Abstract
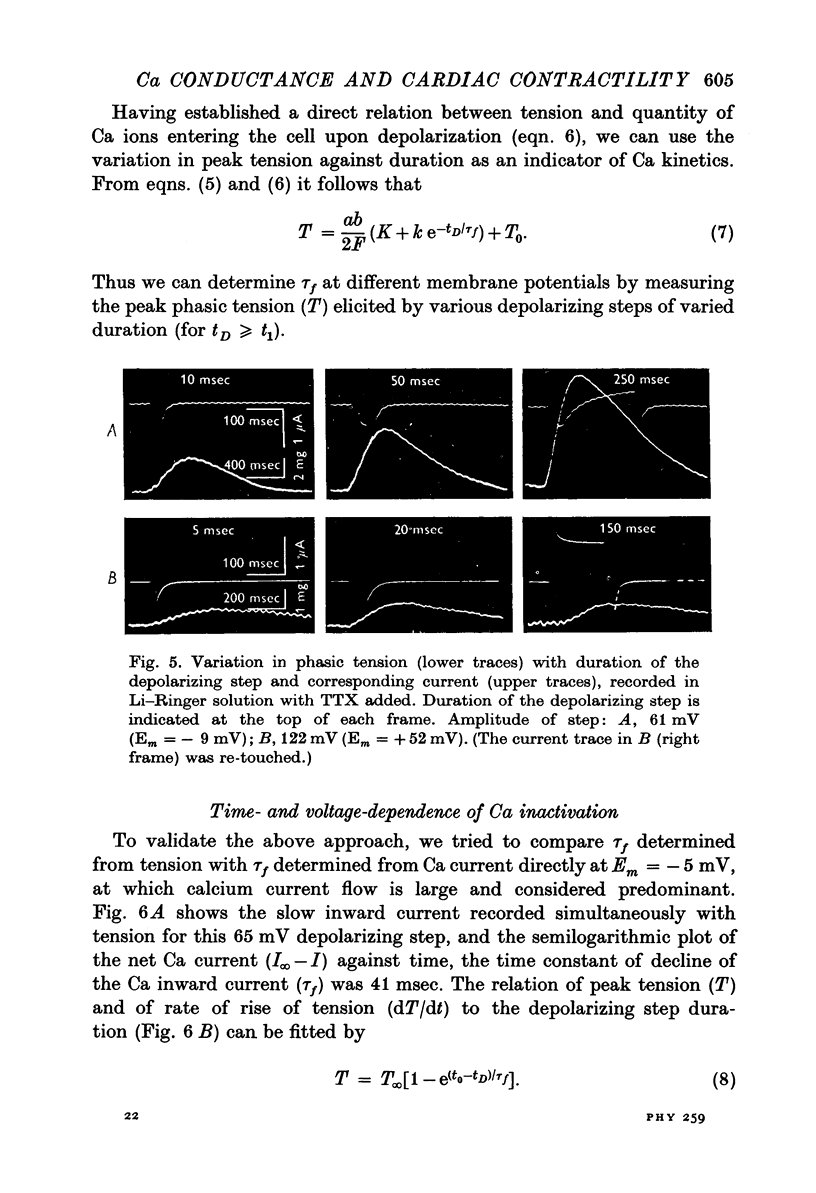
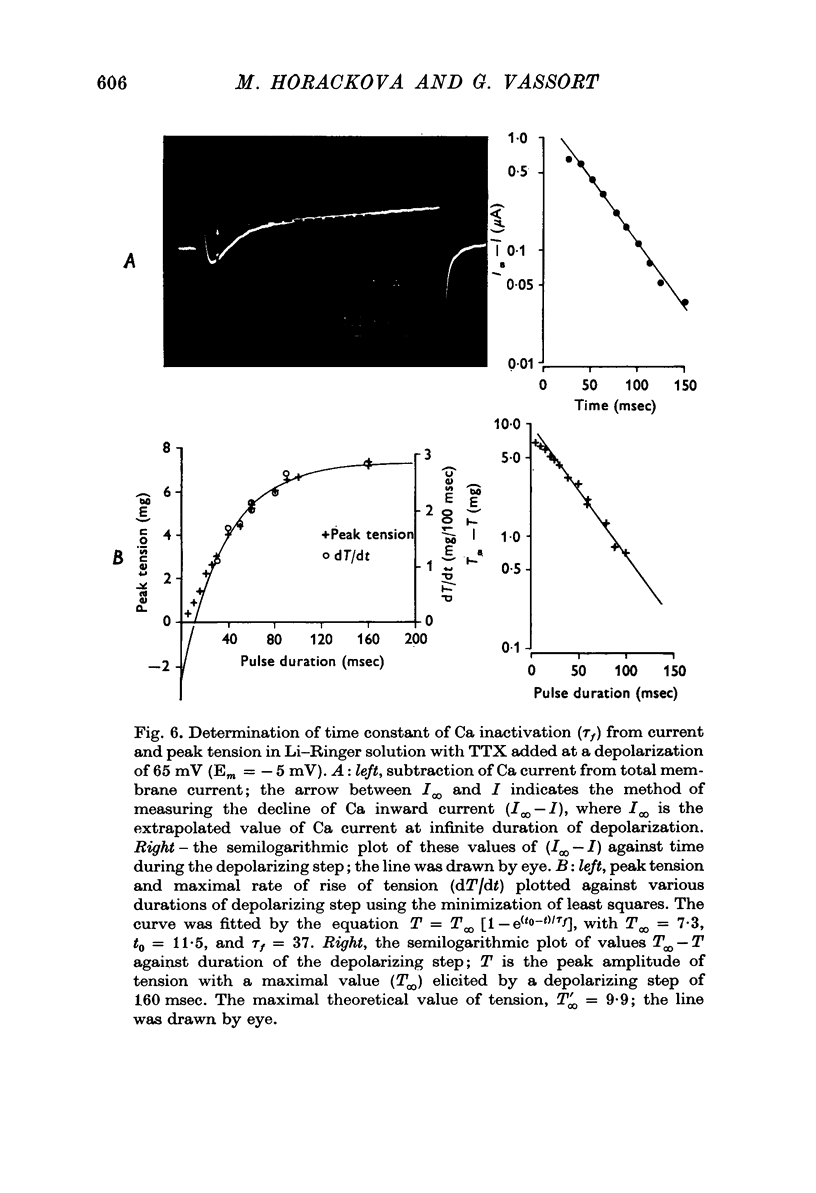
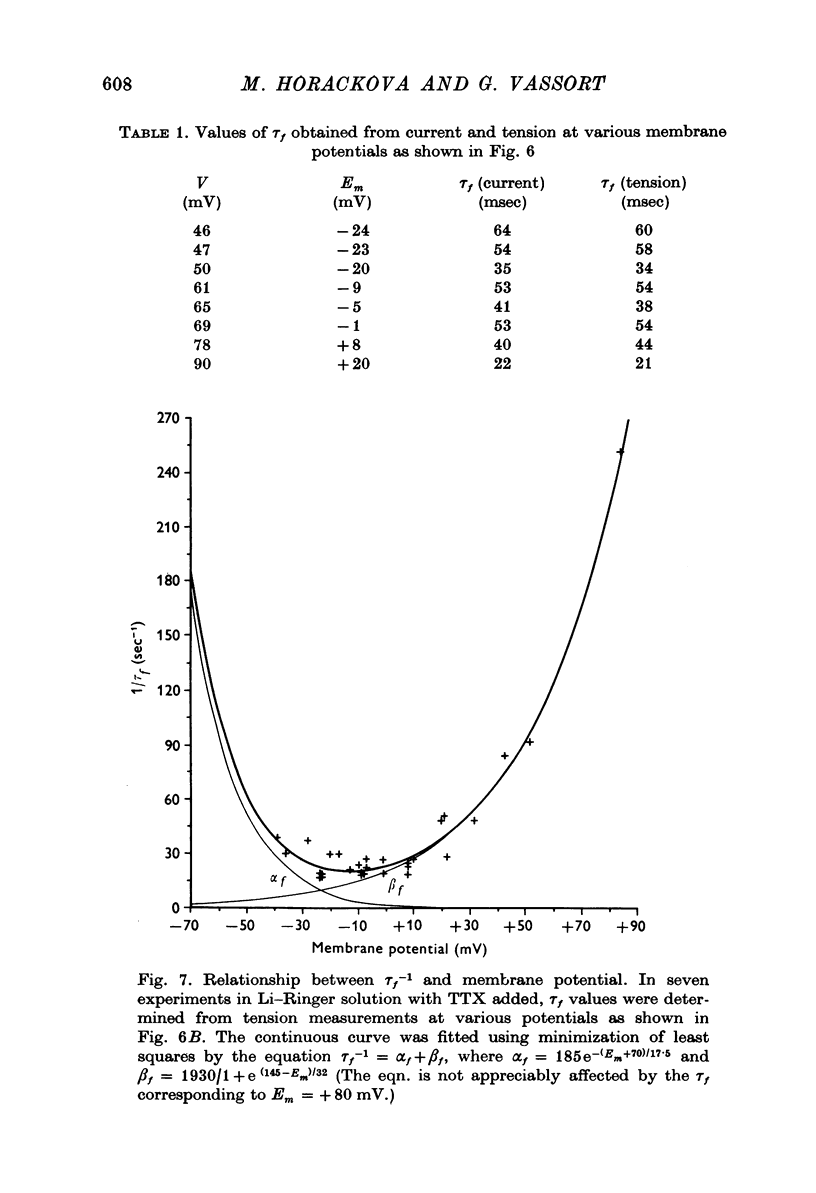
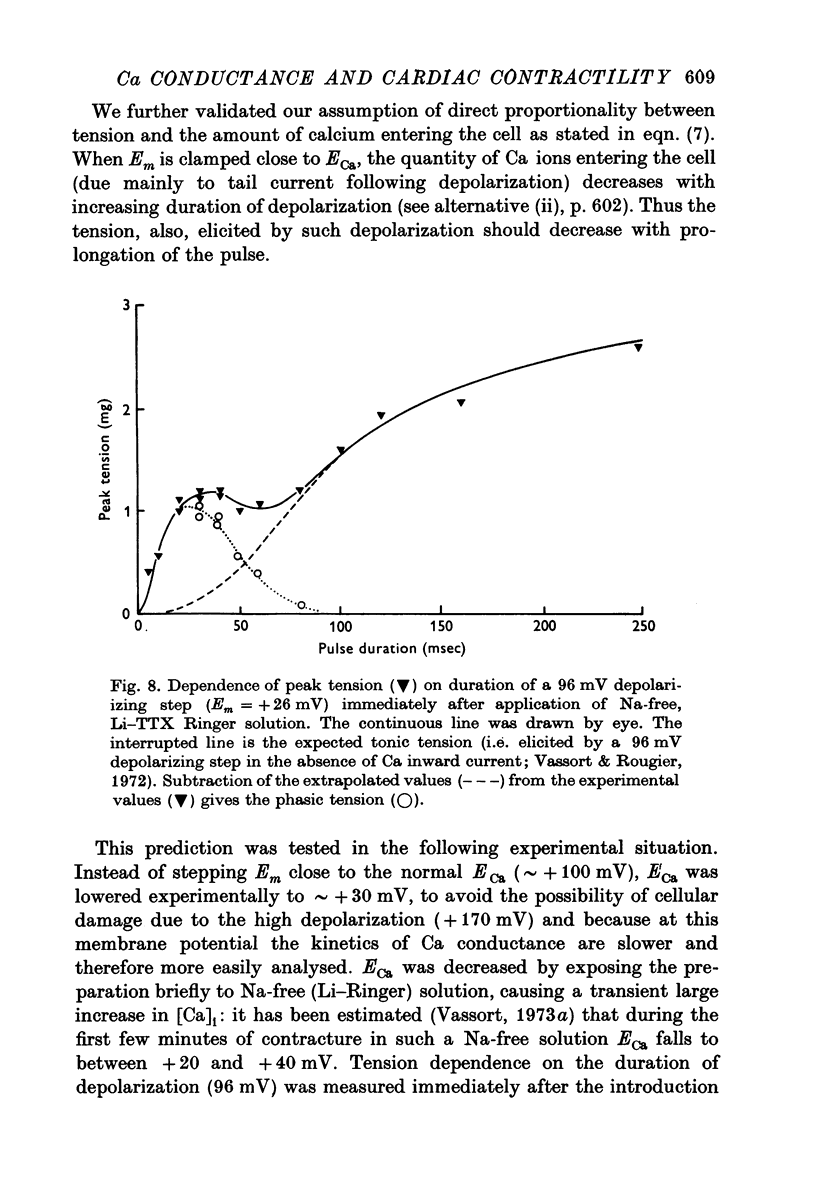
1. Ca inward current and the corresponding phasic component of tension were measured in frog atrial muscle under voltage-clamp conditions in Na-free (Li) Ringer solution with tetrodotoxin (TTX) added. 2. The quantity of Ca ions entering the cell upon depolarization, delta[Ca]i, was linearly related to peak phasic tension. 3. The voltage dependence of the steady-state inactivation of the Ca-carrying system, f infinity, against voltage yielded similar relationships whether determined directly from variations of Ca inward current or peak phasic tension. The Ca system was almost fully available at potentials more negative than -45 mV and almost fully inactivated at potentials more positive than +10 mV. 4. It was established that the time- and voltage-dependence of Ca current and of phasic tension are directly related. The time constants of Ca activation, tau f, were comparable in the range of membrane potential investigated (-20 to +25 mV), whether determined directly from the decay of Ca current or indirectly from peak phasic tension. 5. It was concluded that the Ca current, ICa, directly activates phasic contraction and that either parameter can be used as an indicator of the kinetics of the Ca-carrying system. Peak phasic tension was used to determine tau f further in the membrane potential range in which interference by other membrane currents renders direct analysis of Ca current difficult. 6. The tau f against voltage relationship determined from phasic tension showed that the inactivation process of the Ca-carrying system is slowest at membrane potentials around -13 mV (tau f = 55 msec) and that the rate of inactivation increases with both increasing and decreasing depolarizations. 7. It is suggested that normal repolarization in frog myocardium depends mainly on the decay of Ca inward current rather than on an increase of outward current.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley C. C., Ridgway E. B. On the relationships between membrane potential, calcium transient and tension in single barnacle muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Jul;209(1):105–130. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. Membrane calcium current in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):191–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler G. W., Jr, Reuter H. The relation between membrane potential, membrane currents and activation of contraction in ventricular myocardial fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Mar;207(1):211–229. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besseau A. Analyse, selon le modèle de Hodgkin-Huxley, des conductances membranaires du myocarde de grenouille (Rana esculenta. J Physiol (Paris) 1972;64(6):647–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. F., Noble S. J. Membrane currents underlying delayed rectification and pace-maker activity in frog atrial muscle. J Physiol. 1969 Oct;204(3):717–736. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einwächter H. M., Haas H. G., Kern R. Membrane current and contraction in frog atrial fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):141–171. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozzard H. A., Hellman D. C. Relationship between membrane voltage and tension in voltage-clamped cardiac purkinje fibres. Nature. 1968 May 11;218(5141):588–589. doi: 10.1038/218588a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons W. R., Fozzard H. A. High potassium and low sodium contractures in sheep cardiac muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Nov;58(5):483–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.5.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebisch G., Weidmann S. Membrane currents in mammalian ventricular heart muscle fibers using a voltage-clamp technique. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Mar;57(3):290–296. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.3.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Kimoto Y., Kato Y. A study on the excitation-contraction coupling of the bullfrog ventricle with voltage clamp technique. Jpn J Physiol. 1971 Apr;21(2):159–173. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.21.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Kimoto Y., Suetsugu Y. Membrane currents responsibile for contraction and relaxation of the bullfrog ventricle. Jpn J Physiol. 1972 Jun;22(3):315–331. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.22.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A. M. Contractile proteins of the heart. Physiol Rev. 1970 Jan;50(1):63–158. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.1.63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlhardt M., Krause H., Kübler M., Herdey A. Kinetics of inactivation and recovery of the slow inward current in the mammalian ventricular myocardium. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Mar 22;355(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00584795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenfant J., Mironneau J., Aka J. K. Activité répétive de la fibre sino-auriculaire de grenouille: analyse des courants membranaires responsables de l'automatisme cardiaque. J Physiol (Paris) 1972;64(1):5–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léoty C., Raymond G. Mechanical activity and ionic currents in frog atrial trabeculae. Pflugers Arch. 1972;334(2):114–128. doi: 10.1007/BF00586785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan J. A. Some limitations of the double sucrose gap, and its use in a study of the slow outward current in mammalian ventricular muscle. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;240(3):775–806. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Orkand R. K. Excitation-concentration coupling in frog ventricle: evidence from voltage clamp studies. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(1):167–189. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morad M., Trautwein W. The effect of the duration of the action potential on contraction in the mammalian heart muscle. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1968;299(1):66–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00362542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- New W., Trautwein W. Inward membrane currents in mammalian myocardium. Pflugers Arch. 1972;334(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00585997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi R., Trautwein W. The dependence of cardiac contraction on depolarization and slow inward current. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(3):187–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00586383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda C., Rougier O. Kinetic analysis of the delayed outward currents in frog atrium. Existence of two types of preparation. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):51–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Divalent cations as charge carriers in excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1973;26:1–43. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(73)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougier O., Vassort G., Garnier D., Gargouil Y. M., Coraboeuf E. Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(2):91–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00587018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solaro R. J., Wise R. M., Shiner J. S., Briggs F. N. Calcium requirements for cardiac myofibrillar activation. Circ Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):525–530. doi: 10.1161/01.res.34.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumbera J. Induced changes of action potential on cardiac contraction. Experientia. 1970;26(7):738–739. doi: 10.1007/BF02232516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein W., McDonald T. F., Tripathi O. Calcium conductance and tension in mammalian ventricular muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1975;354(1):55–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00584503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G. Existence of two components in frog cardiac mechanical activity. Influence of Na ions. Eur J Cardiol. 1973 Dec;1(2):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G., Rougier O. Membrane potential and slow inward current dependence of frog cardiac mechanical activity. Pflugers Arch. 1972;331(3):191–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00589126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M., Trautwein W. Slow inward current and action potential in cardiac Purkinje fibres. The effect of Mn plus,plus-ions. Pflugers Arch. 1971;323(3):204–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00586384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Effect of current flow on the membrane potential of cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1951 Oct 29;115(2):227–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


