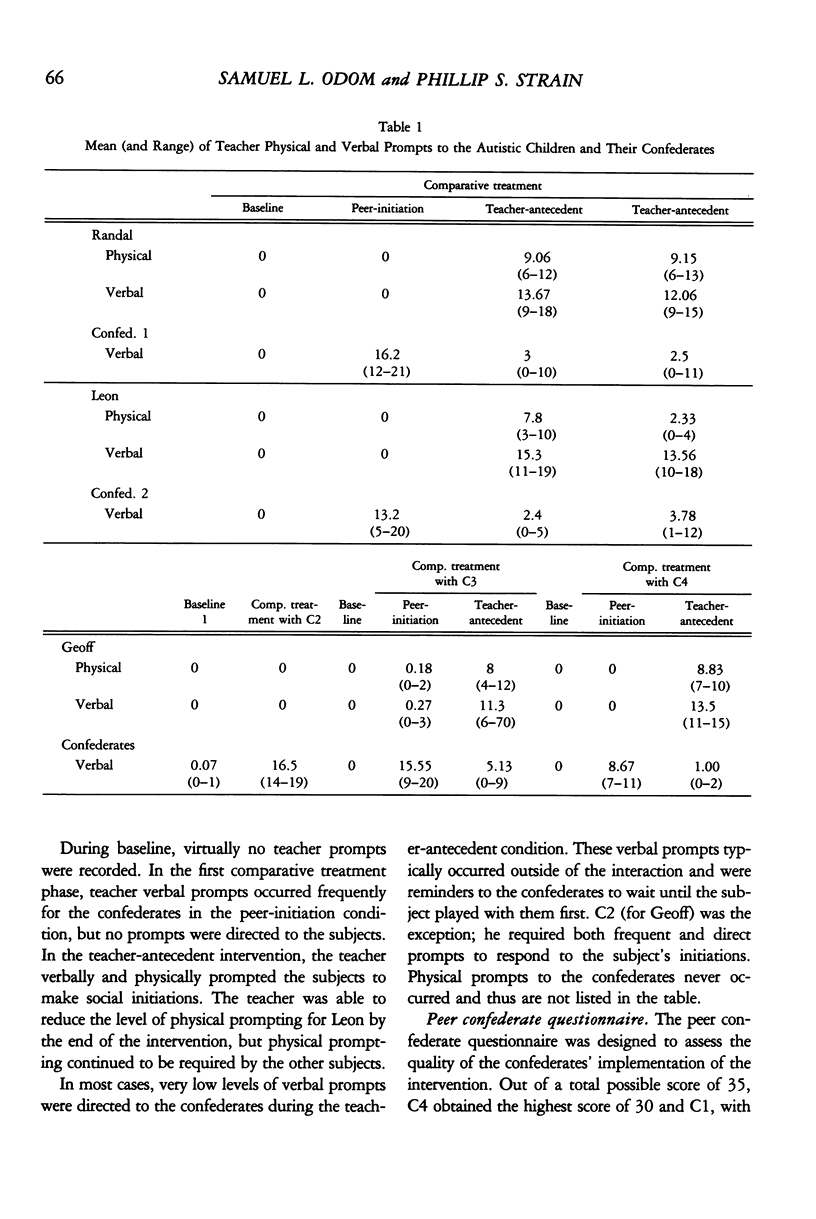
Abstract
We compared two procedures for improving the social interactions of three autistic children. In a peer-initiation condition, confederates were taught to initiate interaction with the autistic children. In a teacher-antecedent condition, teachers prompted the autistic children to initiate with confederates, who had been taught to reciprocate. Using an alternating treatment design, differential effects were found. The peer-initiation procedure reliably increased the social responses of the autistic children, whereas the teacher-antecedent condition increased the initiations and responses of the autistic children. In addition, longer chains of social interaction occurred during the teacher-antecedent condition.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN K. E., HART B., BUELL J. S., HARRIS F. R., WOLF M. M. EFFECTS OF SOCIAL REINFORCEMENT ON ISOLATE BEHAVIOR OF A NURSERY SCHOOL CHILD. Child Dev. 1964 Jun;35:511–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1964.tb05188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaylord-Ross R. J., Haring T. G., Breen C., Pitts-Conway V. The training and generalization of social interaction skills with autistic youth. J Appl Behav Anal. 1984 Summer;17(2):229–247. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1984.17-229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halle J. W., Marshall A. M., Spradlin J. E. Time delay: a technique to increase language use and facilitate generalization in retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Fall;12(3):431–439. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. M., Reynolds N. J., Baer D. M., Brawley E. R., Harris F. R. Effect of contingent and non-contingent social reinforcement on the cooperative play of a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):73–76. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom S. L., Hoyson M., Jamieson B., Strain P. S. Increasing handicapped preschoolers' peer social interactions: cross-setting and component analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1985 Spring;18(1):3–16. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1985.18-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom S. L., Strain P. S. Peer-mediated approaches to promoting children's social interaction: a review. Am J Orthopsychiatry. 1984 Oct;54(4):544–557. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-0025.1984.tb01525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczyk R. G., Diament C., Goren E. R., Trunell G., Harris S. L. Increasing isolate and social play in severely disturbed children: intervention and postintervention effectiveness. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1975 Mar;5(1):57–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01537972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter M. Diagnosis and definition of childhood autism. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1978 Jun;8(2):139–161. doi: 10.1007/BF01537863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopler E., Reichler R. J., DeVellis R. F., Daly K. Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). J Autism Dev Disord. 1980 Mar;10(1):91–103. doi: 10.1007/BF02408436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Fox J. J. Peer social initiations and the modification of social withdrawal: a review and future perspective. J Pediatr Psychol. 1981 Dec;6(4):417–433. doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/6.4.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S. Identification of social skill curriculum targets for severely handicapped children in mainstream preschools. Appl Res Ment Retard. 1983;4(4):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0270-3092(83)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Shores R. E. Social reciprocity: a review of research and educational implications. Except Child. 1977 May;43(8):526–530. doi: 10.1177/001440297704300806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchette P. E., Howard J. S. Errorless learning: reinforcement contingencies and stimulus control transfer in delayed prompting. J Appl Behav Anal. 1984 Summer;17(2):175–188. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1984.17-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



