Abstract
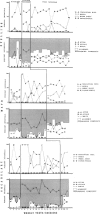
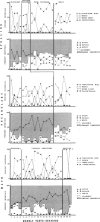
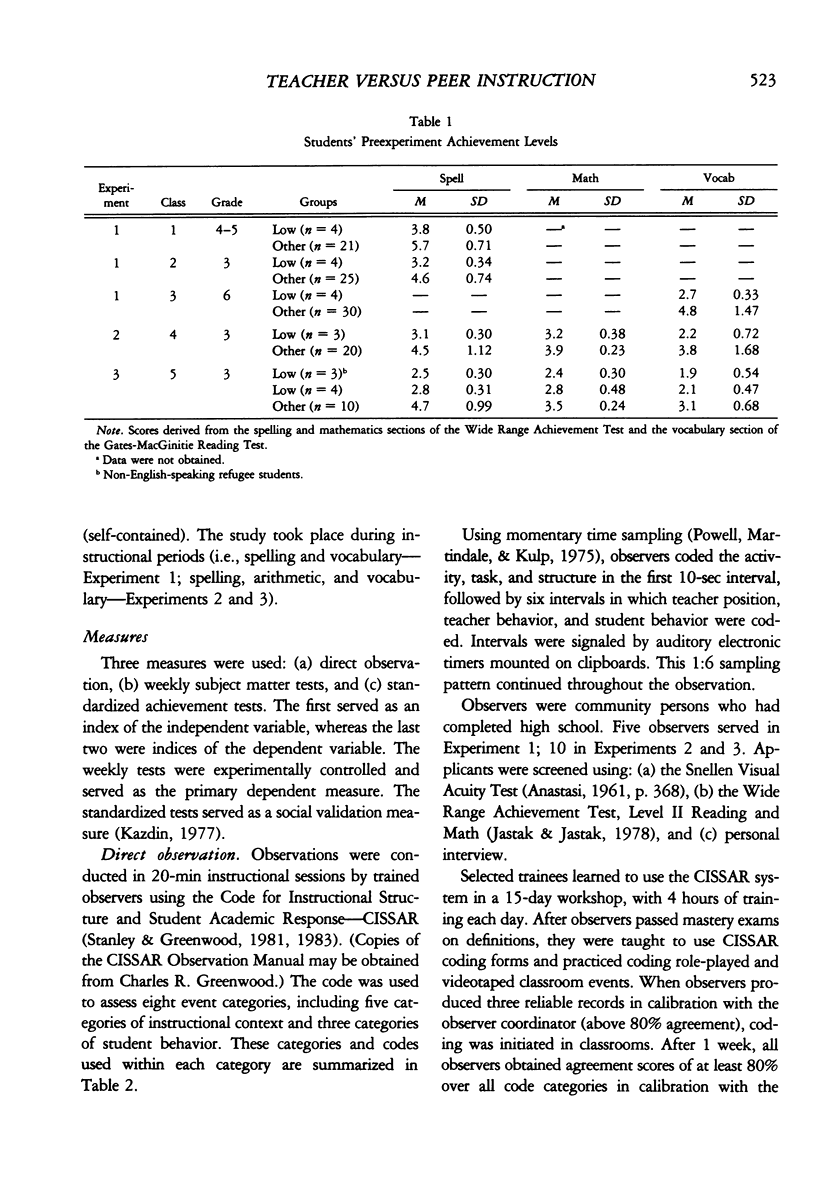
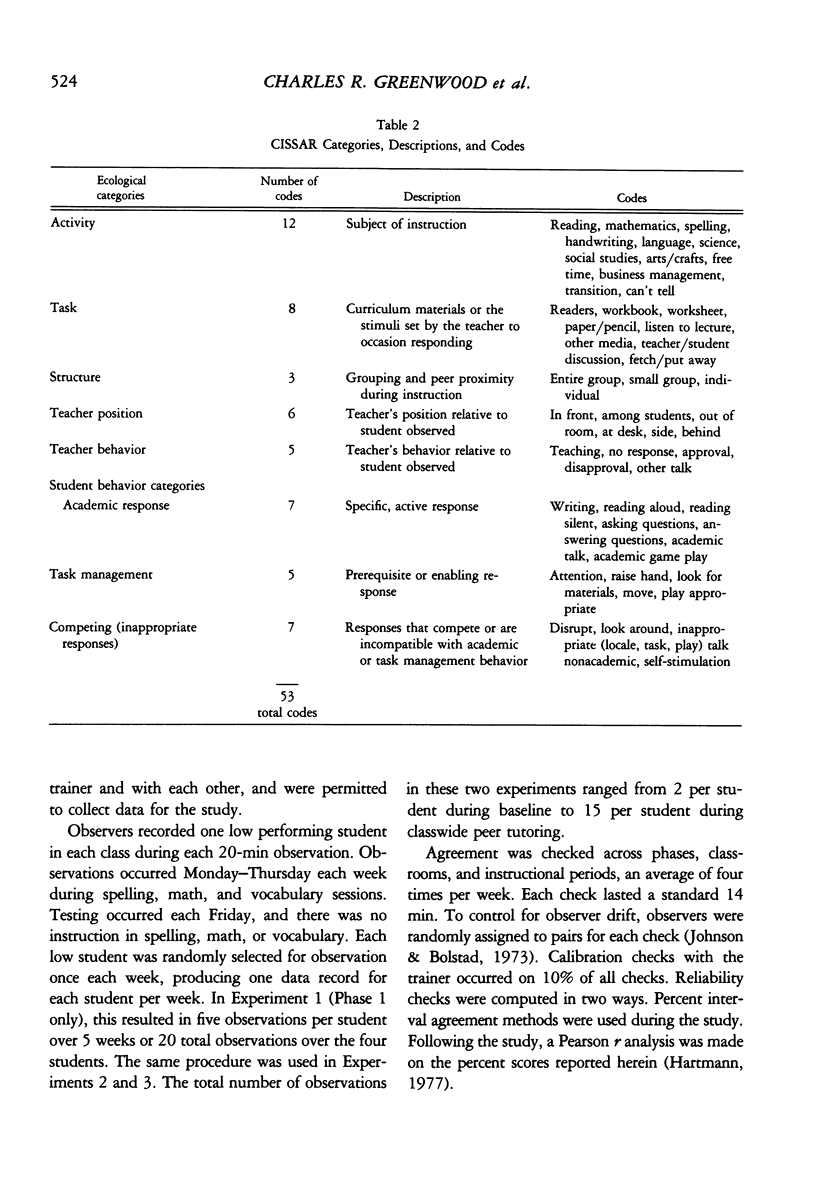
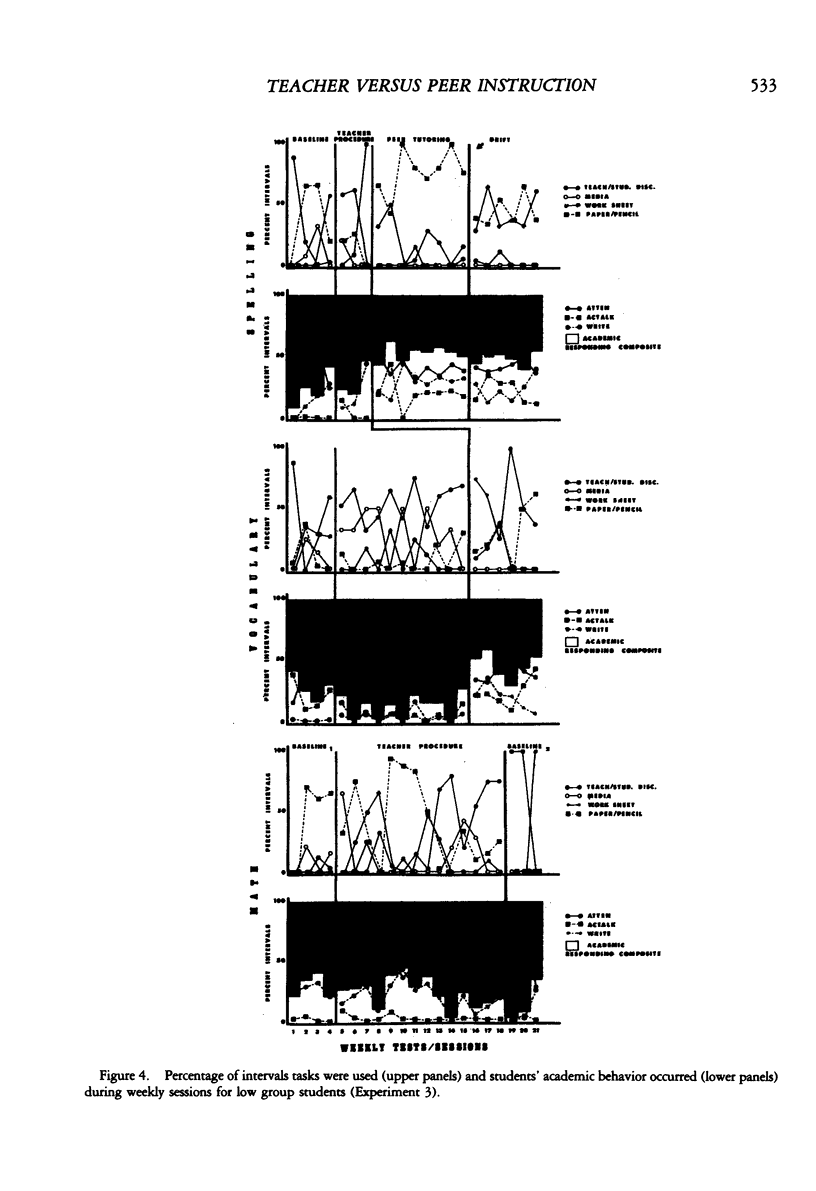
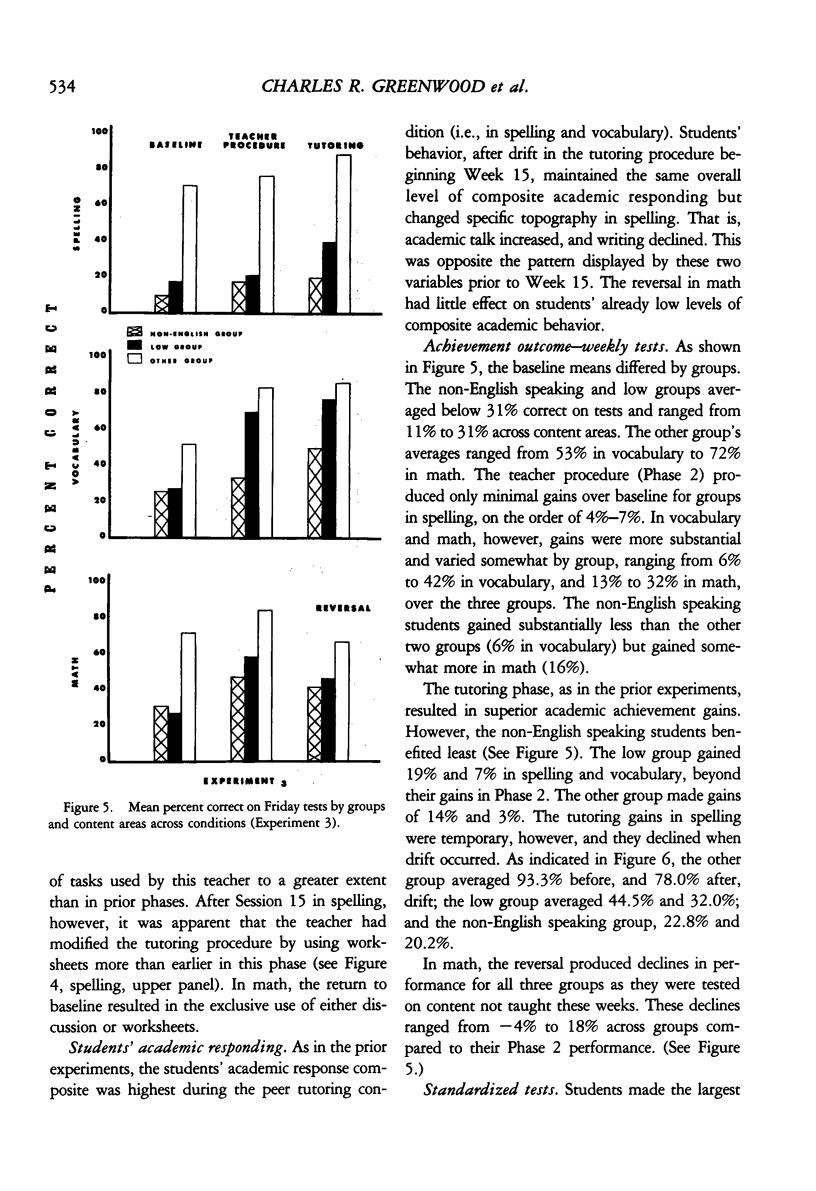
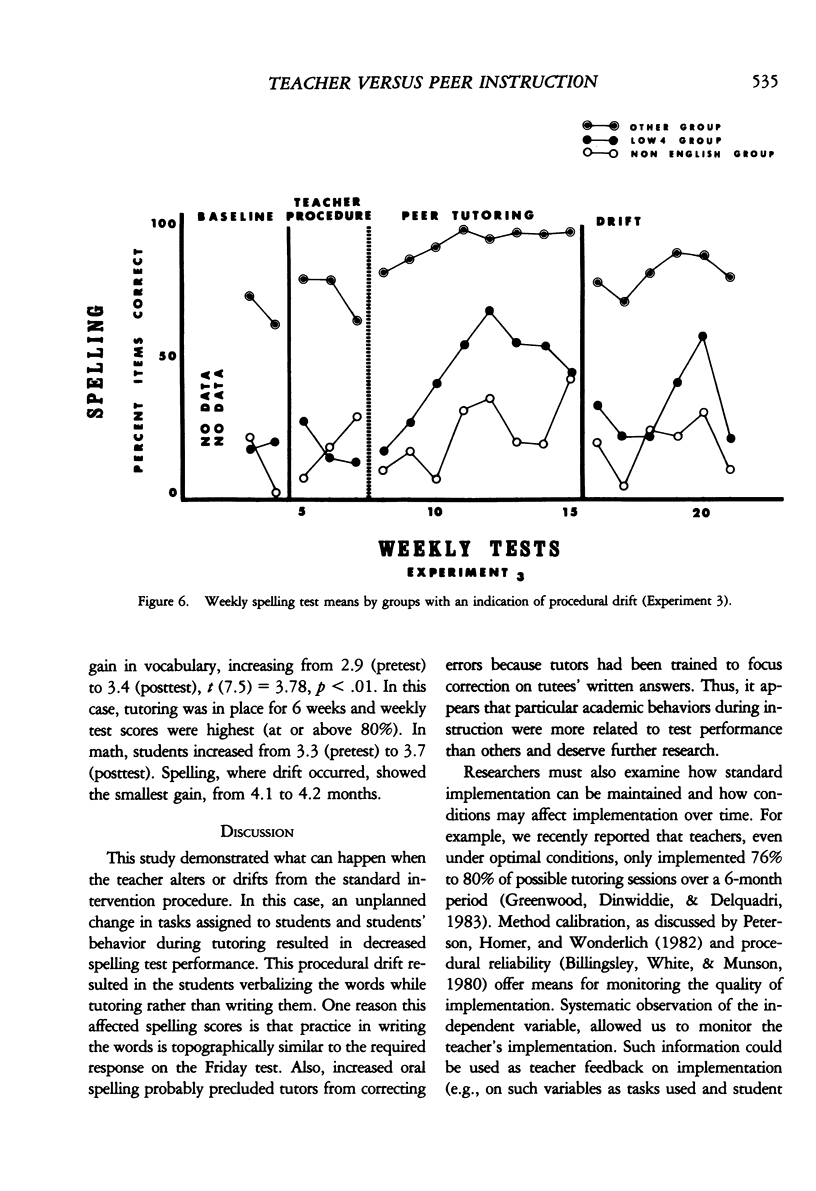
In three experiments, we compared the effects of instructional arrangements that varied in: teacher versus peer mediators, methods used, levels of student academic responding generated, and content taught and tested. Instructional arrangements (i.e., tasks, structure, teacher position, teacher behavior) and students' levels of academic responding were measured by an observation system which served as an index of the independent variables. Students' accuracy on weekly spelling, arithmetic, and vocabulary tests and pre- and post-standardized achievement tests (Experiments 2 and 3 only) were the dependent variables. Results indicated that the classwide peer tutoring, compared to the teacher's procedure, produced more student academic responding and higher weekly test scores, regardless of treatment order or subject matter content (Experiment 1). The four lowest performing students in each class, in particular, benefited from peer tutoring, often performing as well as the other students. These findings were replicated in Experiments 2 and 3 wherein content taught/tested was also manipulated. Standardized test score gains were higher in those areas in which peer tutoring was used longest. Issues related to the functional analysis of instruction and achievement gain are discussed.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Born D. G., Gledhill S. M., Davis M. L. Examination performance in lecture-discussion and personalized instruction courses. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):33–43. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnine D. W. Effects of two teacher-presentation rates on off-task behavior, answering correctly, and participation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Summer;9(2):199–206. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dineen J. P., Clark H. B., Risley T. R. Peer tutoring among elementary students: educational benefits to the tutor. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):231–238. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C. R., Hops H., Walker H. M., Guild J. J., Stokes J., Young K. R., Keleman K. S., Willardson M. Standardized classroom management program: Social validation and replication studies in Utah and Oregon. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):235–253. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann D. P. Considerations in the choice of interobserver reliability estimates. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Spring;10(1):103–116. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirigin K. A., Braukmann C. J., Atwater J. D., Wolf M. M. An evaluation of Teaching-Family (Achievement Place) group homes for juvenile offenders. J Appl Behav Anal. 1982 Spring;15(1):1–16. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1982.15-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medland M. B., Stachnik T. J. Good-behavior game: a replication and systematic analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):45–51. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packard R. G. The control of "classroom attention": a group contingency for complex behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Spring;3(1):13–28. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson L., Homer A. L., Wonderlich S. A. The integrity of independent variables in behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1982 Winter;15(4):477–492. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1982.15-477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J., Martindale A., Kulp S. An evaluation of time-sample measures of behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):463–469. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb G., Hopkins B. L., Hursh D. E. The effects of study questions and grades on student test performance in a college course. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):631–642. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavin R. E., Madden N. A., Leavey M. Effects of cooperative learning and individualized instruction on mainstreamed students. Except Child. 1984 Feb;50(5):434–443. doi: 10.1177/001440298405000506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trovato J., Bucher B. Peer tutoring with or without home-based reinforcement, for reading remediation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):129–141. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]