Abstract
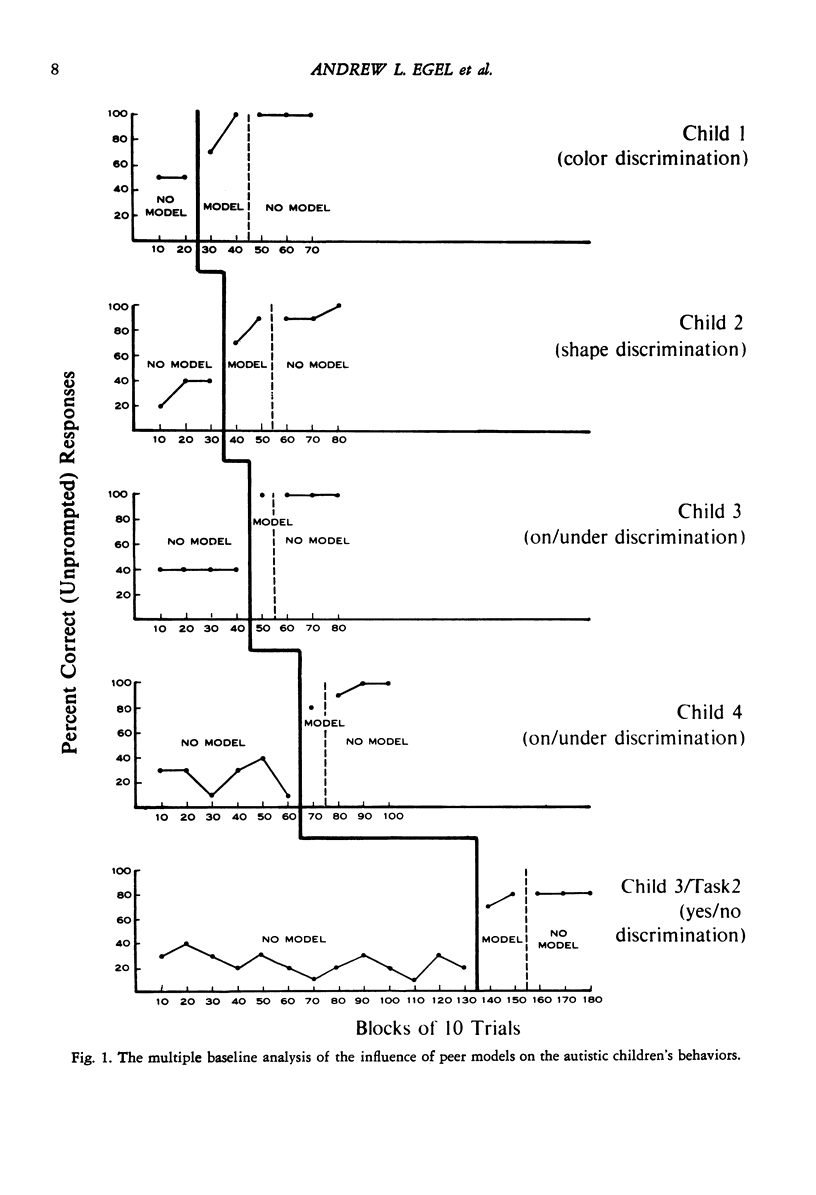
Present research and legislation regarding mainstreaming autistic children into normal classrooms have raised the importance of studying whether autistic children can benefit from observing normal peer models. The present investigation systematically assessed whether autistic children's learning of discrimination tasks could be improved if they observed normal children perform the tasks correctly. In the context of a multiple baseline design, four autistic children worked on five discrimination tasks that their teachers reported were posing difficulty. Throughout the baseline condition the children evidenced very low levels of correct responding on all five tasks. In the subsequent treatment condition, when normal peers modeled correct responses, the autistic children's correct responding increased dramatically. In each case, the peer modeling procedure produced rapid achievement of the acquisition which was maintained after the peer models were removed. These results are discussed in relation to issues concerning observational learning and in relation to the implications for mainstreaming autistic children into normal classrooms.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANDURA A., ROSS D., ROSS S. A. Imitation of film-mediated agressive models. J Abnorm Soc Psychol. 1963 Jan;66:3–11. doi: 10.1037/h0048687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A., Grusec J. E., Menlove F. L. Vicarious extinction of avoidance behavior. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1967 Jan;5(1):16–23. doi: 10.1037/h0024182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandura A., Menlove F. L. Factors determining vicarious extinction of avoidance behavior through symbolic modeling. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1968 Feb;8(2):99–108. doi: 10.1037/h0025260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry N. J., Jr, Overmann P. B. Comparison of the effectiveness of adult and peer models with EMR children. Am J Ment Defic. 1977 Jul;82(1):33–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlyne D. E., Ditkofsky J. Effects of novelty and oddity on visual selective attention. Br J Psychol. 1976 May;67(2):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1976.tb01508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap G., Koegel R. L., Egel A. L. Autistic children in school. Except Child. 1979 Apr;45(7):552–558. doi: 10.1177/001440297904500709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap G., Koegel R. L. Motivating autistic children through stimulus variation. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Winter;13(4):619–627. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egel A. L. The effects of constant vs varied reinforcer presentation on responding by autistic children. J Exp Child Psychol. 1980 Dec;30(3):455–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(80)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS D. J. IMITATION AND RETENTION OF FILM-MEDIATED AGGRESSIVE PEER AND ADULT MODELS. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1965 Jul;2:97–100. doi: 10.1037/h0022075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartup W. W., Coates B. Imitation of a peer as a function of reinforcement from the peer group and rewardingness of the model. Child Dev. 1967 Dec;38(4):1003–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Rincover A. Treatment of psychotic children in a classroom environment: I. Learning in a large group. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Spring;7(1):45–59. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Russo D. C., Rincover A. Assessing and training teachers in the generalized use of behavior modification with autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):197–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koegel R. L., Schreibman L. Teaching autistic children to respond to simultaneous multiple cues. J Exp Child Psychol. 1977 Oct;24(2):299–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(77)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornhaber R. C., Schroeder H. E. Importance of model similarity on extinction of avoidance behavior in children. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1975 Oct;43(5):601–607. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.43.5.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Koegel R. L., Schreibman L. Stimulus overselectivity in autism: a review of research. Psychol Bull. 1979 Nov;86(6):1236–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. L., England G., Kaprowy E., Kilgour K., Pilek V. Operant conditioning of kindergarten-class behavior in autistic children. Behav Res Ther. 1968 Aug;6(3):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(68)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHale S. M., Simeonsson R. J. Effects of interaction on nonhandicapped children's attitudes toward autistic children. Am J Ment Defic. 1980 Jul;85(1):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz E. M., Ritvo E. R. Perceptual inconstancy in early infantile autism. The syndrome of early infant autism and its variants including certain cases of childhood schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1968 Jan;18(1):76–98. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1968.01740010078010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C., Peterson J., Scriven G. Peer imitation by nonhandicapped and handicapped preschoolers. Except Child. 1977 Jan;43(4):223–224. doi: 10.1177/001440297704300404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincover A., Koegel R. L. Classroom treatment of autistic children: II. Individualized instruction in a group. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1977;5(2):113–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00913087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincover A. Variables affecting stimulus fading and discriminative responding in psychotic children. J Abnorm Psychol. 1978 Oct;87(5):541–553. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.87.5.541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosekrans M. A. Imitation in children as a function of perceived similarity to a social model and vicarious reinforcement. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1967 Nov;7(3):307–315. doi: 10.1037/h0025072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo D. C., Koegel R. L. A method for integrating an autistic child into a normal public-school classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Winter;10(4):579–590. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopler E. Early infantile autism and receptor processes. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1965 Oct;13(4):327–335. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01730040037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibman L. Effects of within-stimulus and extra-stimulus prompting on discrimination learning in autistic children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Spring;8(1):91–112. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shores R. E., Apolloni T., Norman C. W. Changes in peer verbalizations accompanying individual and group contingencies to modify on-task behavior. Percept Mot Skills. 1976 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):1155–1162. doi: 10.2466/pms.1976.43.3f.1155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L., Apolloni T., Cooke T. P. Integrated settings at the early childhood level: the role of nonretarded peers. Except Child. 1977 Feb;43(5):262–266. doi: 10.1177/001440297704300502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Kerr M. M., Ragland E. U. Effects of peer-mediated social initiations and prompting/reinforcement procedures on the social behavior of autistic children. J Autism Dev Disord. 1979 Mar;9(1):41–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01531291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varni J. W., Lovaas O. I., Koegel R. L., Everett N. L. An analysis of observational learning in autistic and normal children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1979 Mar;7(1):31–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00924508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


