Abstract
1. Electrophysiological properties of the rat chromaffin cell were studied using intracellular recording techniques. 2. The resting potential in the chromaffin cell was -49 +/- 6 mV (mean +/- S.D., n = 14) in standard saline containing 10 mM-Ca whereas that in Na-free saline was -63 +/- 9 mV (n = 17). At rest, the membrane has a substantial Na permeability. 3. Action potentials were evoked by passing current through the recording electrode. In standard saline the major fraction of the action potential disappeared either upon omission of external Na ions from standard saline or addition of 1 muM tetrodotoxin (TTX). We conclude that action potentials in the chromaffin cell are due mainly to an increase in the permeability of the membrane to Na ions. 4. Small but significant regenerative action potentials were observed in Na-free saline, and when Ca in Na-free saline was replaced by Ba, prolonged action potentials occurred. We conclude that action potentials in the chromaffin cell also have a Ca component. 5. Iontophoretic application of acetylcholine (ACh) produced a transient membrane depolarization in standard saline. 6. Spontaneous action potentials were recorded extracellularly by microsuction electrodes. They occurred at a rate of 0-05-0-1/sec in almost all cells. 7. When the perfusion fluid contained 3 x 10(-7) M to 10(-4) M ACh the spike frequency increased up to about 2/sec. This stimulatory effect of ACh was blocked by 10(-7) M atropine but not by 10(-3) M hexamethonium nor by 10(-5) M-d-tubocurarine. 8. The importance of Ca entry during action potentials for catecholamine secretion is discussed
Full text
PDF
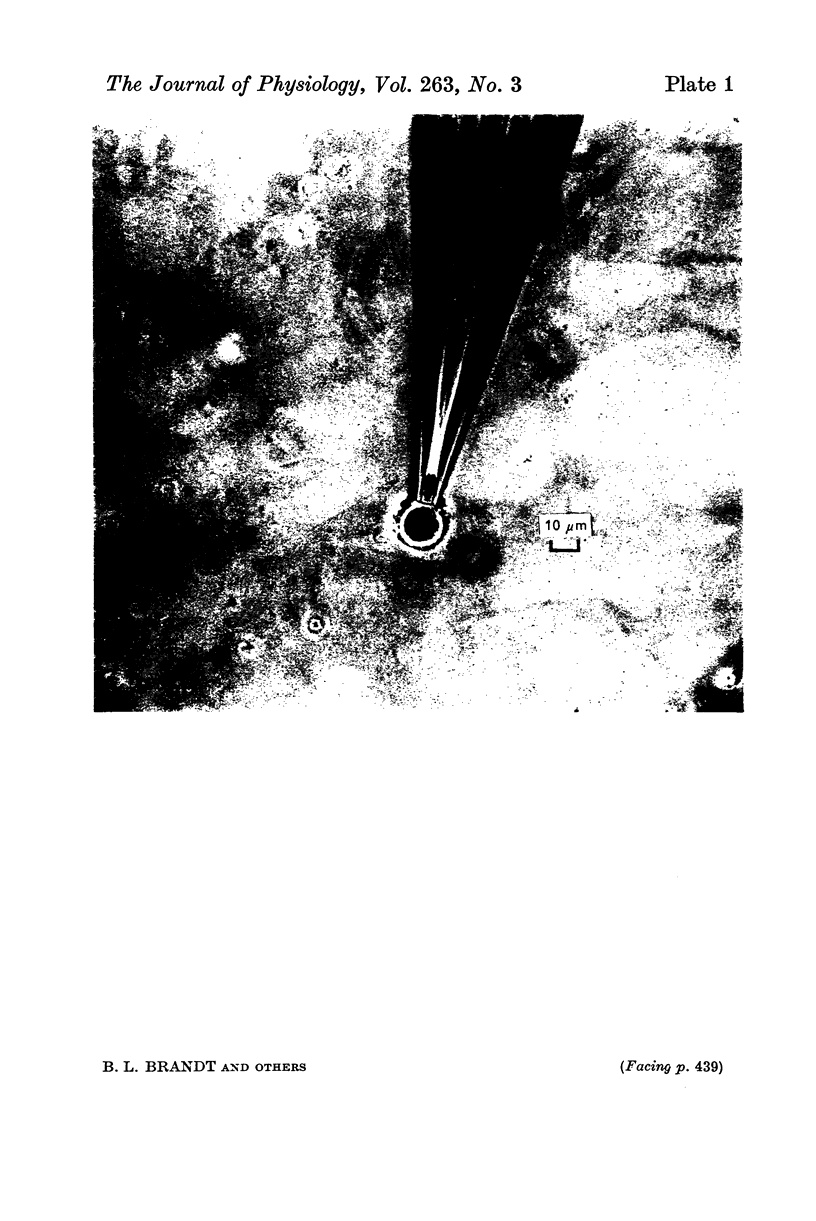



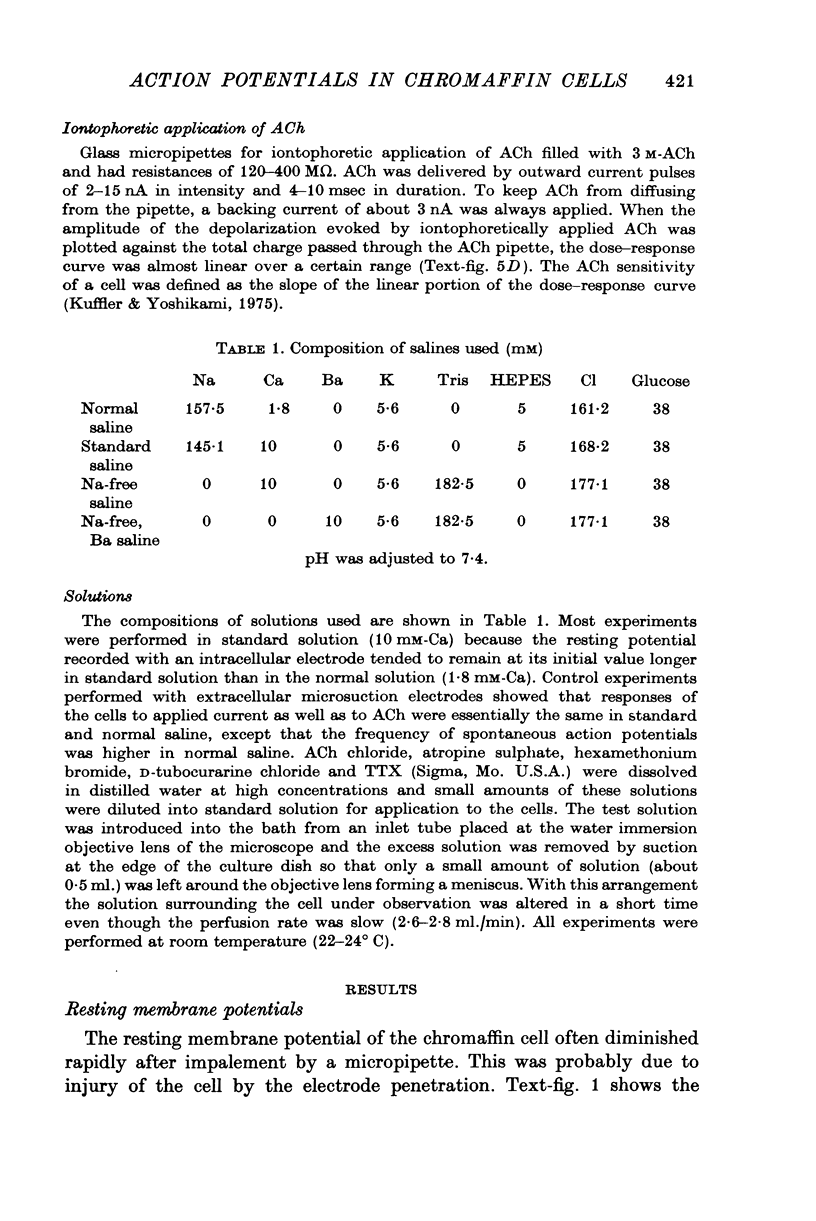
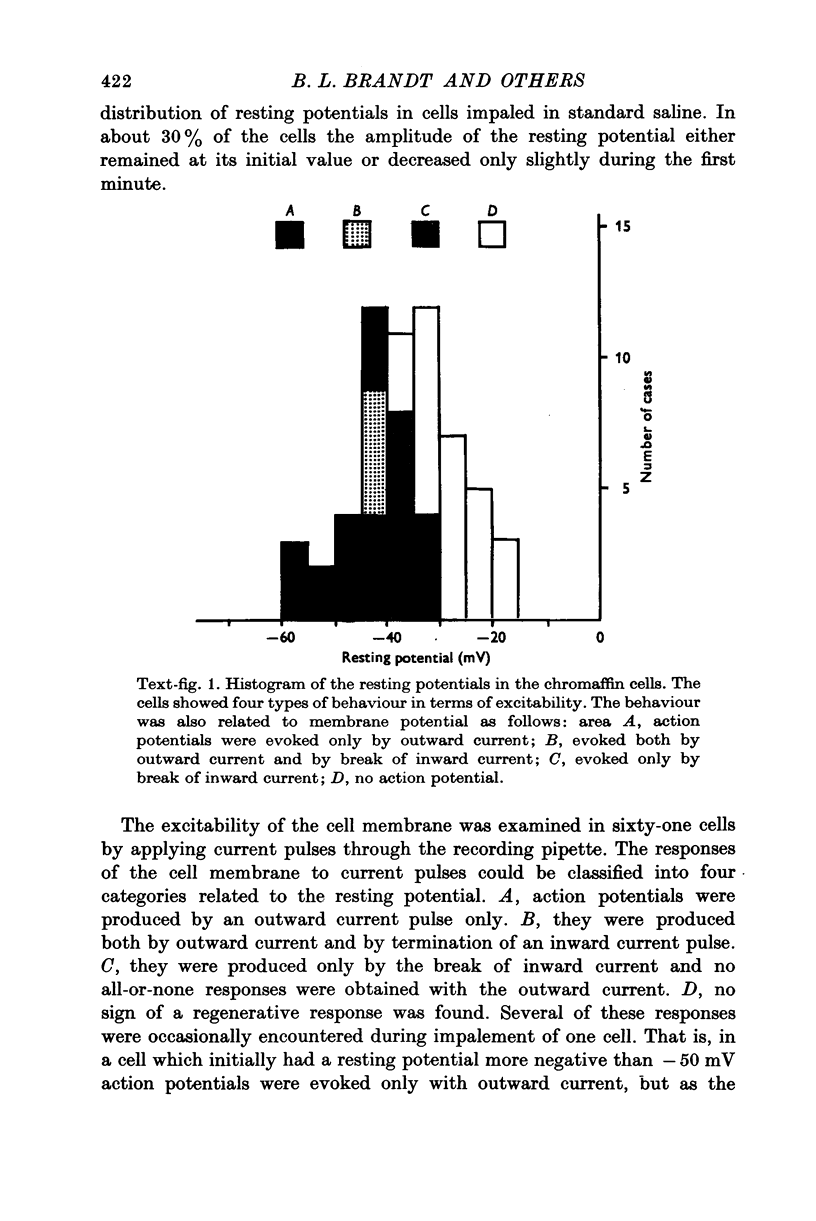

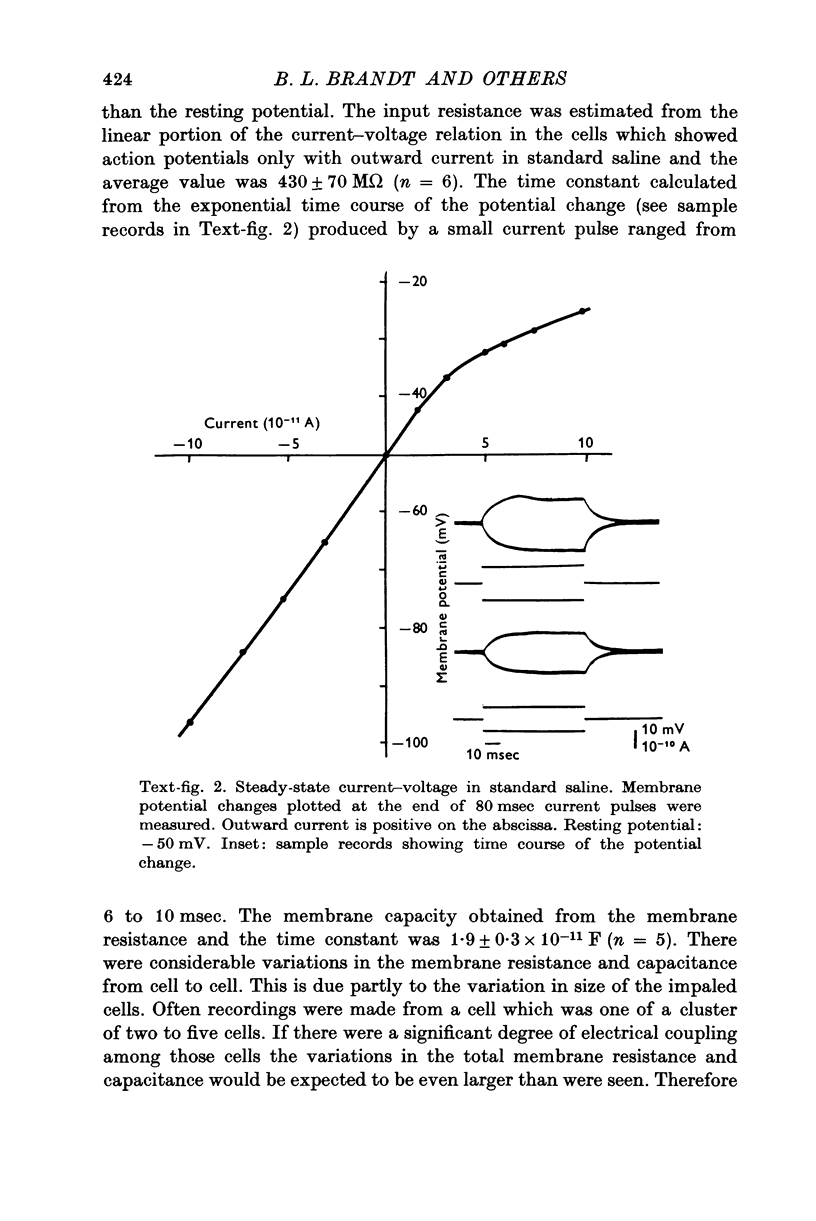
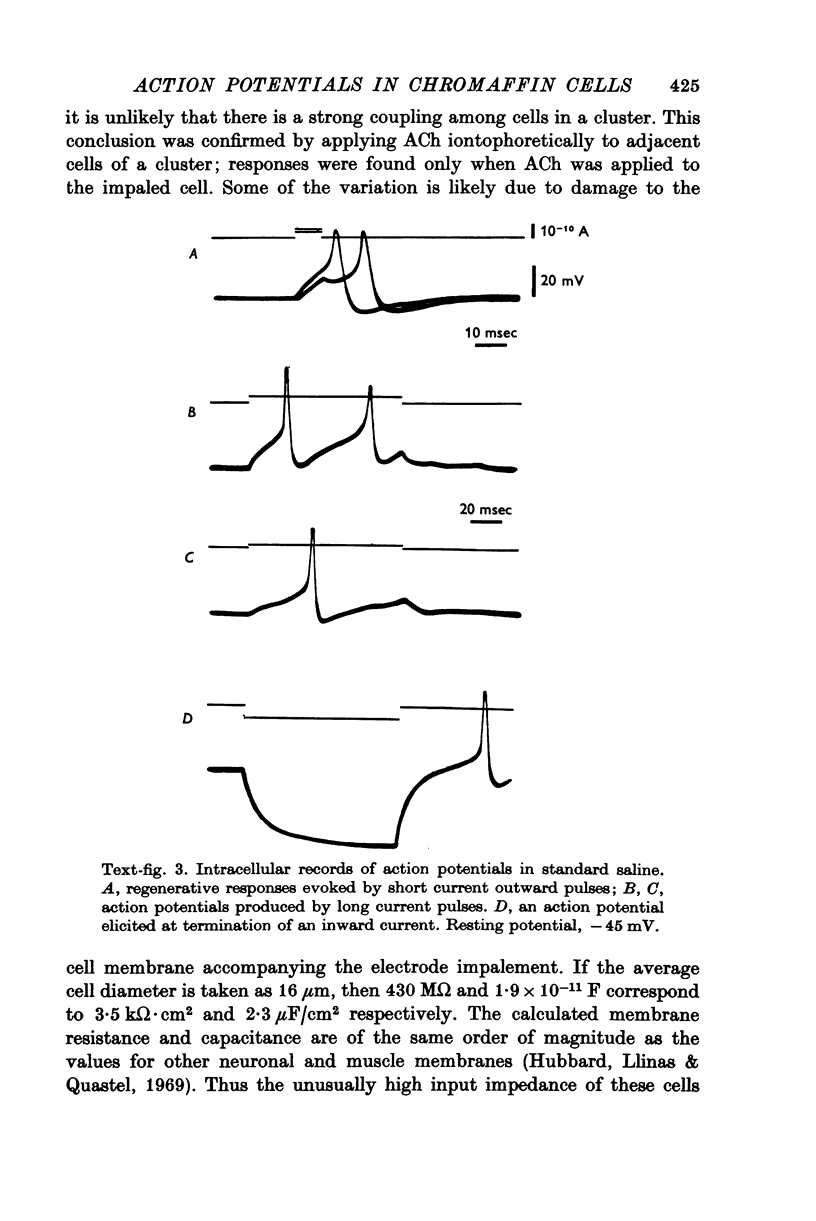










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., POISNER A. M. On the mode of action of acetylcholine in evoking adrenal medullary secretion: increased uptake of calcium during the secretory response. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:385–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. STIMULANT ACTION OF BARIUM ON THE ADRENAL MEDULLA. Nature. 1964 Jul 18;203:305–307. doi: 10.1038/203305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RUBIN R. P. The role of calcium in the secretory response of the adrenal medulla to acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1961 Nov;159:40–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Kanno T., Sampson S. R. Effects of acetylcholine and other medullary secretagogues and antagonists on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells: an analysis employing techniques of tissue culture. J Physiol. 1967 Jan;188(1):107–120. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Kanno T., Sampson S. R. Influence of the ionic environment on the membrane potential of adrenal chromaffin cells and on the depolarizing effect of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):107–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Poisner A. M. Preferential release of adrenaline from the adrenal medulla by muscarine and pilocarpine. Nature. 1965 Dec 11;208(5015):1102–1103. doi: 10.1038/2081102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W., Rubin R. P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J Physiol. 1963 Jul;167(2):288–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas W. W. Stimulus-secretion coupling: the concept and clues from chromaffin and other cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;34(3):451–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb08474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., GINSBORG B. L. The ionic requirements for the production of action potentials in crustacean muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 6;142(3):516–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foreman J. C., Mongar J. L., Gomperts B. D. Calcium ionophores and movement of calcium ions following the physiological stimulus to a secretory process. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):249–251. doi: 10.1038/245249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., NAKA K. I. THE INITIATION OF SPIKE POTENTIAL IN BARNACLE MUSCLE FIBERS UNDER LOW INTRACELLULAR CA++. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:141–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLARP N. A., HOKFELT B. Histochemical demonstration of noradrenaline and adrenaline in the adrenal medulla. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 Jan;3(1):1–5. doi: 10.1177/3.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Kidokoro Y. Na and Ca components of action potential in amphioxus muscle cells. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):217–232. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. J., Kuffler S. W., Dennis M. J. Differential chemosensitivity of synaptic and extrasynaptic areas on the neuronal surface membrane in parasympathetic neurons of the frog, tested by microapplication of acetylcholine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):541–553. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman J., Perlman R. L. Catecholamine secretion by isolated adrenal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 14;421(1):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno T., Cochrane D. E., Douglas W. W. Exocytosis (secretory granule extrusion) induced by injection of calcium into mast cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;51(12):1001–1004. doi: 10.1139/y73-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Developmental changes of membrane electrical properties in a rat skeletal muscle cell line. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):129–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Sodium and calcium components of the action potential in a developing skeletal muscle cell line. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(1):145–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Spontaneous calcium action potentials in a clonal pituitary cell line and their relationship to prolactin secretion. Nature. 1975 Dec 25;258(5537):741–742. doi: 10.1038/258741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Dennis M. J., Harris A. J. The development of chemosensitivity in extrasynaptic areas of the neuronal surface after denervation of parasympathetic ganglion cells in the heart of the frog. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1971 Apr 27;177(1049):555–563. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1971.0047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuffler S. W., Yoshikami D. The distribution of acetylcholine sensitivity at the post-synaptic membrane of vertebrate skeletal twitch muscles: iontophoretic mapping in the micron range. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):703–730. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: ionic dependence of the membrane potential and acetycholine-induced depolarization. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):283–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J., Minna J. An active electrical response in fibroblasts. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jul;60(1):58–71. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Harris A. J., Devine C. E., Heinemann S. Characterization of a unique muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):398–413. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI N. Effects of calcium on the conductance change of the end-plate membrane during the action of transmitter. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:141–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I. Resting and action potentials of reversed polarity in frog nerve cells. Nature. 1959 Nov 14;184(Suppl 20):1574–1575. doi: 10.1038/1841574a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R. Steps in the neoplastic transformation of hamster embryo cells by polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Feb 15;49:171–179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The secretion of the denervated adrenal medulla of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1952 Jun;7(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1952.tb01329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Grant G. In vitro pituitary hormone secretion assay for hypophysiotropic substances. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:82–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD J. G. Identification of and observations on epinephrine and norepinephrine containing cells in the adrenal medulla. Am J Anat. 1963 May;112:285–303. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001120302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



