Abstract
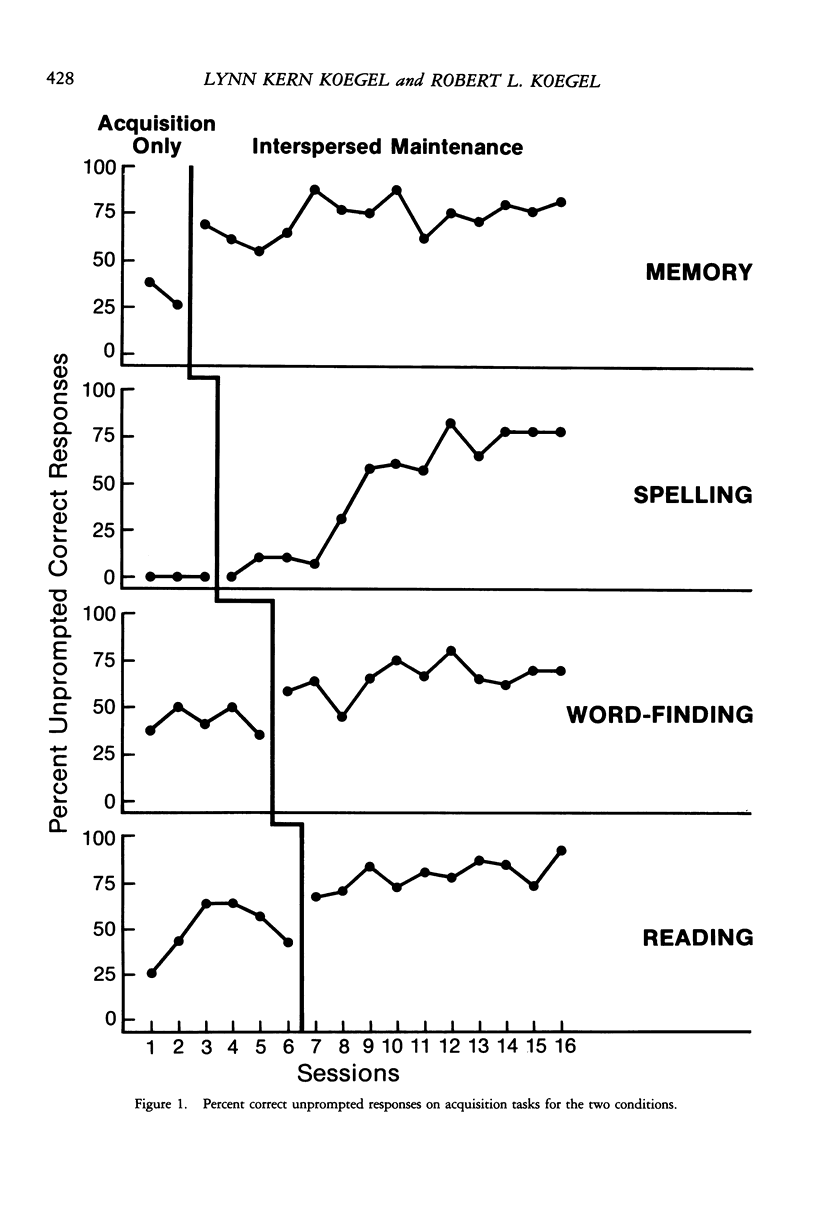
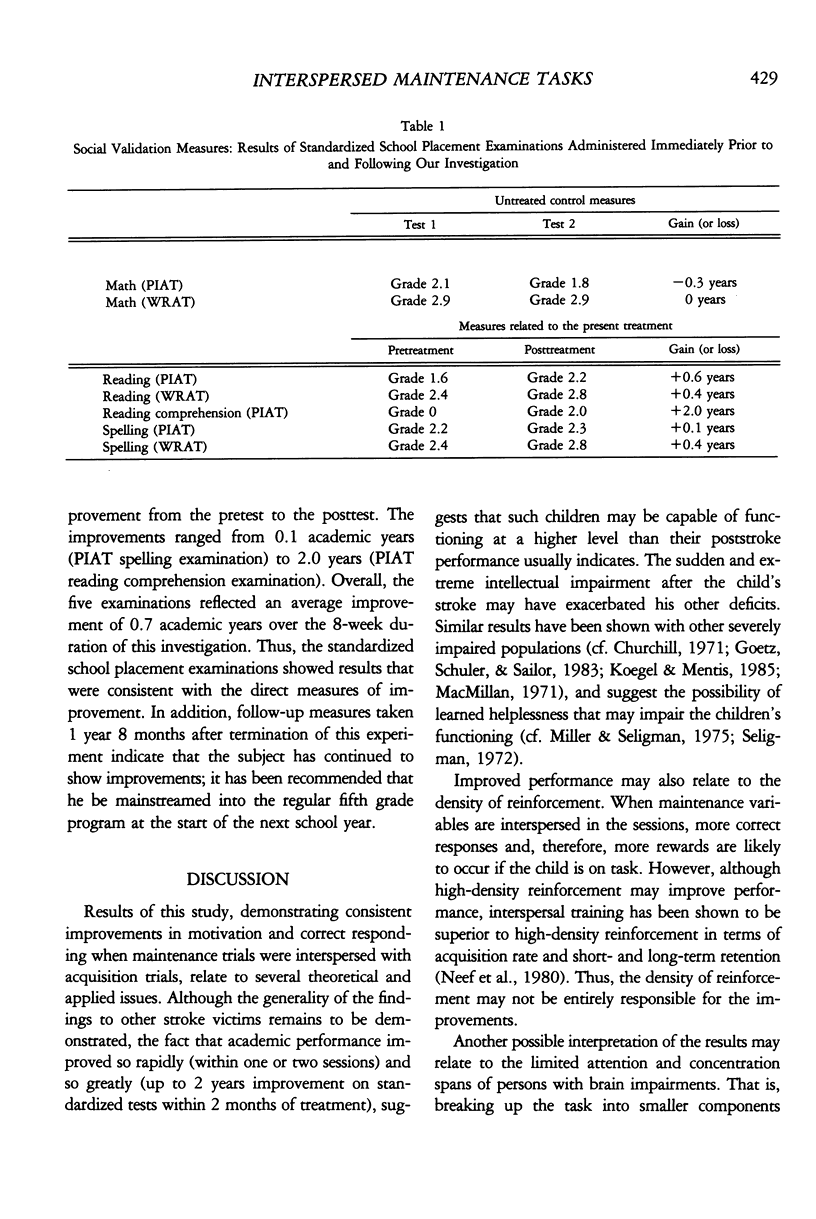
We examined the effects of task-sequencing variables on the academic performance of an 8-year-old severe stroke victim. Within a multiple baseline design, previously acquired (maintenance) task trials were systematically interspersed at designated points in treatment among new (acquisition) task trials. The results showed improvements in both academic responding and subjective ratings of motivation in each of four treated areas (spelling, reading, word-finding, and memory). Social validation data obtained from standardized school placement examinations suggested marked improvement in a variety of related areas of academic functioning. Results suggest that children suffering severe strokes may be capable of learning more than has previously been suspected, and that behavioral treatments may improve such children's functioning.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alajouanine T., Lhermitte F. Acquired aphasia in children. Brain. 1965 Nov;88(4):653–662. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.4.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. D., Binkoff J. A. Escape as a factor in the aggressive behavior of two retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):101–117. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap G., Koegel R. L. Motivating autistic children through stimulus variation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Winter;13(4):619–627. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap G. The influence of task variation and maintenance tasks on the learning and affect of autistic children. J Exp Child Psychol. 1984 Feb;37(1):41–64. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(84)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrist E., Wilkinson M. Some factors determining prognosis in young people with severe head injuries. Arch Neurol. 1979 Jun;36(6):355–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1979.00500420065008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klonoff H., Low M. D., Clark C. Head injuries in children: a prospective five year follow-up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1977 Dec;40(12):1211–1219. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.40.12.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Egel A. L. Motivating autistic children. J Abnorm Psychol. 1979 Aug;88(4):418–426. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.88.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Mentis M. Motivation in childhood autism: can they or won't they? J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 1985 Mar;26(2):185–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7610.1985.tb02259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan D. L. The problem of motivation in the education of the mentally retarded. Except Child. 1971 Apr;37(8):579–586. doi: 10.1177/001440297103700803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. R., Seligman M. E. Depression and learned helplessness in man. J Abnorm Psychol. 1975 Jun;84(3):228–238. doi: 10.1037/h0076720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neef N. A., Iwata B. A., Page T. J. The effects of interspersal training versus high-density reinforcement on spelling acquisition and retention. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):153–158. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligman M. E. Learned helplessness. Annu Rev Med. 1972;23:407–412. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.23.020172.002203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stover S. L., Zeiger H. E., Jr Head injury in children and teenagers; functional recovery correlated with the duration of coma. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1976 May;57(5):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


