Abstract
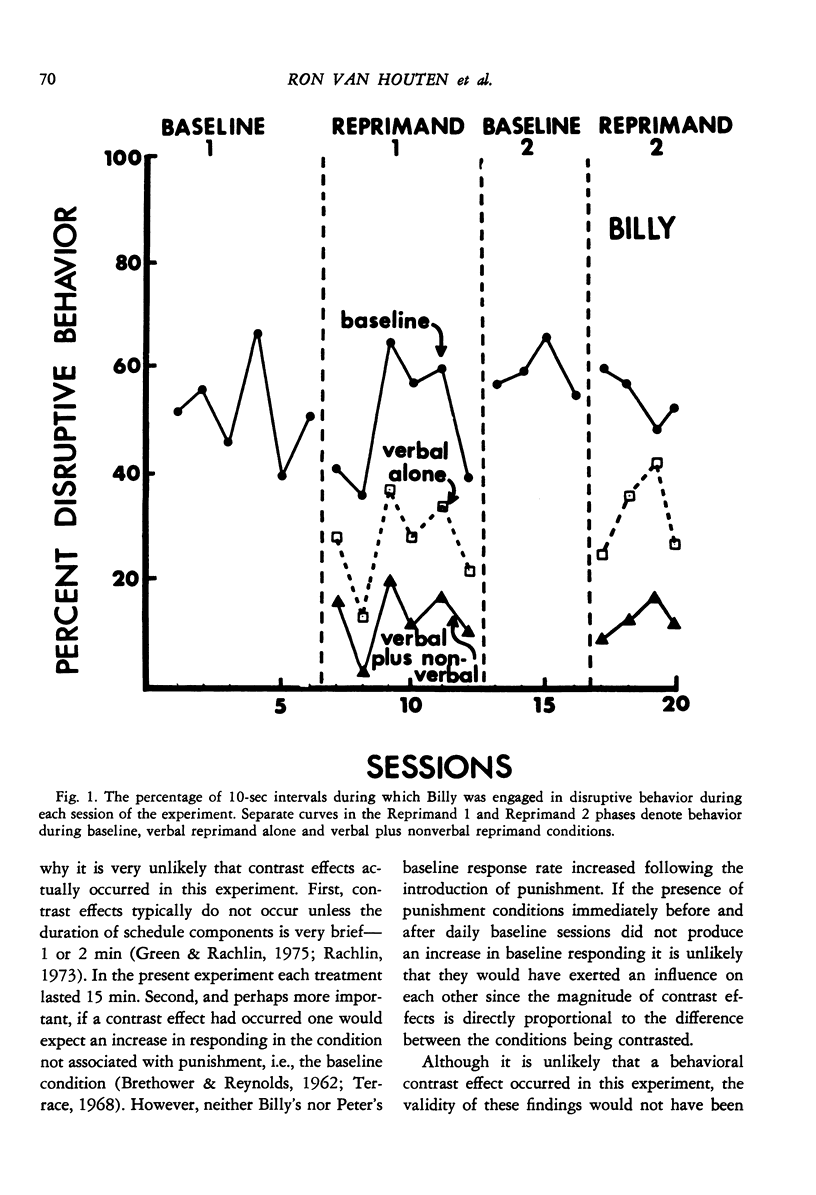
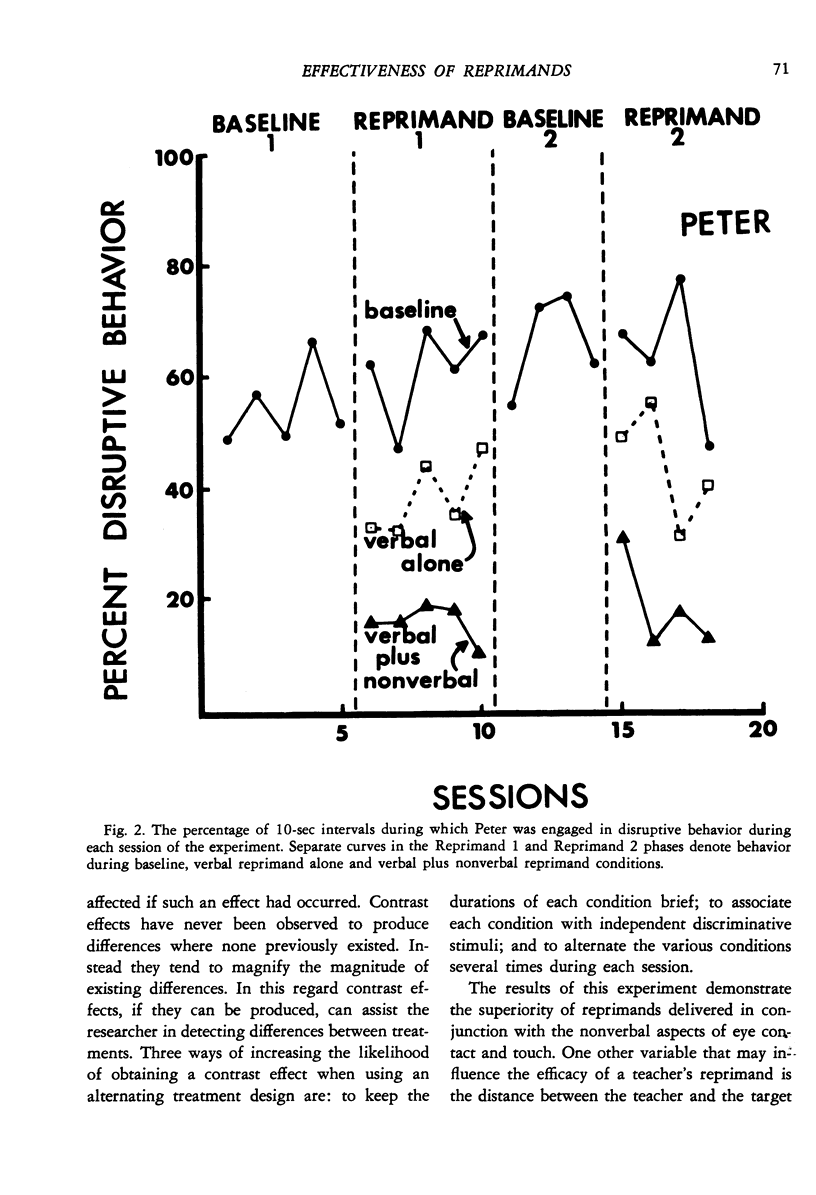
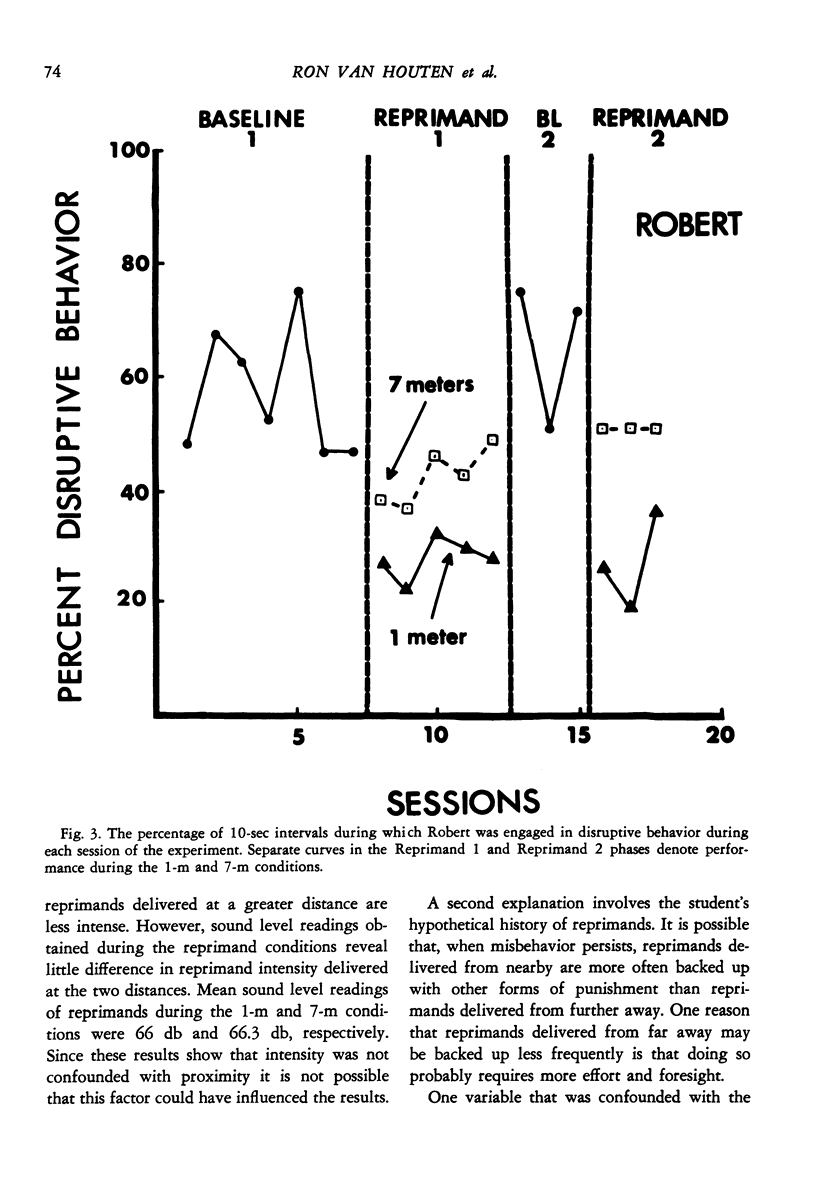
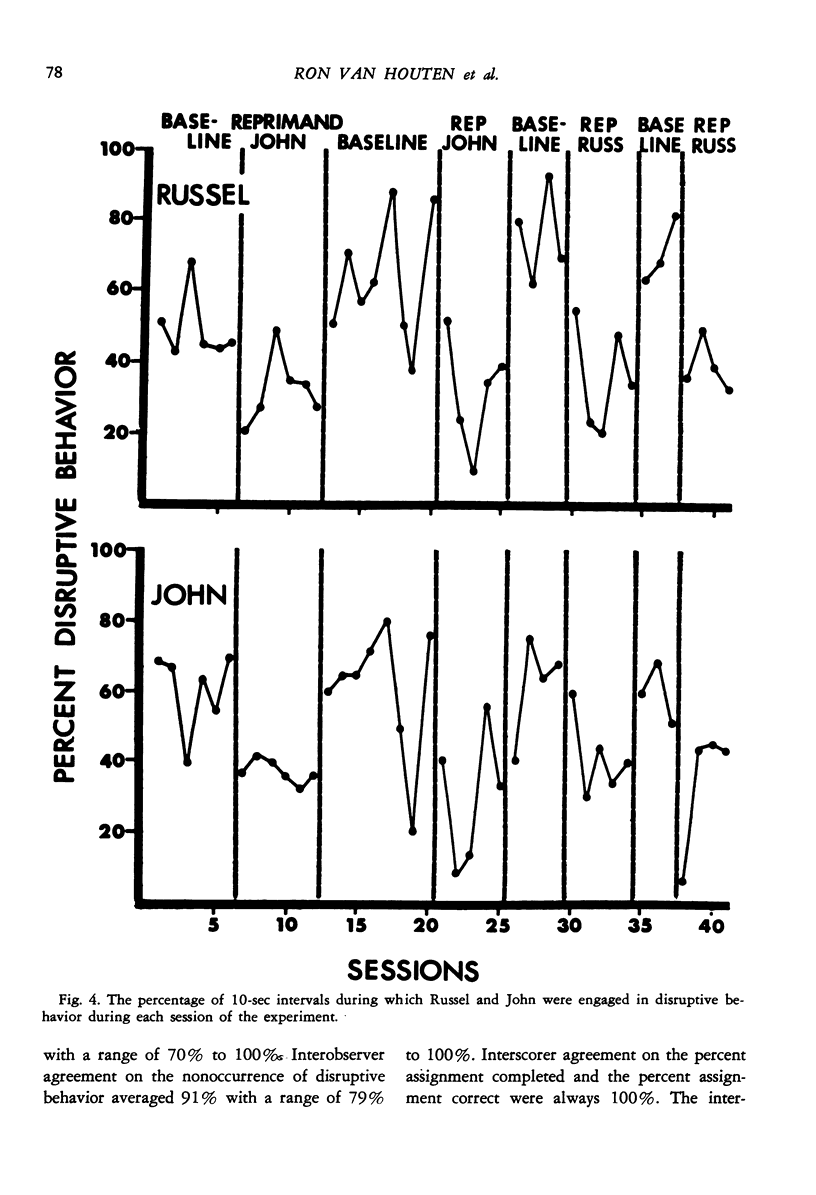
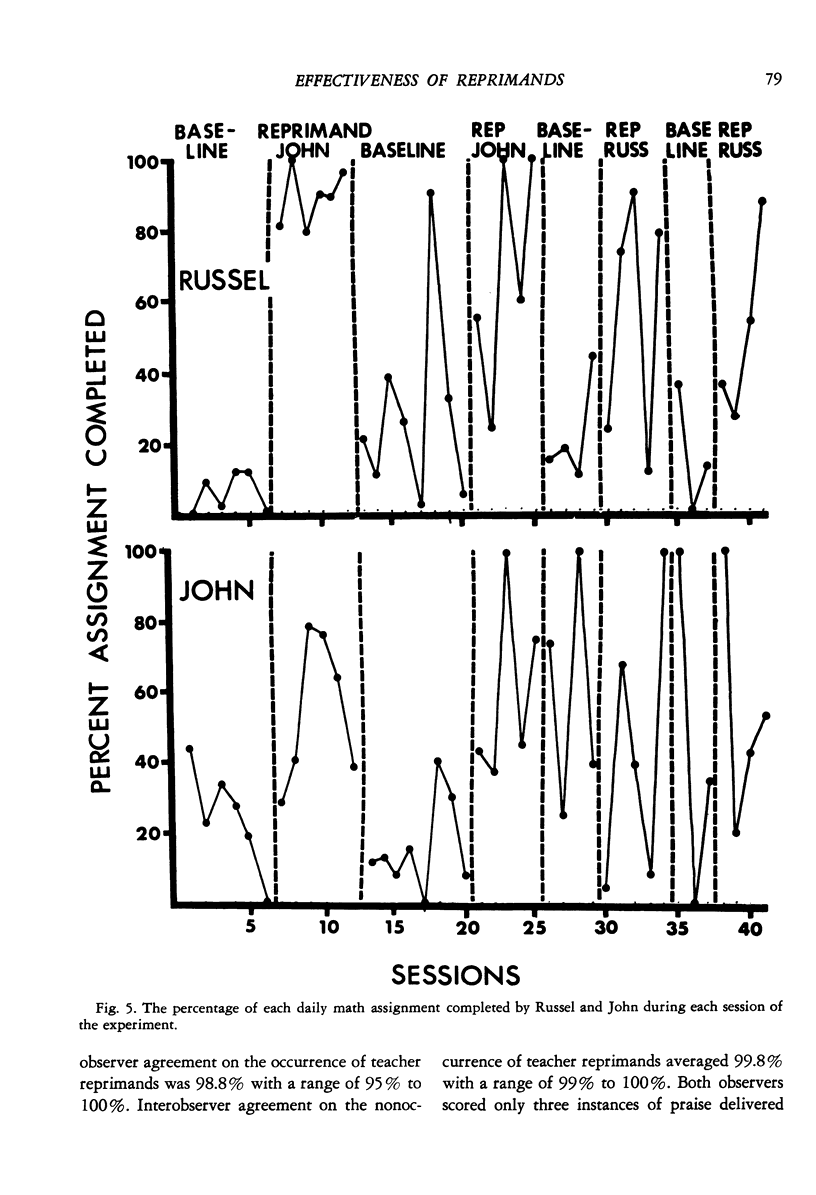
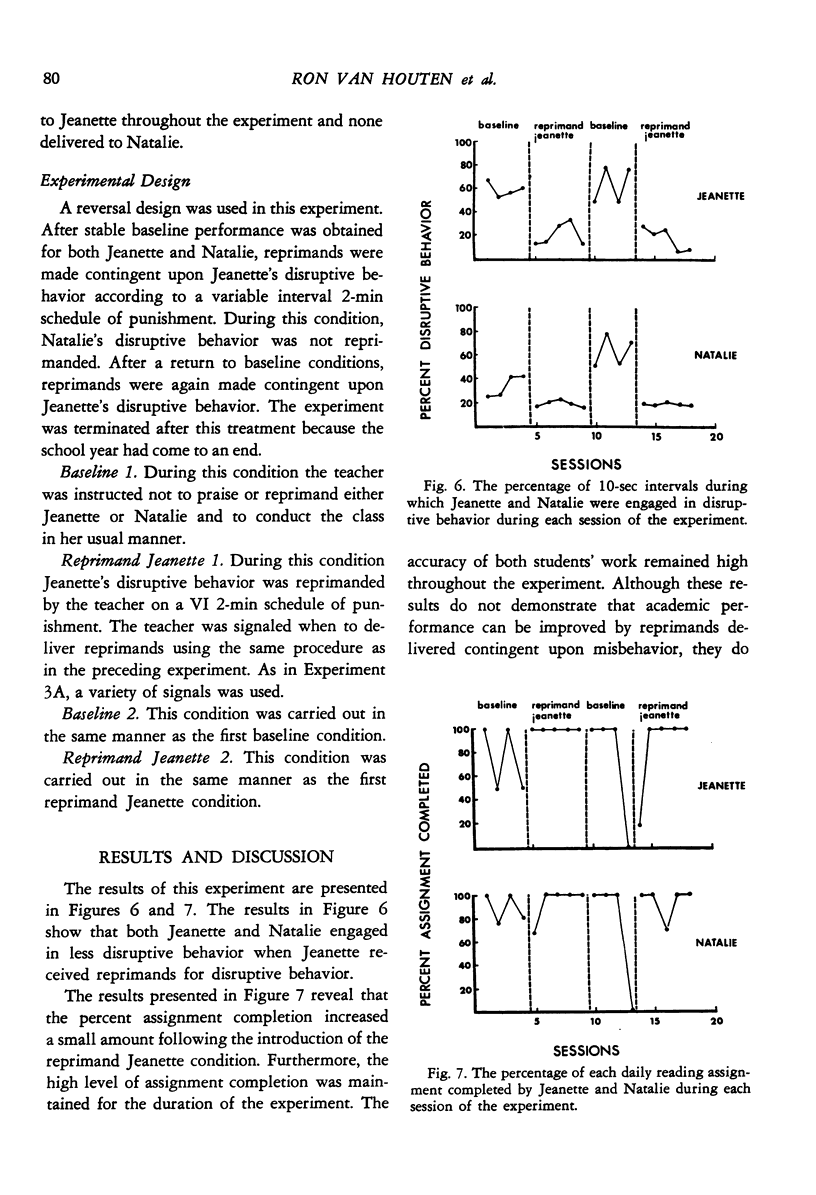
Although several studies have shown that social reprimands can function as punishers, no study reported to data has isolated any of the factors influencing reprimand efficacy. Three experiments were conducted to investigate several factors. Experiment 1 used an alternating treatments design and was conducted on two elementary school boys, one of whom was in a special education class. Results showed that verbal reprimands delivered with eye contact and firm grasp of the student's shoulders reduced disruptive behavior to a greater extent than did verbal reprimands delivered without eye contact and grasp. Both types of reprimand were more effective than a baseline condition during which disruptive behavior was ignored. Experiment 2 also used an alternating treatments design and was conducted on one elementary school boy. Results demonstrated that reprimands delivered from one meter away were considerably more effective than reprimands delivered from seven meters away. Experiment 3 used a reversal design and was conducted on two pairs of elementary school children, one a pair of boys and the other a pair of girls. Results demonstrated that reprimands delivered to just one member of the pair reduced the disruptive behavior of both members of the pair. Thus, the effects of reprimands "spilled" over to nonreprimanded students.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRETHOWER D. M., REYNOLDS G. S. A facilitative effect of punishment on unpunished behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:191–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. H., Hayes S. C. Alternating treatments design: one strategy for comparing the effects of two treatments in a single subject. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):199–210. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broden M., Bruce C., Mitchell M. A., Carter V., Hall R. V. Effects of teacher attention on attending behavior of two boys at adjacent desks. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Fall;3(3):199–203. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doleys D. M., Wells K. C., Hobbs S. A., Roberts M. W., Cartelli L. M. The effects of social punishment on noncompliance: a comparison with timeout and positive practice. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 WINTER;9(4):471–482. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L., Rachlin H. Economic and biological influences on a pigeon's key peck. J Exp Anal Behav. 1975 Jan;23(1):55–62. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1975.23-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E., Klock J. The effect of nonverbal teacher approval on student attentive behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):643–654. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E., Silverman N. A., Sittler J. L. The use of prompts to enhance vicarious effects of nonverbal approval. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Fall;8(3):279–286. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E. The effect of vicarious reinforcement on attentive behavior in the classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):71–78. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary K. D., Kaufman K. F., Kass R. E., Drabman R. S. The effects of loud and soft reprimands on the behavior of disruptive students. Except Child. 1970 Oct;37(2):145–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrace H. S. Discrimination learning, the peak shift, and behavioral contrast. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Nov;11(6):727–741. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. R., Becker W. C., Armstrong M. Production and elimination of disruptive classroom behavior by systematically varying teacher's behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):35–45. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Presland I. E., Grant M. D., Glynn T. L. Natural rates of teacher approval and disapproval in grade-7 classrooms. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Spring;11(1):91–94. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. A. Natural rates of teacher approval and disapproval in the classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):367–372. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willner A. G., Braukmann C. J., Kirigin K. A., Fixsen D. L., Phillips E. L., Wolf M. M. The training and validation of youth-preferred social behaviors of child-care personnel. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):219–230. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


