Abstract
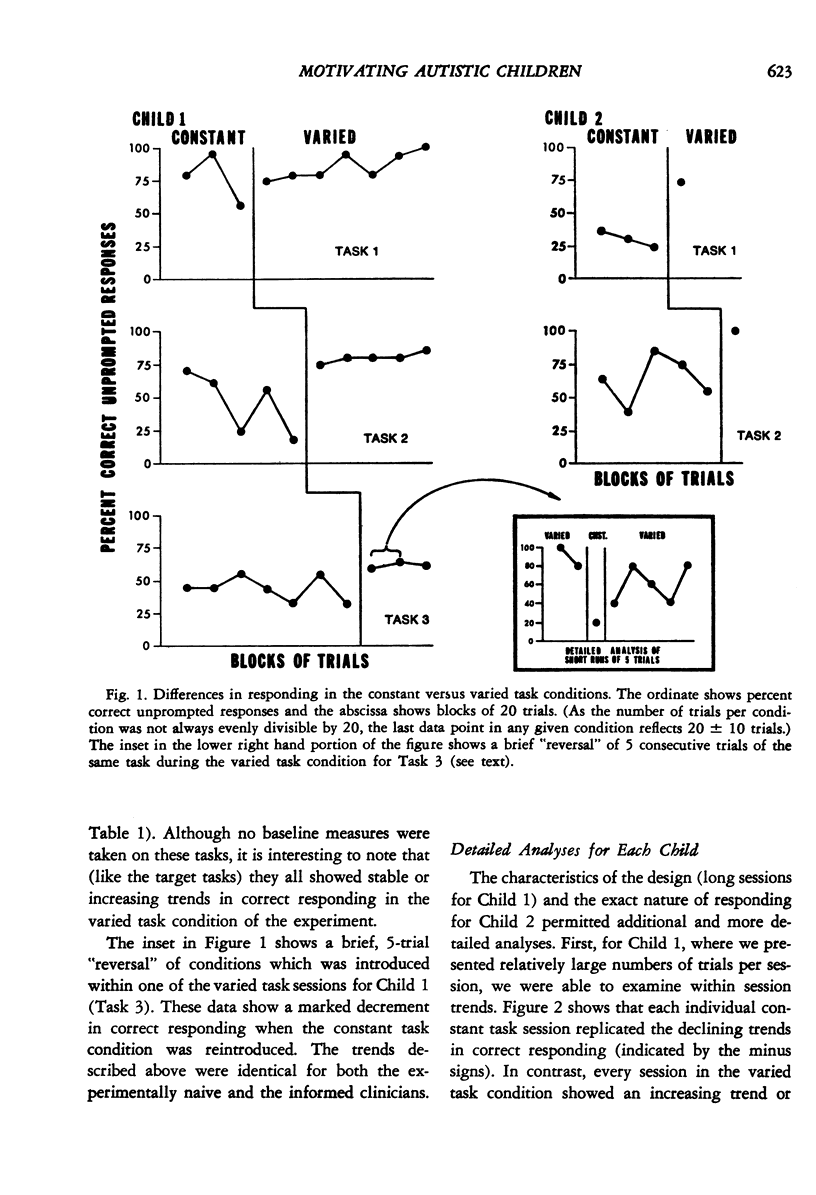
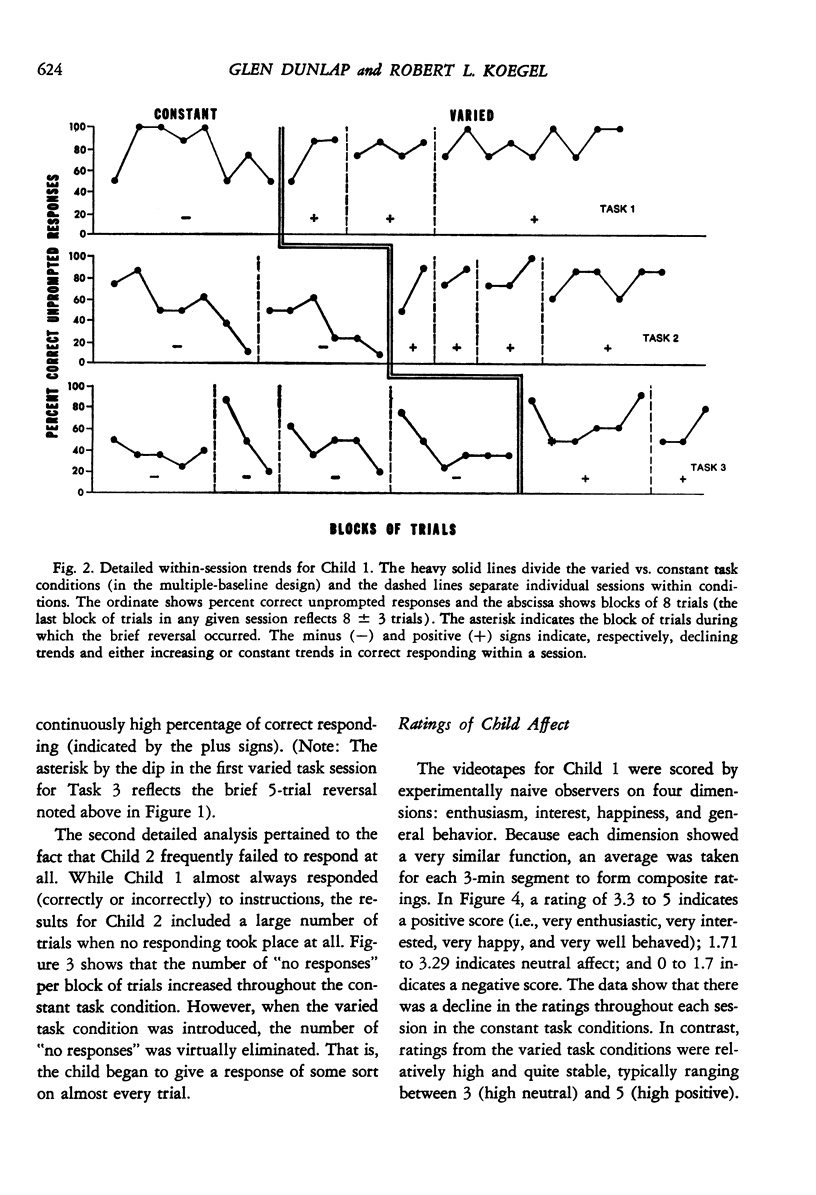
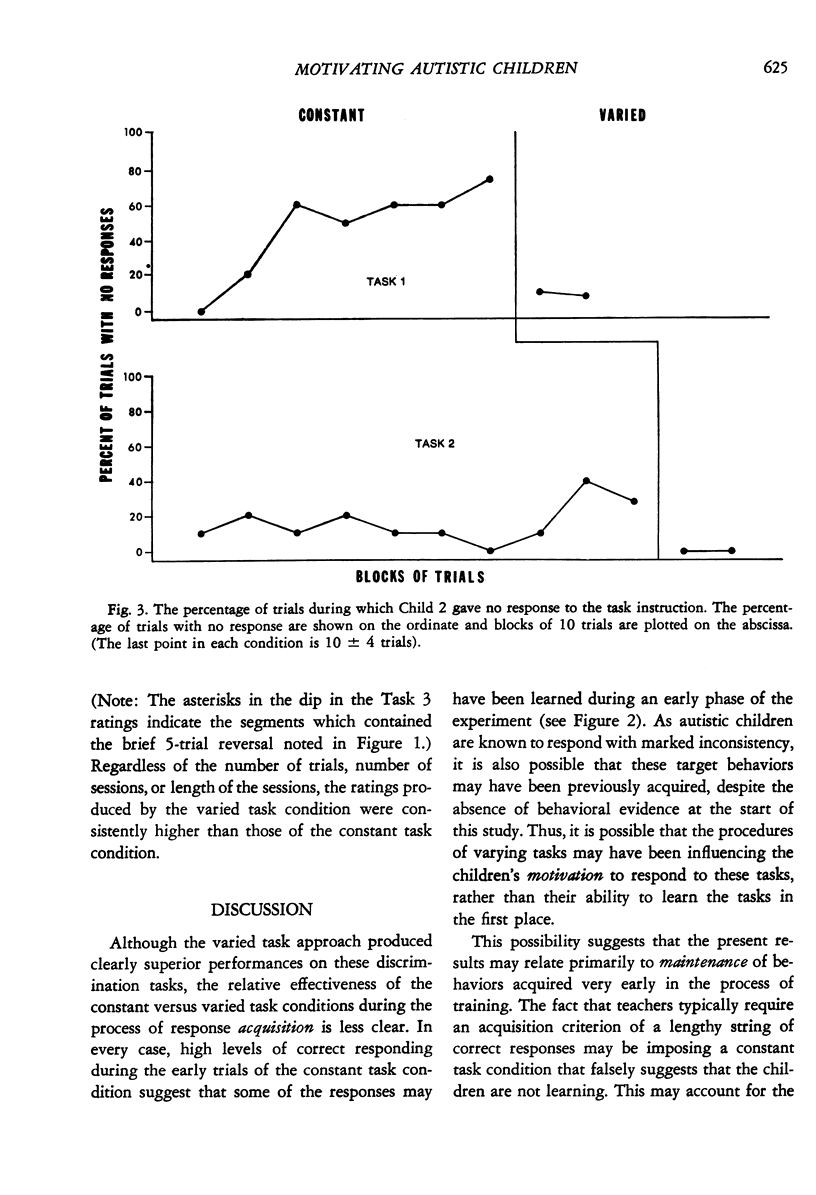
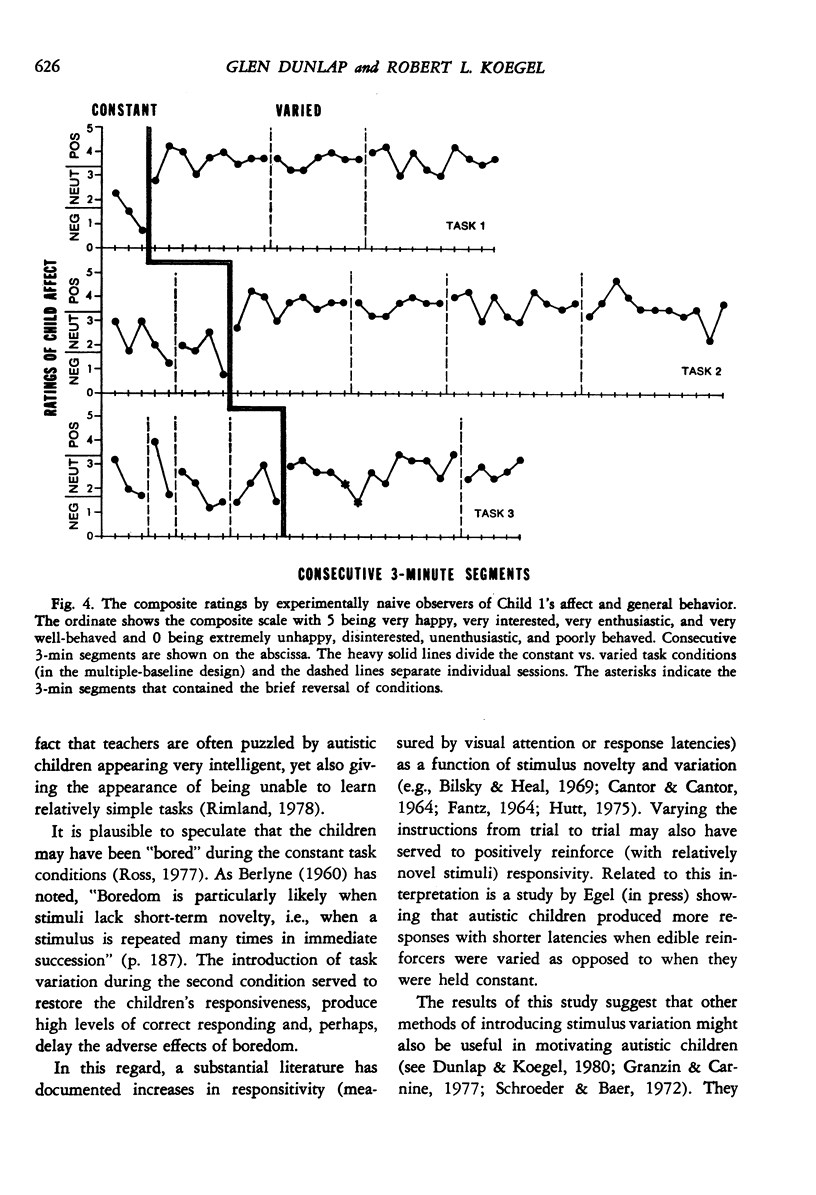
This study evaluated the differential effectiveness of two methods of presenting discrimination tasks when teaching autistic children. In a constant task condition, the common method of presenting a single task throughout a session was used. In a varied task condition, the same task was interspersed with a variety of other tasks from the children's clinic curricula. Results showed declining trends in correct responding during the constant task condition, with substantially improved and stable responding during the varied task conditions. In addition, naive observers judged the children to be more enthusiastic, interested, happier, and better behaved during the varied task sessions. These results suggest that "boredom" may be a particularly important variable to control in the treatment of autistic children, and that particular care may be necessary when defining criteria for task acquisition. The results are discussed in relation to the literature on increased responsivity to stimulus novelty and variation.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilsky L., Heal L. W. Cue novelty and training level in the discrimination shift performance of retardates. J Exp Child Psychol. 1969 Dec;8(3):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(69)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANTOR J. H., CANTOR G. N. OBSERVING BEHAVIOR IN CHILDREN AS A FUNCTION OF STIMULUS NOVELTY. Child Dev. 1964 Mar;35:119–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1964.tb05923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G., Newsom C. D., Binkoff J. A. Stimulus control of self-destructive behavior in a psychotic child. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(2):139–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00916518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANTZ R. L. VISUAL EXPERIENCE IN INFANTS: DECREASED ATTENTION TO FAMILIAR PATTERNS RELATIVE TO NOVEL ONES. Science. 1964 Oct 30;146(3644):668–670. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3644.668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faw T. T., Nunnally J. C. The influence of stimulus complexity, novelty, and affective value on children's visual fixations. J Exp Child Psychol. 1968 Mar;6(1):141–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(68)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Dunlap G., Dyer K. Intertrial interval duration and learning in autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):91–99. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Egel A. L. Motivating autistic children. J Abnorm Psychol. 1979 Aug;88(4):418–426. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.88.4.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Russo D. C., Rincover A. Assessing and training teachers in the generalized use of behavior modification with autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):197–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National Society for Autistic Children definition of the syndrome of autism. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1978 Jun;8(2):162–169. doi: 10.1007/BF01537864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyan M. C., Hall R. V. Effects of serial versus concurrent task sequencing an acquisition, maintenance, and generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Spring;11(1):67–74. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZEAMAN D., HOUSE B. J., ORLANDO R. Use of special training conditions in visual discrimination learning with imbeciles. Am J Ment Defic. 1958 Nov;63(3):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


