Abstract
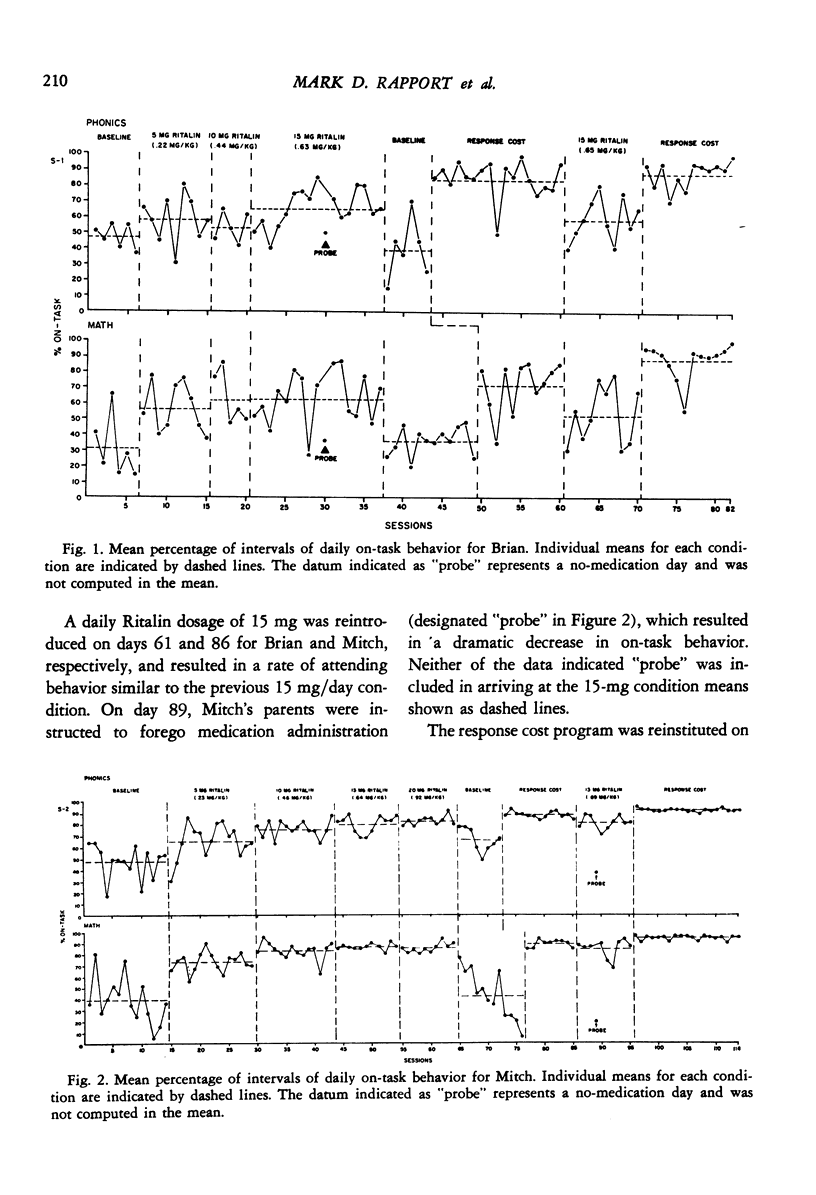
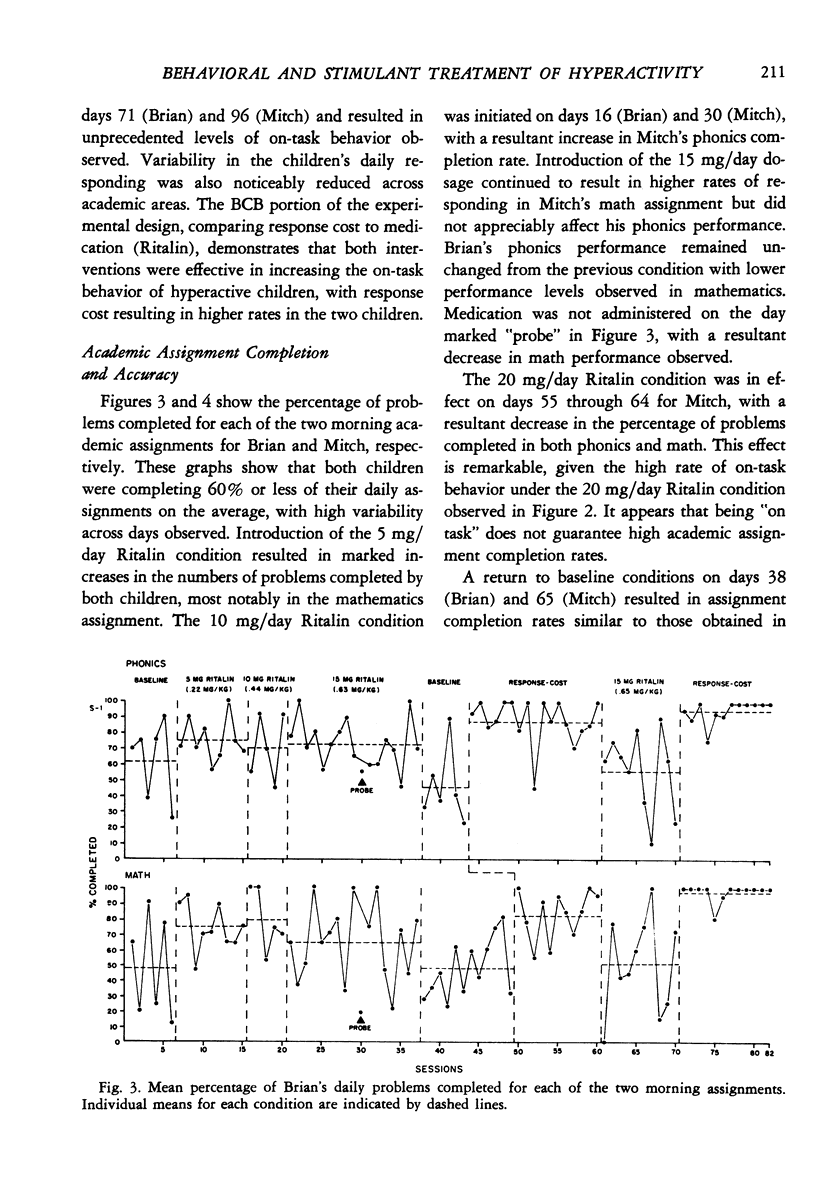
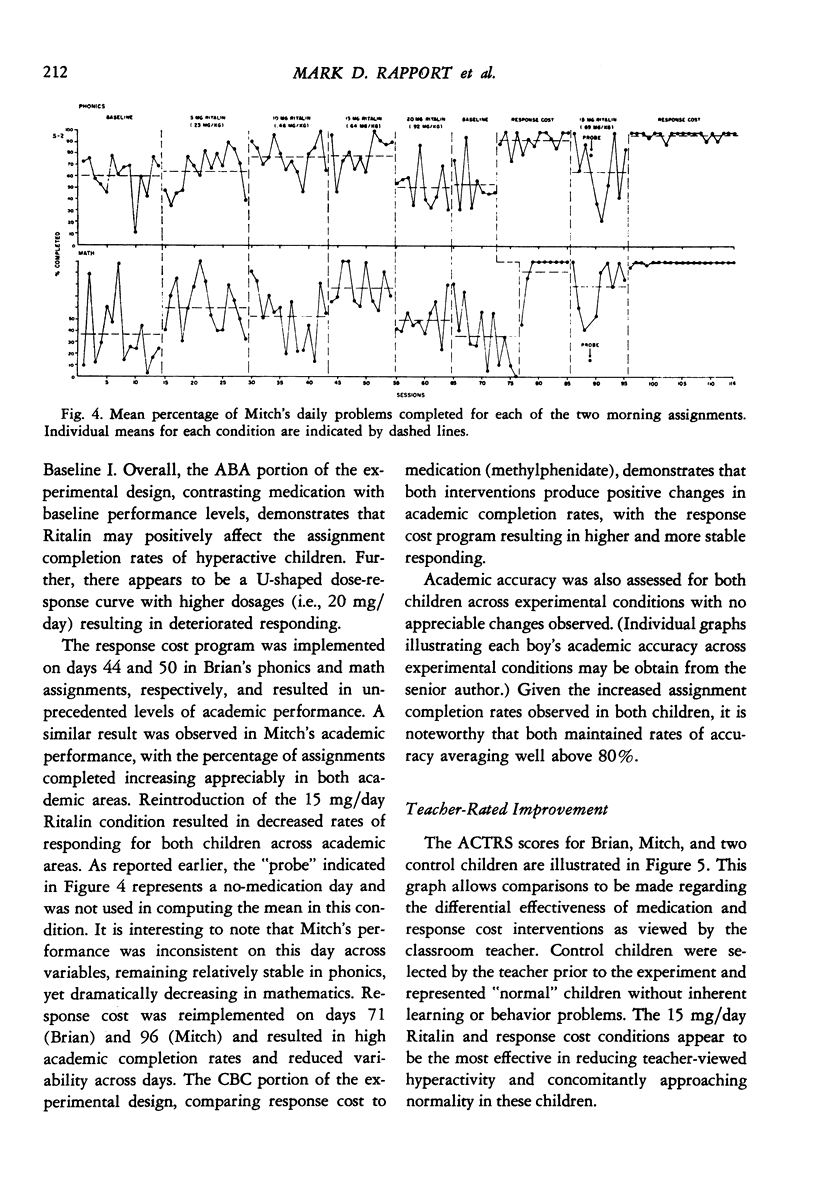
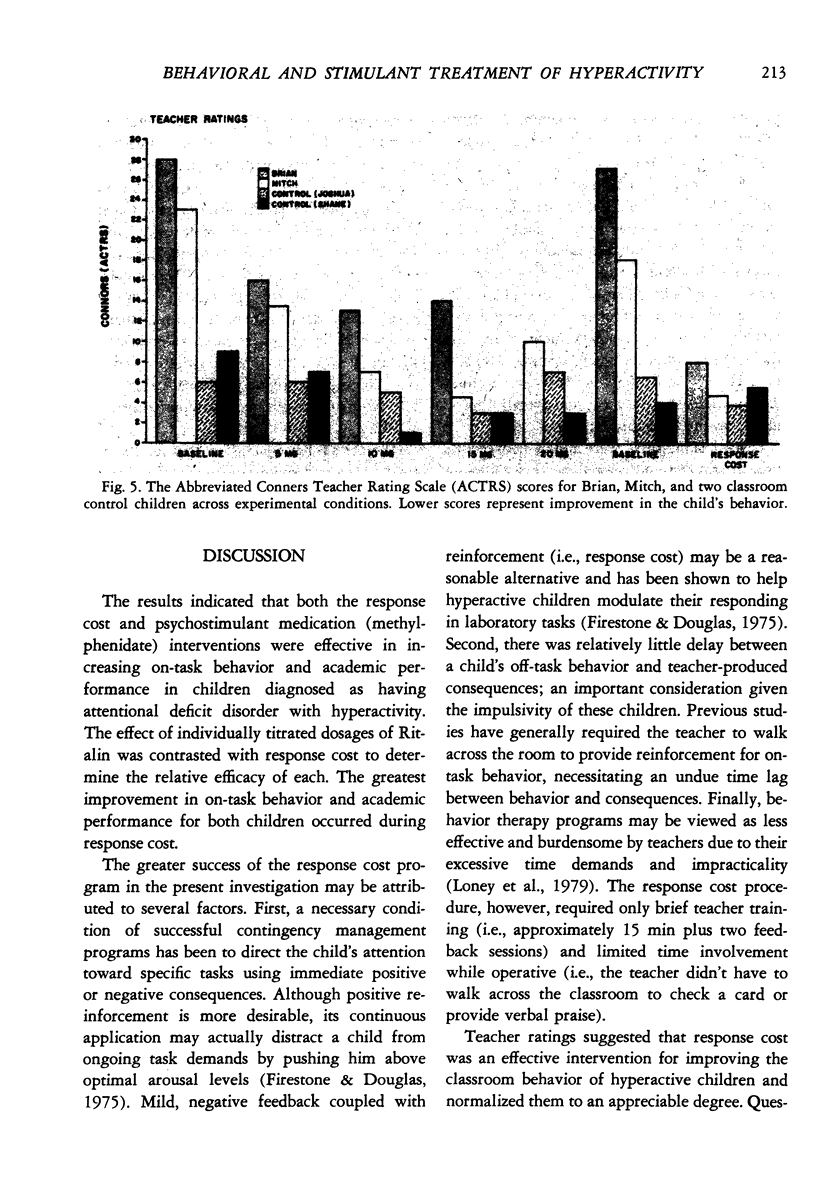
A within-subject comparison was made of the effects of methylphenidate (Ritalin) and response cost in reducing the off-task behavior of two boys, 7 and 8 years of age, who had been diagnosed as having an attentional deficit disorder with hyperactivity, Several dosages of Ritalin (5 to 20 mg/day) were evaluated with the results indicating varying effects of the drug for both children. Response cost (with free-time as the reinforcer) was superior to Ritalin in raising levels of on-task behavior and in improving academic performance.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayllon T., Layman D., Kandel H. J. A behavioral-educational alternative to drug control of hyperactive children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Summer;8(2):137–146. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkley R. A., Cunningham C. E. Do stimulant drugs improve the academic performance of hyperkinetic children? A review of outcome studies. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1978 Jan;17(1):85–92. doi: 10.1177/000992287801700112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijou S. W., Peterson R. F., Ault M. H. A method to integrate descriptive and experimental field studies at the level of data and empirical concepts. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):175–191. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen D. E. Effects of combining methylphenidate and a classroom token system in modifying hyperactive behavior. Am J Ment Defic. 1975 Nov;80(3):266–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestone P., Douglas V. The effects of reward and punishment on reaction times and autonomic activity in hyperactive and normal children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1975;3(3):201–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00916751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittelman-Klein R., Klein D. F., Abikoff H., Katz S., Gloisten A. C., Kates W. Relative efficacy of methylphenidate and behavior modification in hyperkinetic children: an interim report. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(4):361–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00922533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittelman-Klein R., Klein D. F., Katz S., Saraf K., Pollack E. Comparative effects of methylphenidate and thioridazine in hyperkinetic children. I. Clinical results. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1976 Oct;33(10):1217–1231. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1976.01770100079008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henker B., Whalen C. K., Collins B. E. Double-blind and triple-blind assessments of medication and placebo responses in hyperactive children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1979 Mar;7(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00924506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundert J. The effectiveness of reinforcement, response cost, and mixed programs on classroom behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Spring;9(1):107–107. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata B. A., Bailey J. S. Reward versus cost token systems: an analysis of the effects on students and teacher. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):567–576. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman K. F., O'leary K. D. Reward, cost, and self-evaluation procedures for disruptive adolescents in a psychiatric hospital school. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Fall;5(3):293–309. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert N. M., Sandoval J. H., Sassone D. M. Prevalence estimates of hyperactivity in schoolchildren. Pediatr Ann. 1978 May;7(5):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loney J., Weissenburger F. E., Woolson R. F., Lichty E. C. Comparing psychological and pharmacological treatments for hyperkinetic boys and their classmates. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1979 Jun;7(2):133–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00918894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary K. D., Pelham W. E., Rosenbaum A., Price G. H. Behavioral treatment of hyperkinetic children. An experimental evaluation of its usefulness. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1976 Jun;15(6):510–515. doi: 10.1177/000992287601500603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary K. D. Pills or skills for hyperactive children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Spring;13(1):191–204. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary S. G., Pelham W. E. Behavior therapy and withdrawal of stimulant medication in hyperactive children. Pediatrics. 1978 Feb;61(2):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham W. E., Schnedler R. W., Bologna N. C., Contreras J. A. Behavioral and stimulant treatment of hyperactive children: a therapy study with methylphenidate probes in a within-subject design. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Summer;13(2):221–236. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle K. D., Rapoport J. L. A 2-year follow-up of 72 hyperactive boys. Classroom behavior and peer acceptance. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1976 Feb;162(2):126–134. doi: 10.1097/00005053-197602000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafto F., Sulzbacher S. Comparing treatment tactics with a hyperactive preschool child: stimulant medication and programmed teacher intervention. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Spring;10(1):13–20. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleator E. K., Von Neumann A. W. Methylphenidate in the treatment of hyperkinetic children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1974 Jan;13(1):19–24. doi: 10.1177/000992287401300103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague R. L., Sleator E. K. Methylphenidate in hyperkinetic children: differences in dose effects on learning and social behavior. Science. 1977 Dec 23;198(4323):1274–1276. doi: 10.1126/science.337493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss G., Kruger E., Danielson U., Elman M. Effect of long-term treatment of hyperactive children with methylphenidate. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jan 25;112(2):159–165. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werry J. S., Sprague R. L., Cohen M. N. Conners' Teacher Rating Scale for use in drug studies with children--an empirical study. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1975;3(3):217–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00916752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H. The hyperactive child syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 1977 Apr;15(4):100–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worland J. Effects of positive and negative feedback on behavior control in hyperactive and normal boys. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1976;4(4):315–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00922530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulbert M., Dries R. The relative efficacy of methylphenidate (ritalin) and behavior-modification techniques in the treatment of a hyperactive child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Spring;10(1):21–31. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


