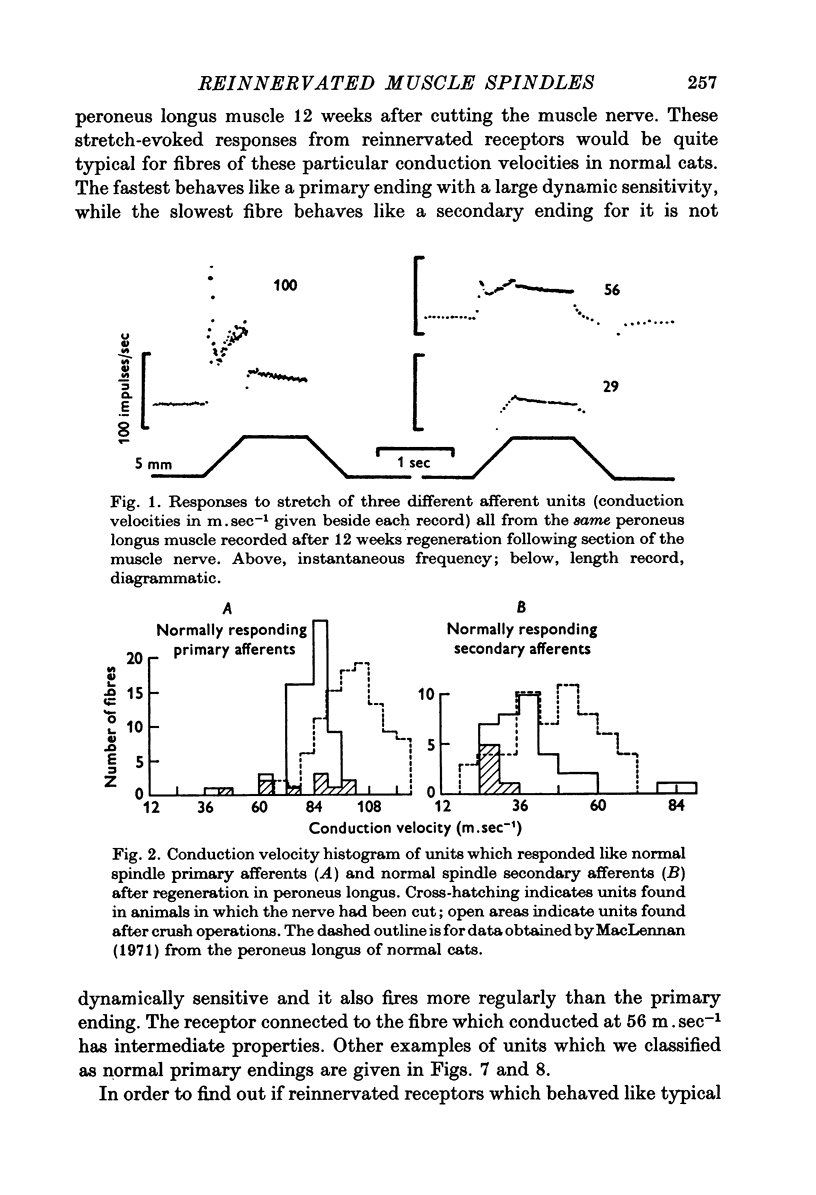
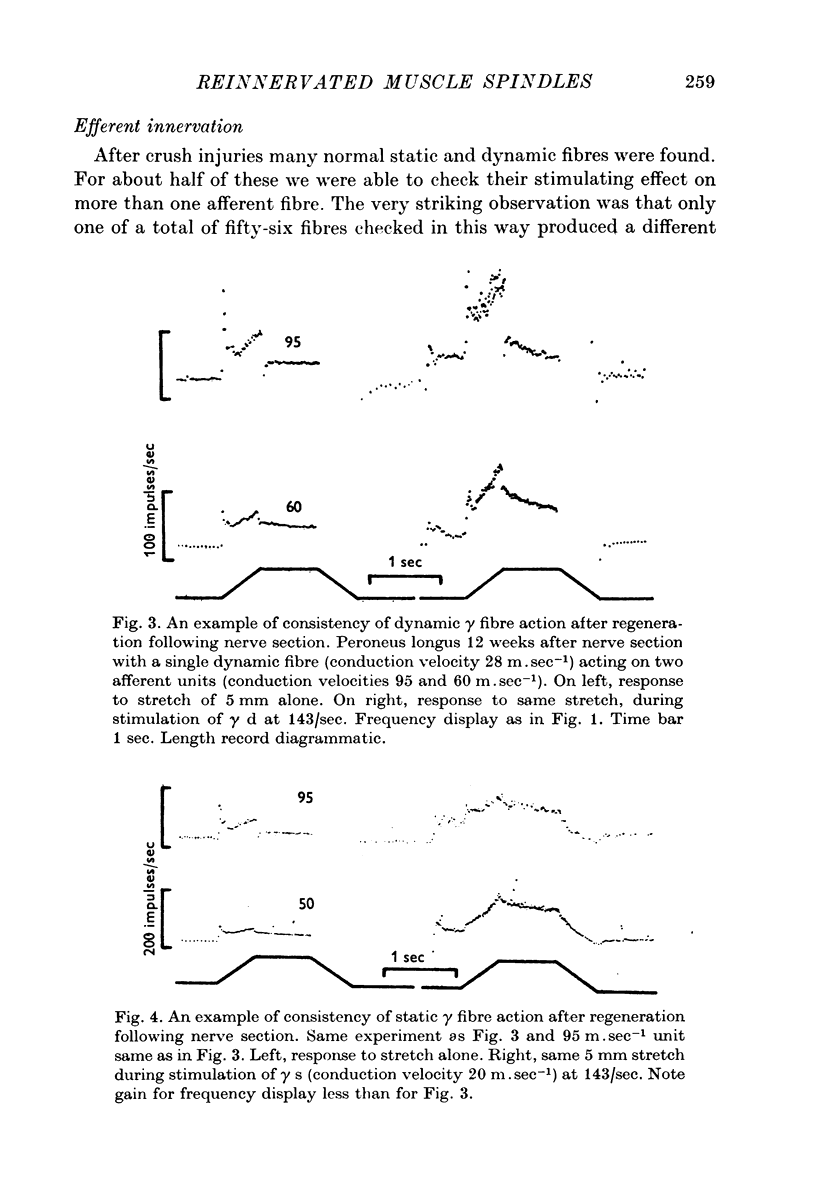
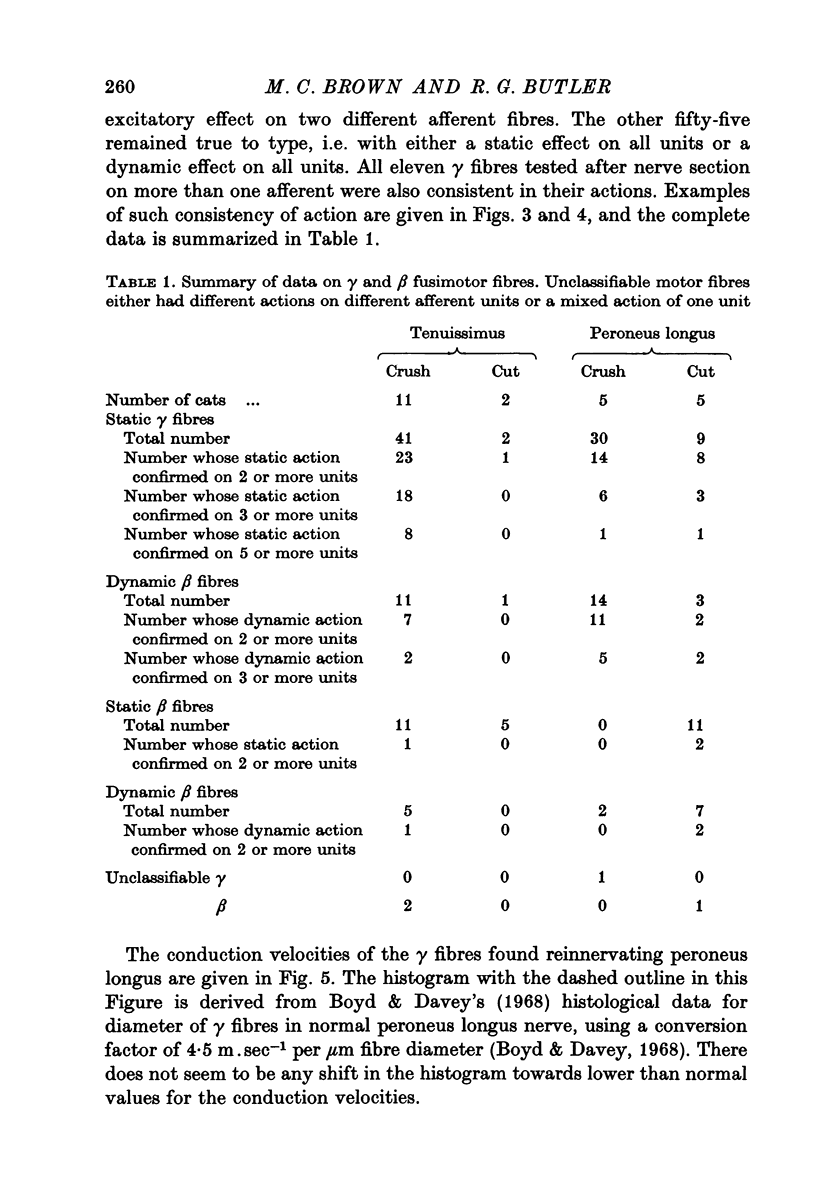
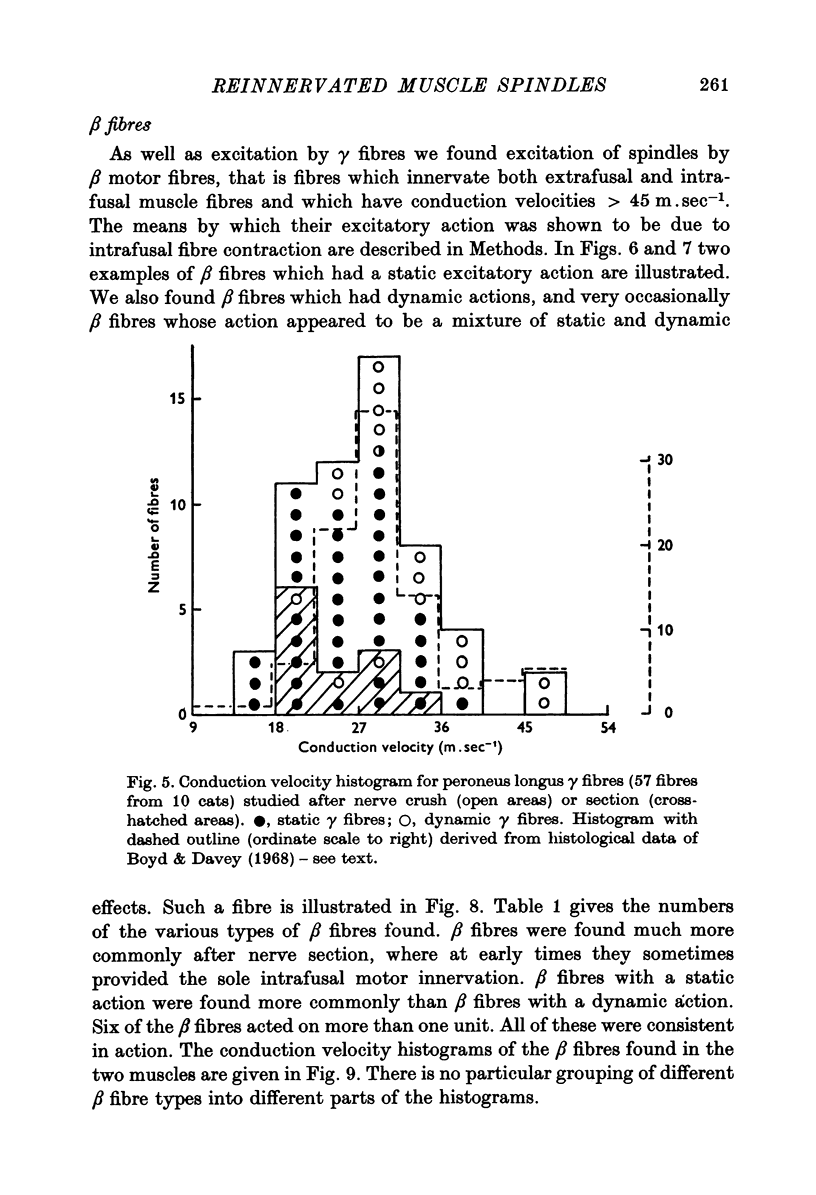
Abstract
1. The nerves to cat peroneus longus and tenuissimus muscles were either cut or crushed close to the muscle and the afferent and efferent nerve supply to the muscle spindles was studied electrophysiologically between 2 and 32 weeks later. 2. Recovery was more rapid and complete after crush than section for both afferent and efferent fibres. After recovery from either procedure normal primary and secondary afferents and static and dynamic gamma efferent fibres were found. 3. Some abnormally occurring neurones were found. One group consisted of beta fibres which had a static action on muscle spindles. Static beta fibres are very rarely found in normal muscles. 4. The results indicate that some guidance mechanism exists which after crush injuries of nerves may restore muscle receptor function almost to normal. Even after nerve section some muscle spindles may become correctly reinnervated.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN M. C., CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF THE TIBIALIS POSTERIOR MUSCLE OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:140–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Motor fibres innervating extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):649–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Laporte Y., Pagès B. Observations sur la ré-innervation de fuseaux neuro-musculaires de chat. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1966;160(2):408–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., English K. B., Horch K. W., Stensaas L. J. Patterning in the regeneration of type I cutaneous receptors. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):57–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess P. R., Horch K. W. Specific regeneration of cutaneous fibers in the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1973 Jan;36(1):101–114. doi: 10.1152/jn.1973.36.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAGG B. G., THOMAS P. K. Changes in conduction velocity and fibre size proximal to peripheral nerve lesions. J Physiol. 1961 Jul;157:315–327. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. FURTHER STUDIES OF STATIC AND DYNAMIC FUSIMOTOR FIBRES. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:132–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Jami L., Laporte Y. Skeleto-fusimotor axons in the hind-limb muscles of the cat. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):153–166. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTH L. Regeneration in the mammalian peripheral nervous system. Physiol Rev. 1956 Oct;36(4):441–478. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennerstrand G., Thoden U. Muscle spindle responses to concomitant variations in lenght and in fusimotor activation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Sep-Oct;74(1):153–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWilliam P. N. The incidence and properties of beta axons to muscle spindles in the cat hind limb. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1975 Jan;60(1):25–36. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1975.sp002287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THULIN C. A. Electrophysiological studies of peripheral nerve regeneration with special reference to the small diameter (gamma) fibers. Exp Neurol. 1960 Dec;2:598–612. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(60)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner J. K. Mixed intra- and extrafusal muscle fibers produced by temporary denervation in newborn rats. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Aug;150(3):279–302. doi: 10.1002/cne.901500304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZELENA J., HNIK P. Irreversible elimination of muscle receptors. Nature. 1960 Dec 10;188:946–947. doi: 10.1038/188946a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


