Abstract
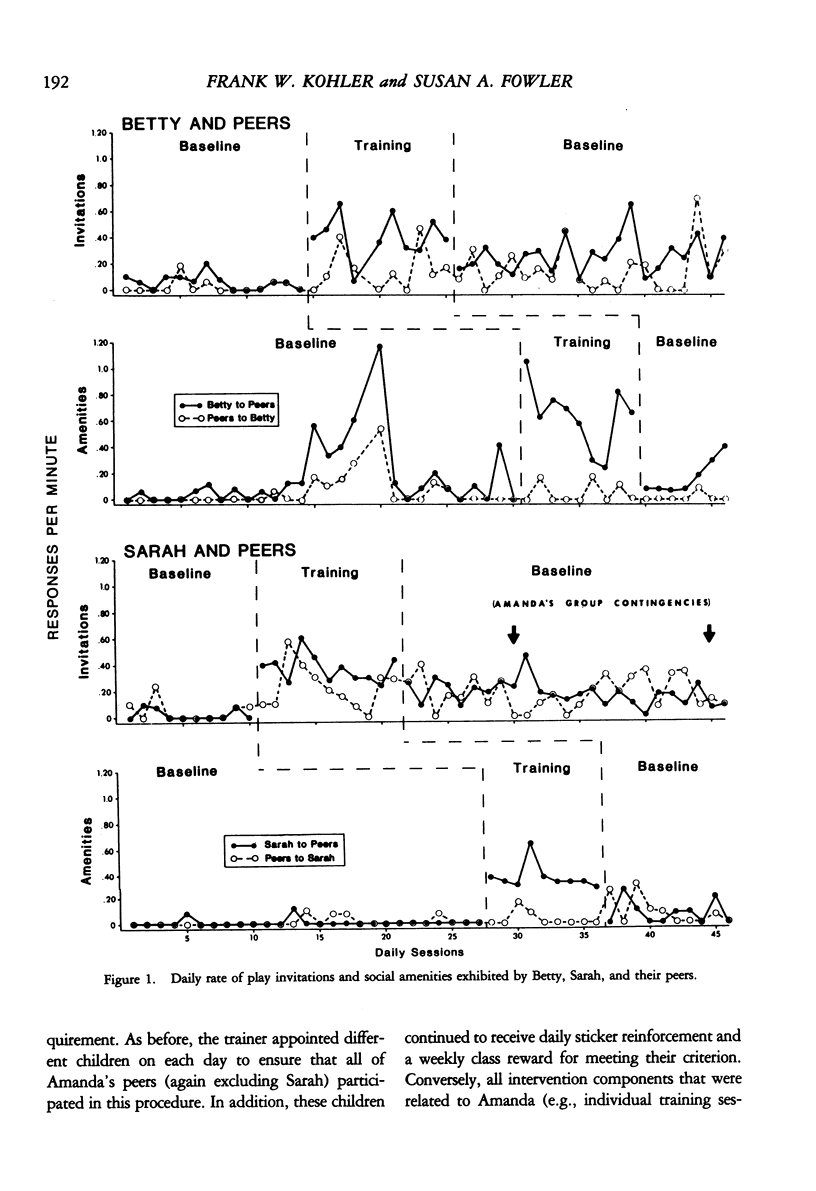
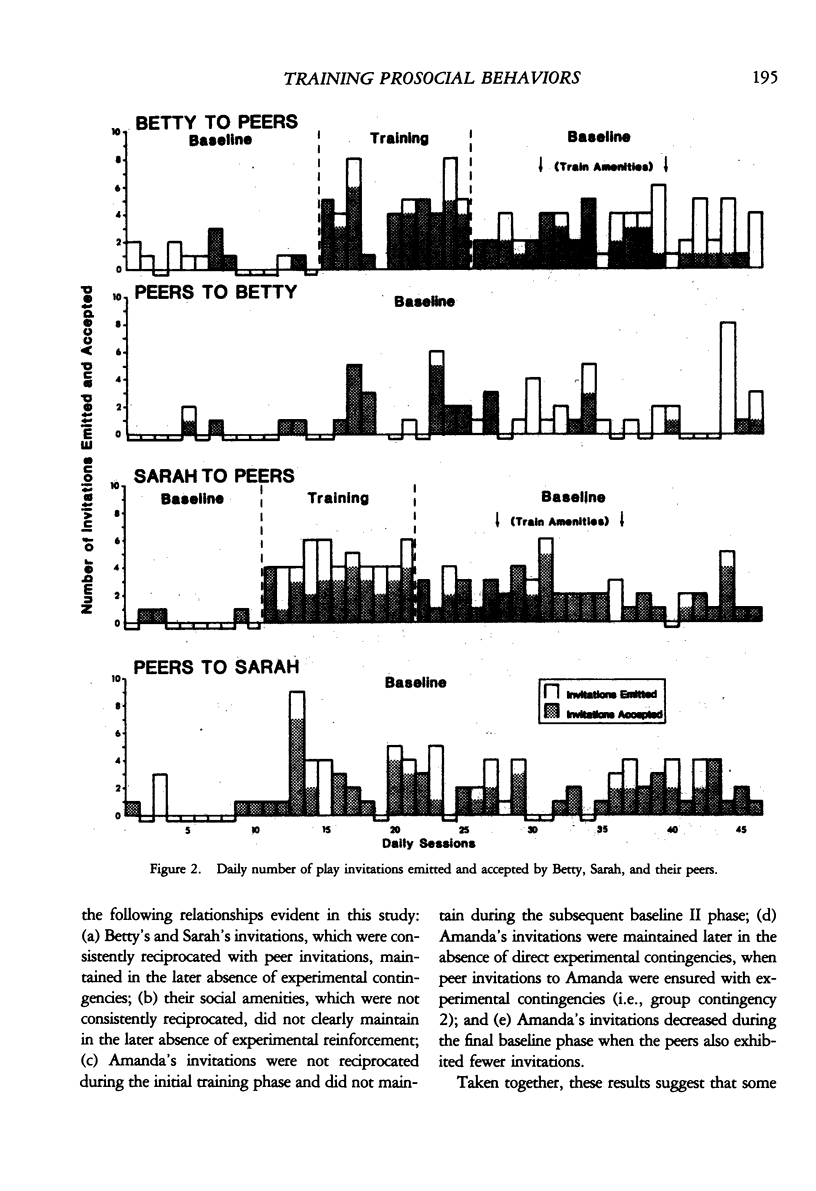
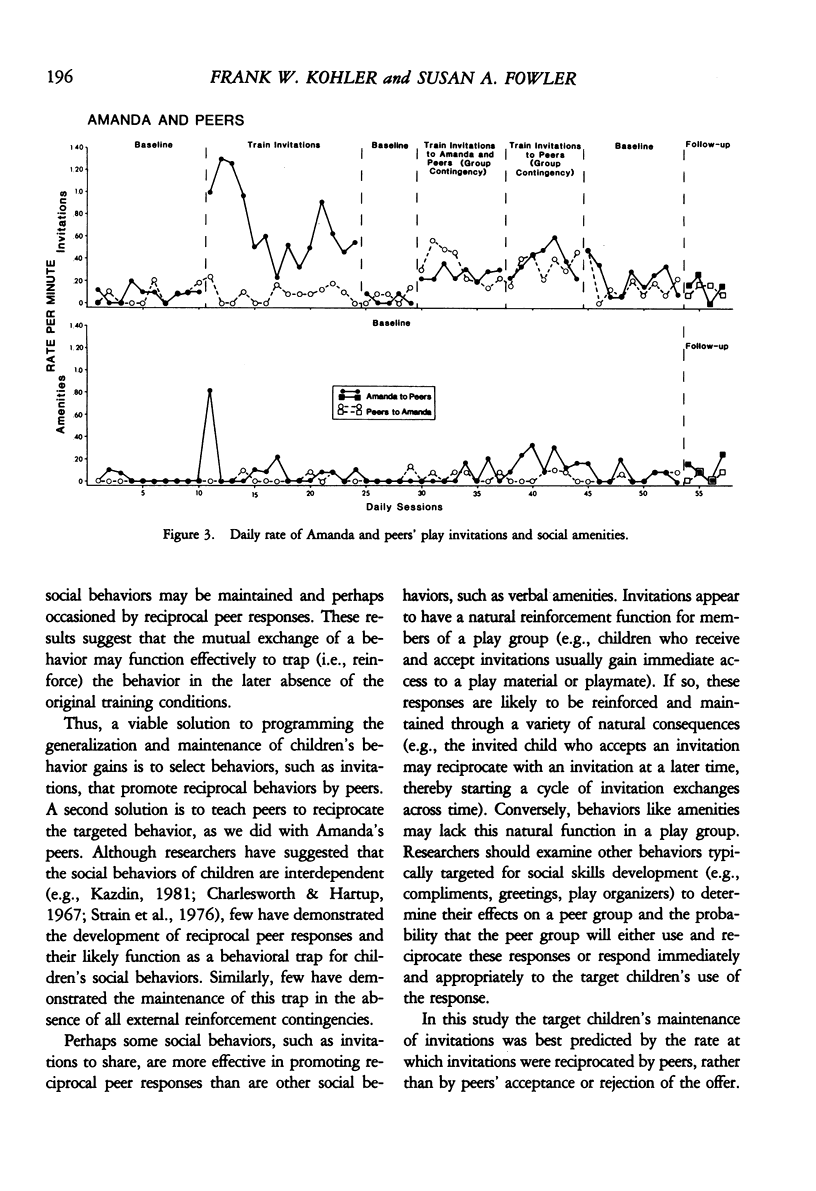
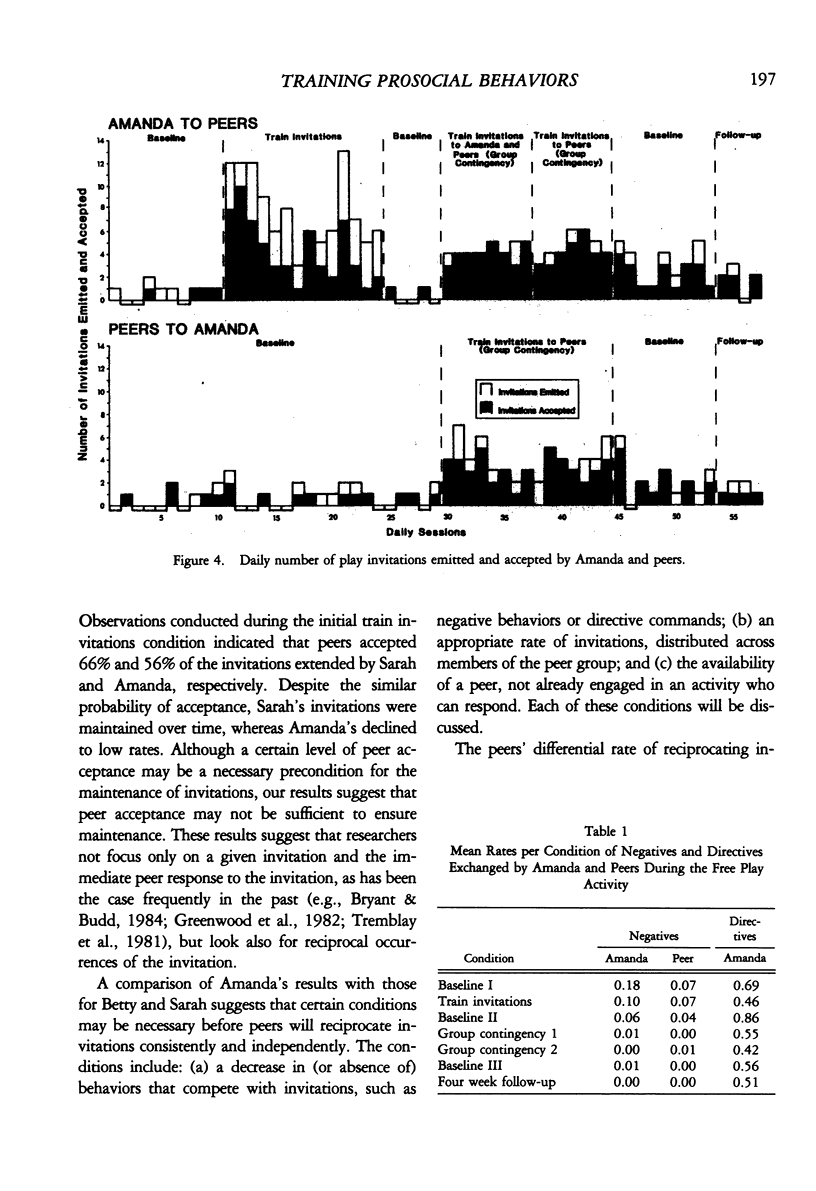
We examined the effects of a social skills training package on the play behaviors of three young girls. Two children were taught to invite their peers to play and to use social amenities during their conversations with other children. A combined reversal and multiple baseline across responses design demonstrated that both children directed more social behaviors to their classroom peers after training and that these two children's play invitations were maintained in the later absence of experimental contingencies. In addition, both target children received a greater number of play invitations from their peers during the free play periods. In contrast, a third child's play invitations were not reciprocated by peers; her invitations subsequently decreased in rate after training was discontinued. An interdependent group contingency produced a reciprocal exchange of invitations between this child and her classroom peers. A reversal design demonstrated partial maintenance of subject-peer exchanges after the group intervention was discontinued. The results obtained with the three target children suggest that peer reciprocity may facilitate the maintenance of children's play invitations over time.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN K. E., HART B., BUELL J. S., HARRIS F. R., WOLF M. M. EFFECTS OF SOCIAL REINFORCEMENT ON ISOLATE BEHAVIOR OF A NURSERY SCHOOL CHILD. Child Dev. 1964 Jun;35:511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1964.tb05188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton E. J., Ascione F. R. Sharing in preschool children: Facilitation, stimulus generalization, response generalization, and maintenance. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Fall;12(3):417–430. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berler E. S., Gross A. M., Drabman R. S. Social skills training with children: proceed with caution. J Appl Behav Anal. 1982 Spring;15(1):41–53. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1982.15-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant L. E., Budd K. S. Teaching behaviorally handicapped preschool children to share. J Appl Behav Anal. 1984 Spring;17(1):45–56. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1984.17-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth R., Hartup W. W. Positive social reinforecement in the nursery school peer group. Child Dev. 1967 Dec;38(4):993–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. P., Apolloni T. Developing positive social-emotional behaviors: a study of training and generalization effects. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):65–78. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S. A., Baer D. M. "Do I have to be good all day? The timing of delayed reinforcement as a factor in generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1981 Spring;14(1):13–24. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1981.14-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. M., Reynolds N. J., Baer D. M., Brawley E. R., Harris F. R. Effect of contingent and non-contingent social reinforcement on the cooperative play of a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):73–76. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman S. H., Tramontana J. Instructions and group versus individual reinforcement in modifying disruptive group behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Summer;4(2):113–119. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B. L. Effects of candy and social reinforcement, instructions, and reinforcement schedule leaning on the modification and maintenance of smiling. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):121–129. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J., Martindale A., Kulp S. An evaluation of time-sample measures of behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):463–469. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quilitch H. R., Risley T. R. The effects of play materials on social play. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):573–578. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers-Warren A., Baer D. M. Correspondence between saying and doing: teaching children to share and praise. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Fall;9(3):335–354. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon R. W., Wahler R. G. Peer reinforcement control of classroom problem behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):49–56. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. F., Baer D. M., Jackson R. L. Programming the generalization of a greeting response in four retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):599–610. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. F., Fowler S. A., Baer D. M. Training preschool children to recruit natural communities of reinforcement. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):285–303. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Shores R. E., Kerr M. M. An experimental analysis of "spillover" effects on the social interaction of behaviorally handicapped preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):31–40. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Shores R. E. Social reciprocity: a review of research and educational implications. Except Child. 1977 May;43(8):526–530. doi: 10.1177/001440297704300806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Timm M. A. An experimental analysis of social interaction between a behaviorally disordered preschool child and her classroom peers. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):583–590. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hasselt V. B., Hersen M., Whitehill M. B., Bellack A. S. Social skill assessment and training for children: an evaluative review. Behav Res Ther. 1979;17(5):413–437. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(79)90059-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G. Child-child interactions in free field settings: some experimental analyses. J Exp Child Psychol. 1967 Jun;5(2):278–293. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(67)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker H. M., Buckley N. K. Programming generalization and maintenance of treatment effects across time and across settings. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Fall;5(3):209–224. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S. F., Rogers-Warren A., Baer D. M. The role of offer rates in controlling sharing by young children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 WINTER;9(4):491–497. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



