Abstract
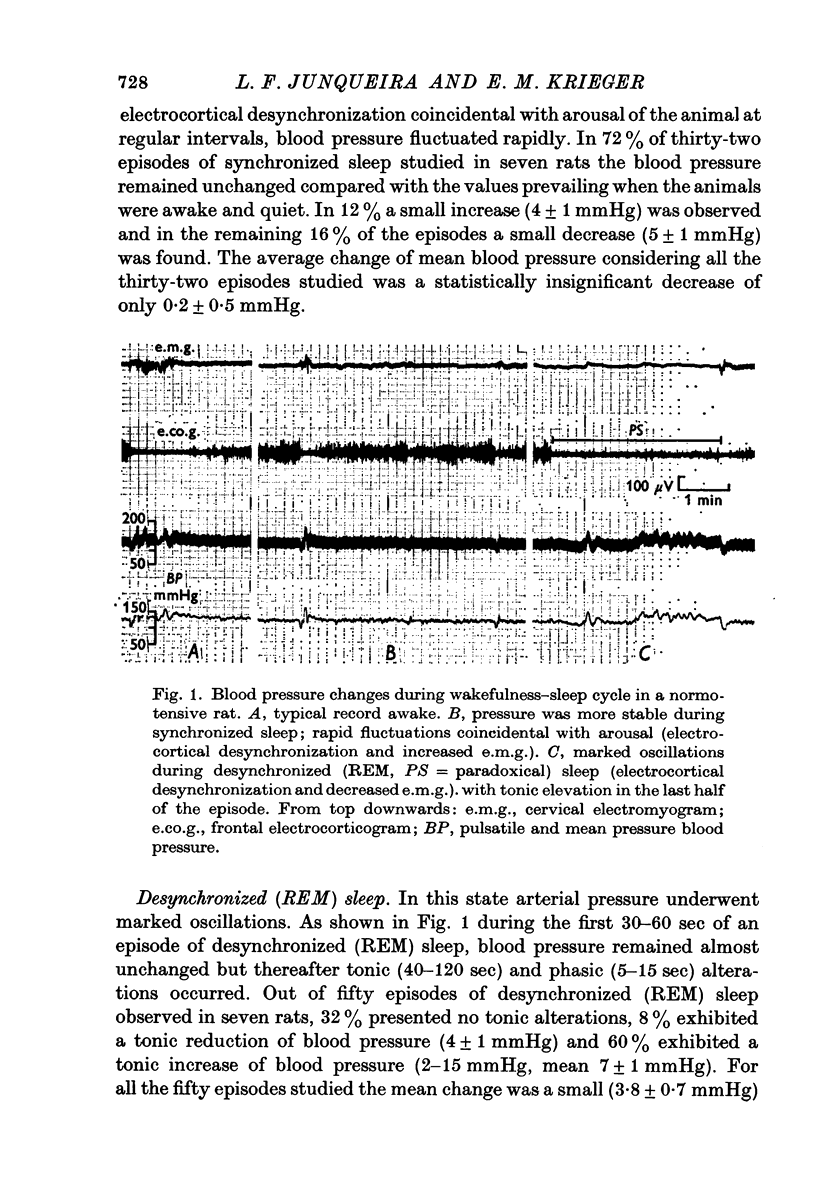
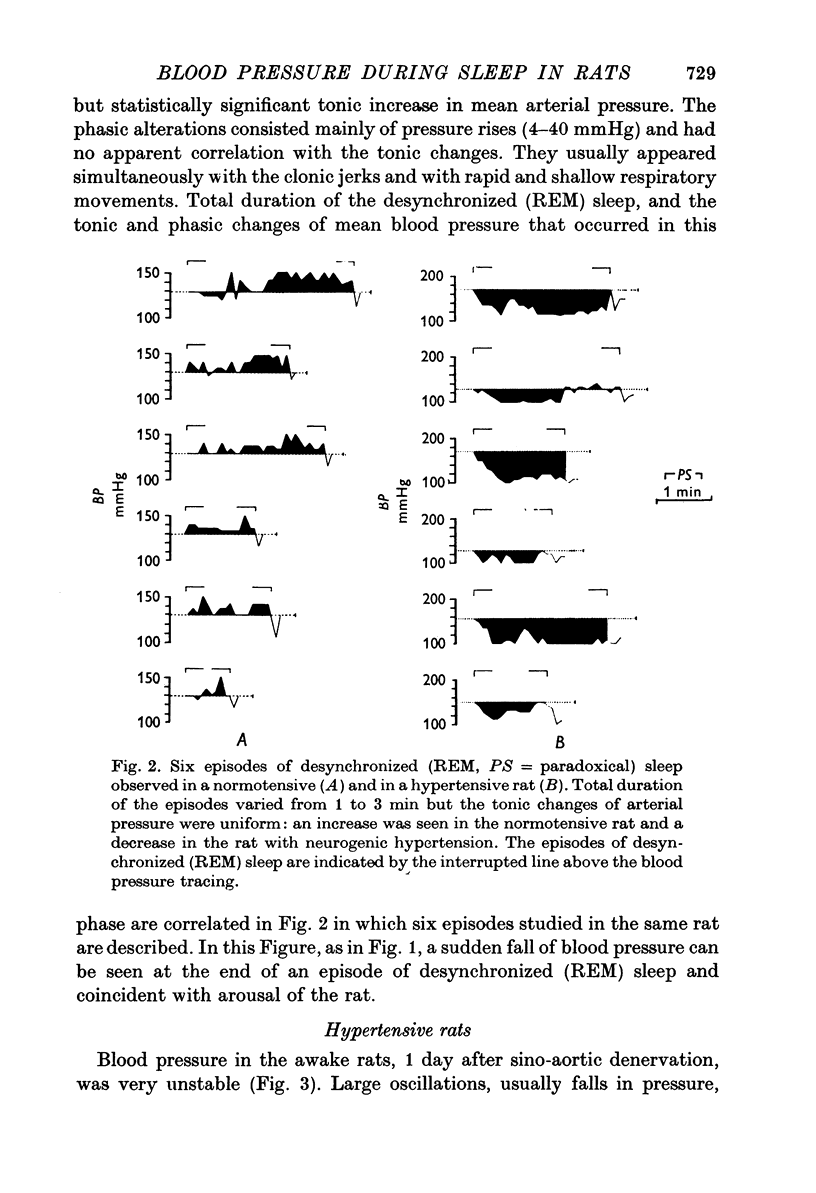
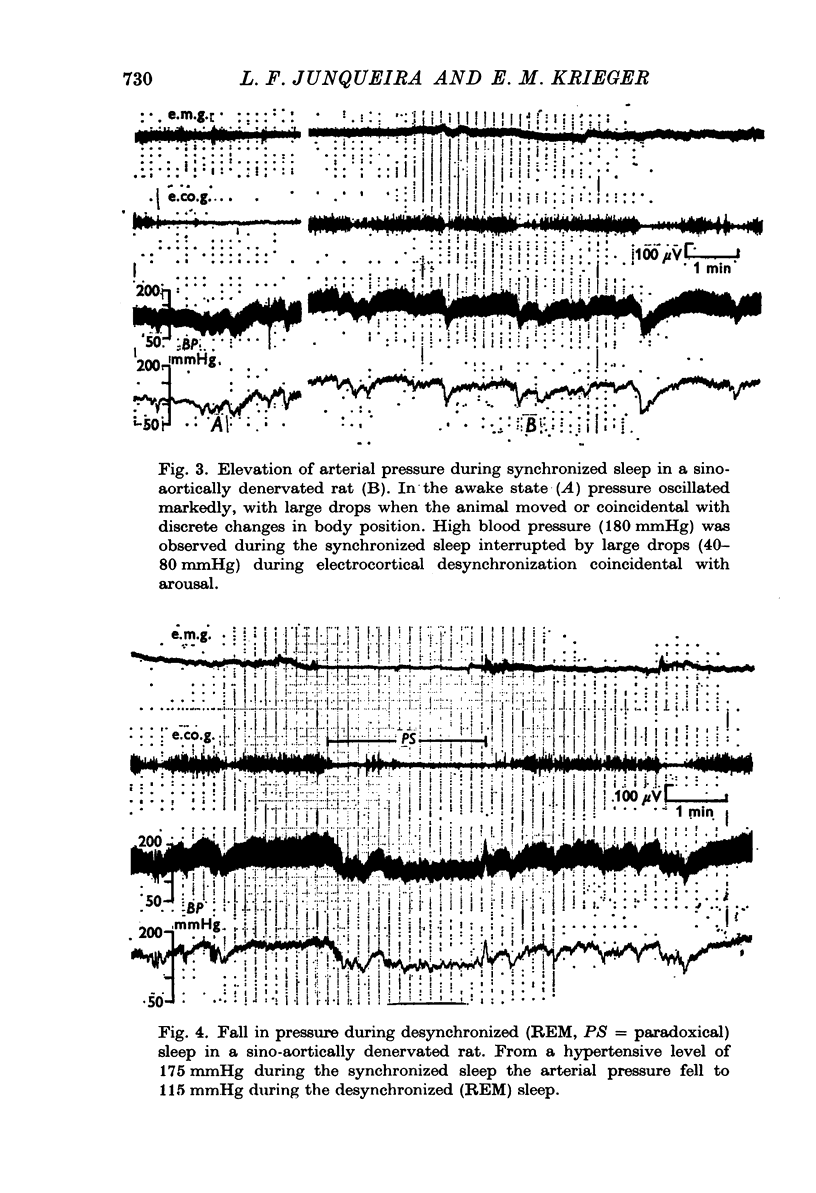
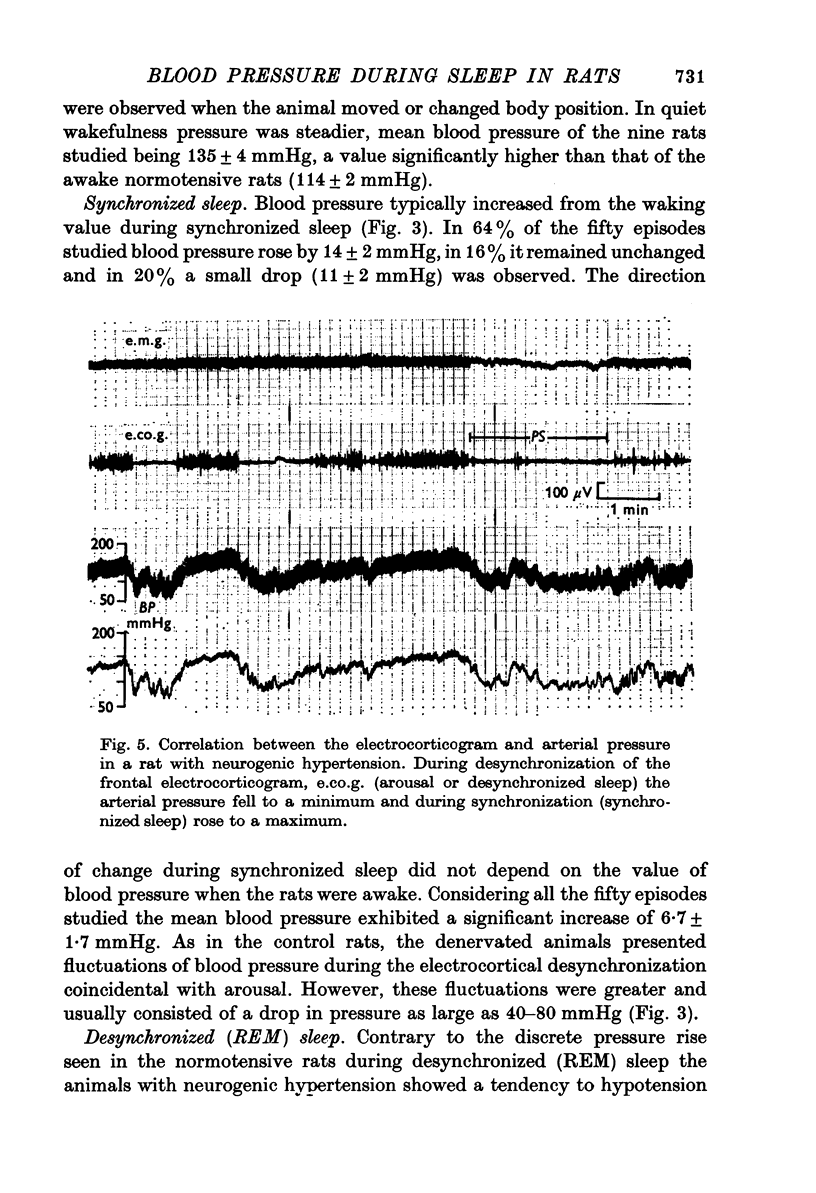
1. Blood pressure was recorded in normotensive rats (114 +/- 2 mmHg) and in those made hypertensive by baroreceptor denervation (135 +/- 4 mmHg) during natural sleep. The different states of the wakefulness-sleep cycle were identified by analysis of the frontal electrocorticogram, the cervical electromyogram and by behavioural changes. 2. During synchronized sleep the arterial pressure in the control animals usually remained unchanged as compared to values prevailing when the rats were awake and quiet. The blood pressure usually attained higher levels in the sino-aortically denervated rats during this state. 3. Coincidently with the short episodes of electrocortical desynchronization of the synchronized sleep the blood pressure exhibited rapid oscillations. These fluctuations were greater in the rats with neurogenic hypertension where there were large pressure drops. 4. During desynchronized (REM) sleep arterial pressure underwent marked oscillations. While in the control rats the pressure usually rose, the baroreceptor-denervated rats showed a severe reduction in pressure. Arterial pressure in denervated animals became lower than that of the control rats, 106 +/- 2 and 121 +/- 2 mmHg, respectively. 5. We interpret these results to mean that in the rat alterations in the sensitivity of the baroreceptor reflex could be an important factor in preventing the arterial pressure from rising to hypertensive levels during syndhronized sleep and from dropping to low values during desynchronized (REM) sleep.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRZIS L., TACHIBANA S. LOCAL CEREBRAL IMPEDANCE AND BLOOD FLOW DURING SLEEP AND AROUSAL. Exp Neurol. 1964 Apr;9:269–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(64)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baust W., Weidinger H., Kirchner F. Sympathetic activity during natural sleep and arousal. Arch Ital Biol. 1968 Dec;106(4):379–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bristow J. D., Honour A. J., Pickering T. G., Sleight P. Cardiovascular and respiratory changes during sleep in normal and hypertensive subjects. Cardiovasc Res. 1969 Oct;3(4):476–485. doi: 10.1093/cvr/3.4.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANDIA O., FAVALE E., GIUSSANI A., ROSSI G. F. Blood pressure during natural sleep and during sleep induced by electrical stimulation of the brain stem reticular formation. Arch Ital Biol. 1962;100:216–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coccagna G., Mantovani M., Brignani F., Manzini A., Lugaresi E. Laboratory note. Arterial pressure changes during spontaneous sleep in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1971 Sep;31(3):277–281. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(71)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrario C. M., McCubbin J. W., Page I. H. Hemodynamic characteristics of chronic experimental neurogenic hypertension in unanesthetized dogs. Circ Res. 1969 Jun;24(6):911–922. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.6.911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GASSEL M. M., GHELARDUCCI B., MARCHIAFAVA P. L., POMPEIANO O. PHASIC CHANGES IN BLOOD PRESSURE AND HEART RATE DURING THE RAPID EYE MOVEMENT EPISODES OF DESYNCHRONIZED SLEEP IN UNRESTRAINED CATS. Arch Ital Biol. 1964 Jul;102:530–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi M., Baccelli G., Zanchetti A. Reflex chemoceptive regulation of arterial pressure during natural sleep in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):969–978. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guazzi M., Zanchetti A. Blood pressure and heart rate during natural sleep of the cat and their regulation by carotid sinus and aortic reflexes. Arch Ital Biol. 1965 Dec 10;103(4):789–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODES R., SUZUKI J. I. COMPARATIVE THRESHOLDS OF CORTEX, VESTIBULAR SYSTEM AND RETICULAR FORMATION IN WAKEFULNESS, SLEEP AND RAPID EYE MOVEMENT PERIODS. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1965 Feb;18:239–248. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(65)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamura Y., Uchino Y., Kidokoro Y. Blood pressure and heart rate changes during para-sleep in vagotomized and atropinized cats. Brain Res. 1968 Feb;7(2):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(68)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouvet M. Neurophysiology of the states of sleep. Physiol Rev. 1967 Apr;47(2):117–177. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1967.47.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junqueira L. F., Jr, Krieger E. M. Circulatory responses of conscious rats to hemorrhage. Role of the baroreceptors. Acta Physiol Lat Am. 1973 Apr;23(4):270–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANZOW E., KRAUSE D., KUEHNEL H. [The vasomotor system of the cerebral cortex in the phases of desynchronized EEG activity during natural sleep in cats]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1962;274:593–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANZOW E., KRAUSE D. [Vasomotor activity of the cerebral cortex and EEG activity of non-sleeping, unrestrained cats]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1962;274:447–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER E. M., MARSEILLAN R. F. AORTIC DEPRESSOR FIBERS IN THE RAT: AN ELECTROPHYSIOLOGICAL STUDY. Am J Physiol. 1963 Oct;205:771–774. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.4.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIEGER E. M. NEUROGENIC HYPERTENSION IN THE RAT. Circ Res. 1964 Dec;15:511–521. doi: 10.1161/01.res.15.6.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri I. M., Freis E. D. Hemodynamic changes during sleep. J Appl Physiol. 1967 May;22(5):867–873. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.5.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger E. M. Effect of sinoaortic denervation on cardiac output. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jul;213(1):139–142. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger E. M. The acute phase of neurogenic hypertension in the rat. Experientia. 1970 Jun 15;26(6):628–629. doi: 10.1007/BF01898727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancia G., Baccelli G., Adams D. B., Zanchetti A. Vasomotor regulation during sleep in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1971 Apr;220(4):1086–1093. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.4.1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moruzzi G. The sleep-waking cycle. Ergeb Physiol. 1972;64:1–165. doi: 10.1007/3-540-05462-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON D. W., HONOUR A. J., FENTON G. W., STOTT F. H., PICKERING G. W. VARIATION IN ARTERIAL PRESSURE THROUGHOUT THE DAY AND NIGHT. Clin Sci. 1964 Jun;26:445–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROLDAN E., WEISS T. The cycle of sleep in the rat (preliminary report). Bol Inst Estud Med Biol Univ Nac Auton Mex. 1962 Aug;20:155–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., HOBSON J. A., MORRISON D. F., GOLDFRANK F. CHANGES IN RESPIRATION, HEART RATE, AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD PRESSURE IN HUMAN SLEEP. J Appl Physiol. 1964 May;19:417–422. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.3.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidek W. R., Hoshino K., Schmidek M., Timo-Iaria C. Influence of environmental temperature on the sleep-wakefulness cycle in the rat. Physiol Behav. 1972 Feb;8(2):363–371. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(72)90384-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth H. S., Sleight P., Pickering G. W. Reflex regulation of arterial pressure during sleep in man. A quantitative method of assessing baroreflex sensitivity. Circ Res. 1969 Jan;24(1):109–121. doi: 10.1161/01.res.24.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoyva J., Forsyth R. P., Kamiya J. Blood pressure during sleep in the rhesus monkey, before and after stress. Am J Physiol. 1968 May;214(5):1122–1125. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.214.5.1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timo-Iaria C., Negrão N., Schmidek W. R., Hoshino K., Lobato de Menezes C. E., Leme da Rocha T. Phases and states of sleep in the rat. Physiol Behav. 1970 Sep;5(9):1057–1062. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(70)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


