Abstract
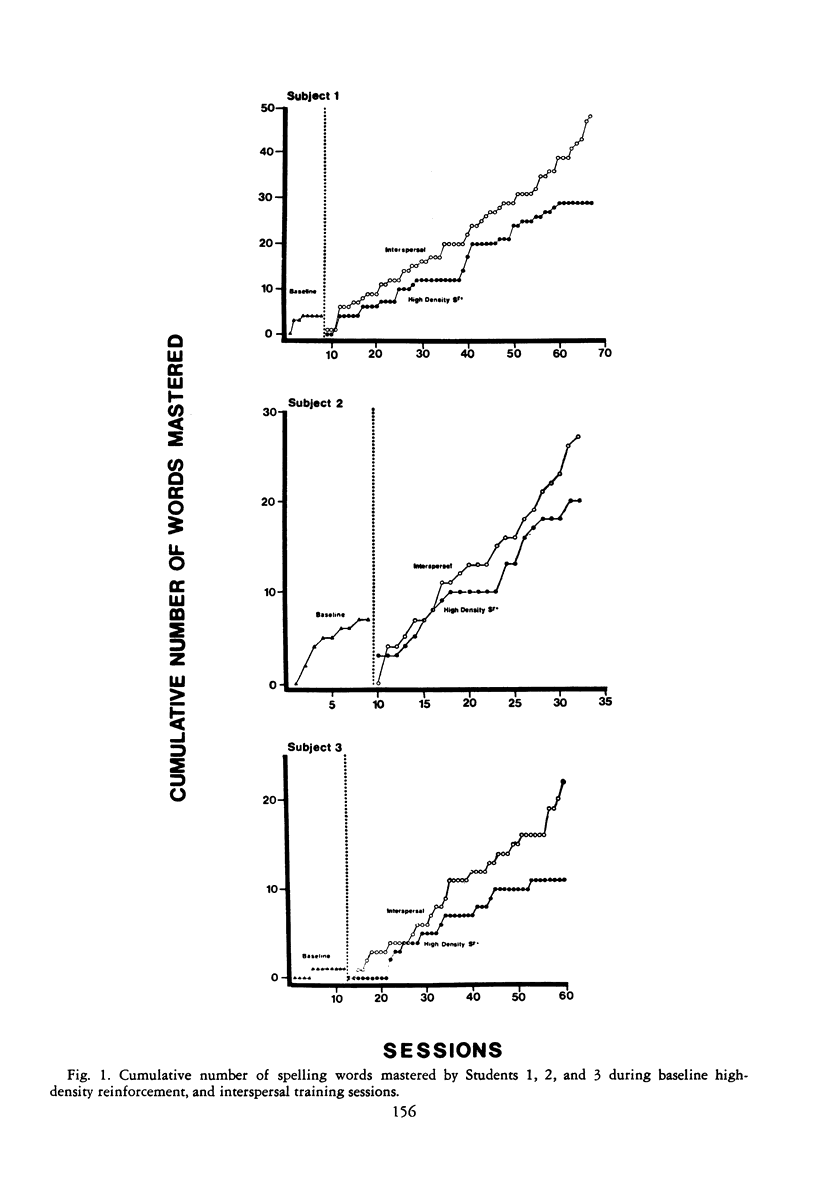
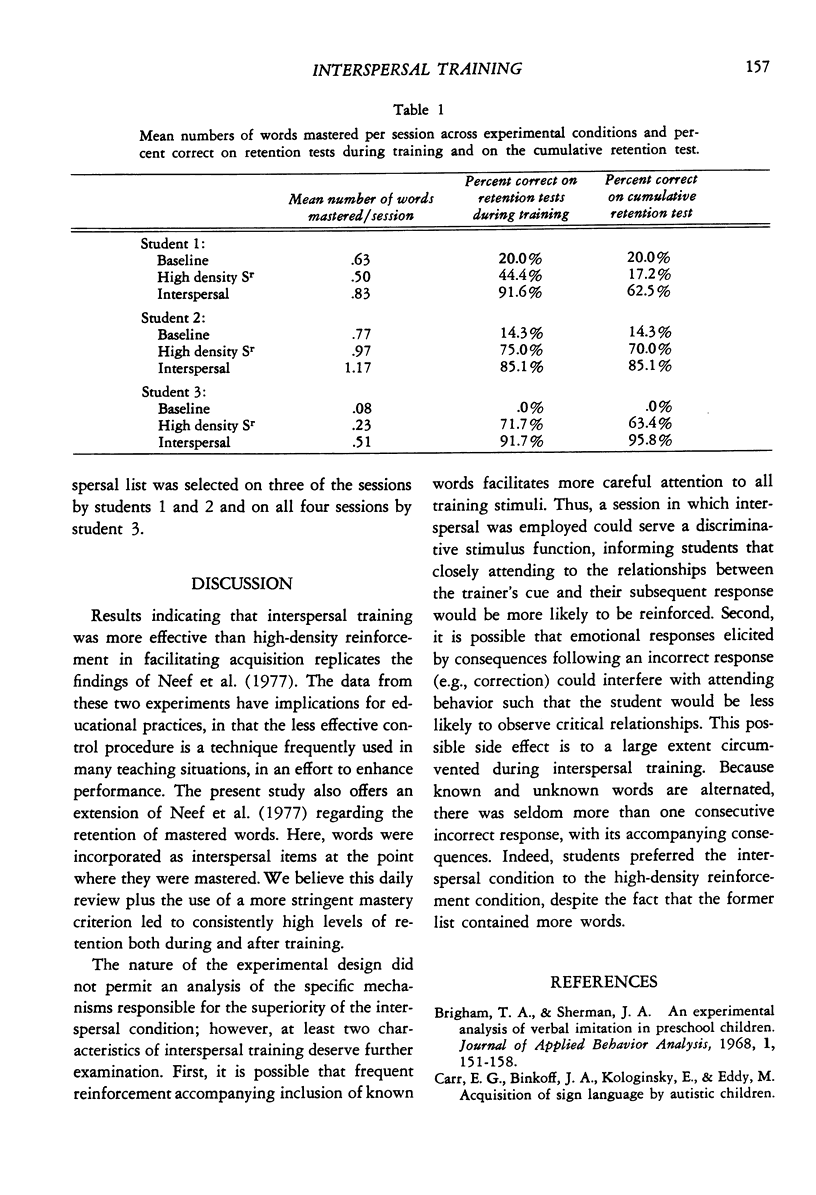
This study investigated the effects of interspersing known items during spelling instruction on new words for three mentally retarded students. Following a baseline consisting of the presentation of 10 test words per session, a multielement design was implemented. During interspersal training sessions, previously mastered words were presented alternately with each of 10 test words. During high-density reinforcement sessions, 10 test words were presented and additional reinforcement was provided for task-related behaviors. Throughout all conditions, test words were deleted and replaced after meeting a mastery criterion. Periodic retention tests were administered over mastered words and a cumulative retention test was administered at the end of the experiment. Results showed that high-density reinforcement did facilitate performance over baseline; however, intersperal training was superior to the other conditions in terms of both acquisition rate and short- and long-term retention. In addition, students preferred the interspersal condition when offered a choice.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brigham T. A., Sherman J. A. An experimental analysis of verbal imitation in preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):151–158. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Binkoff J. A., Kologinsky E., Eddy M. Acquisition of sign language by autistic children. I: Expressive labelling. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Winter;11(4):489–501. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisch S. A., Schumaker J. B. Training generalized receptive prepositions in retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):611–621. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kircher A. S., Pear J. J., Martin G. L. Shock as punishment in a picture-naming task with retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Fall;4(3):227–233. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Berberich J. P., Perloff B. F., Schaeffer B. Acquisition of imitative speech by schizophrenic children. Science. 1966 Feb 11;151(3711):705–707. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3711.705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. F. Some experiments on the organization of a class of imitative behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):225–235. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker J., Sherman J. A. Training generative verb usage by imitation and reinforcement procedures. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Winter;3(4):273–287. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


