Abstract
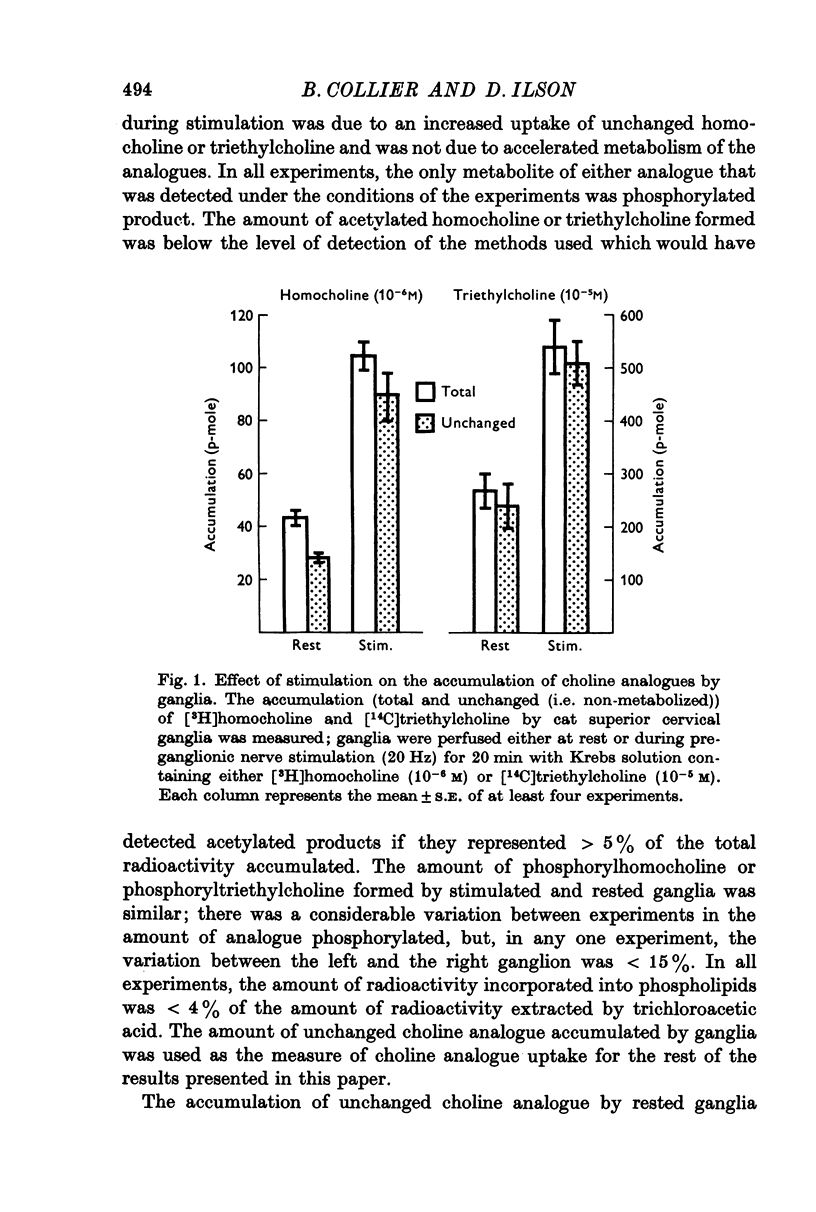
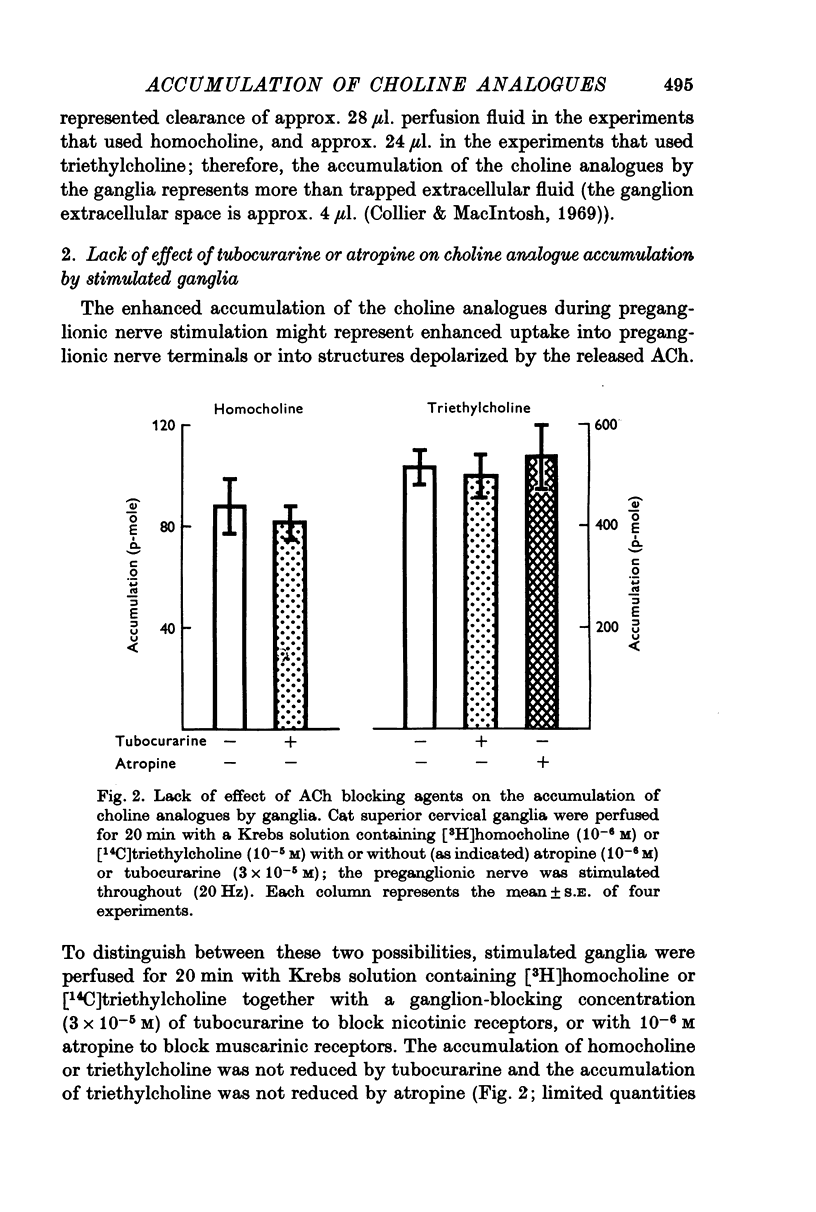
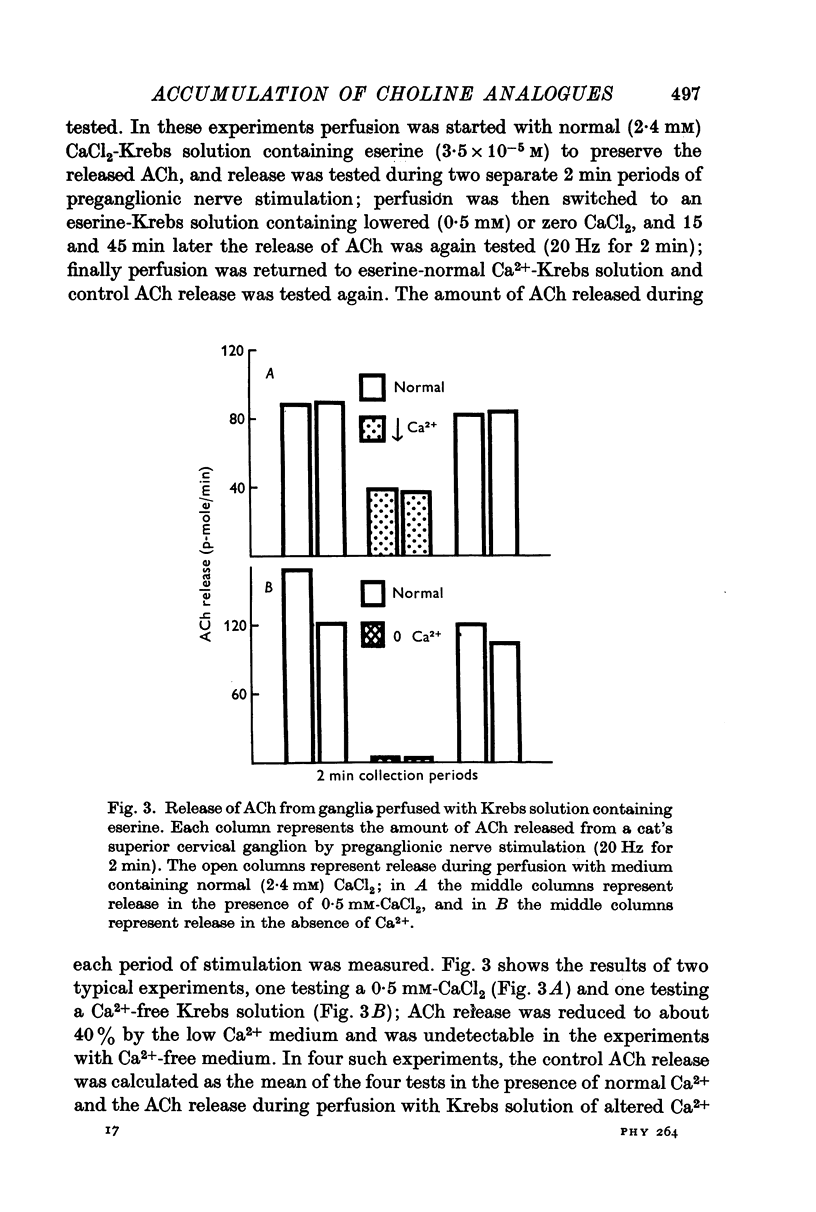
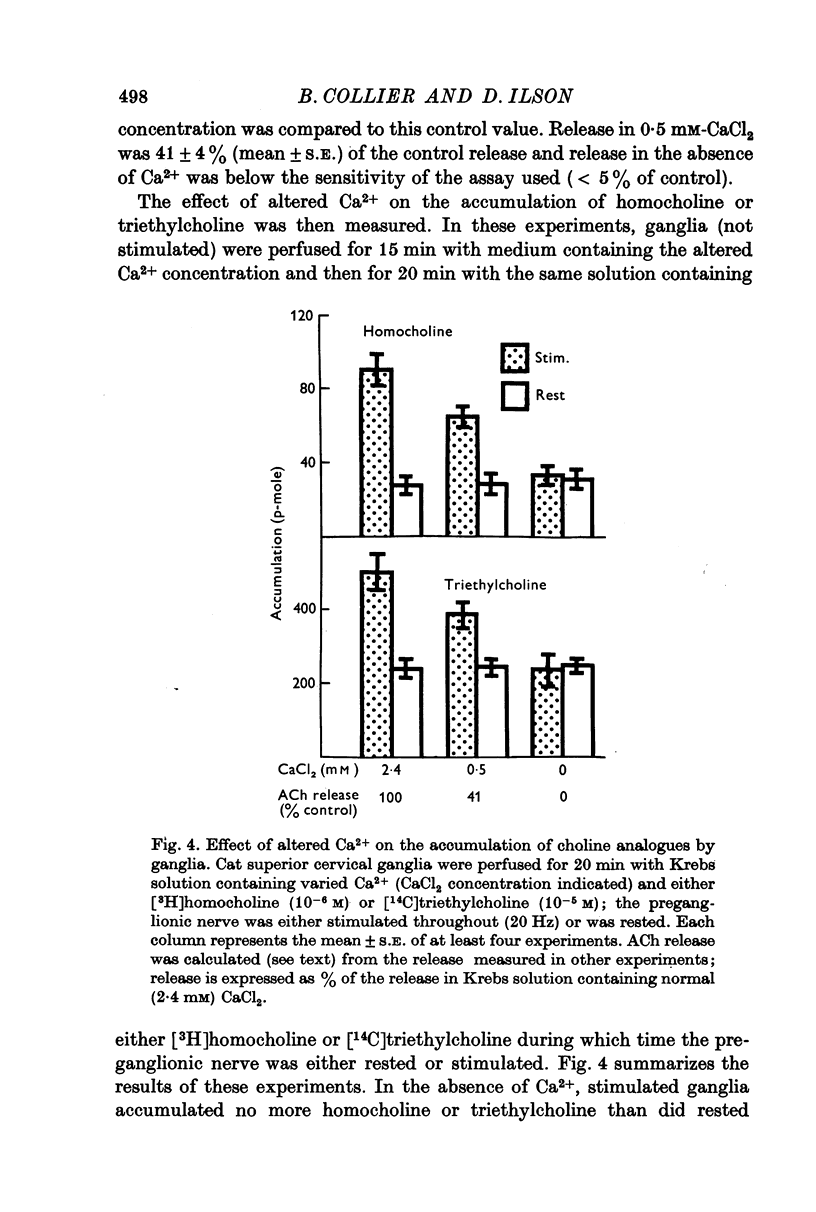
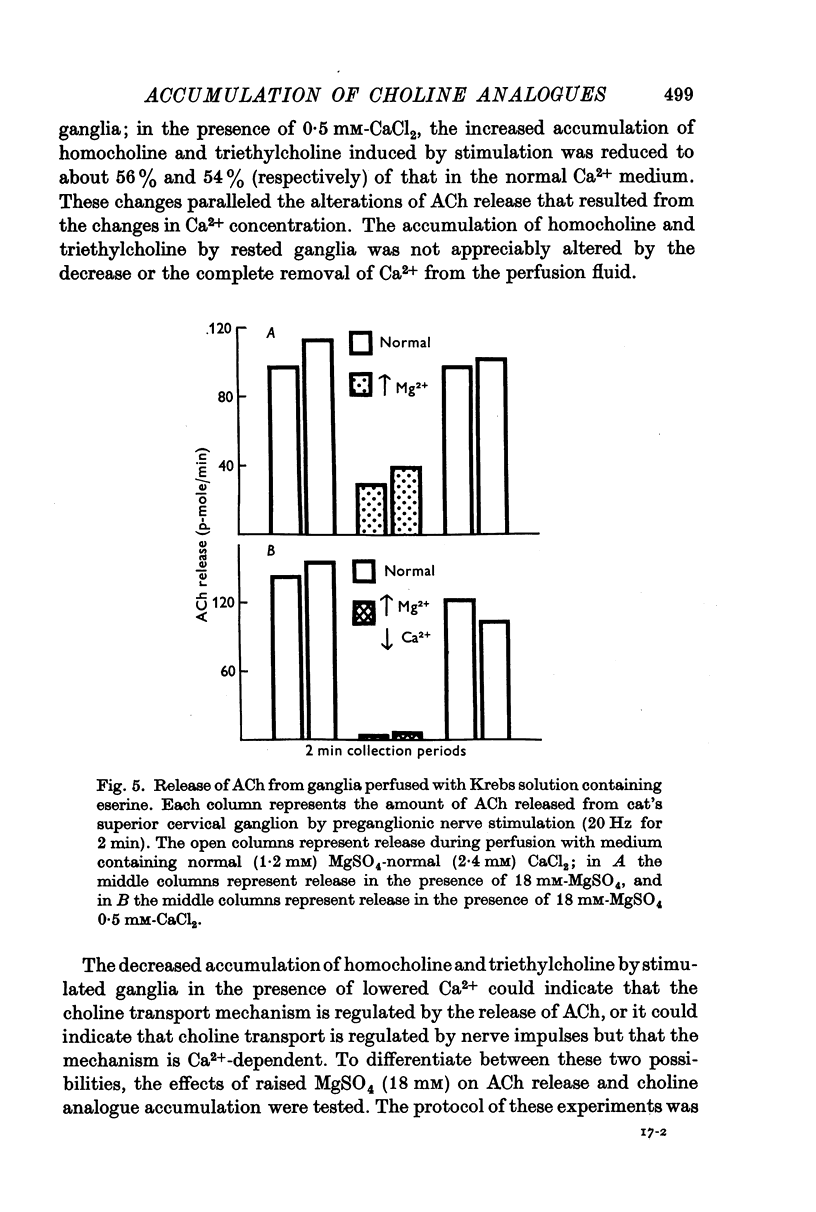
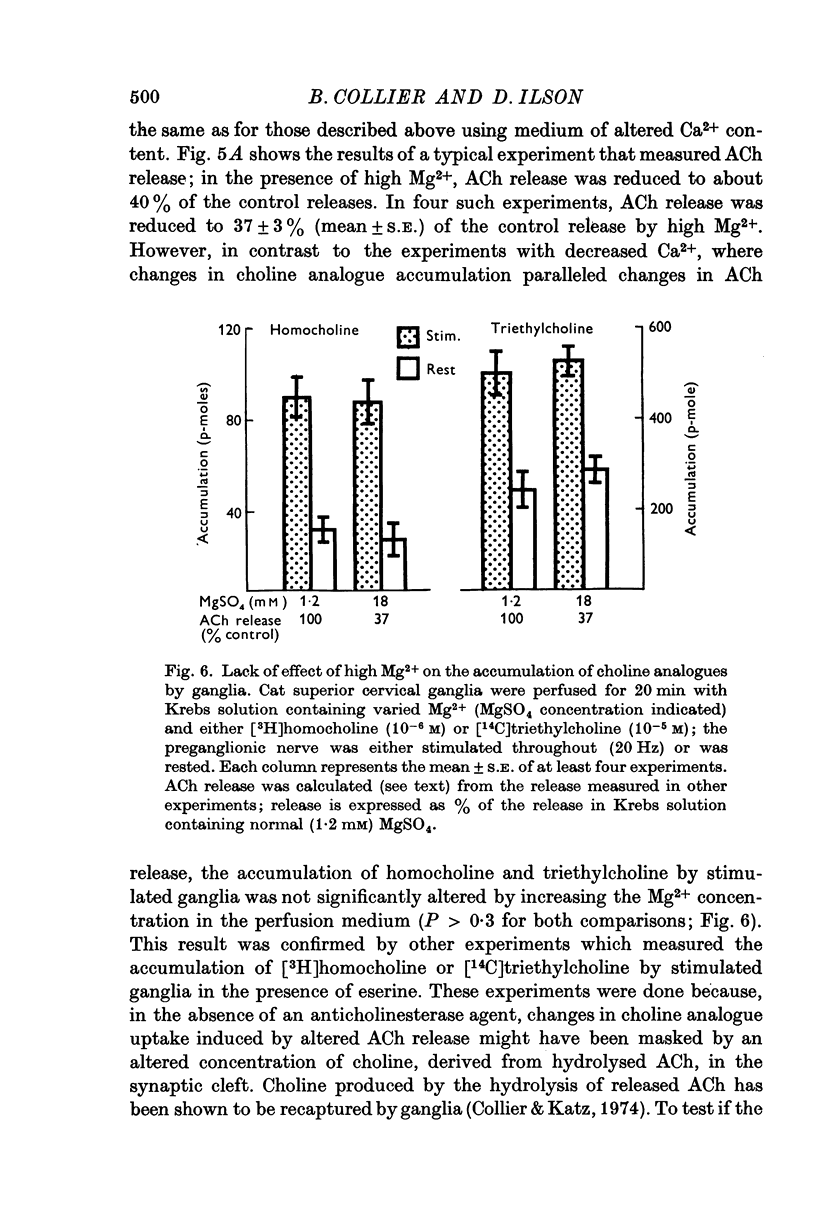
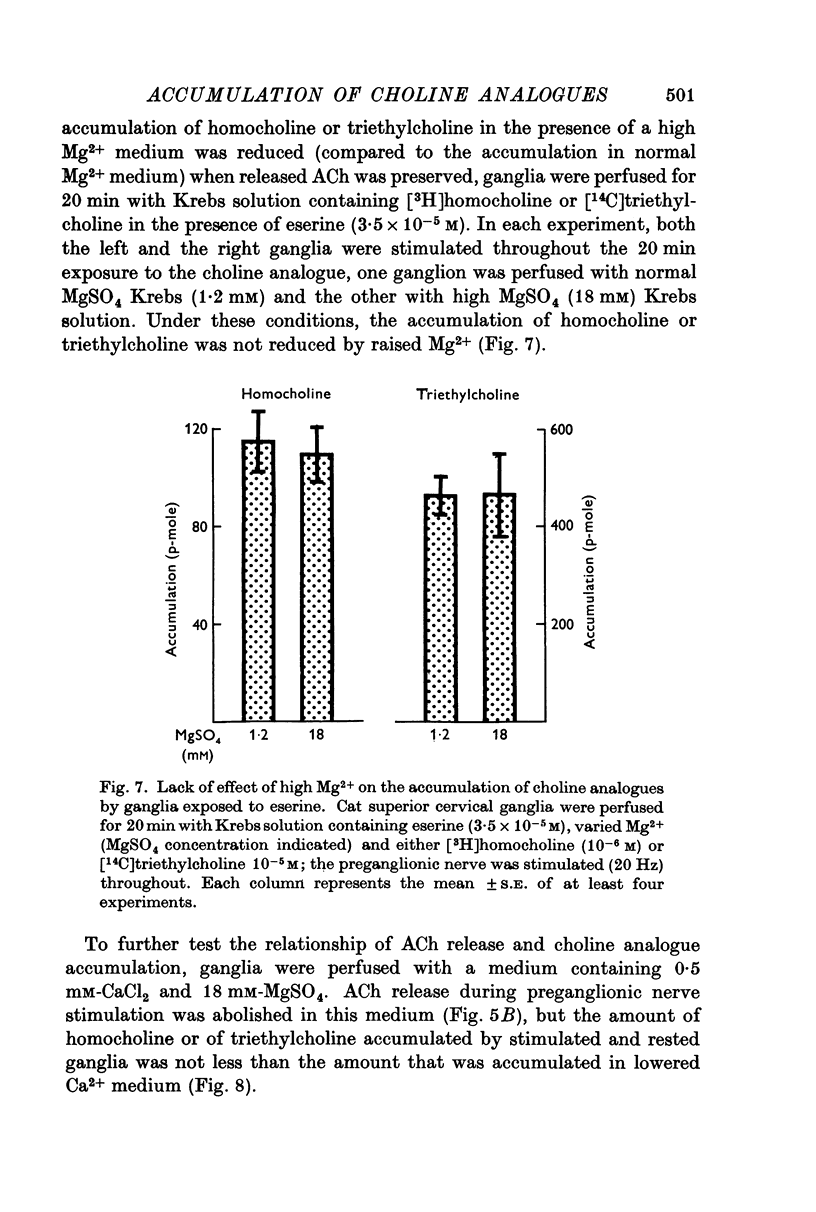
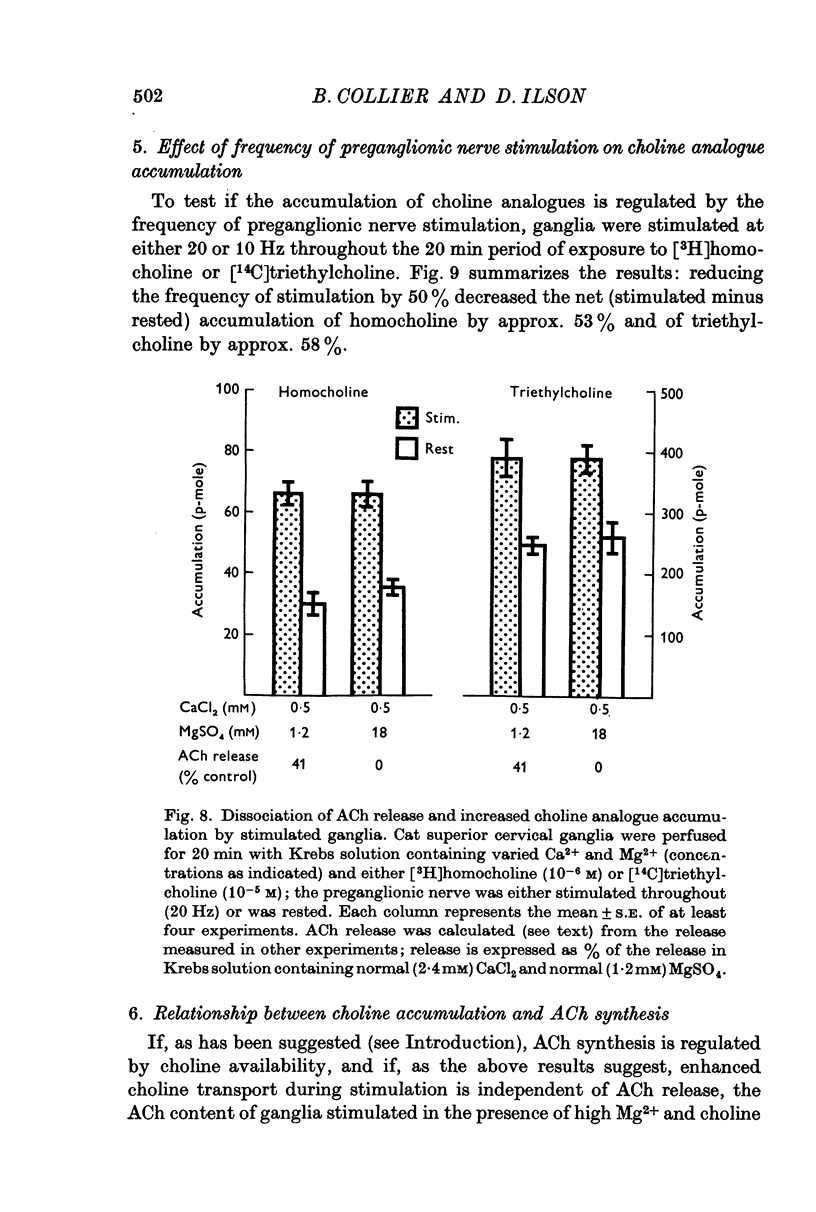
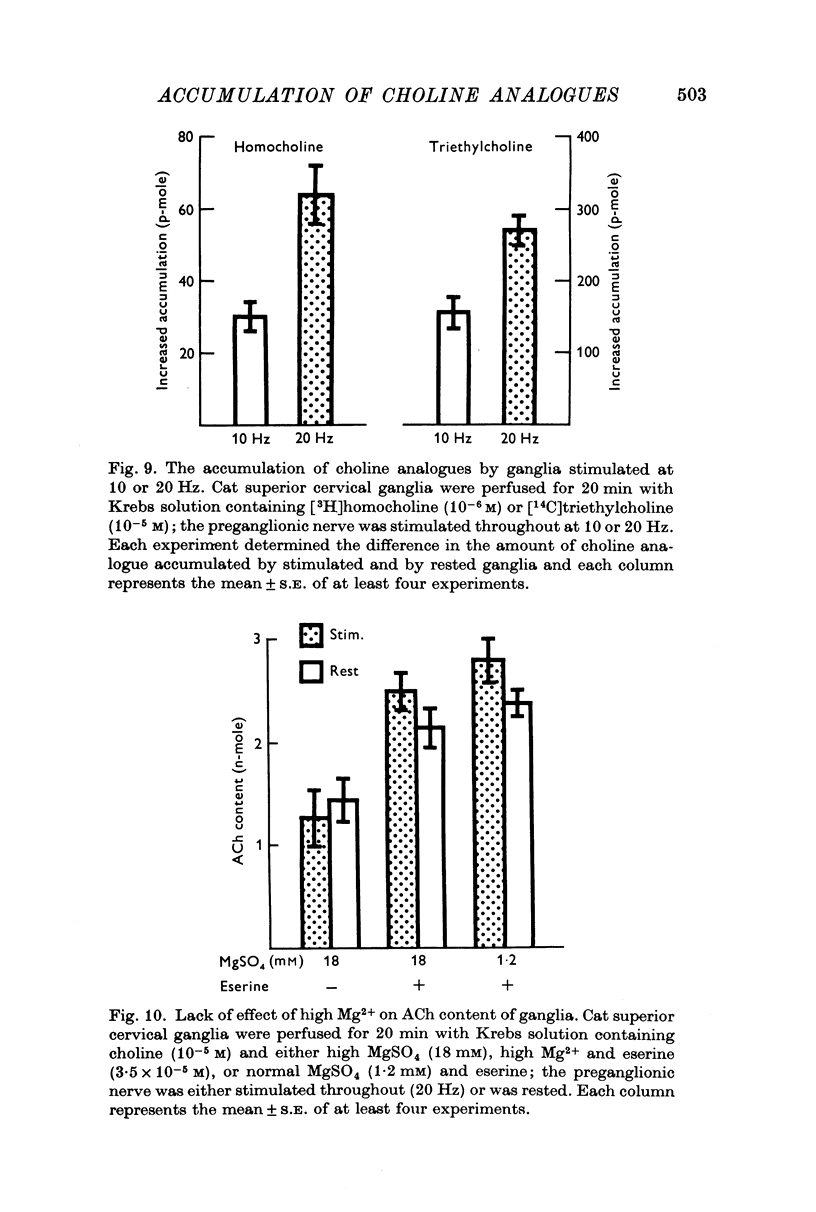
1. Cat superior cervical ganglia were perfused with a Krebs solution containing 10(-6) M [3H]homocholine (2-hydroxypropyl-trimethylammonium) or 10(-5) M [14C]triethylcholine (2-hydroxyethyl-triethylammonium). Preganglionic nerve stimulation (20 Hz) increased the accumulation of homocholine (3-2-fold) and of triethylcholine (2-1-fold). This increased accumulation during stimulation was not the result of increased metabolism. 2. The increased accumulation of homocholine or triethylcholine induced by pregnaglionic nerve stimulation was not reduced by tubocurarine or by atropine, but it was blocked by choline and by hemicholinium. These results suggested that preganglionic nerve stimulation increased choline analogue accumulation into cholinergic nerve terminals. 3. The increased accumulation of homocholine or of triethylcholine induced by preganglionic nerve stimulation was reduced when the Ca2+ concentration was reduced and was abolished in the absence of Ca2+. However, changes in the Mg2+ concentration which depressed acetylcholine (ACh) release by amounts comparable to those induced by altered Ca2+ concentrations did not alter the uptake of homocholine or triethylcholine. It is concluded that the uptake of choline analogues is not regulated by transmitter release but that stimulation increases the uptake of the choline analogues by a Ca2+-dependent mechanism. 4. The accumulation of ACh by ganglia perfused with a Krebs solution containing choline and high MgSO4 (18 mM) was measured. The ACh content of these ganglia did not increase, although choline transport presumably exceeded that necessary for ACh synthesis to replace released ACh. It is concluded that choline transport does not limit ACh synthesis in ganglia.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acara M., Kowalski M., Rennick B., Hemsworth B. Renal tubular excretion of triethylcholine (TEC) in the chicken: enhancement and inhibition of renal excretion of choline and acetylcholine by TEC. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 May;54(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. Studies on the origin of choline in the brain of the rat. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(5):741–750. doi: 10.1042/bj1220741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansell G. B., Spanner S. The metabolism of labelled ethanolamine in the brain of the rat in vivo. J Neurochem. 1967 Sep;14(9):873–885. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S., Simon J. R., Kuhar M. J. Utilization of sodium-dependent high affinity choline uptake in vitro as a measure of the activity of cholinergic neurons in vivo. Life Sci. 1975 Nov 15;17(10):1535–1544. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90174-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKS R. I., MACINTOSH F. C., SASTRY P. B. Pharmacological inhibition of acetylcholine synthesis. Nature. 1956 Nov 24;178(4543):1181–1181. doi: 10.1038/1781181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGEN A. S., BURKE G., DESBARATSSCHONBAUM M. L. The specificity of brain choline acetylase. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1956 Sep;11(3):308–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. A., Mittag T. W. Comparative studies of substrates and inhibitors of choline transport and choline acetyltransferase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Jan;192(1):86–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker L. A. Modulation of synaptosomal high affinity choline transport. Life Sci. 1976 Apr 1;18(7):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning E. T., Schulman M. P. (14C) acetylcholine synthesis by cortex slices of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1968 Dec;15(12):1391–1405. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1968.tb05921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll P. T., Buterbaugh G. G. Regional differences in high affinity choline transport velocity in guinea-pig brain. J Neurochem. 1975 Feb;24(2):229–232. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb11869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Wurtman R. J. Brain acetylcholine: control by dietary choline. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):561–562. doi: 10.1126/science.1251187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen E. L., Wurtman R. J. Brain acetylcholine: increase after systemic choline administration. Life Sci. 1975 Apr 1;16(7):1095–1102. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90194-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B., Katz H. S. Acetylcholine synthesis from recaptured choline by a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1974 May;238(3):639–655. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B., Katz H. S. The synthesis, turnover and release of surplus acetylcholine in a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):537–552. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier B., Lang C. The metabolism of choline by a sympathetic ganglion. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1969 Feb;47(2):119–126. doi: 10.1139/y69-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier S. F., Mautner H. G. On the mechanism of action of choline acetyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3355–3358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAUTERMAN W. C., MEHROTRA K. N. The N-alkyl group specificity of choline acetylase from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1963 Feb;10:113–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1963.tb11470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Milfay D. Uptake of ( 3 H-methyl)choline by microsomal, synaptosomal, mitochondrial and synaptic vesicle fractions of rat brain. The effects of hemicholinium. J Neurochem. 1972 Aug;19(8):1899–1909. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Gaddum J. H. The chemical transmitter at synapses in a sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1934 Jun 9;81(3):305–319. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1934.sp003137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDINER J. E. The inhibition of acetylcholine synthesis in brain by a hemicholinium. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:297–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0810297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. M., McCaman R. E. The determination of picomole amounts of acetylcholine in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grewaal D. S., Quastel J. H. Control of synthesis and release of radioactive acetylcholine in brain slices from the rat. Effects of neurotropic drugs. Biochem J. 1973 Jan;132(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj1320001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P., Lefresne P., Rossier J., Beaujouan J. C., Glowinski J. Effect of sodium, hemicholinium-3 and antiparkinson drugs on (14C)acetylcholine synthesis and (3H)choline uptake in rat striatal synaptosomes. Brain Res. 1973 Nov 23;62(2):523–529. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90717-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P., Lefresne P., Rossier J., Beaujouan J. C., Glowinski J. Inhibition by hemicholinium-3 of (14C)acetylcholine synthesis and (3H)choline high-affinity uptake in rat striatal synaptosomes. Mol Pharmacol. 1973 Sep;9(5):630–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMSWORTH B. A., MORRIS D. A COMPARISON OF THE N-ALKYL GROUP SPECIFICITY OF CHOLINE ACETYLTRANSFERASE FROM DIFFERENT SPECIES. J Neurochem. 1964 Nov;11:793–803. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1964.tb06728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T., Noda H. Choline uptake systems of rat brain synaptosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 26;291(2):564–575. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90508-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haga T. Synthesis and release of ( 14 C)acetylcholine in synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):781–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubrich D. R., Wedeking P. W., Wang P. F. Increase in tissue concentration of acetylcholine in guinea pigs in vivo induced by administration of choline. Life Sci. 1974 Mar 1;14(5):921–927. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth B. A., Bosmann H. B. The incorporation of triethylcholine into isolated guinea pig cerebral cortex synaptosoma and synaptic vesicle fractions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;16(2):164–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemsworth B. A., Smith J. C. The enzymic acetylation of choline analogues. J Neurochem. 1970 Feb;17(2):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb02198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. T., Rossier J., Beaujouan J. C., Guyenet P., Glowinski J. Inhibition of high-affinity choline transport in rat striatal synaptosomes by alkyl bisquaternary ammonium compounds. Mol Pharmacol. 1975 Jan;11(1):19–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilson D., Collier B. Triethylcholine as a precursor to a cholinergic false transmitter. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):618–619. doi: 10.1038/254618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A. C., Collier B., Ilson D., Wright J. M. The effect of atropine upon acetylcholine release from cat superior cervical ganglia and rat cortical slices: measurement by a radio-enzymic method. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1975 Dec;53(6):1050–1057. doi: 10.1139/y75-146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., DeHaven R. N., Yamamura H. I., Rommel-Spacher H., Simon J. R. Further evidence for cholinergic habenulo-interpeduncular neurons: pharmacologic and functional characteristics. Brain Res. 1975 Oct 31;97(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90449-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Sethy V. H., Roth R. H., Aghajanian G. K. Choline: selective accumulation by central cholinergic neurons. J Neurochem. 1973 Feb;20(2):581–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann P. J., Tennenbaum M., Quastel J. H. On the mechanism of acetylcholine formation in brain in vitro. Biochem J. 1938 Feb;32(2):243–261. doi: 10.1042/bj0320243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. P., Hebb C. Inhibition of choline acetyltransferase by quaternary ammonium analogues of choline. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 May 1;24(9):1013–1017. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90438-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchbanks R. M. The uptake of [14C] choline into synaptosomes in vitro. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(3):533–541. doi: 10.1042/bj1100533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder A. H., Yamamura H. I., Kuhar M. J., Snyder S. H. Release of acetylcholine from hippocampal slices by potassium depolarization: dependence on high affinity choline uptake. Brain Res. 1974 Apr 19;70(2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. High affinity transport of choline into the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig intestine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Oct;191(1):102–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter L. T. Synthesis, storage and release of [14C]acetylcholine in isolated rat diaphragm muscles. J Physiol. 1970 Jan;206(1):145–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkawi M., Schulman M. P. Relationship between acetylcholine synthesis and its concentration in rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1969 Jun;36(2):373–379. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1969.tb09512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Atweh S., Kuhar M. J. Sodium-dependent high affinity choline uptake: a regulatory step in the synthesis of acetylcholine. J Neurochem. 1976 May;26(5):909–922. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb06472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. R., Kuhar M. G. Impulse-flow regulation of high affinity choline uptake in brain cholinergic nerve terminals. Nature. 1975 May 8;255(5504):162–163. doi: 10.1038/255162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorimachi M., Kataoka K. Choline uptake by nerve terminals: a sensitive and a specific marker of cholinergic innervation. Brain Res. 1974 Jun 7;72(2):350–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90880-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Dowdall M. J., Boyne A. F. The storage and release of acetylcholine by cholinergic nerve terminals: recent results with non-mammalian preparations. Biochem Soc Symp. 1972;(36):49–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. Choline: high-affinity uptake by rat brain synaptosomes. Science. 1972 Nov 10;178(4061):626–628. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4061.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura H. I., Snyder S. H. High affinity transport of choline into synaptosomes of rat brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1355–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


