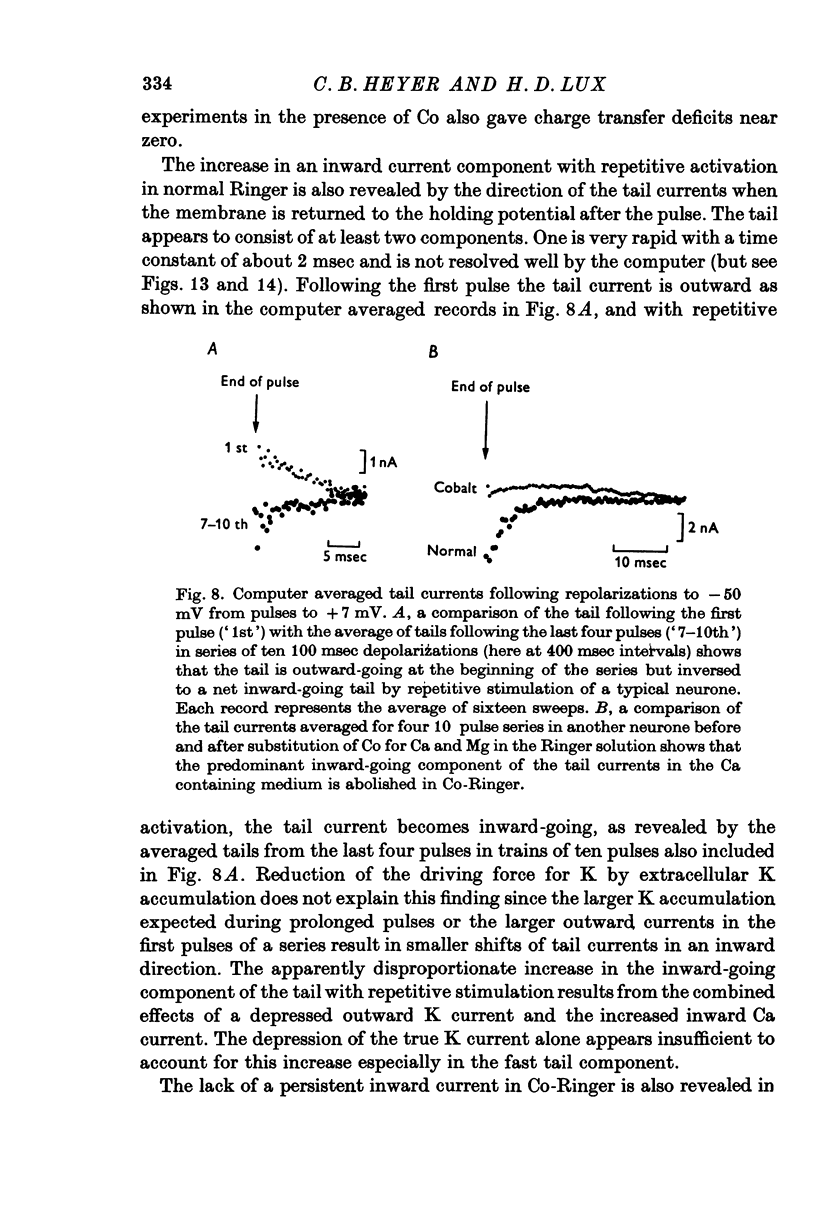
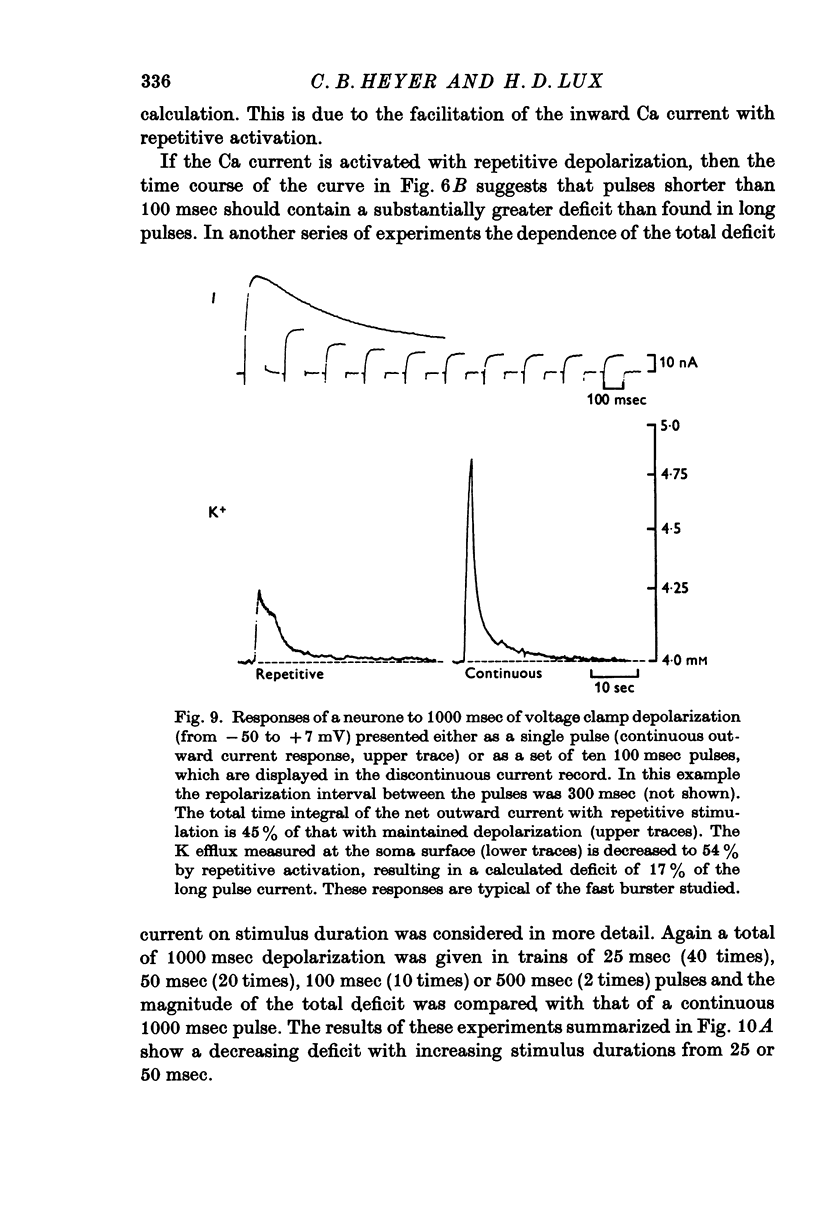
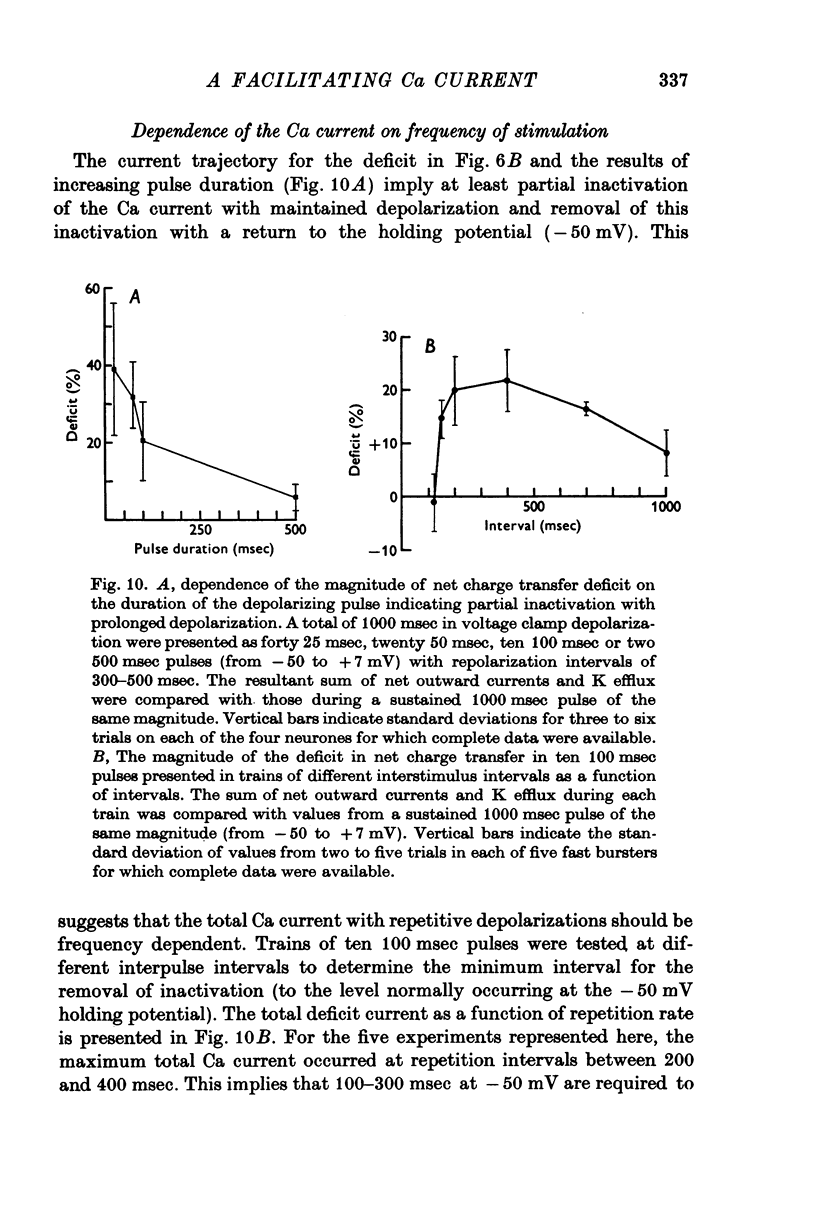
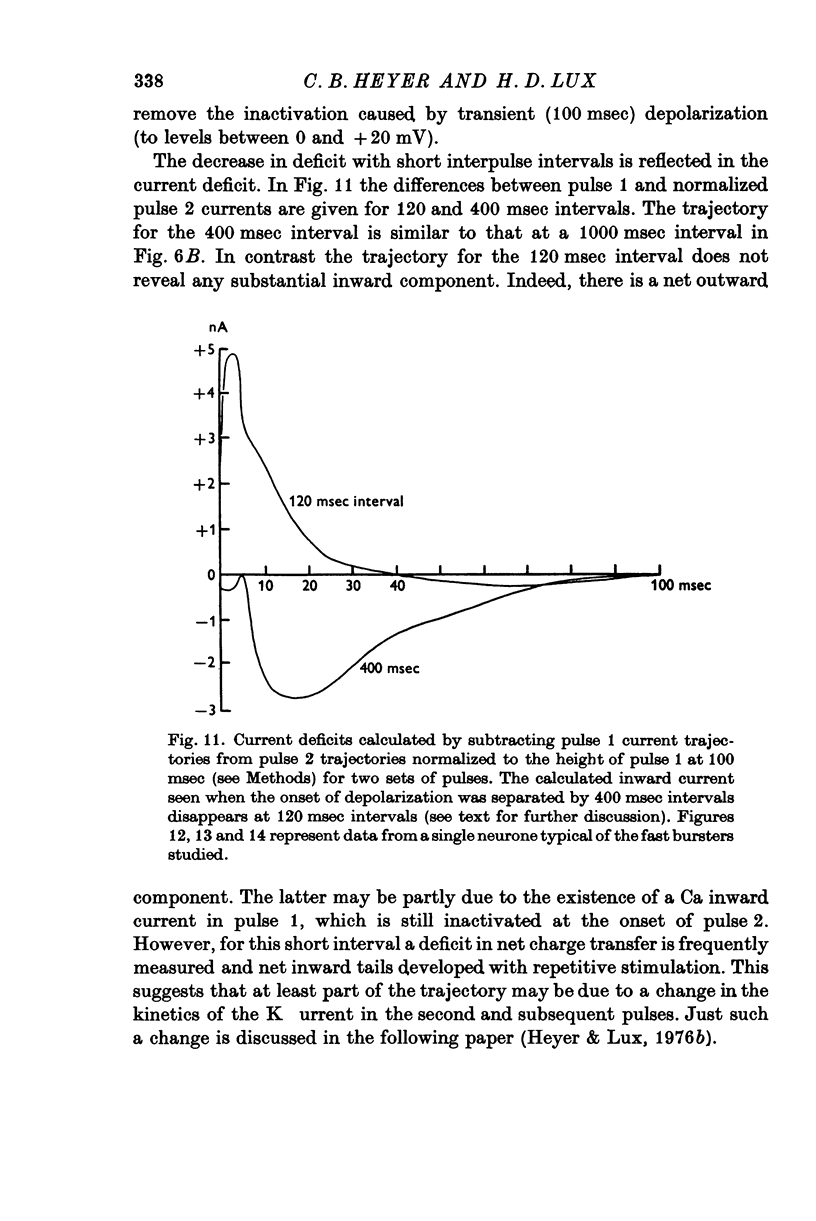
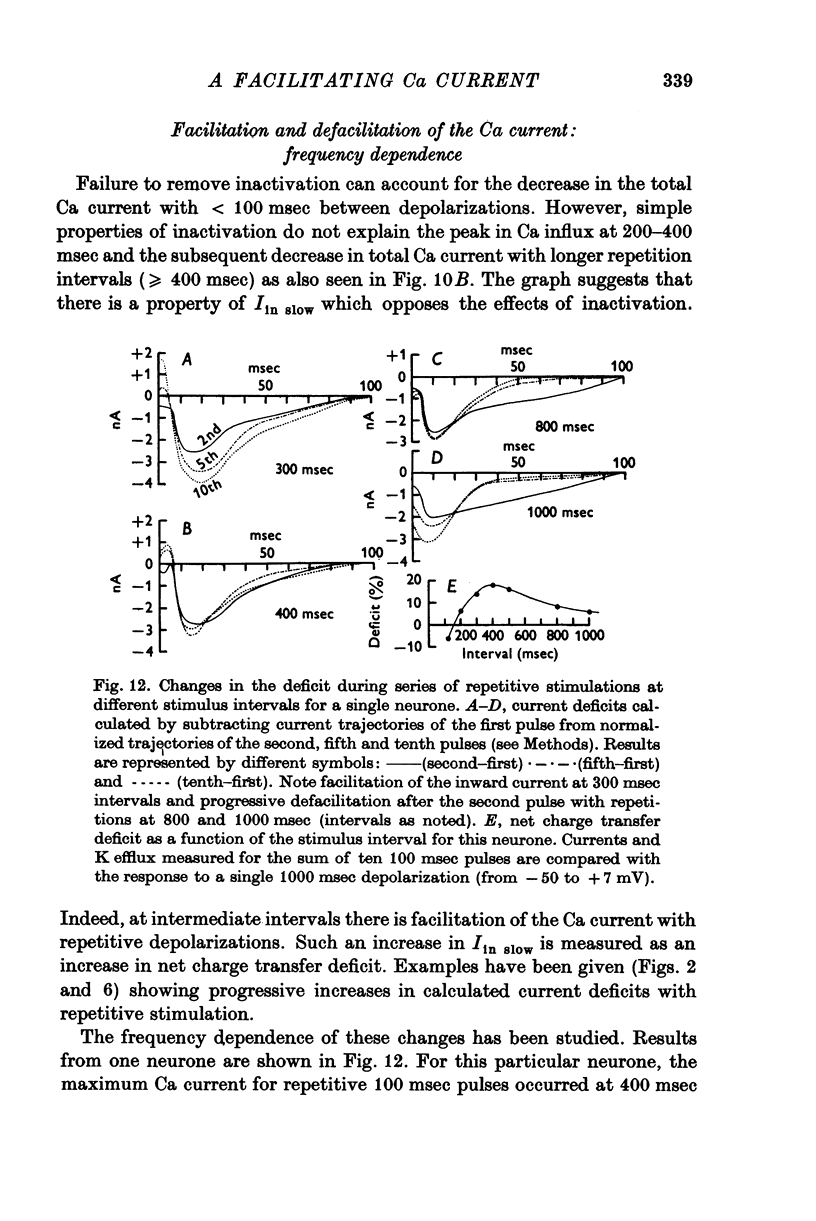
1. Simultaneous measurements of local voltage clamp currents from patches of soma membrane and K activity at the soma surface were used to analyse the time and voltage dependence of the slow inward current in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail (Helix pomatia). 2. At low levels of depolarization (less than or equal to mV) a net inward current is recorded simultaneously with an efflux of K ions from the cell. 3. With larger depolarizations (20-170 mV from holding potential of -50 mV) the deficit in net outward charge transfer compared with K efflux and the appearance of inward-going tail currents following repolarization, reveal a persistent inward-going current also under these conditions. This inward current is carried primarily by Ca ions, as demonstrated by its voltage dependence (a minimum at about + 115 mV) and its disappearance in Co-Ringer. It is identified with the slow inward Ca current Iin slow (Eckert & Lux, 1976). 4. The inward current predicted from comparisons of current trajectories reaches a maximum at 15-20 msec (for depolarizations from -50 to 0 mV) and gradually declines with sustained depolarization. 5. Partial inactivation is removed by repolarization to -50 mV and the Ca dependent deficit is greater in the sum of repeated voltage clamp pulses than during sustained depolarization. It is largest for pulses of 25-100 msec duration, decreasing as pulse duration increases. 6. Responses to repeated activation with 100 msec pulses with different repolarization intervals reveal a minimum Iin slow at short intervals (e.g. 20 msec) due to failure to remove partial inactivation. At intermediate intervals (e.g. 200-400 msec) Iin slow shows facilitation. This is revealed in calculations of the net charge transfer and current deficits and is also shown in the tail currents following repolarization. The deficit increases progressively with repetitive stimulation. With longer intervals (e.g. 800-1000 msec) defacilitation during repeated stimulation after the first two pulses is revealed in calculations of deficits, current trajectories and in the tail currents. 7. Although facilitation depends on duration of repolarization between pulses, increasing intermediate hyperpolarizations from the holding potential of -50 mV are usually ineffective in increasing Iin slow. Strong preceding hyperpolarization can even decrease the magnitude of Iin slow and prevent its facilitation with repetitive stimulation,whereas preceding depolarizing pulses can increase Iin slow without preventing its facilitation with repetitive stimulation. 8. The properties of Iin slow are contrasted with previously described membrane conductances and compared with properties attributed to Ca fluxes in other systems.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
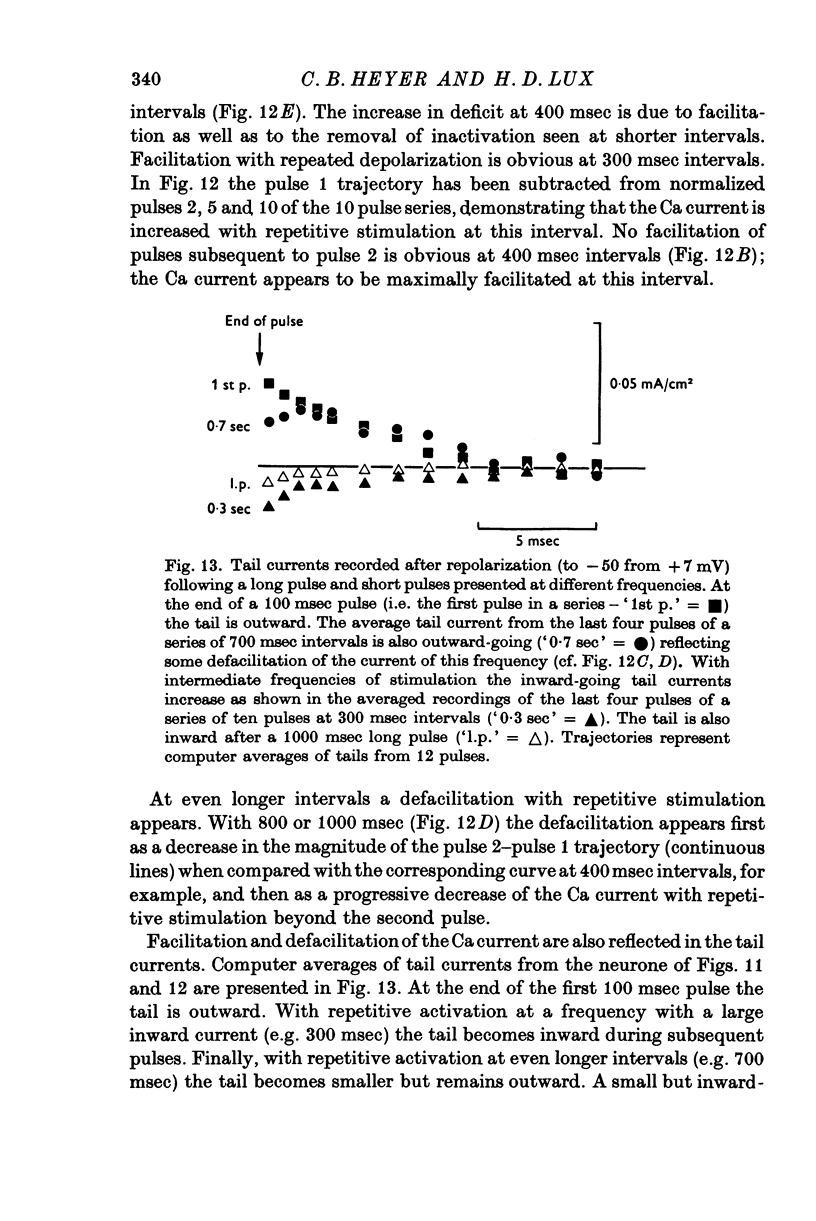
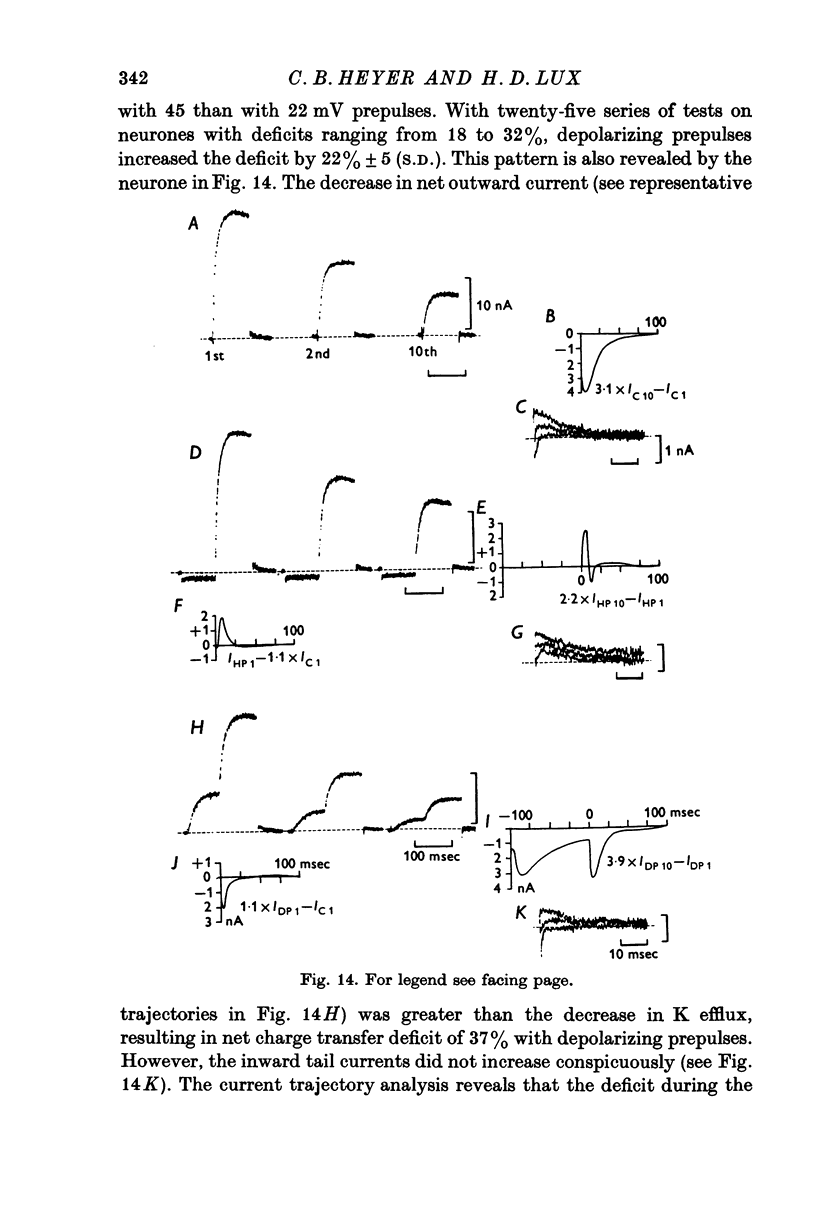
- Baker P. F., Glitsch H. G. Voltage-dependent changes in the permeability of nerve membranes to calcium and other divalent cations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):389–409. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Meves H., Ridgway E. B. Calcium entry in response to maintained depolarization of squid axons. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(3):527–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A non-inactivating inward current recorded during small depolarizing voltage steps in snail pacemaker neurons. Brain Res. 1975 Jan 17;83(3):486–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90840-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. Surface density of calcium ions and calcium spikes in the barnacle muscle fiber membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):583–601. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyer C. B., Lux H. D. Control of the delayed outward potassium currents in bursting pace-maker neurones of the snail, Helix pomatia. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):349–382. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Rojas E., Taylor R. E., Vergara J. Calcium and potassium systems of a giant barnacle muscle fibre under membrane potential control. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(2):409–455. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Eckert R. Inferred slow inward current in snail neurones. Nature. 1974 Aug 16;250(467):574–576. doi: 10.1038/250574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E. The equilibration time course of (K + ) 0 in cat cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1973 Apr 30;17(2):190–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00235028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier Y., Vassort G. Initial and delayed membrane currents in crab muscle fibre under voltage-clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):589–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E., Lux H. D. Rapid changes of potassium concentration at the outer surface of exposed single neurons during membrane current flow. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):385–399. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Armstrong C. Sodium conductance activation without inactivation in pronase-perfused axons. Nat New Biol. 1971 Feb 10;229(6):177–178. doi: 10.1038/newbio229177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakharov D. A., Salánki J. Physiological and pharmacological identification of neurons in the central nervous system of Helix pomatia L. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1969;35(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinnakre J., Tauc L. Calcium influx in active Aplysia neurones detected by injected aequorin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 28;242(117):113–115. doi: 10.1038/newbio242113b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. C. Intracellular sodium activity and the sodium pump in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Jan;220(1):55–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Characteristics of crayfish neuromuscular facilitation and their calcium dependence. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):91–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker R. S. Crayfish neuromuscular facilitation activated by constant presynaptic action potentials and depolarizing pulses. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):69–89. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


