Abstract
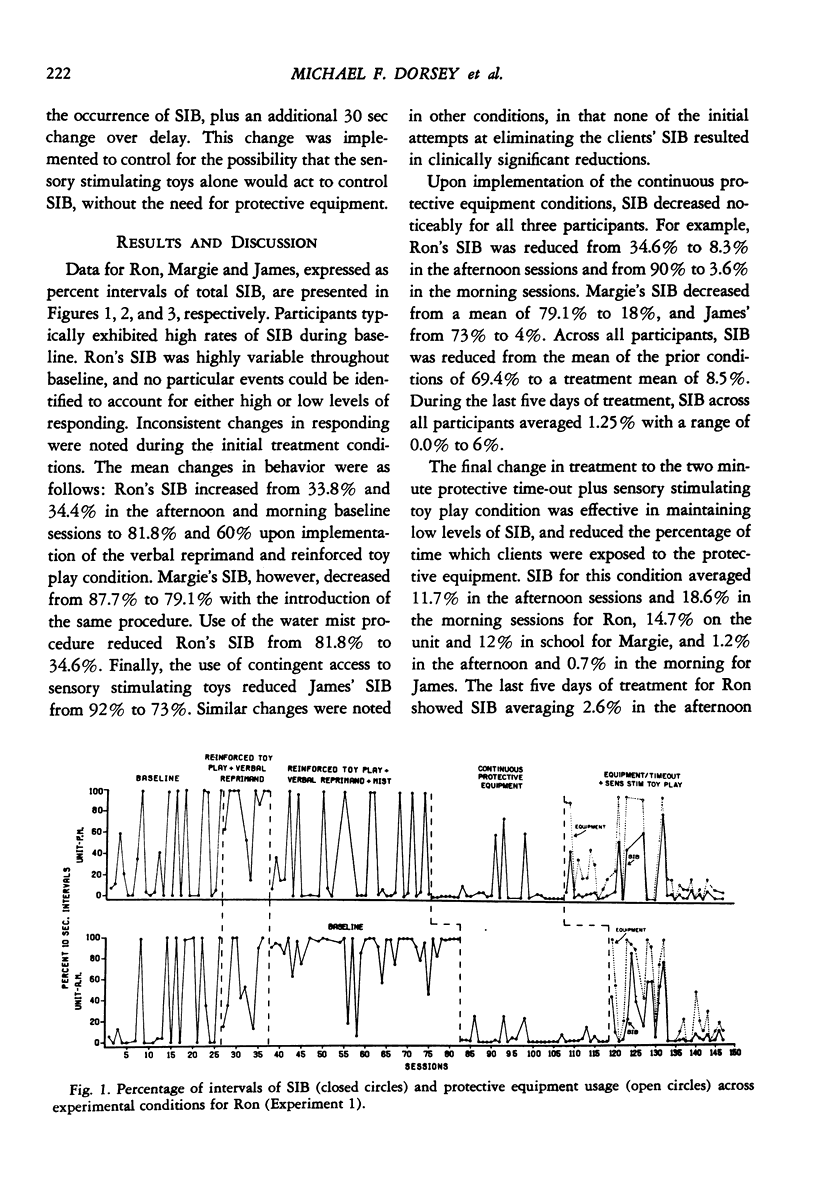
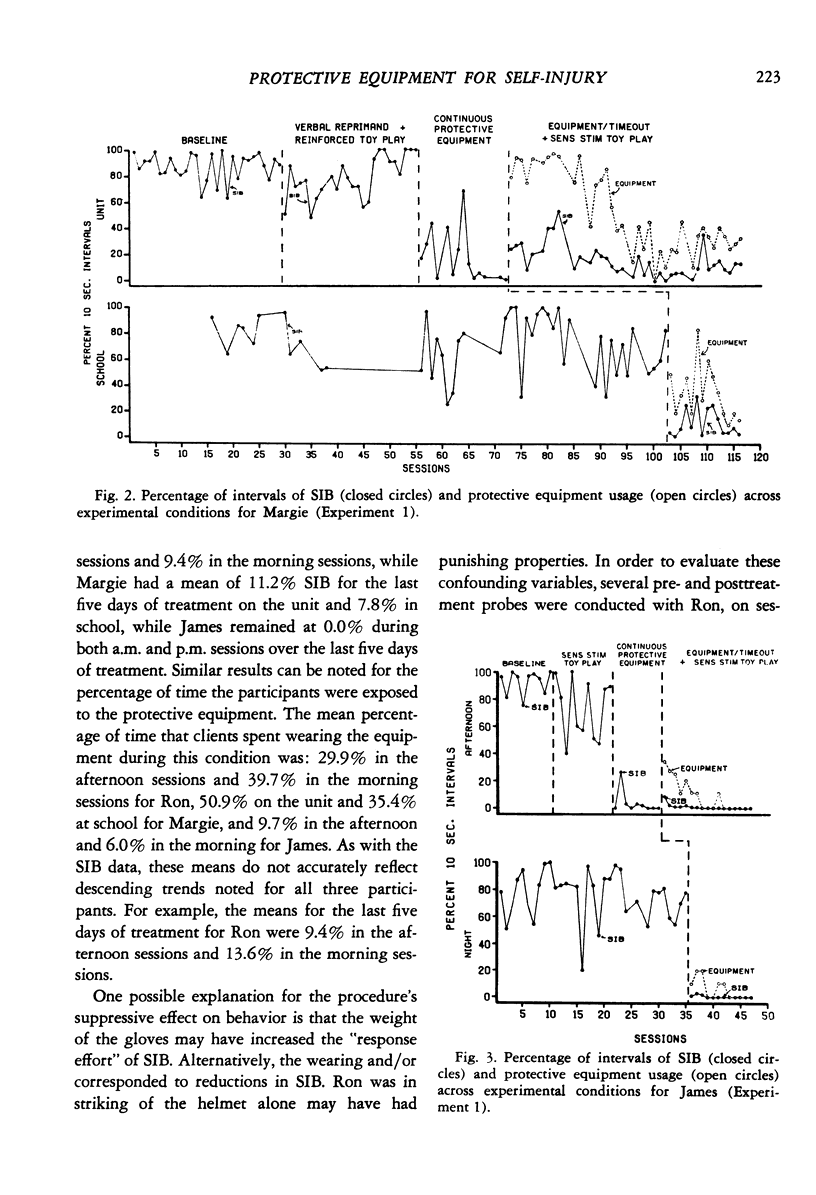
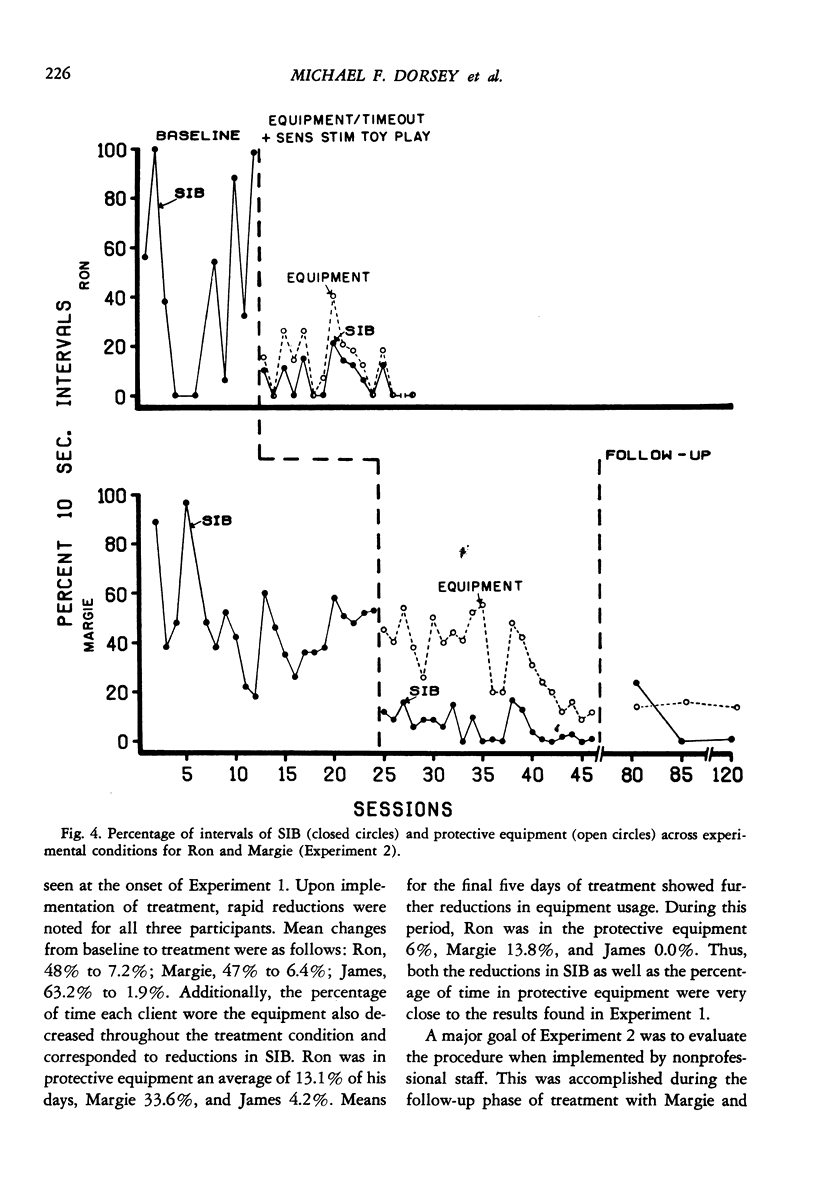
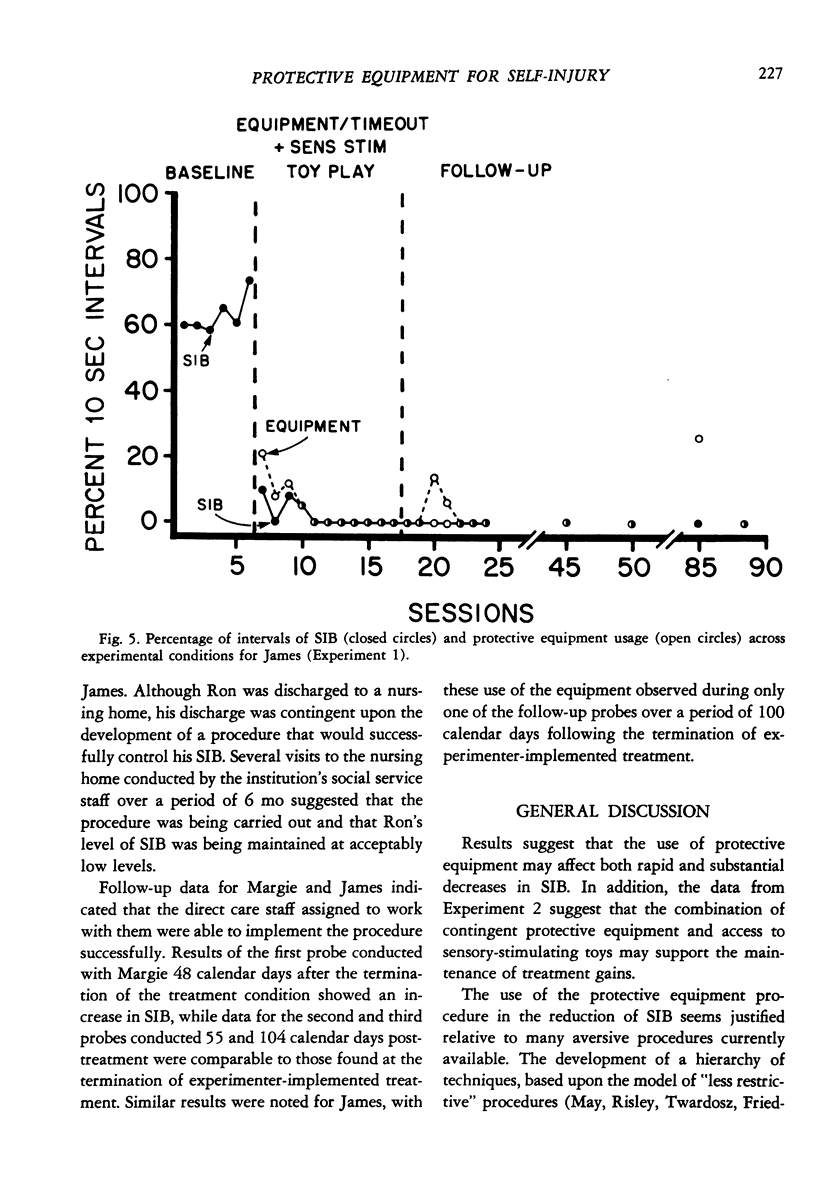
This study evaluated the use of protective equipment in treating self-injurious behavior (SIB) exhibited by three retarded persons. In Experiment 1, the equipment was first applied continuously during 20-min sessions in individual multiple baseline designs across settings. Results showed substantial reductions in head hitting, eye gouging, and hand biting. Brief periods of time-out with the protective equipment were later made contingent on SIB and combined with a differential reinforcement procedure. Reduced levels of SIB was maintained with all subjects. Additionally, the amount of time during which the equipment was applied decreased as the SIB diminished. Experiment 2 evaluated the use of contingent protective equipment (the final condition in Experiment 1) when applied directly in the subjects' living units during the day. During Experiment 2, SIB remained at or below the levels found at the termination of Experiment 1. Finally, in an effort to assess the long-term effectiveness of the procedure, responsibility for implementation was given to the staff who were typically assigned to provide therapy to the subjects. Follow-up probe observations conducted up to 104 days after termination of the final experimental condition showed continued low levels of both SIB and equipment usage. Results of these experiments suggest that contingent protective equipment and differential reinforcement may be effective in reducing chronic self-injury.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr E. G. The motivation of self-injurious behavior: a review of some hypotheses. Psychol Bull. 1977 Jul;84(4):800–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsey M. F., Iwata B. A., Ong P., McSween T. E. Treatment of self-injurious behavior using a water mist: initial response suppression and generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1980 Summer;13(2):343–353. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1980.13-343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favell J. E., McGimsey J. F., Jones M. L., Cannon P. R. Physical restraint as positive reinforcement. Am J Ment Defic. 1981 Jan;85(4):425–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favell J. E., McGimsey J. F., Jones M. L. The use of physical restraint in the treatment of self-injury and as positive reinforcement. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):225–241. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. H. An extinction procedure for eliminating self-destructive behavior in a 9-year-old autistic girl. J Autism Child Schizophr. 1974 Sep;4(3):241–250. doi: 10.1007/BF02115230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovaas O. I., Simmons J. Q. Manipulation of self-destruction in three retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):143–157. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J., Martindale A., Kulp S. An evaluation of time-sample measures of behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Winter;8(4):463–469. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincover A., Cook R., Peoples A., Packard D. Sensory extinction and sensory reinforcement principles for programming multiple adaptive behavior change. J Appl Behav Anal. 1979 Summer;12(2):221–233. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1979.12-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rincover A. Sensory extinction: a procedure form eliminating self-stimulatory behavior in developmentally disabled children. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 1978 Sep;6(3):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00924733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojahn J., Schroeder S. R., Mulick J. A. Ecological assessment of self-protective devices in three profoundly retarded adults. J Autism Dev Disord. 1980 Mar;10(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02408433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


