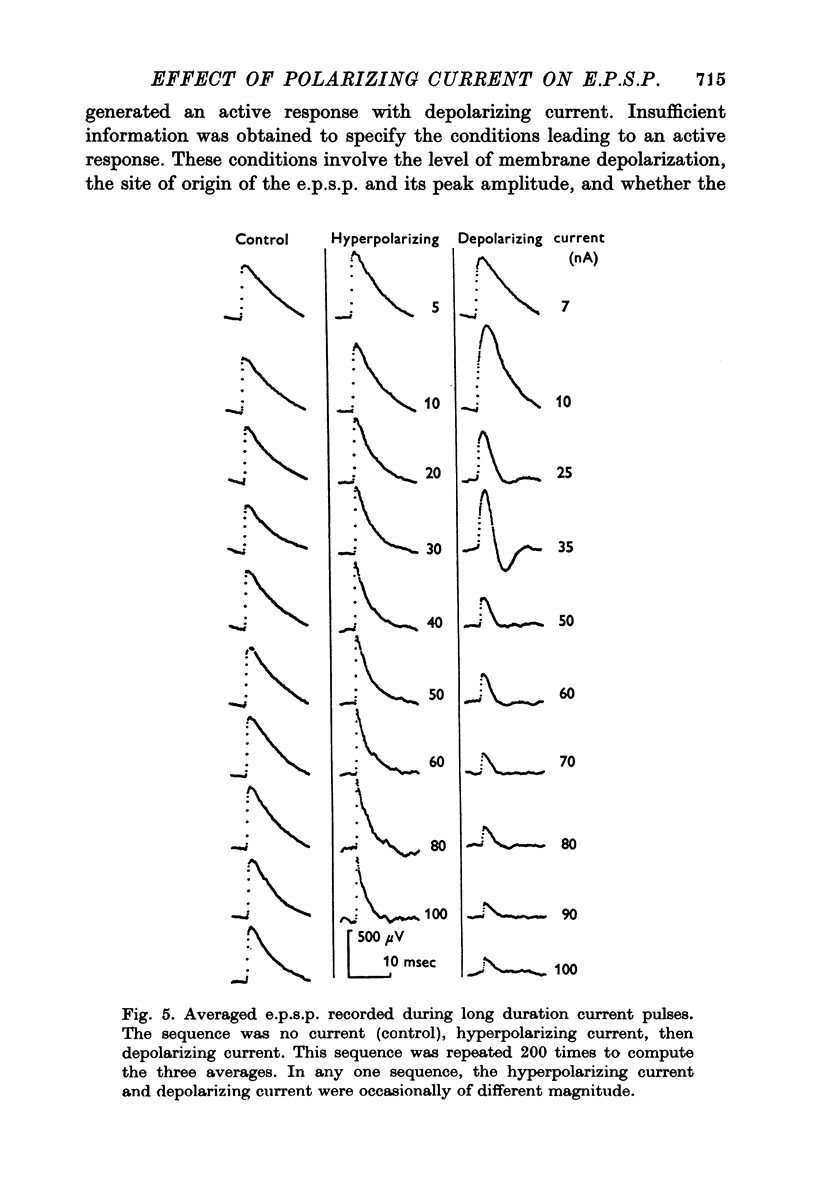
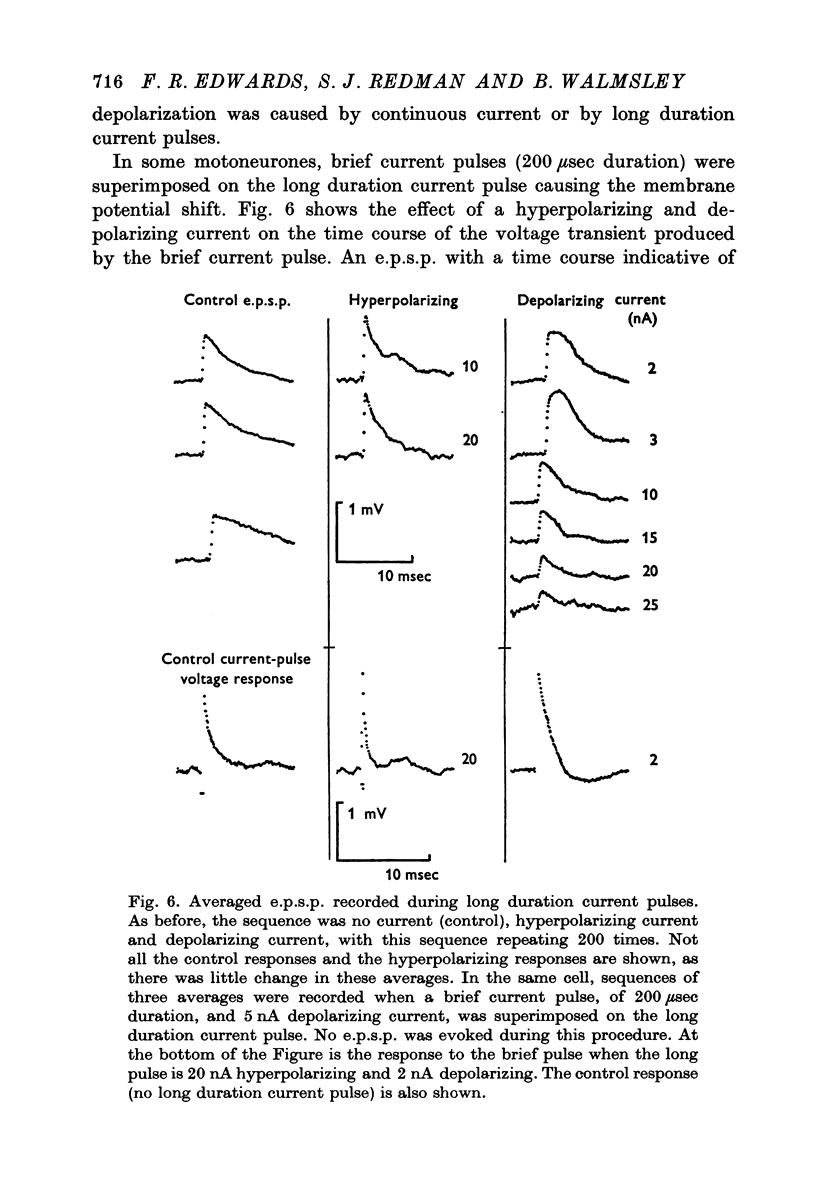
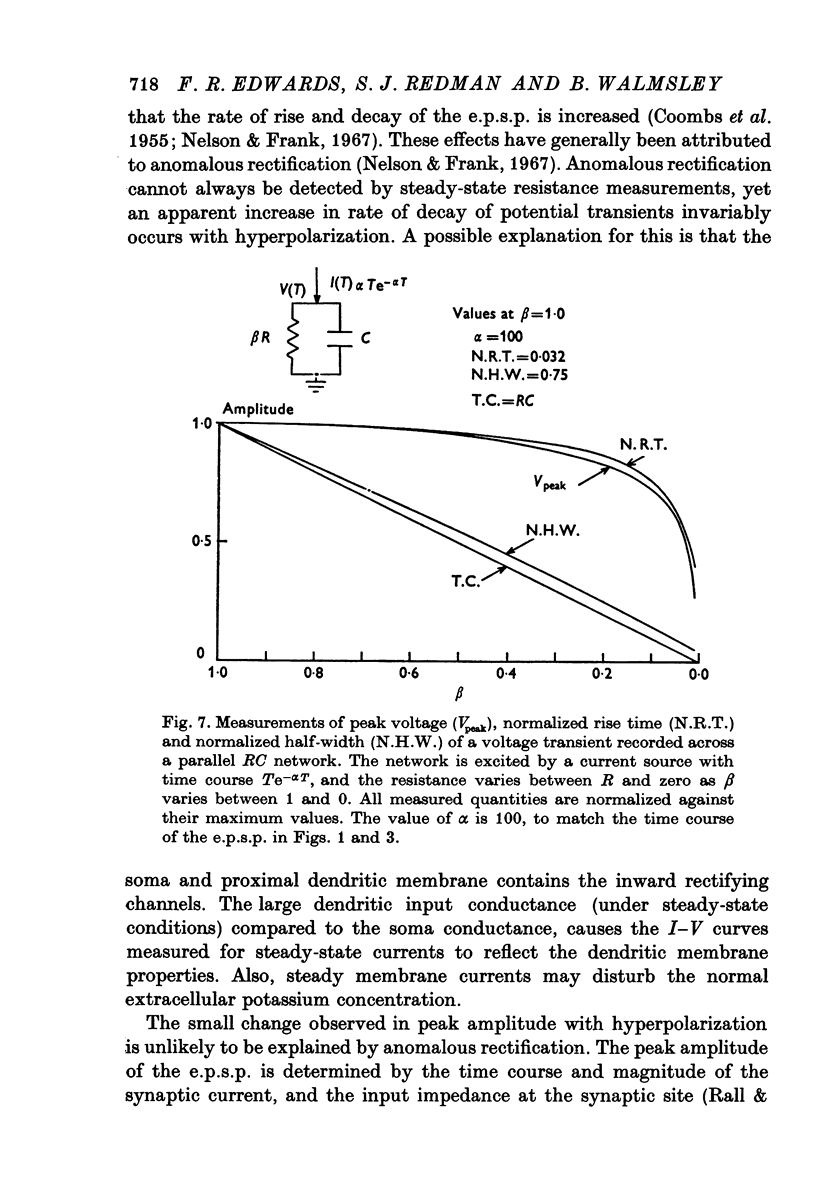
Abstract
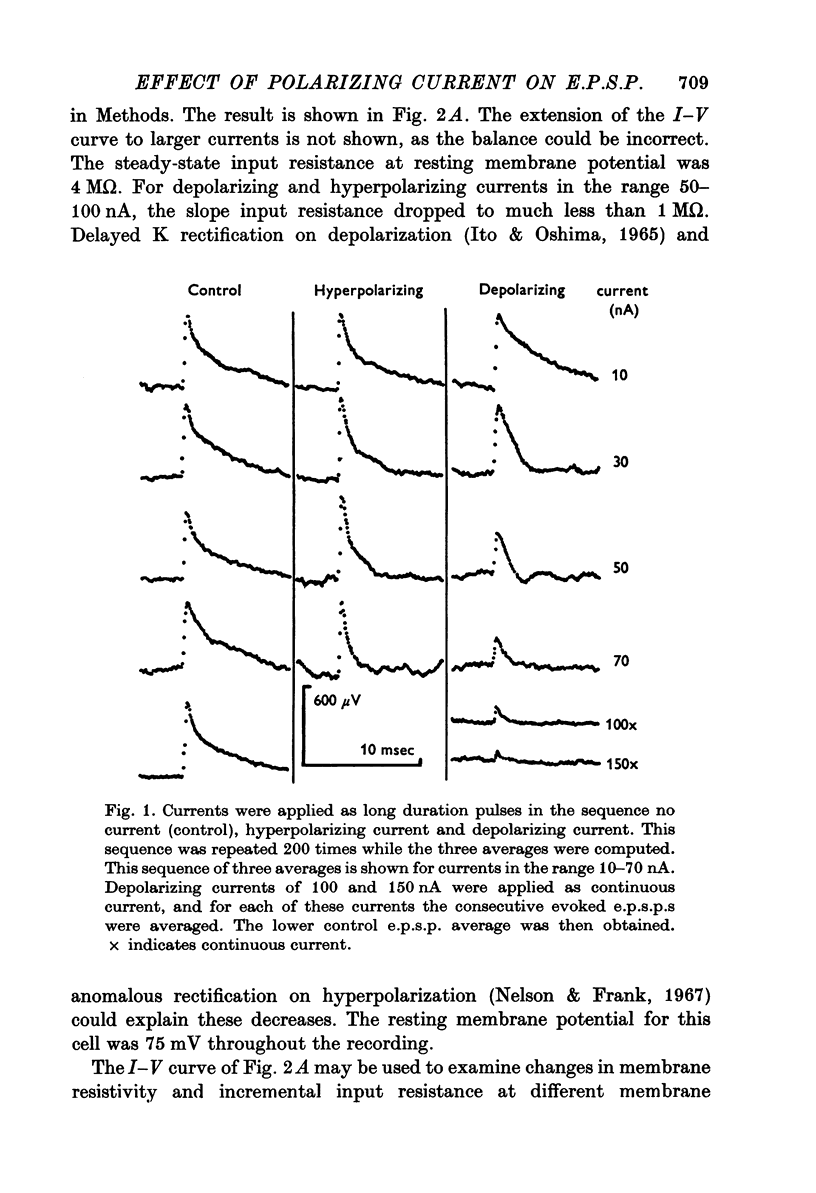
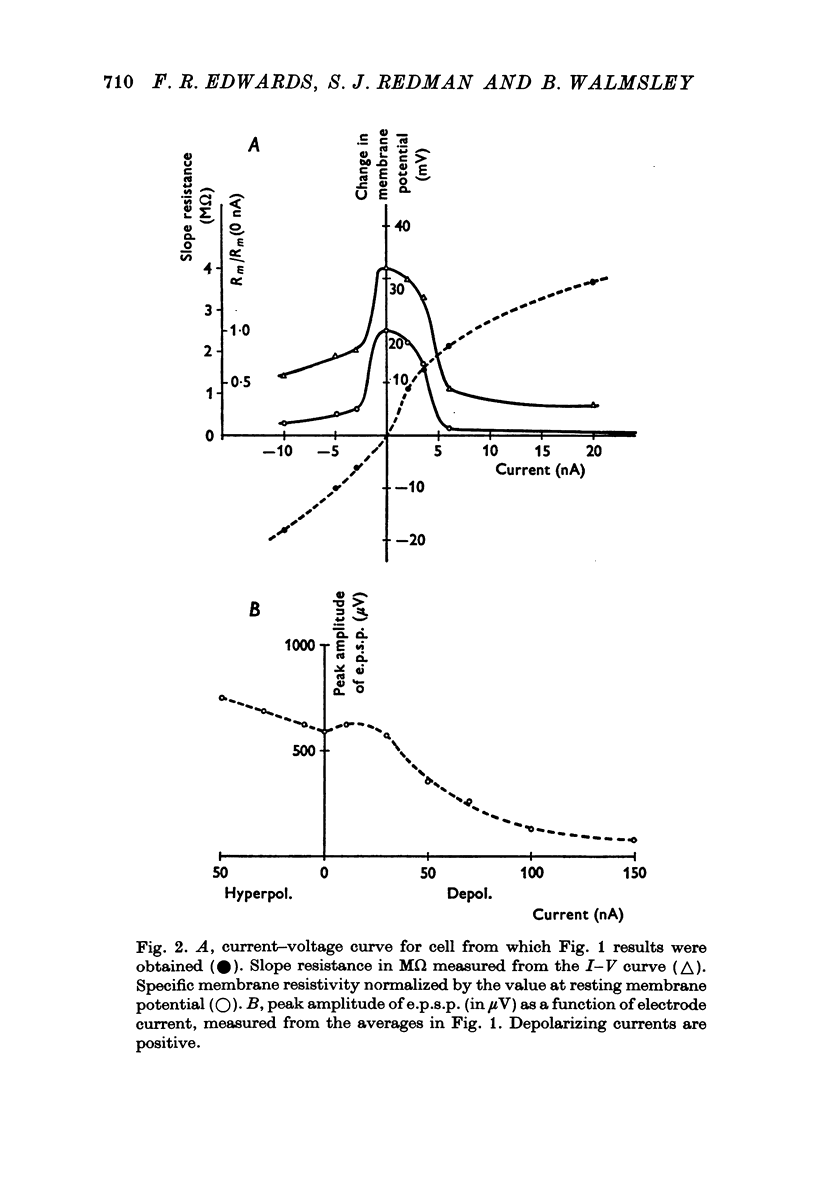
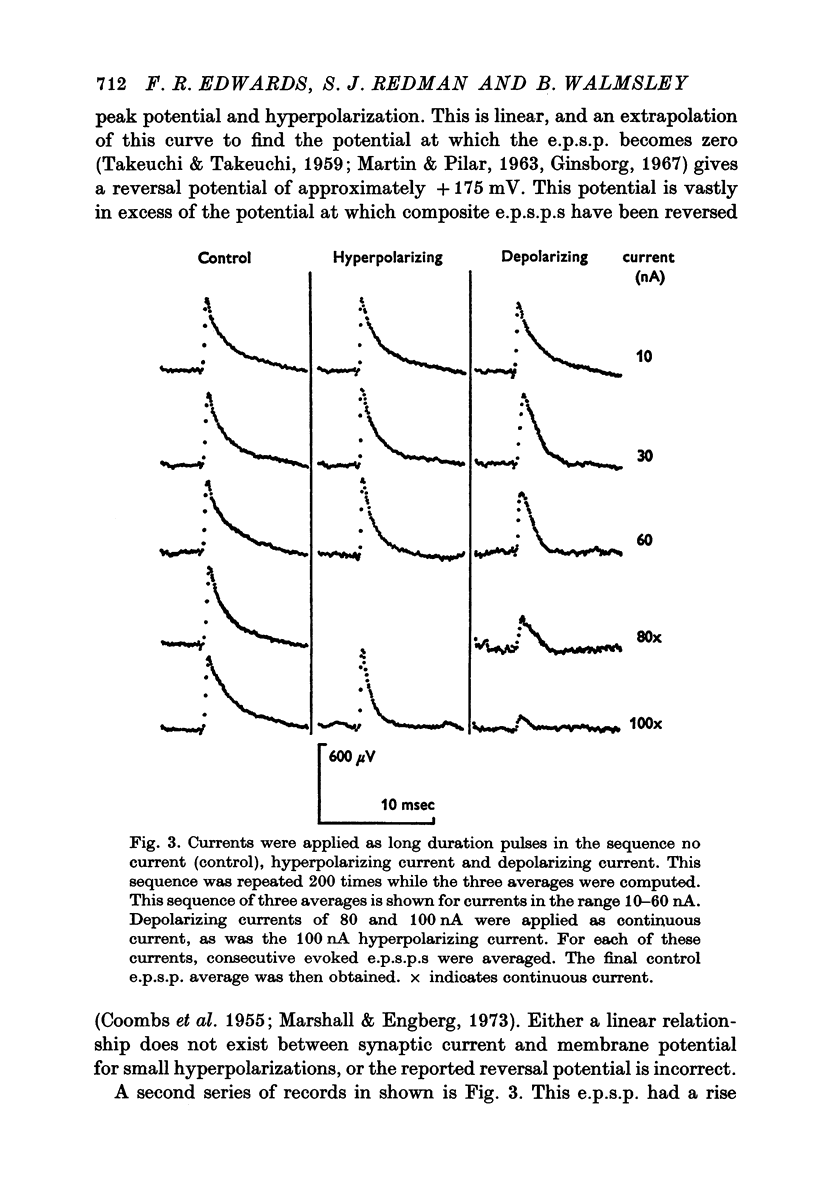
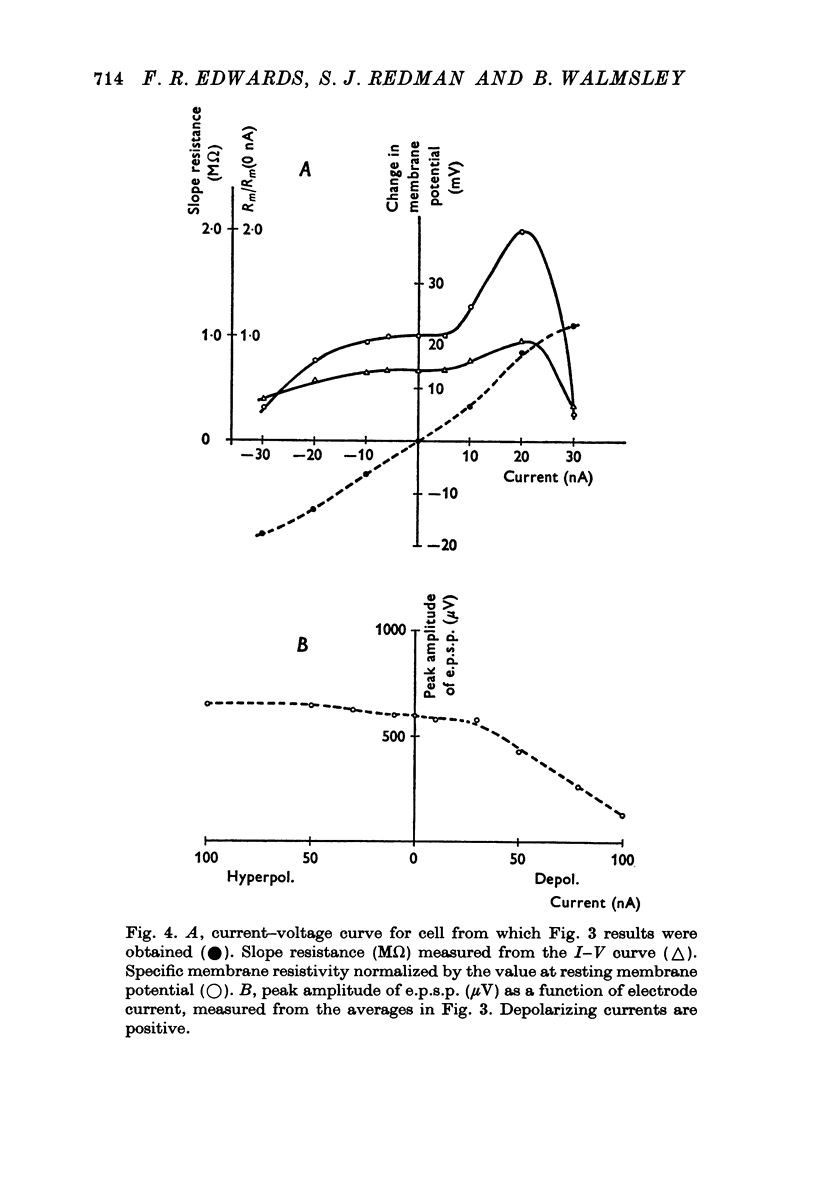
1. Depolarizing and hyperpolarizing currents were applied to motoneurones in which unitary Ia e.p.s.p.s were evoked. The results concentrate on those e.p.s.p.s which had time courses which were compatible with somatically located synapses. 2. No reversal of these e.p.s.p.s was observed. Depolarizing currents up to 150 nA simply reduced the peak amplitude. 3. Hyperpolarizing currents caused little, if any, increase in the peak amplitude of the e.p.s.p. The time course of decay became briefer as the membrane was hyperpolarized. 4. Changes in decay time course of the e.p.s.p. which accompanied depolarization and hyperpolarization could be attributed to changes in membrane conductances, rather than to changes in synaptic current time course. 5. The failure of the e.p.s.p. to increase with hyperpolarization was shown to be due to the failure of the synaptic current to increase, rather than to the shunting of anomalous rectification. 6. Chemical and electrical transmission are evaluated against these results and those of the preceding papers.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett M. V. Physiology of electrotonic junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):509–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. E. Motor unit types of cat triceps surae muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(1):141–160. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., ECCLES J. C., FATT P. Excitatory synaptic action in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1955 Nov 28;130(2):374–395. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin W. H. Dendritic synapses and reversal potentials: theoretical implications of the view from the soma. Exp Neurol. 1969 Jun;24(2):248–264. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudel J. Nonlinear voltage dependence of excitatory synaptic current in crayfish muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1974;352(3):227–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00590488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Redman S. J., Walmsley B. Non-quantal fluctuations and transmission failures in charge transfer at Ia synapses on spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):689–704. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Redman S. J., Walmsley B. Statistical fluctuations in charge transfer at Ia synapses on spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Aug;259(3):665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eide E., Fedina L., Jansen J., Lundberg A., Vyklický L. Unitary components in the activation of Clarke's column neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 Sep-Oct;77(1):145–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK K., FUORTES M. G. Stimulation of spinal motoneurones with intracellular electrodes. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):451–470. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsborg B. L. Ion movements in junctional transmission. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):289–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iansek R., Redman S. J. The amplitude, time course and charge of unitary excitatory post-synaptic potentials evoked in spinal motoneurone dendrites. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;234(3):665–688. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Oshima T. Electrical behaviour of the motoneurone membrane during intracellularly applied current steps. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):607–635. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack J. J., Redman S. J. An electrical description of the motoneurone, and its application to the analysis of synaptic potentials. J Physiol. 1971 Jun;215(2):321–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNO M. QUANTAL COMPONENTS OF EXCITATORY SYNAPTIC POTENTIALS IN SPINAL MOTONEURONES. J Physiol. 1964 Dec;175:81–99. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. A study of synaptic transmission in the absence of nerve impulses. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(2):407–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Llinás R. Alterations of synaptic action in chromatolysed motoneurones of the cat. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;210(4):823–838. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M., Muñoz-Martinez E. J., Randić M. Synaptic action on Clarke's column neurones in relation to afferent terminal size. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(2):343–360. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno M. Quantum aspects of central and ganglionic synaptic transmission in vertebrates. Physiol Rev. 1971 Oct;51(4):647–678. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Nicholson C. Calcium role in depolarization-secretion coupling: an aequorin study in squid giant synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):187–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN A. R., PILAR G. DUAL MODE OF SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION IN THE AVIAN CILIARY GANGLION. J Physiol. 1963 Sep;168:443–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Frank K. Anomalous rectification in cat spinal motoneurons and effect of polarizing currents on excitatory postsynaptic potential. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1097–1113. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W., Burke R. E., Smith T. G., Nelson P. G., Frank K. Dendritic location of synapses and possible mechanisms for the monosynaptic EPSP in motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1169–1193. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall W. Distinguishing theoretical synaptic potentials computed for different soma-dendritic distributions of synaptic input. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1138–1168. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinzel J., Rall W. Transient response in a dendritic neuron model for current injected at one branch. Biophys J. 1974 Oct;14(10):759–790. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85948-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapovalov A. I., Kurchavyi G. G. Effects of trans-membrane polarization and TEA injection on monosynaptic actions from motor cortex, red nucleus and group Ia afferents on lumbar motoneurons in the monkey. Brain Res. 1974 Dec 20;82(1):49–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90892-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. G., Wuerker R. B., Frank K. Membrane impedance changes during synaptic transmission in cat spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1967 Sep;30(5):1072–1096. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.5.1072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Active phase of frog's end-plate potential. J Neurophysiol. 1959 Jul;22(4):395–411. doi: 10.1152/jn.1959.22.4.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Changes in potassium concentration around motor nerve terminals, produced by current flow, and their effects on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:46–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


