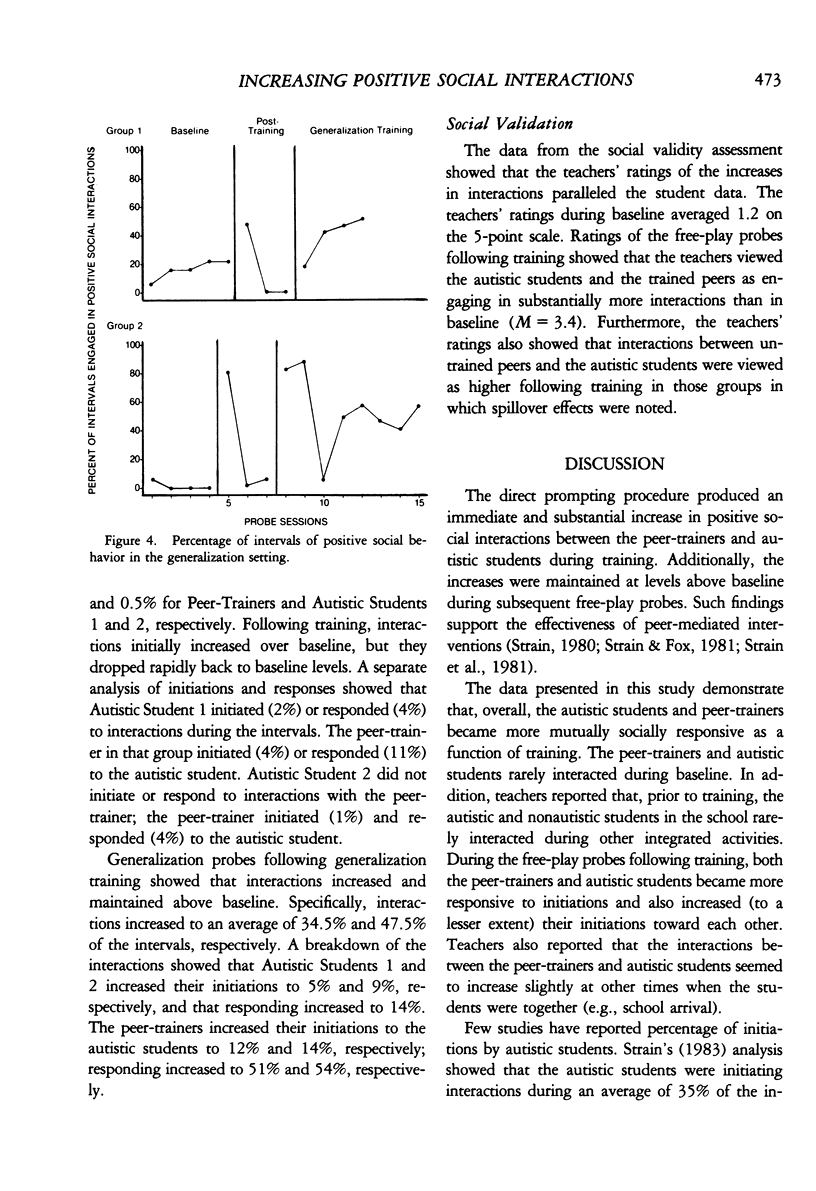
Abstract
We evaluated the effects of a peer-training strategy, consisting of direct prompting and modeling, on the occurrence and duration of interactions between autistic students and nonautistic peer-trainers. Data were obtained in both training and generalization settings. The results of a multiple-baseline design across students demonstrated that:the direct prompting procedure produced immediate and substantial increases in the occurrences and durations of positive social interactions between the peer-trainers and autistic students; these increases were maintained across time at levels above baseline during subsequent free-play probes; these findings were judged by teachers to be socially valid; untrained peers increased their interactions with the autistic students in three of the four groups; generalization of behavior change across settings occurred only after specific programming; and interactions between untrained peers and peer-trainers decreased following training. Variables that may account for the results and the implications of these findings for peer-mediated interventions are discussed.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Rincover A. Research on the difference between generalization and maintenance in extra-therapy responding. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Spring;10(1):1–12. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancioni G. E. Normal children as tutors to teach social responses to withdrawn mentally retarded schoolmates: training, maintenance, and generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1982 Spring;15(1):17–40. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1982.15-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National Society for Autistic Children definition of the syndrome of autism. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1978 Jun;8(2):162–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01537864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M. Diagnosis and definition of childhood autism. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1978 Jun;8(2):139–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01537863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S. An experimental analysis of peer social initiations on the behavior of withdrawn preschool children: some training and generalization effects. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1977 Dec;5(4):445–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00915092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Kerr M. M., Ragland E. U. Effects of peer-mediated social initiations and prompting/reinforcement procedures on the social behavior of autistic children. J Autism Dev Disord. 1979 Mar;9(1):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01531291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Shores R. E., Kerr M. M. An experimental analysis of "spillover" effects on the social interaction of behaviorally handicapped preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):31–40. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Timm M. A. An experimental analysis of social interaction between a behaviorally disordered preschool child and her classroom peers. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):583–590. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M. M. Social validity: the case for subjective measurement or how applied behavior analysis is finding its heart. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):203–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


