Abstract
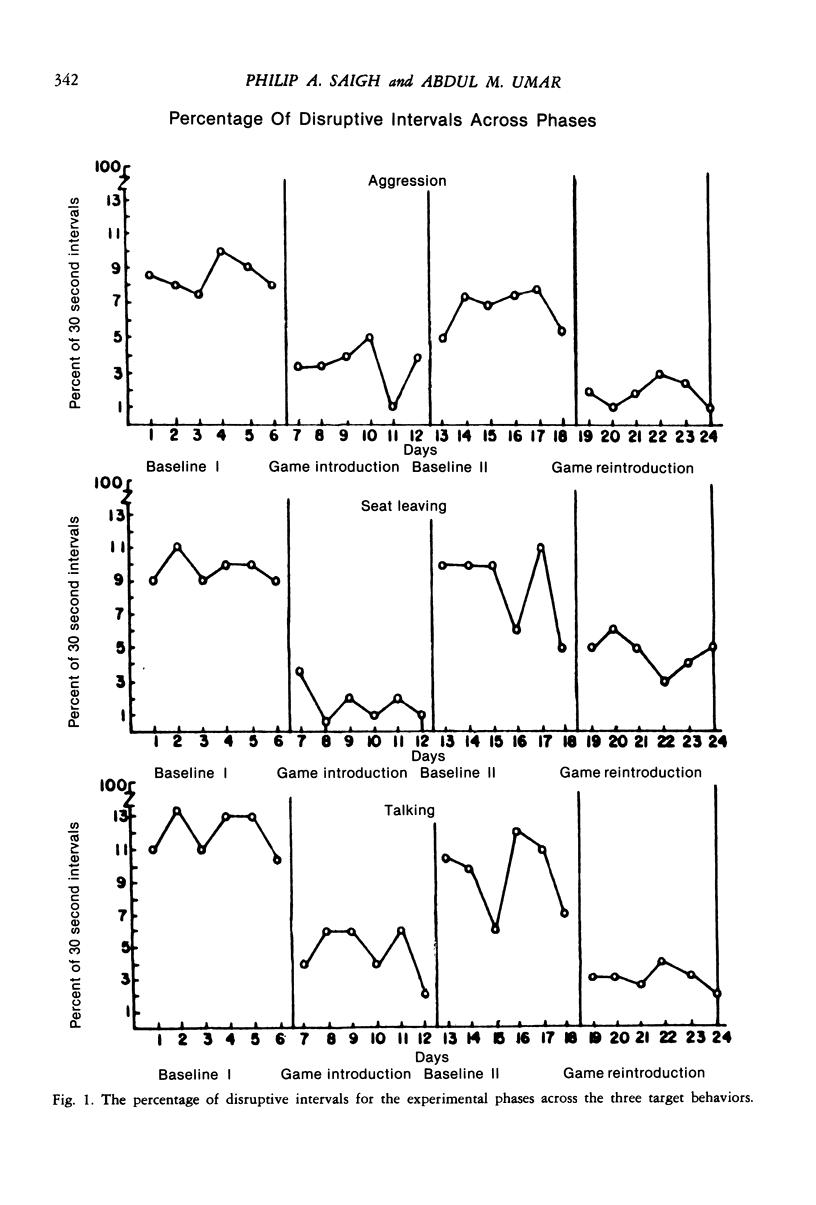
An endemic version of the Good Behavior Game was applied in a rural Sudanese second-grade classroom. Official letters of commendation, extra time for recess, victory tags, and a winner's chart were used as backup reinforcers. The class was divided into two teams, and the teacher indicated she would place a check on the board after every rule violation. The students were also told that the team with the fewest marks would win the game and receive the aforementioned prizes. After an initial adaptation period, the rate of disruption was charted across four treatment phases: viz., baseline I, introduction of the game, baseline II, and reintroduction of the game. It was observed that the game phases were associated with marked decreases in the rate of seat leaving, talking without permission, and aggression. The teacher, principal, parents, and students were consequently individually interviewed, and their comments spoke strongly for the social validity of the game.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrish H. H., Saunders M., Wolf M. M. Good behavior game: effects of individual contingencies for group consequences on disruptive behavior in a classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):119–124. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saigh P. A., Khan S. Token reinforcement in a Pakistani classroom. J Soc Psychol. 1982 Oct;118(FIRST):11–16. doi: 10.1080/00224545.1982.9924412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. M. Social validity: the case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


