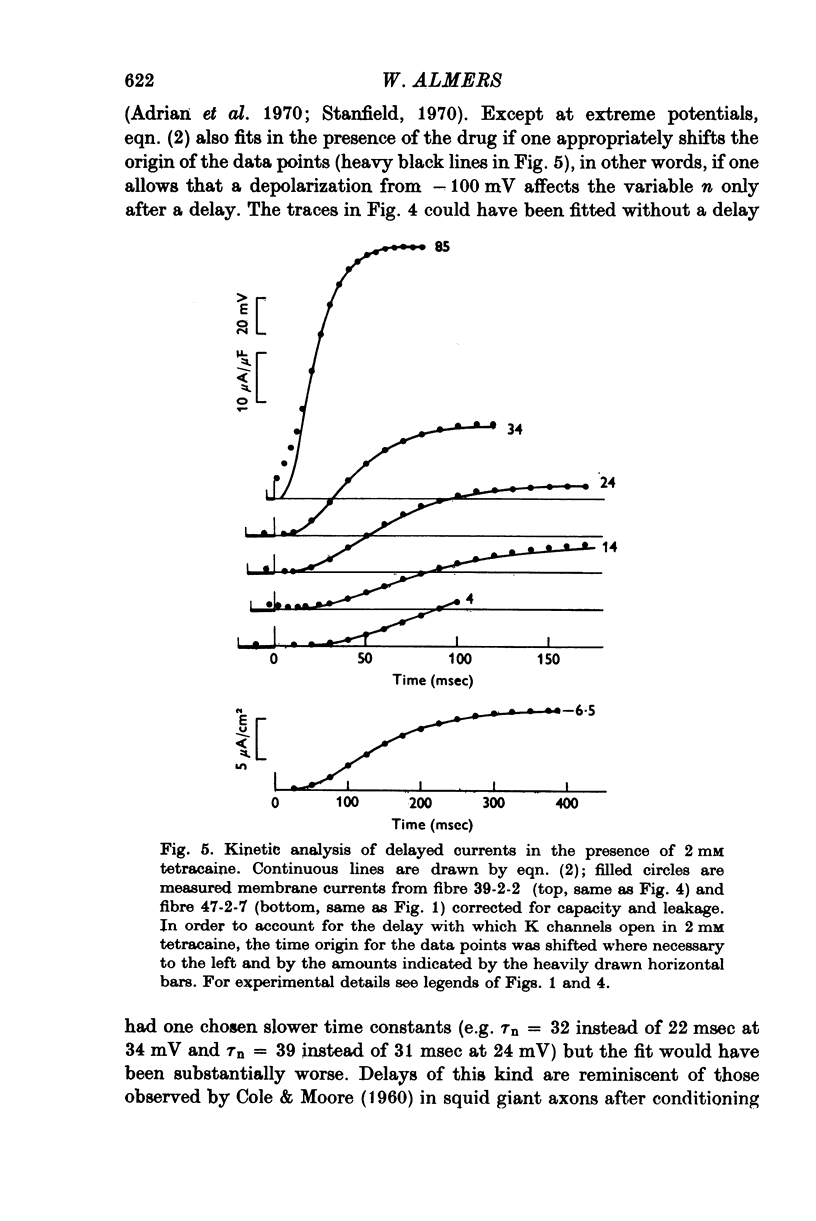
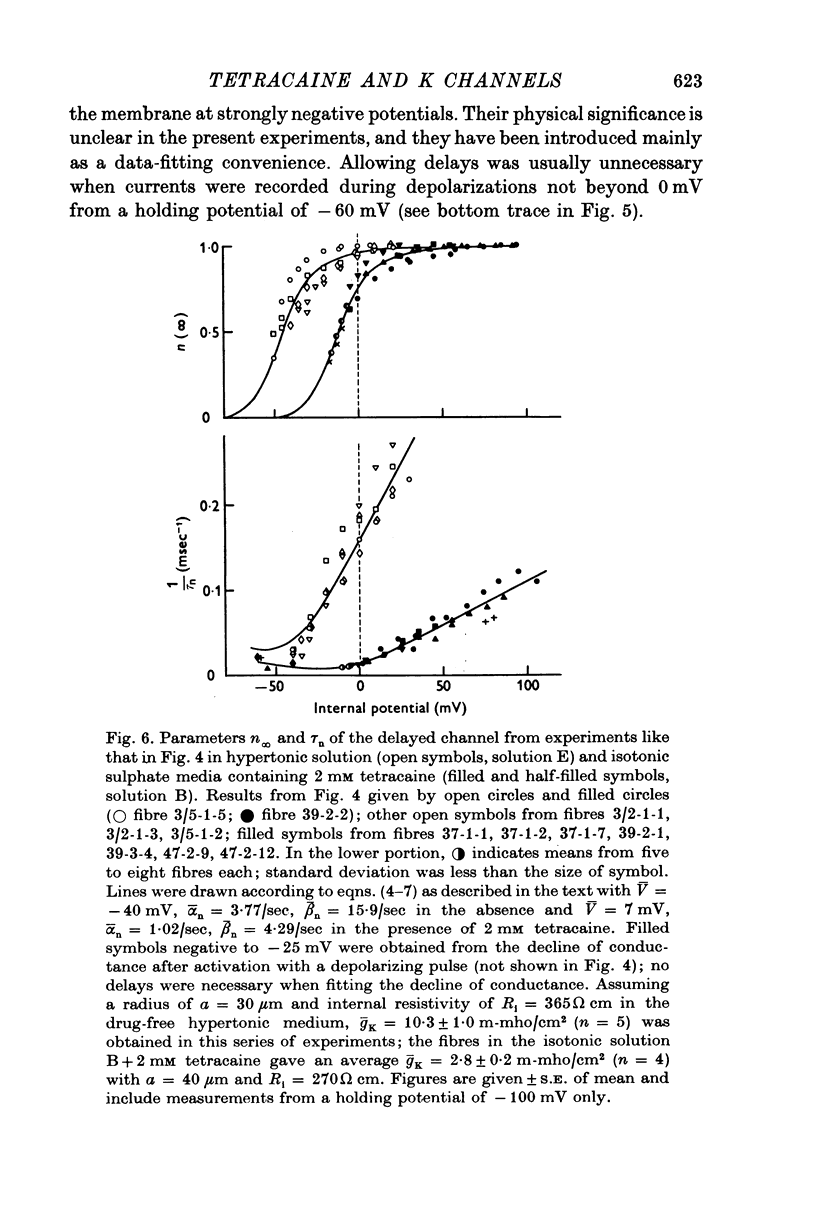
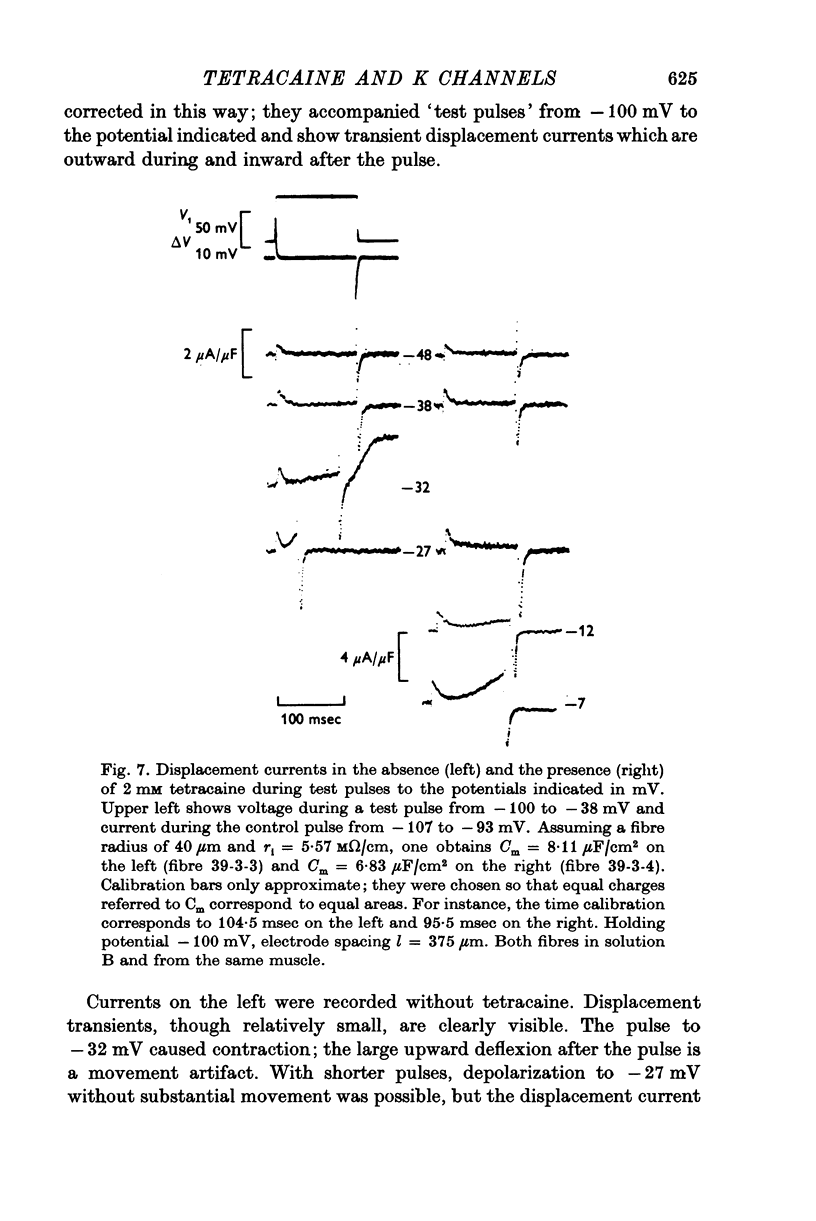
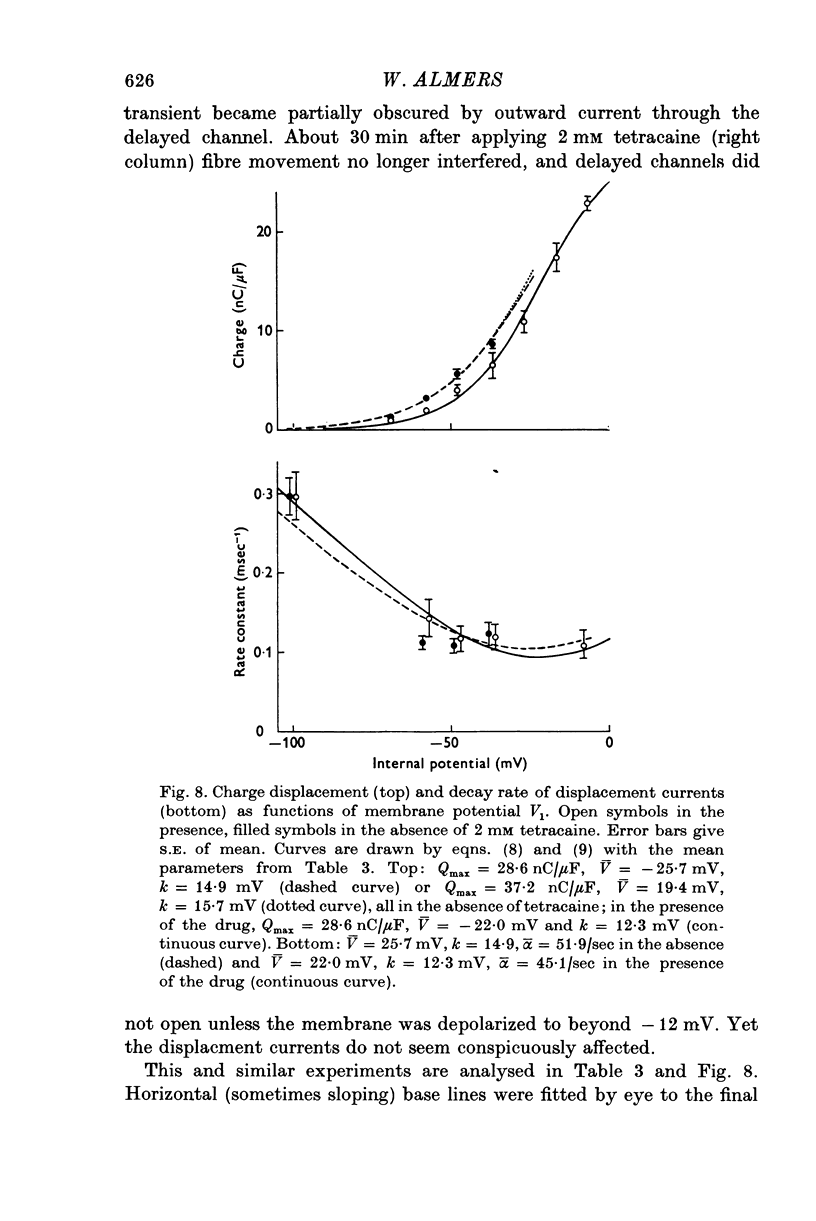
Abstract
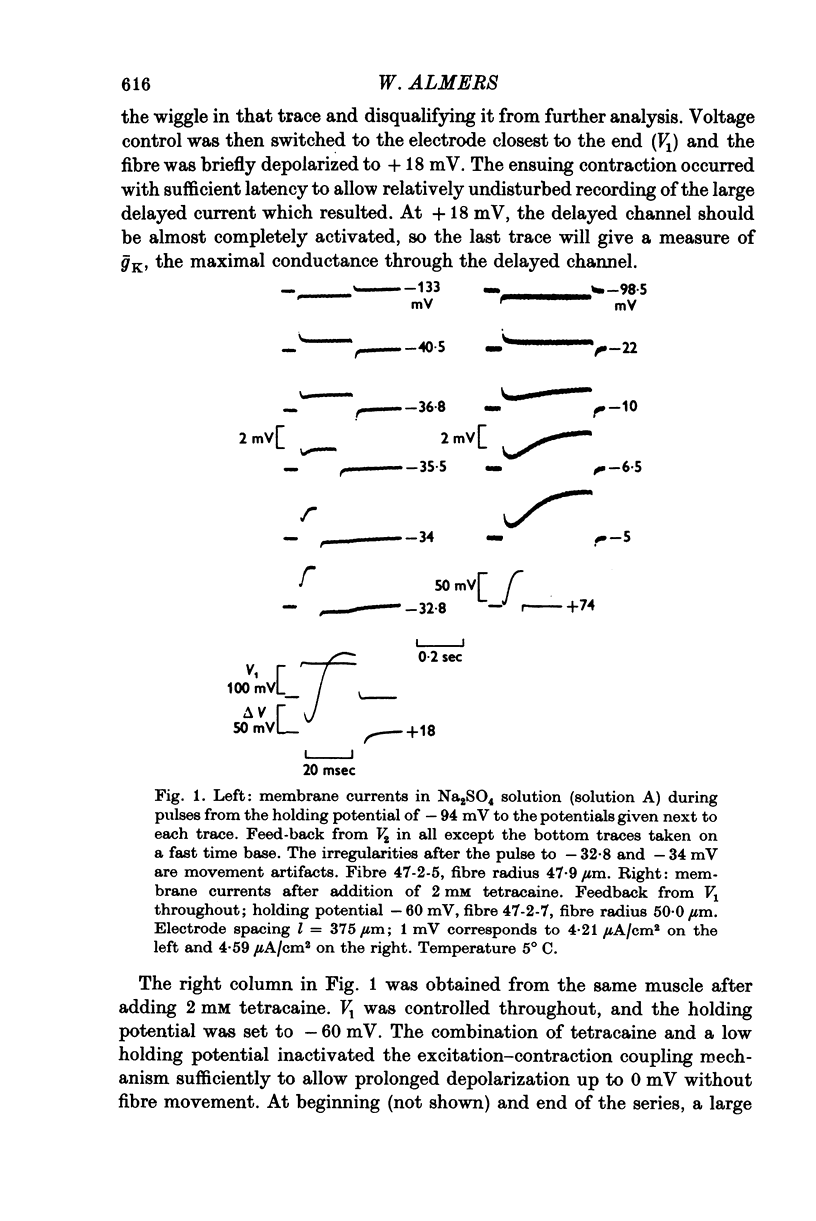
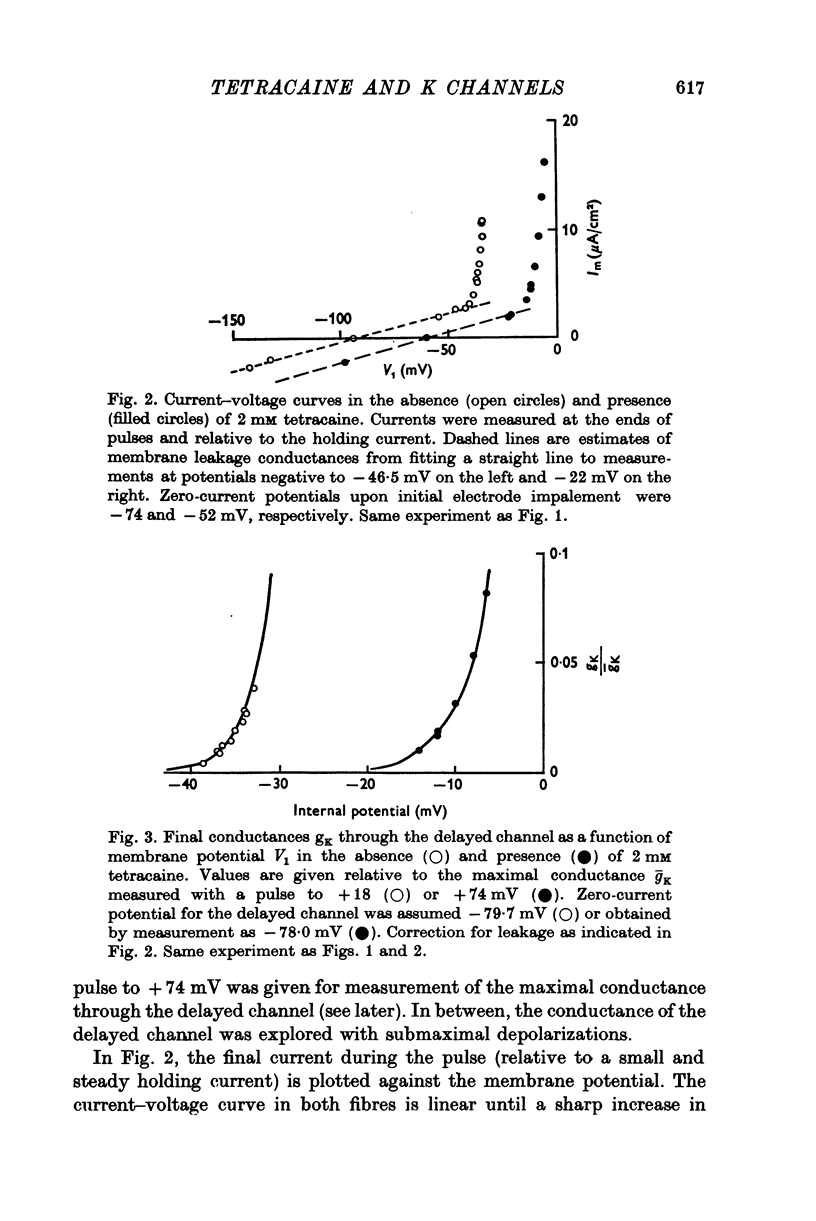
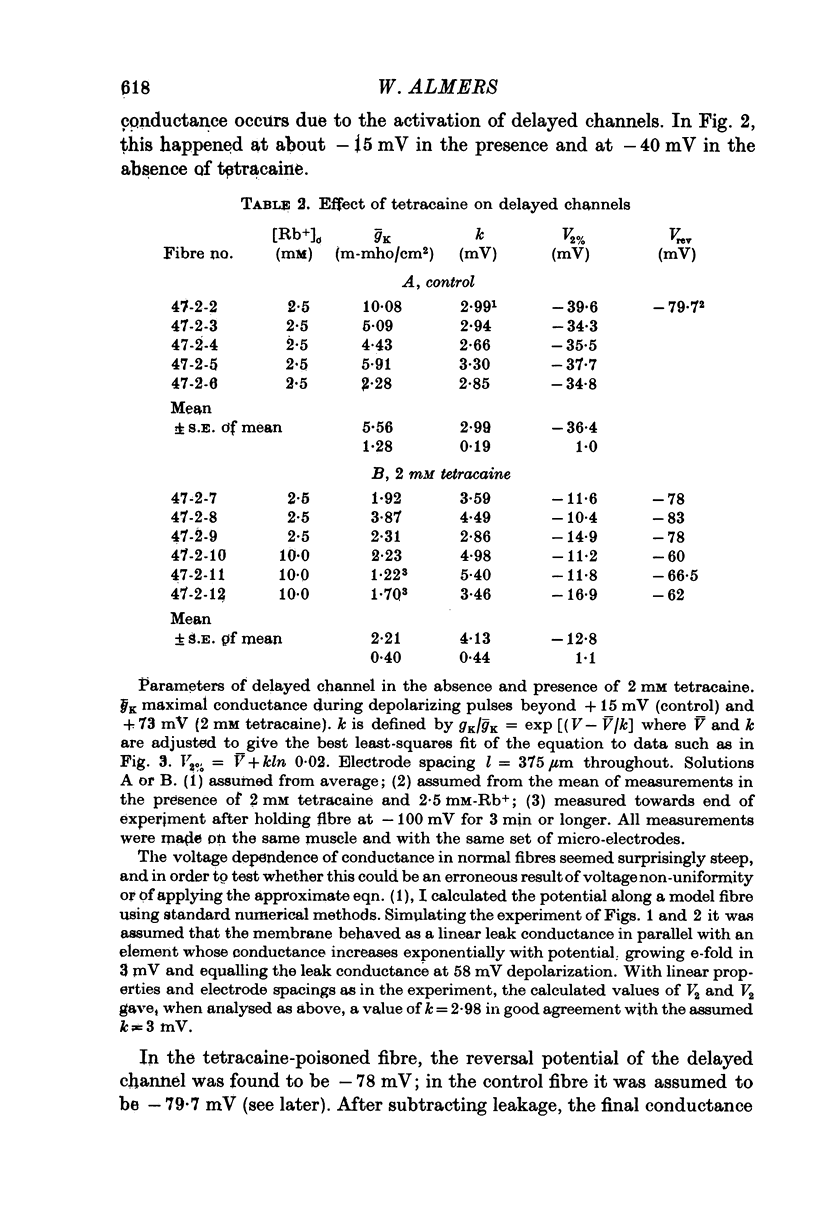
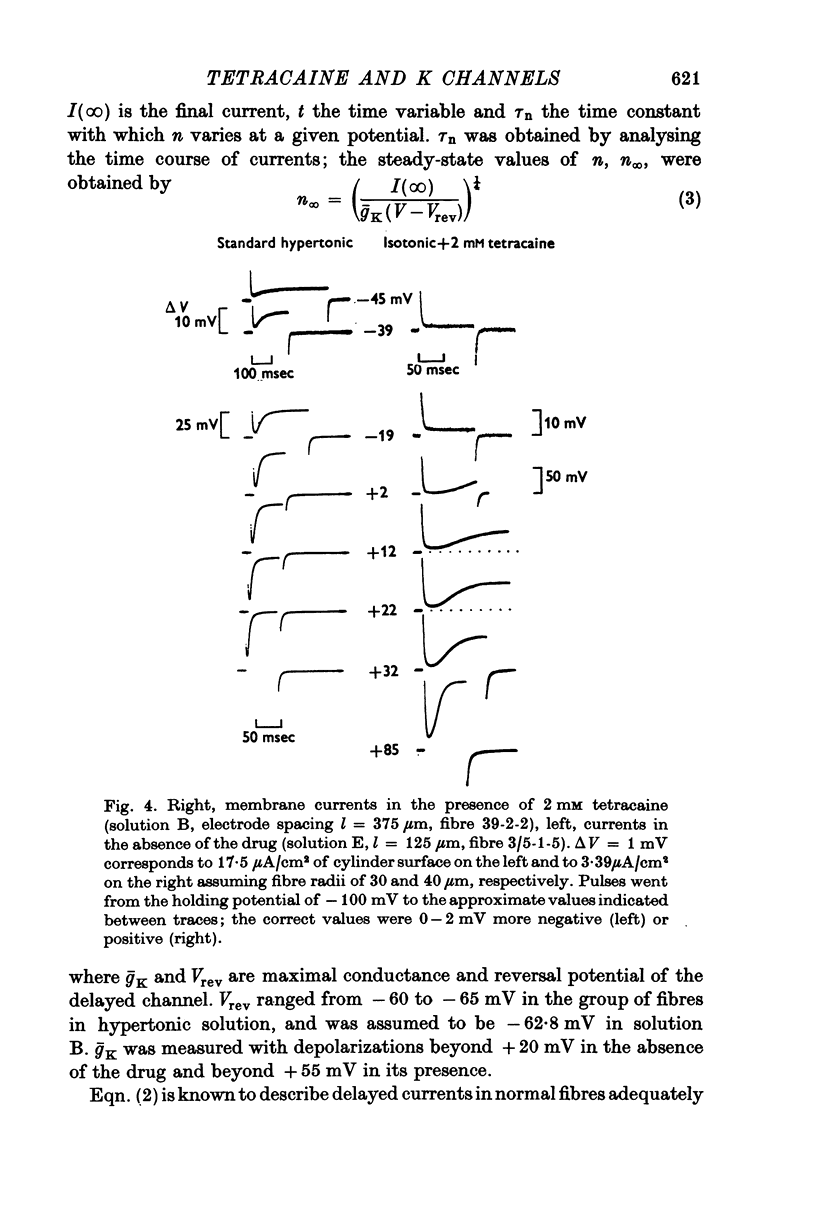
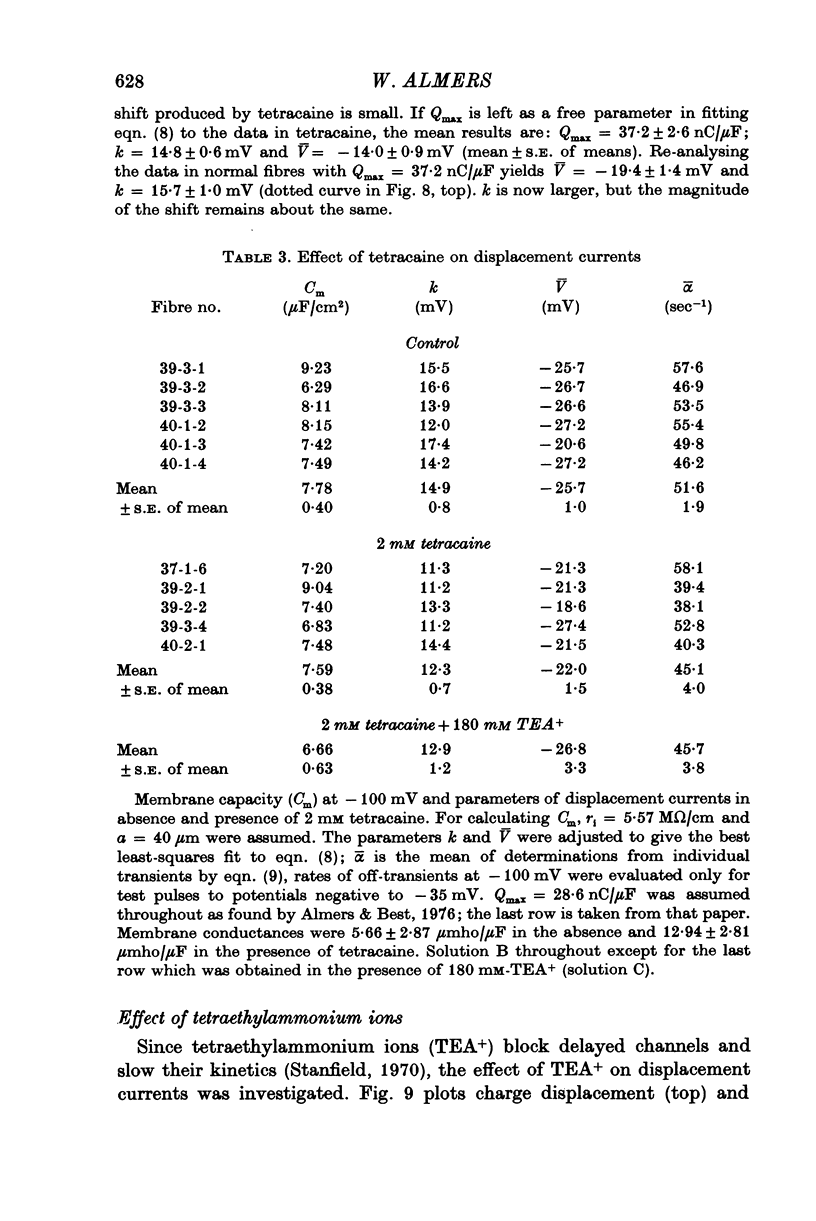
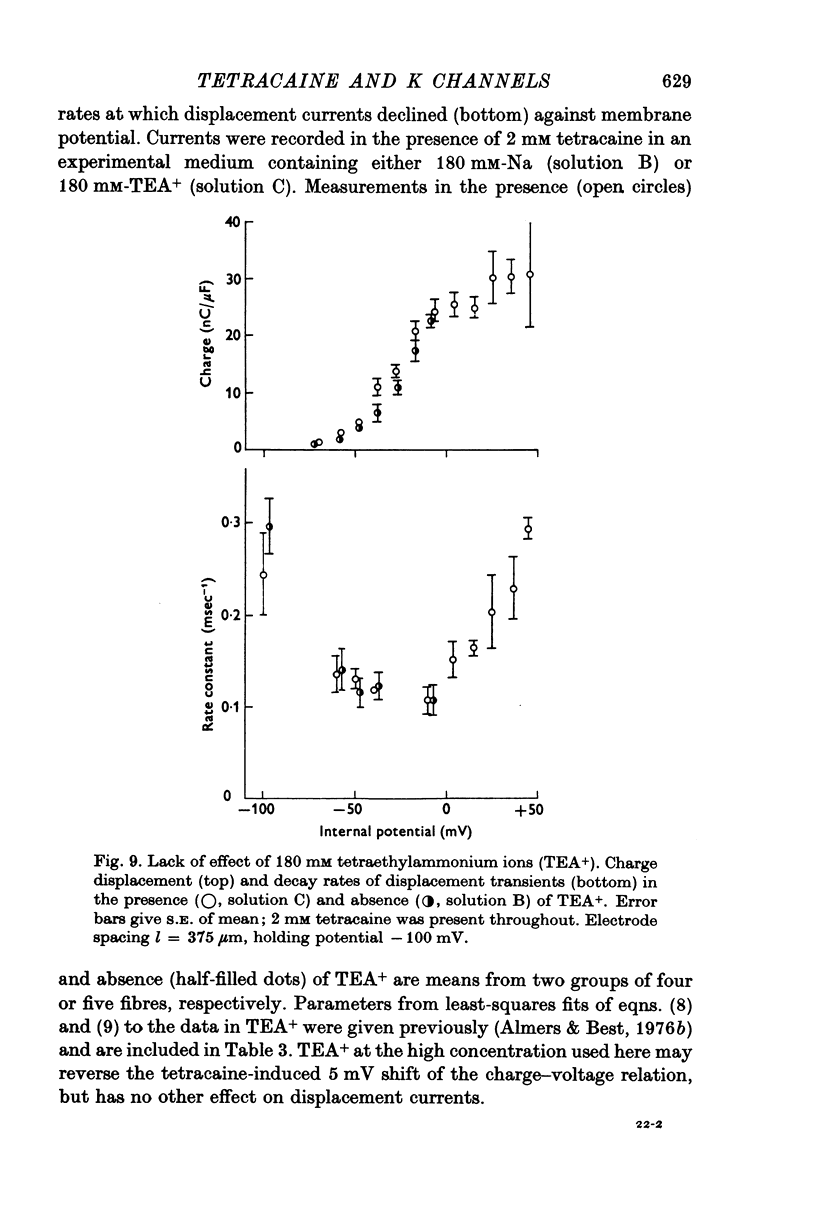
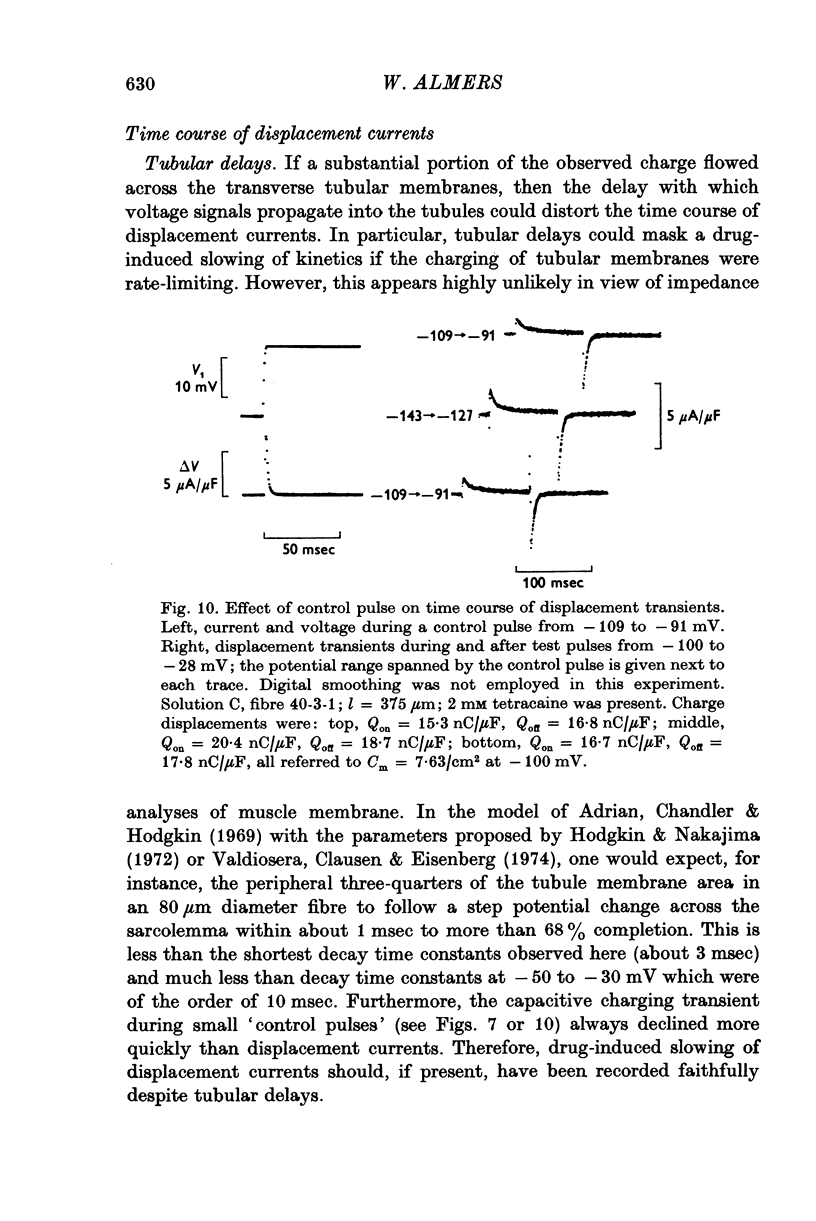
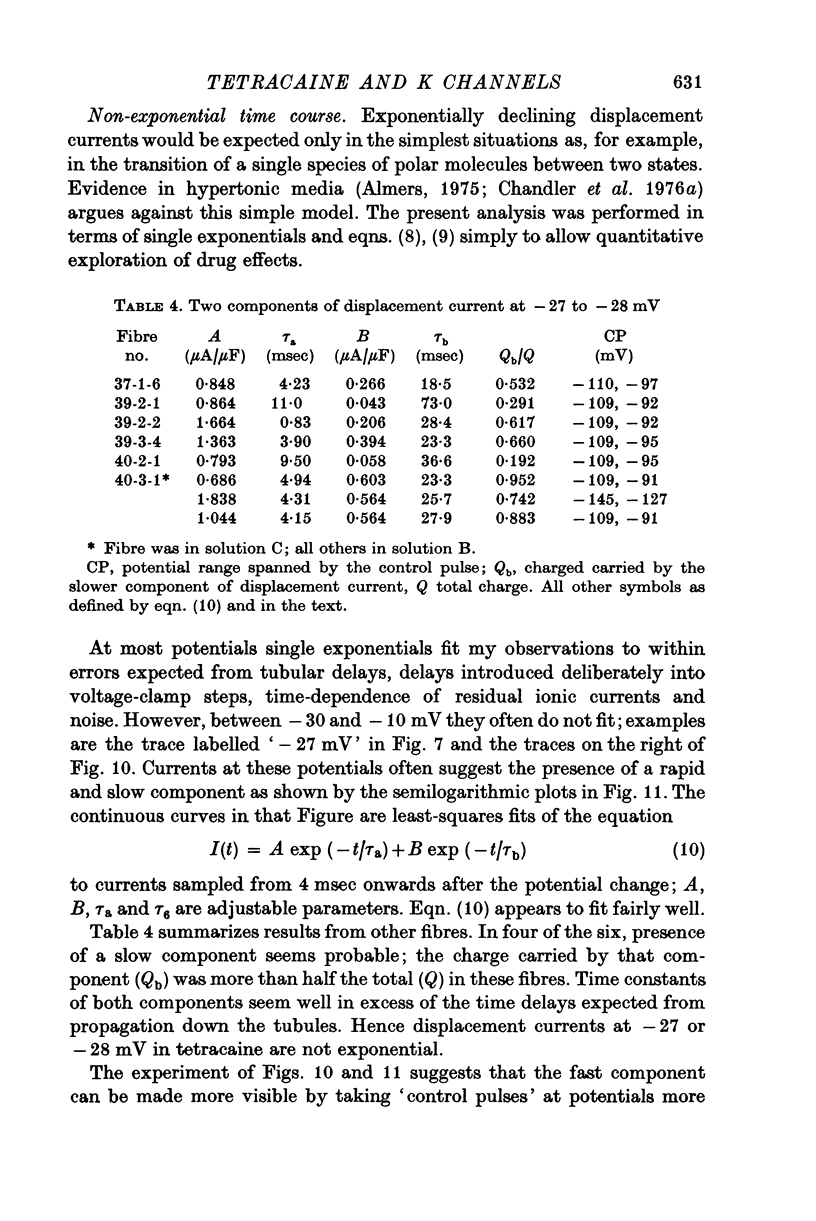
1. Delayed K+-currents and displacement currents were studied with a voltage-clamp technique. 2. In normal fibres, the conductance of the delayed channel grows e-fold per 3 millivolts at sufficiently negative potentials and reaches a limiting value of 2-10 m-mho/cm2 (mean 5-8 m-mho/cm2) at positive potentials. Adding tetracaine (2 mM) reduces the limiting conductance, shifts the voltage-dependence of the delayed channel to +25 mV more positive potentials and slows the kinetics fourfold. 3. By contrast, the displacement currents are virtually unaltered by 2 mM tetracaine. Their voltage-dependence is shifted by less than 5 mV and their kinetics are unaffected. 4. Tetraethylammonium ions (TEA) are known to slow the kinetics of delayed K+-channels fivefold but fail, like tetracaine, to change the kinetics of the displacement currents. 5. Both tetracaine and TEA have thus large effects on the 'gating' of the delayed channel, yet little or none on the displacement currents. This suggests that the displacement currents in skeletal muscle are for the most part unrelated to the opening and closing of delayed channels. It is estimated that 'gating' the delayed channel in muscle may require no more than 1 or 2% of the observed charge displacement.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. Charge movement in the membrane of striated muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):339–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Almers W. The voltage dependence of membrane capacity. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):317–338. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. The kinetics of mechanical activation in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):207–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L. Voltage clamp experiments in striated muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;208(3):607–644. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian R. H., Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F. Charge movement and mechanical repriming in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):361–388. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Best P. M. Effects of tetracaine on displacement currents and contraction of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(3):583–611. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W., Levinson S. R. Tetrodotoxin binding to normal depolarized frog muscle and the conductance of a single sodium channel. J Physiol. 1975 May;247(2):483–509. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almers W. Some dielectric properties of muscle membrane and their possible importance for excitation-contraction coupling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:278–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arhem P., Frankenhaeuser B. Local anesthetics: effects on permeability properties of nodal membrane in myelinated nerve fibres from xenopus. Potential clamp experiments. Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 May;91(1):11–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F. Charge movement associated with the opening and closing of the activation gates of the Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1974 May;63(5):533–552. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Begenisich T., Stevens C. F. How many conductance states do potassium channels have? Biophys J. 1975 Aug;15(8):843–846. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85858-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein M. P., Goldman D. E. Competitive action of calcium and procaine on lobster axon. A study of the mechanism of action of certain local anesthetics. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):1043–1063. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Potassium ion current in the squid giant axon: dynamic characteristic. Biophys J. 1960 Sep;1:1–14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(60)86871-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. A non-linear voltage dependent charge movement in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):245–283. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Rakowski R. F., Schneider M. F. Effects of glycerol treatment and maintained depolarization on charge movement in skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(2):285–316. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Potassium channels in myelinated nerve. Selective permeability to small cations. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):669–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin A. L., Nakajima S. Analysis of the membrane capacity in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1972 Feb;221(1):121–136. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M. Mechanism of action of local anaesthetic agents and biotoxins. Br J Anaesth. 1975 Feb;47 Suppl:191–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. Local anaesthetics. VI. Relation between blocking potency and penetration of a monomolecular layer of lipoids from nerves. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1954;10(4):325–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1954.tb01349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Effects of membrane potential on the capacitance of skeletal muscle fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Feb;67(2):125–163. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. F., Chandler W. K. Voltage dependent charge movement of skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling. Nature. 1973 Mar 23;242(5395):244–246. doi: 10.1038/242244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P. The membrane actions of anesthetics and tranquilizers. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Dec;24(4):583–655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of the tetraethylammonium ion on the delayed currents of frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):209–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of zinc ions on the gating of the delayed potassium conductance of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):711–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. R. The inhibition of sodium currents in myelinated nerve by quaternary derivatives of lidocaine. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jul;62(1):37–57. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. E. Effect of procaine on electrical properties of squid axon membrane. Am J Physiol. 1959 May;196(5):1071–1078. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.5.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdiosera R., Clausen C., Eisenberg R. S. Impedance of frog skeletal muscle fibers in various solutions. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Apr;63(4):460–491. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.4.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


