Abstract
Except for a few studies, most research investigating correspondence training procedures has been more analogue in nature. The purpose of the present set of studies was to examine whether a "say-do" correspondence training technique could be used with children in special education classes to improve classroom behavior. The specific behaviors targeted for change included: out-of-seat behavior (Experiment 1), sitting posture (Experiment 2), and on-task behavior (Experiment 3). The say-do procedure used in Experiment 1 resembled that of previous studies, whereas that in Experiment 2 was more elaborate in the specificity of verbal statements required from the children and the feedback given them. The training procedure in Experiment 3 used a format similar to the say-do approach, but stressed visual rather than verbal cuing because it was used with nonverbal children. All three studies used single-subject designs and examined maintenance and/or generalization questions. Experiments 2 and 3 also evaluated whether concomitant changes in performance on academic tasks occurred. The results of the three studies provide strong evidence that correspondence training can be effectively used with educationally handicapped children. Moreover, the successful modification of the "say-do" to a "show-do" procedure in Experiment 3 points out the flexibility of the correspondence training approach.
Full text
PDF


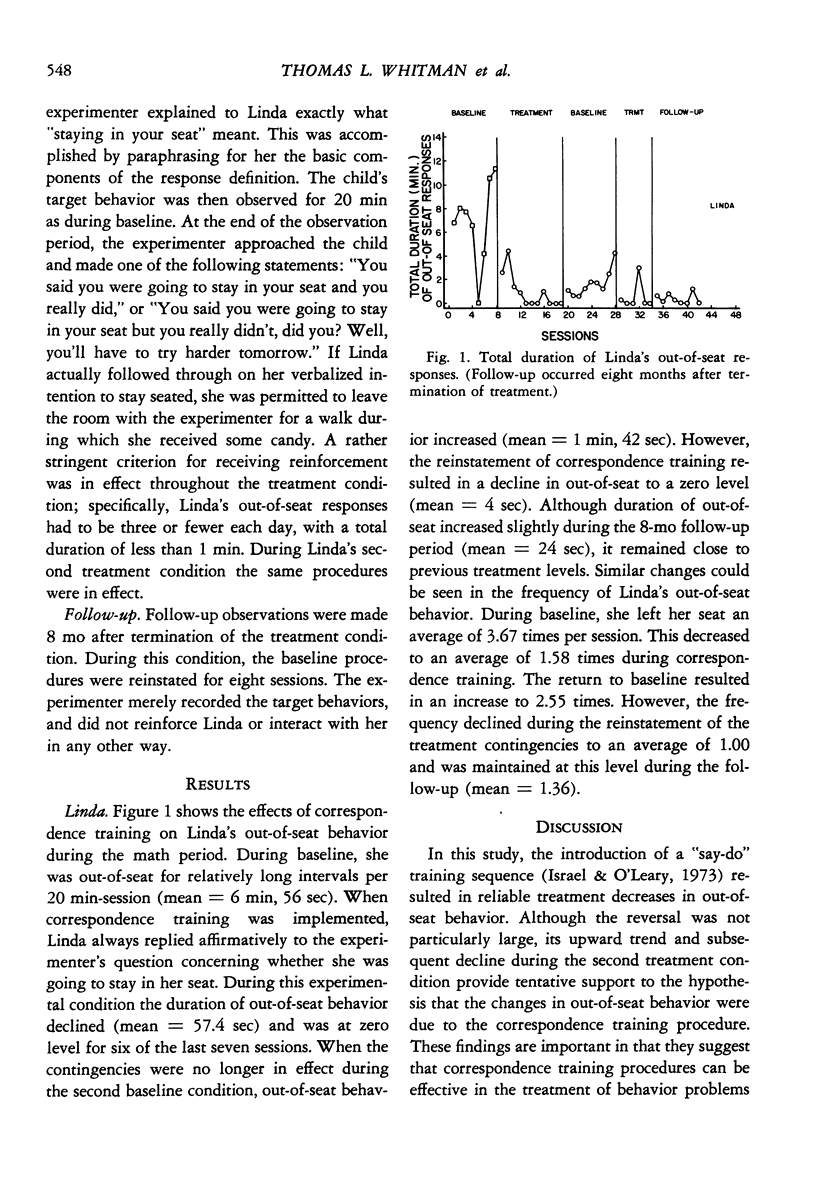




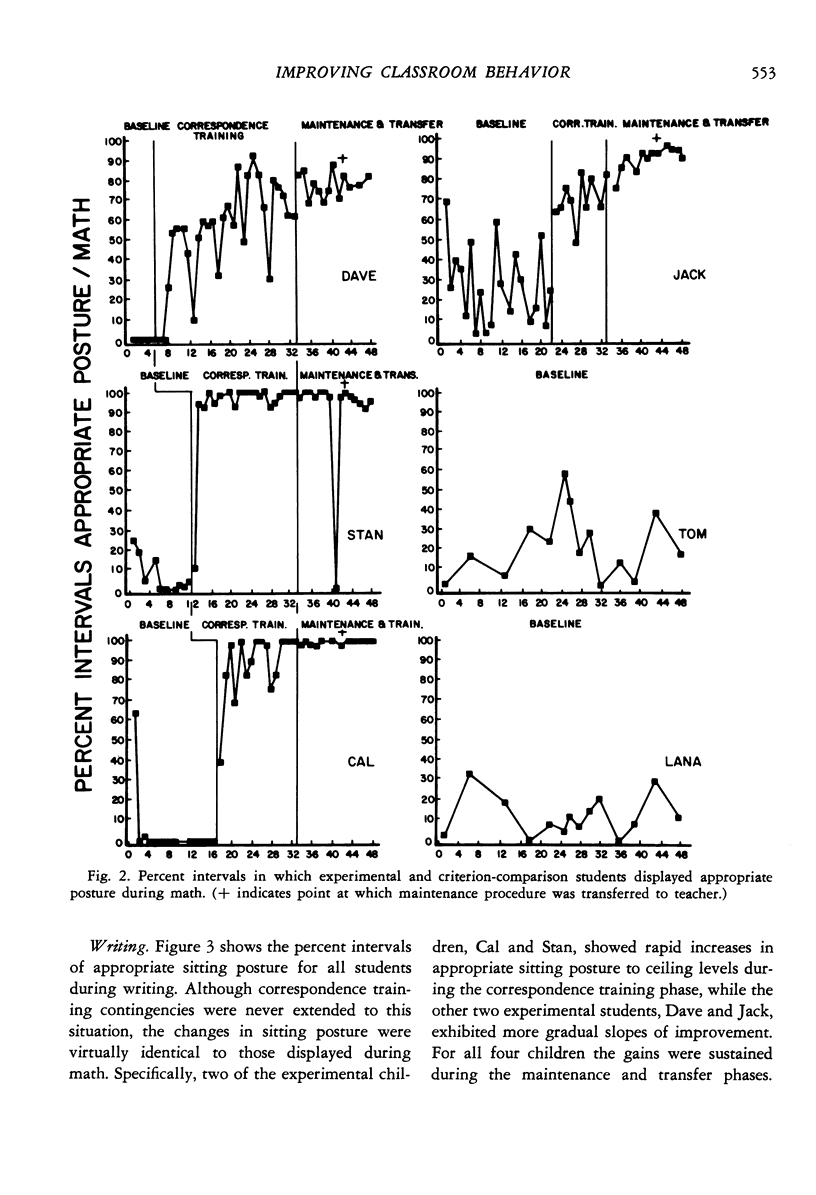
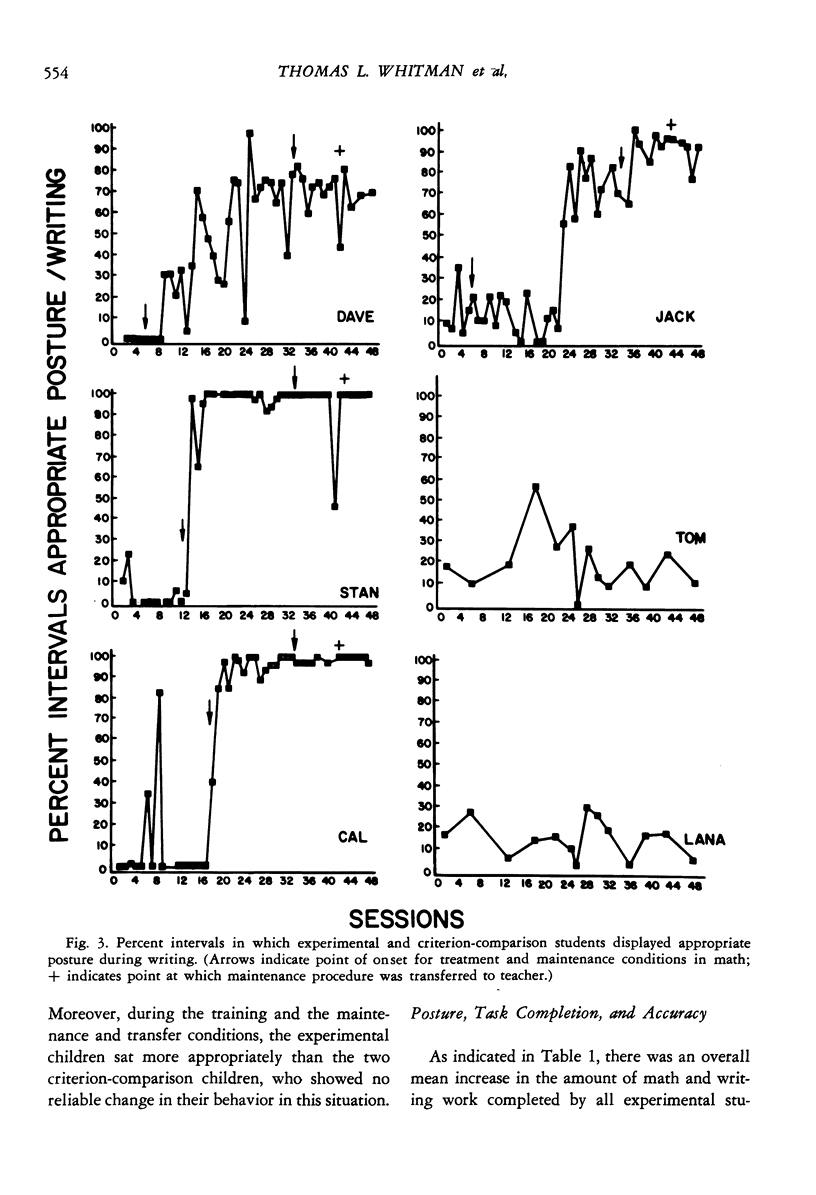
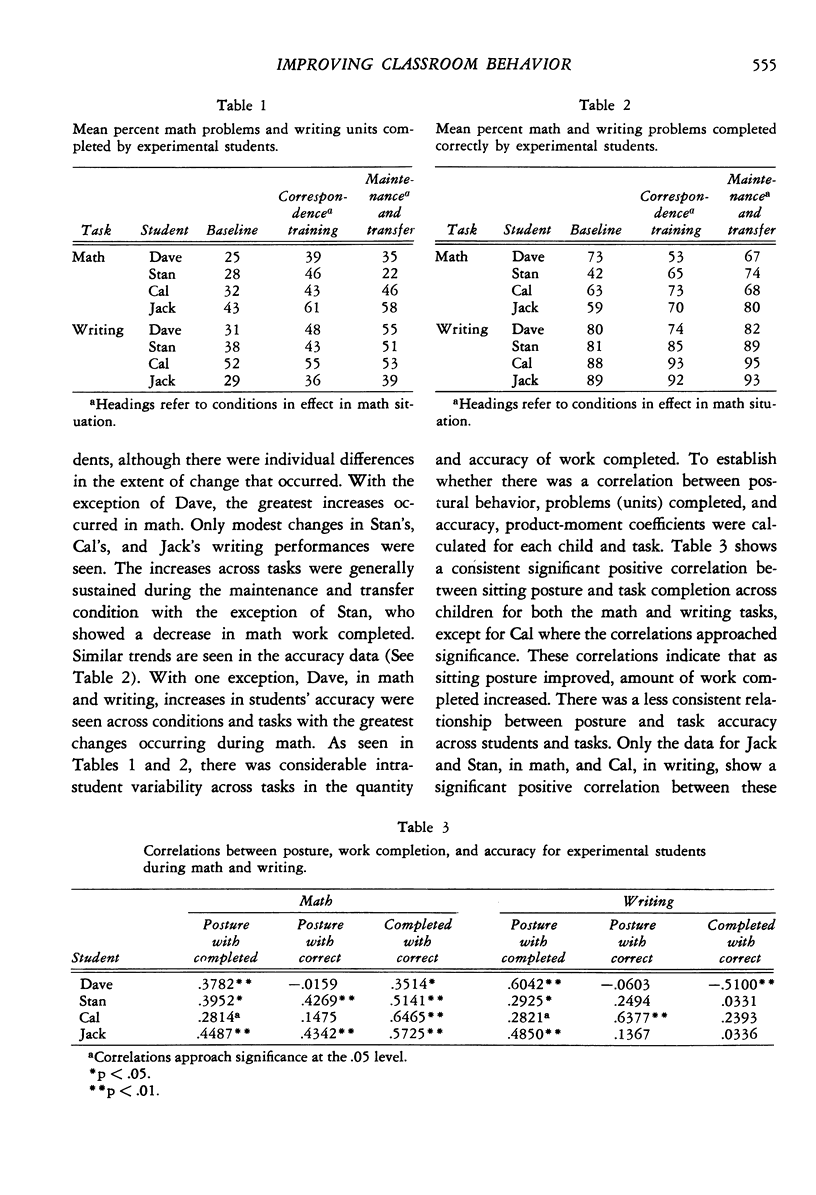








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azrin N., Rubin H., O'brien F., Ayllon T., Roll D. Behavioral engineering: postural control by a portable operant apparatus. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):99–108. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky G. The relation between verbal and non-verbal behavior change. Behav Res Ther. 1967 Aug;5(3):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(67)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy P. R. Does use of tangible rewards with individual children affect peer observers? J Appl Behav Anal. 1975 Summer;8(2):187–196. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1975.8-187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler S. A., Baer D. M. "Do I have to be good all day? The timing of delayed reinforcement as a factor in generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1981 Spring;14(1):13–24. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1981.14-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel A. C. Some thoughts on correspondence between saying and doing. J Appl Behav Anal. 1978 Summer;11(2):271–276. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1978.11-271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata B. A., Bailey J. S. Reward versus cost token systems: an analysis of the effects on students and teacher. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):567–576. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E., Klock J. The effect of nonverbal teacher approval on student attentive behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):643–654. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVAAS O. I. Interaction between verbal and nonverbal behavior. Child Dev. 1961 Jun;32:329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8624.1961.tb05031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMillan D. L. Facilitative effect of verbal mediation on paired-associate learning by EMR children. Am J Ment Defic. 1970 Mar;74(5):611–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen C. H., Becker W. C., Thomas D. R. Rules, praise, and ignoring: elements of elementary classroom control. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):139–150. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgram N. A. Retention of mediation set in paired-associate learning of normal children and retardates. J Exp Child Psychol. 1967 Sep;5(3):341–349. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(67)90062-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'leary K. D., Becker W. C., Evans M. B., Saudargas R. A. A token reinforcement program in a public school: a replication and systematic analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Spring;2(1):3–13. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redd W. H. Effects of mixed reinforcement contingencies on adults' control of children's behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Winter;2(4):249–254. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T. R., Hart B. Developing correspondence between the non-verbal and verbal behavior of preschool children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):267–281. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers-Warren A., Baer D. M. Correspondence between saying and doing: teaching children to share and praise. J Appl Behav Anal. 1976 Fall;9(3):335–354. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1976.9-335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes T. F., Baer D. M. An implicit technology of generalization. J Appl Behav Anal. 1977 Summer;10(2):349–367. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1977.10-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt P. R., Ulrich R. E., Hawkins R. P. An elementary student as a behavioral engineer. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):85–92. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


