Abstract
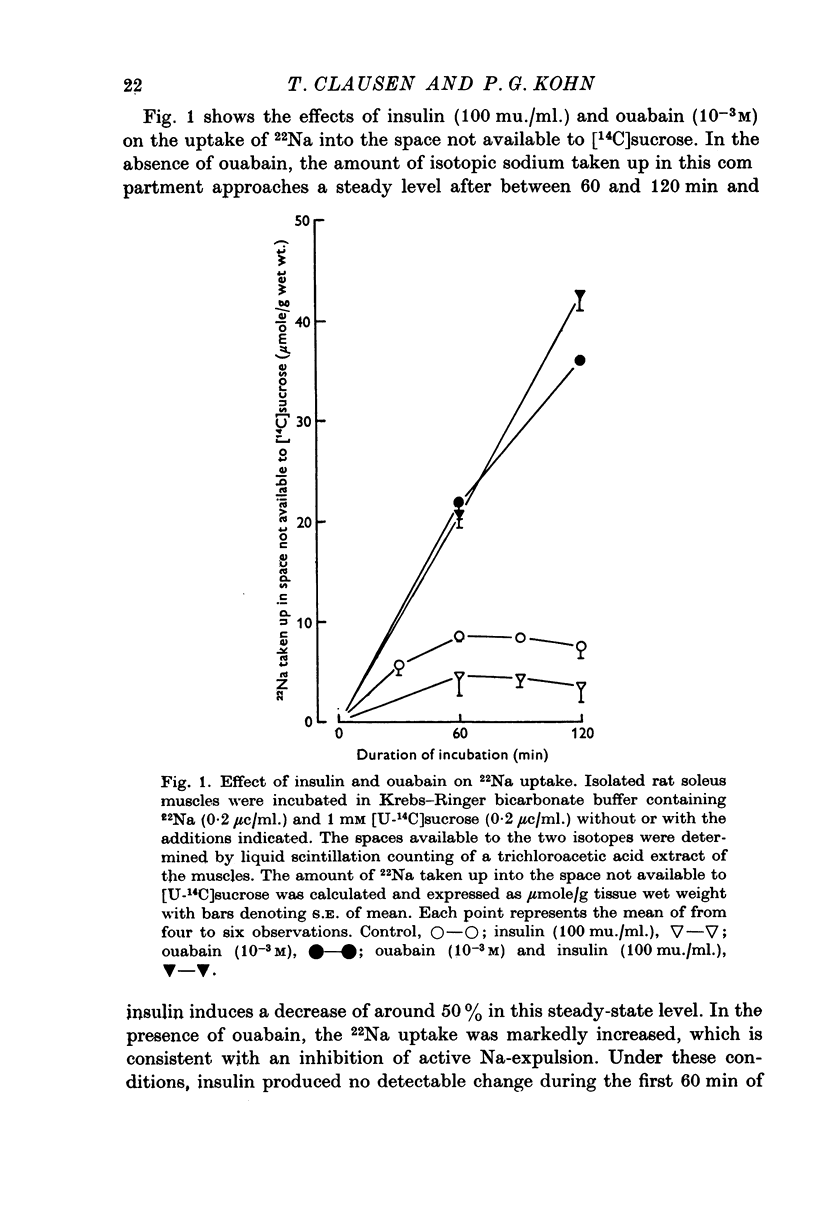
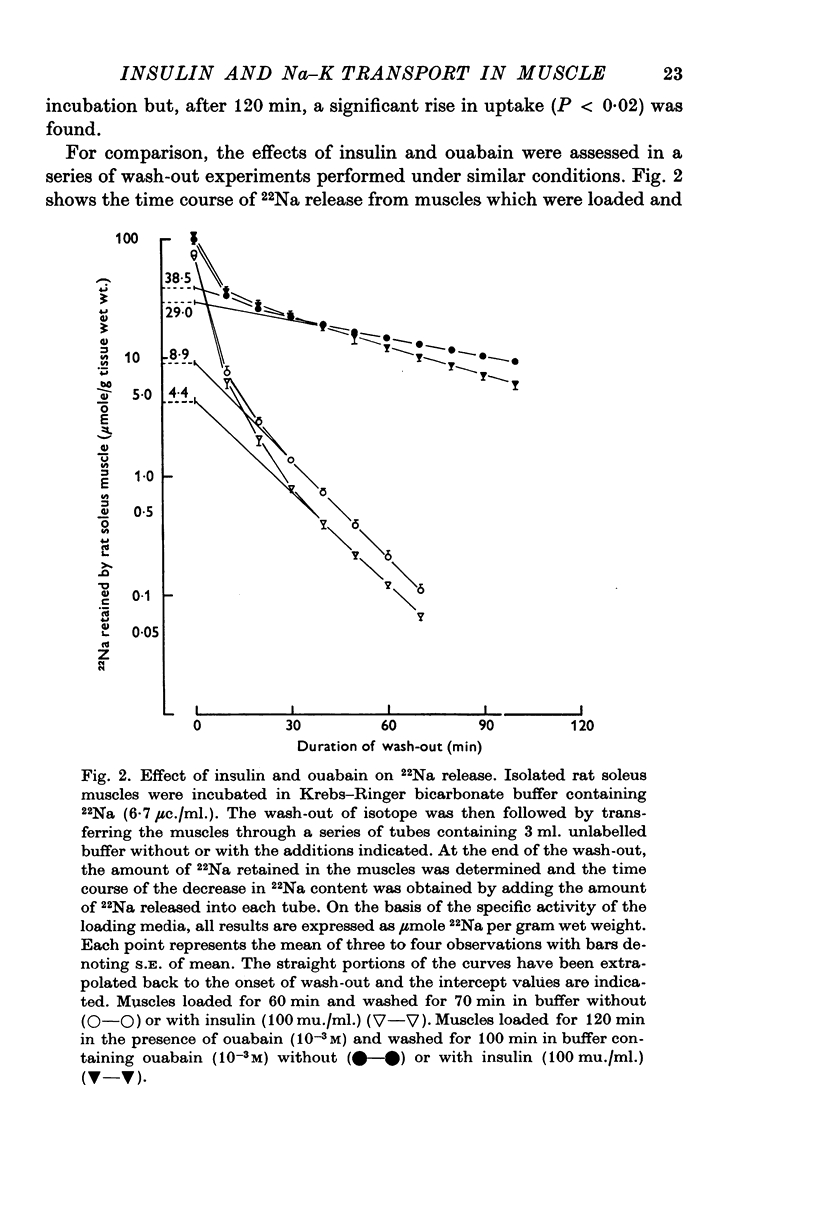
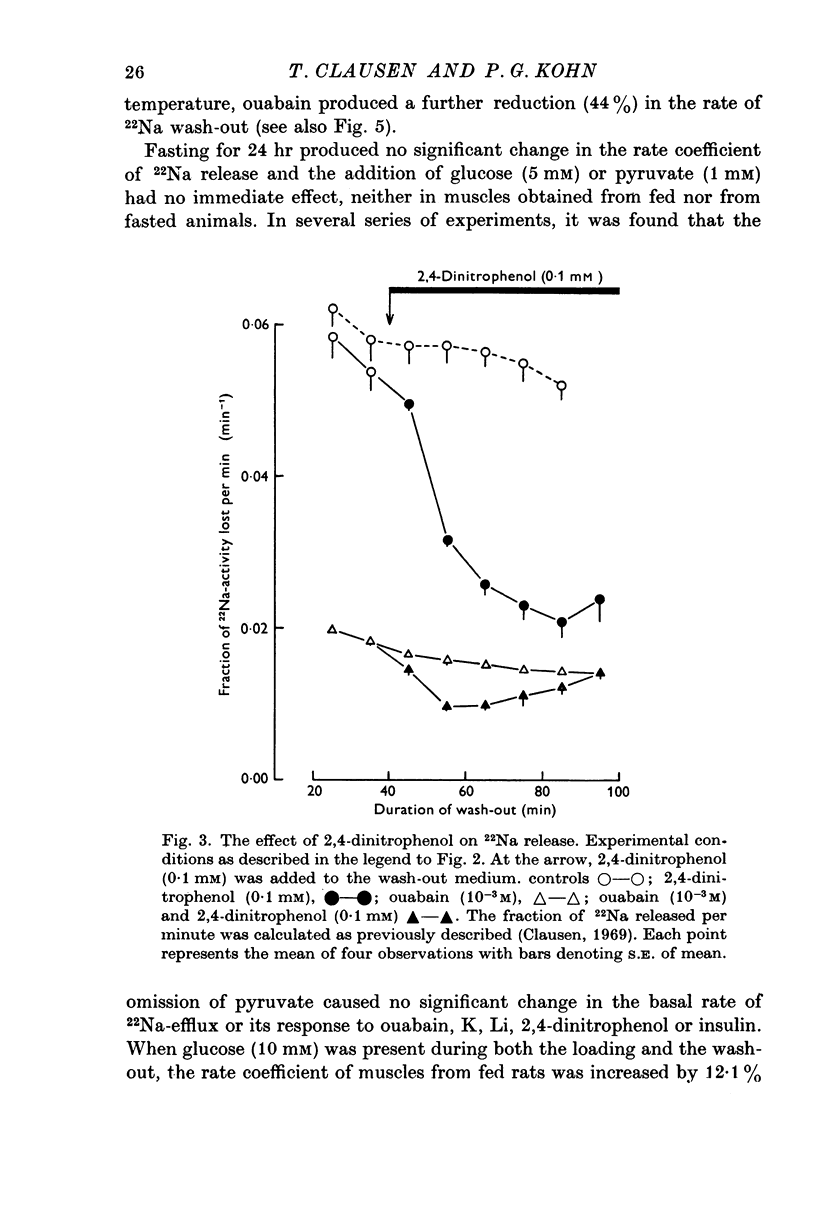
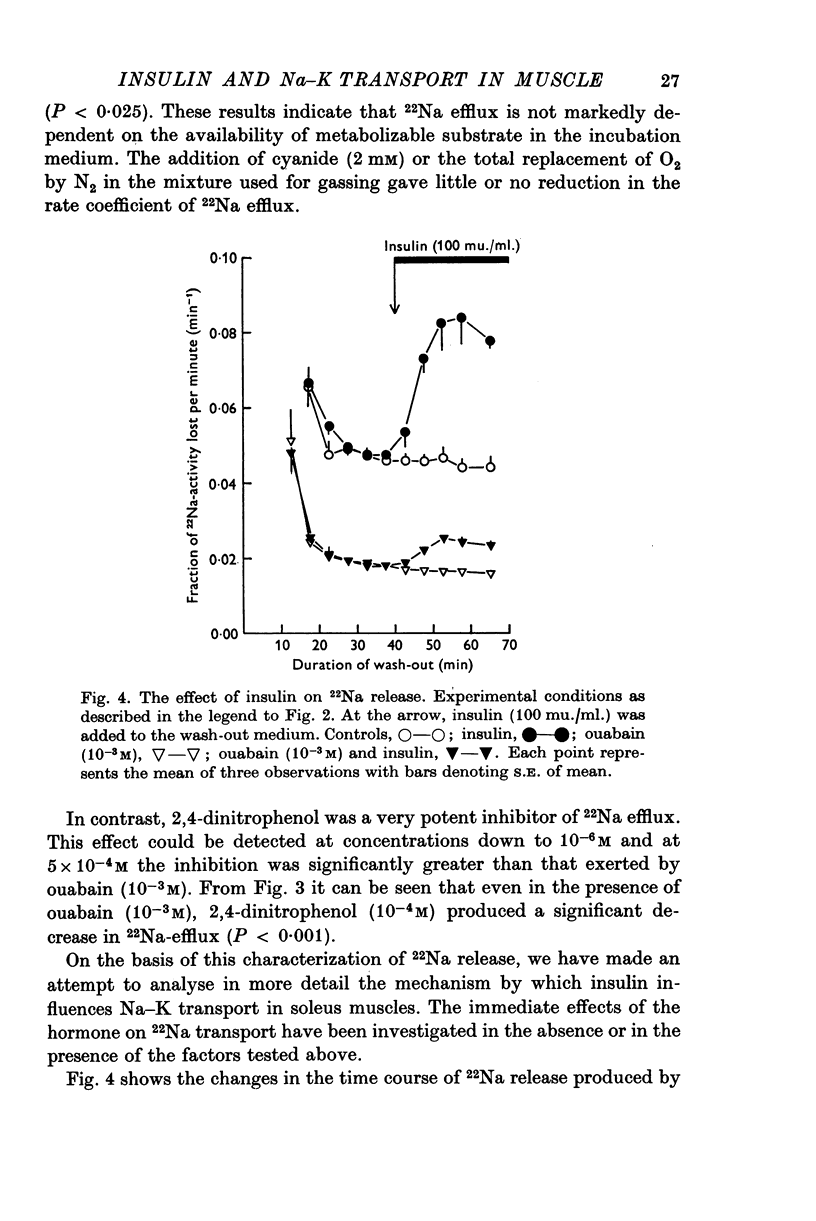
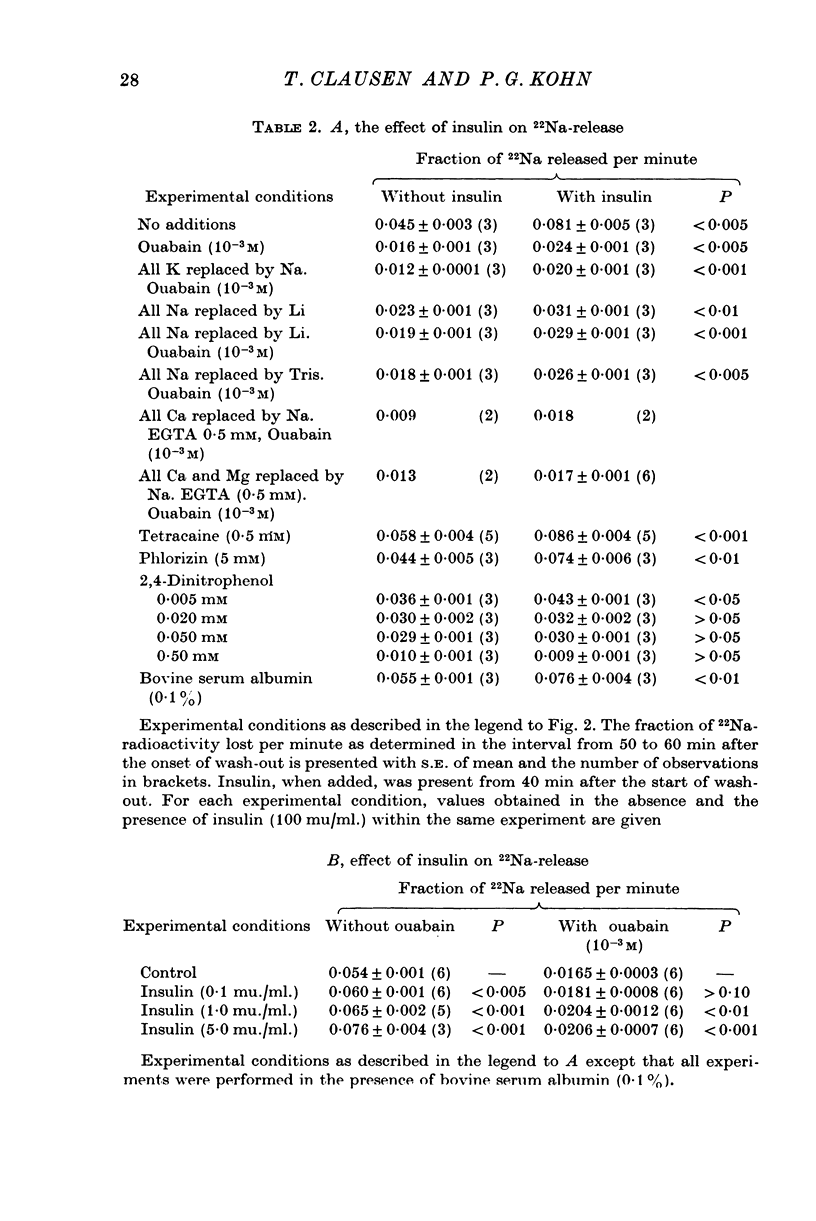
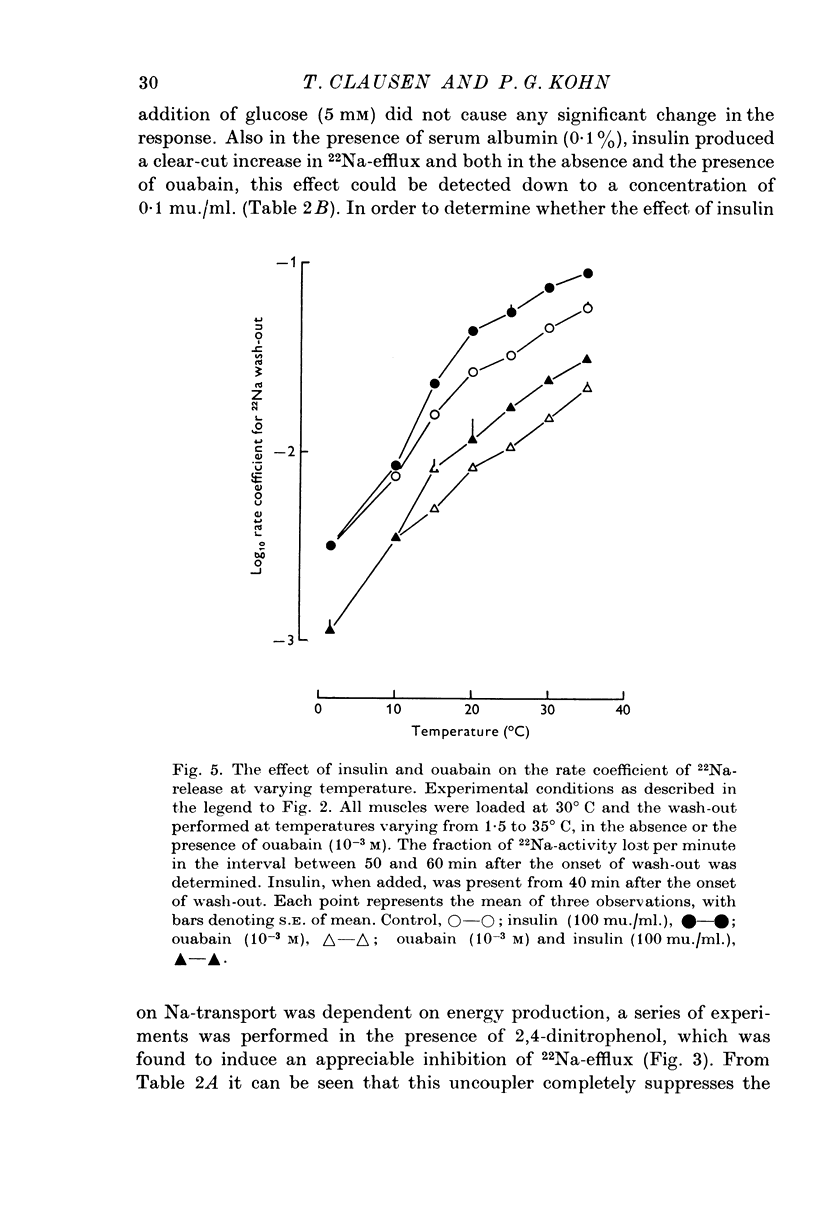
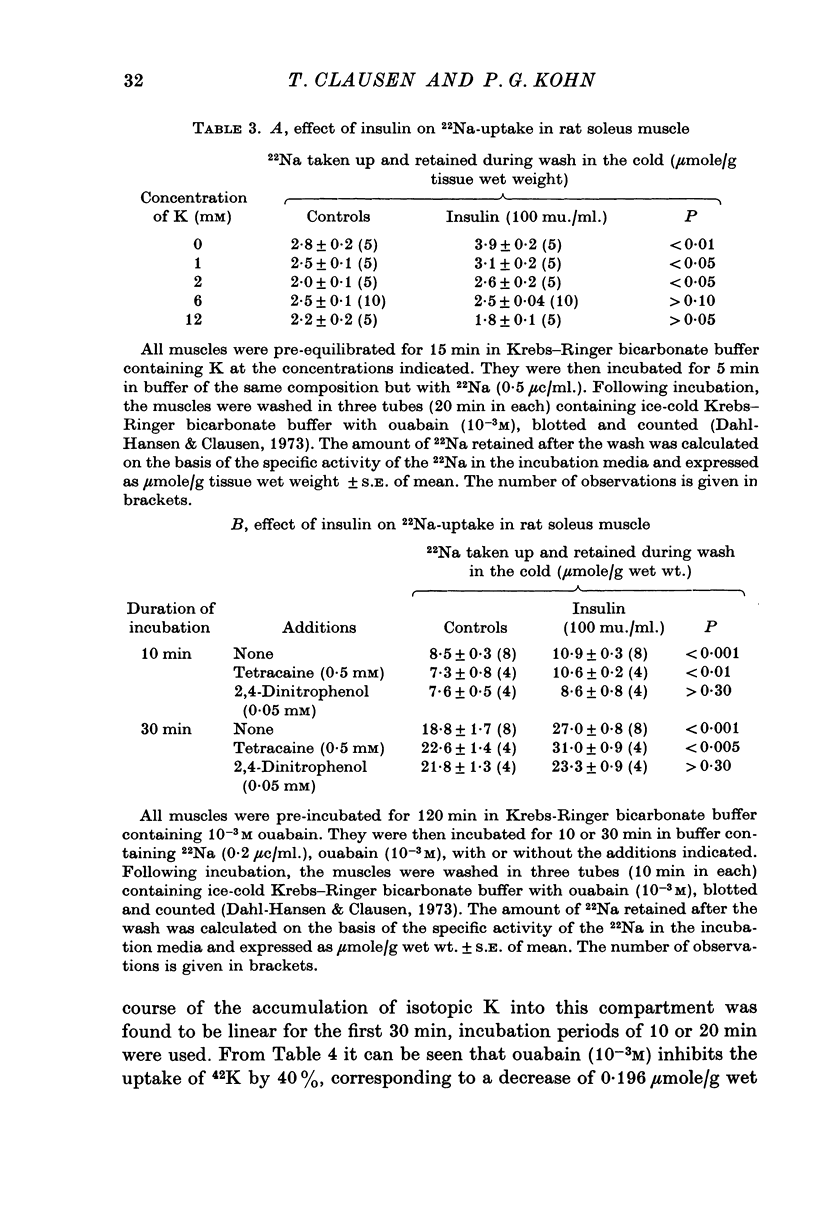
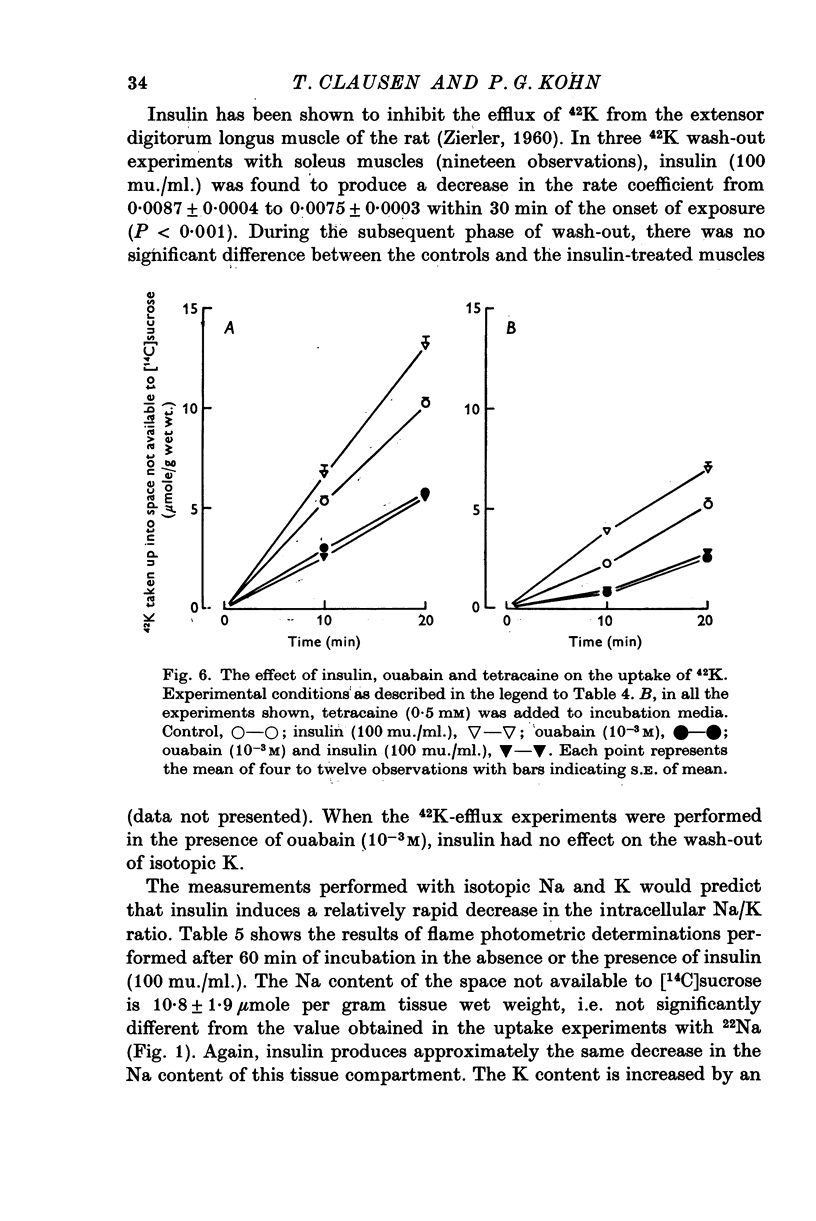
1. The action of insulin on the transport and the distribution of Na and K has been studied in rat soleus muscles incubated at 30 degrees C in glucose-free Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate buffer. 2. Measurements of the uptake and the wash-out of 22Na indicate that the muscles contain an intracellular pool of Na available for transport which is confined to the water space not available to sucrose. Ouabain (10(-4)-10(-3)M) inhibited 22Na efflux by 69% (0-287 micronmole/g tissue wet weight per minute) and 42K-influx by 40% (0-196 micronmole/g tissue wet weight per minute). When all extracellular Na was replaced by Li, both 22Na-efflux adn 42K-influx were inhibited to about the same extent and ouabain produced very little further inhibition. 2,4-dinitrophenol decreased the ouabain-resistant component of 22Na-efflux by 39%. 3. Insulin (from 0-1 to 100 mu./ml.) increased the rate coefficient of 22Na-efflux by from 11 to 46% within 15 min. In the presence of ouabain (10(-3)M), the same relative increase was obtained, indicating that the hormone stimulates the glycoside-sensitive and the glycoside-insensitive Na transport to a similar extent. The effect of insulin on 22Na-efflux was not abolished by tetracaine (0-5 X 10(-3)M), phlorizin (0-5 X 10(-2)M) or by the substitution of Na, K, Mg or Ca. In the presence of 2,4-dinitrophenol (0-5 X 10(-4)M) or at temperatures below 15 degrees C, the hormone produced no detectable change in 22Na-efflux. 4. Insulin increased 42K-influx from 0-525 to 0-664 mumole/g tissue wet weight per minute. This effect was entirely blocked by ouabain but not by tetracaine. Insulin produced a 14% transient decrease in 42K-efflux. 5. The continued exposure to insulin led to a new steady state, in which the intracellular Na pool was decreased from around 10 to around 5 mumole/g tissue wet weight and the K content increased by an equivalent amount. In the presence of ouabain or at low extracellular concentrations of K, insulin increased the rate of 22Na-influx by around 35%. This effect was blocked by 2,4-dinitrophenol but not be tetracaine. 6. It is concluded that insulin stimulates the active coupled transport of Na and K, possibly by increasing the relative Na-affinity of the system mediating this process.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. F. Transport and metabolism of calcium ions in nerve. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1972;24:177–223. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(72)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodal B. P., Jebens E., Oy V., Iversen O. J. Effect of insulin on (Na+, K+)-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity in rat muscle sarcolemma. Nature. 1974 May 3;249(452):41–43. doi: 10.1038/249041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R., NORTHOVER J. Maintenance of isolated diaphragm with normal sodium content. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:343–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Gould M. K. Effect of externally added ATP on glucose uptake by isolated rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):327–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry I. H., Gould M. K. Kinetics of glucose uptake in isolated soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 6;177(3):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Elbrink J., Dahl-Hansen A. B. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. IX. The role of cellular calcium in the activation of the glucose transport system in rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 28;375(2):292–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Harving H., Dahl-Hansen A. B. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. 8. The effect of membrane stabilizers on the transport of K + , Na + and glucose in muscle, adipocytes and erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 16;298(2):393–411. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90367-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. V. Stimulating effect of ouabain, K+-free medium and insulin on efflux of 3-O-methylglucose from epidimal adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;183(3):625–634. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90175-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper G. J., Kohn P. G. The effect of tetracaine on 2-amino-iso-butyric acid transport in muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Feb;229(1):23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese R. Sodium fluxes in diaphragm muscle and the effects of insulin and serum proteins. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):255–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl-Hansen A. B., Clausen T. The effect of membrane stabilizers and ouabain on the transport of Na+ and K+ in rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 9;318(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRITZ G. R., KNOBIL E. THE EFFECT OF INSULIN ON EXTRACELLULAR SPACE AND TISSUE-WATER CONTENT OF THE ISOLATED RAT DIAPHRAGM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 13;78:773–774. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOURLEY D. R. EFFECT OF INSULIN ON POTASSIUM EXCHANGE IN NORMAL AND OUABAIN-TREATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Jun;148:339–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. Facftors affecting the relative magnitudes of the sodium:potassium and sodium:sodium exchanges catalysed by the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):189–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavryck W. A., Moore R. D., Thompson R. C. Effect of insulin upon membrane-bound (Na+ + K+)-ATPase extracted from frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):43–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Erlij D. Insulin unmasks latent sodium pump sites in frog muscle. Nature. 1974 Sep 6;251(5470):57–58. doi: 10.1038/251057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hider R. C., Fern E. B., London D. R. The effect of insulin on free amino acid pools and protein synthesis in rat skeletal muscle in vitro. Biochem J. 1971 Dec;125(3):751–756. doi: 10.1042/bj1250751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERNAN R. P. The role of lactate in the active excretion of sodium by frog muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Jun;162:129–137. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., MAISEL G. W. The energy requirement for sodium extrusion from a frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):383–392. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. VI. The effect of insulin, ouabain, and metabolic inhibitors on the transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in rat soleus muscles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Feb 2;225(2):277–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn P. G., Clausen T. The relationship between the transport of glucose and cations across cell membranes in isolated tissues. VII. The effects of extracellular Na + and K + on the transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in rat soleus muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):798–814. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manery J. F. Effects of Ca ions on membranes. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1804–1810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Effect of insulin upon the sodium pump in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):23–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Otsuki I. Mechanism of muscular paralysis by insulin with special reference to periodic paralysis. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1178–1182. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK C. R., BORNSTEIN J., POST R. L. Effect of insulin on free glucose content of rat diaphragm in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jul;182(1):12–16. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.182.1.12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogus E., Price T., Zierler K. L. Sodium plus potassium-activated, ouabain-inhibited adenosine triphosphatase from a fraction of rat skeletal muscle, and lack of insulin effect on it. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Aug;54(2):188–202. doi: 10.1085/jgp.54.2.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SKOU J. C. ENZYMATIC BASIS FOR ACTIVE TRANSPORT OF NA+ AND K+ ACROSS CELL MEMBRANE. Physiol Rev. 1965 Jul;45:596–617. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.3.596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjodin R. A., Beaugé L. A. Strophanthidin-sensitive components of potassium and sodium movements in skeletal muscle as influenced by the internal sodium concentration. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Sep;52(3):389–407. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. The (Na++K+) activated enzyme system and its relationship to transport of sodium and potassium. Q Rev Biophys. 1974 Jul;7(3):401–434. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Effect of insulin on potassium efflux from rat muscle in the presence and absence of glucose. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:1066–1070. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. L. Possible mechanisms of insulin action on membrane potential and ion fluxes. Am J Med. 1966 May;40(5):735–739. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. L., Rogus E., Hazlewood C. F. Effect of insulin on potassium flux and water and electrolyte content of muscles from normal and from hypophysectomized rats. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jan;49(3):433–456. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


