Abstract
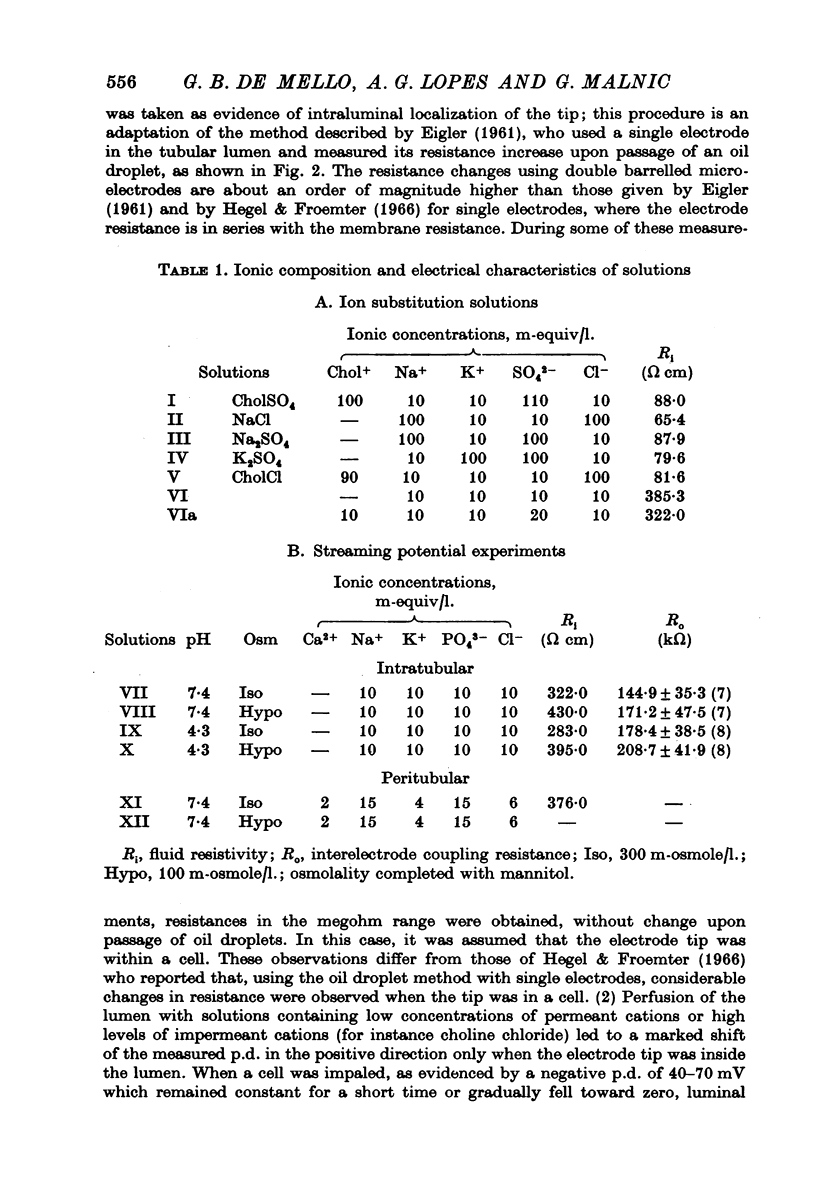
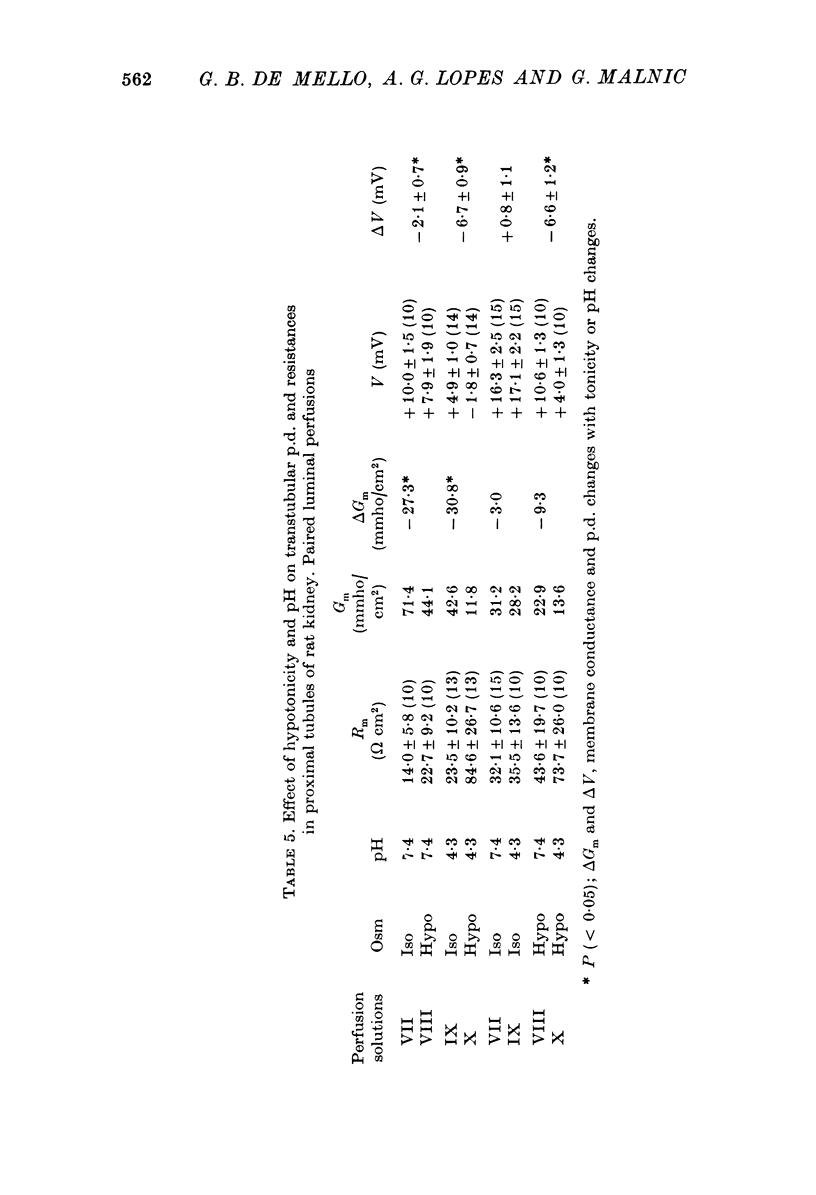
1. Transtubular potential differences and specific resistances were measured in rat proximal tubules by means of single and double barrelled glass micro-electrodes. 2. Tip localization was made by observation of effective resistance changes measured with double barrelled micro-electrodes upon passage of oil droplets, and by perfusion with choline C1. 3. Mean early proximal p.d.s. of the order of -1 to -2 mV, and late values of +0-5 to +1mV were found. Mean specific resistances ranged from 12 to 15 omega cm2. 4. Diffusion potentials and single ion relative conductances were evaluated, perfusing the lumen with solutions differing only with respect to one salt concentration. Na and K conductances were similar and greater than those of C1. 5. Luminal and peritubular perfusions with hypotonic solutions showed the occurrence of streaming potentials in this structure suggesting the existence of pores lined with negative charges. The effective diameter of these pores appeared to be reduced by hypotonic perfusion, as evidenced by a significant increase in resistance, indicating that the main ion path across this structure is represented by intercellular spaces.
Full text
PDF




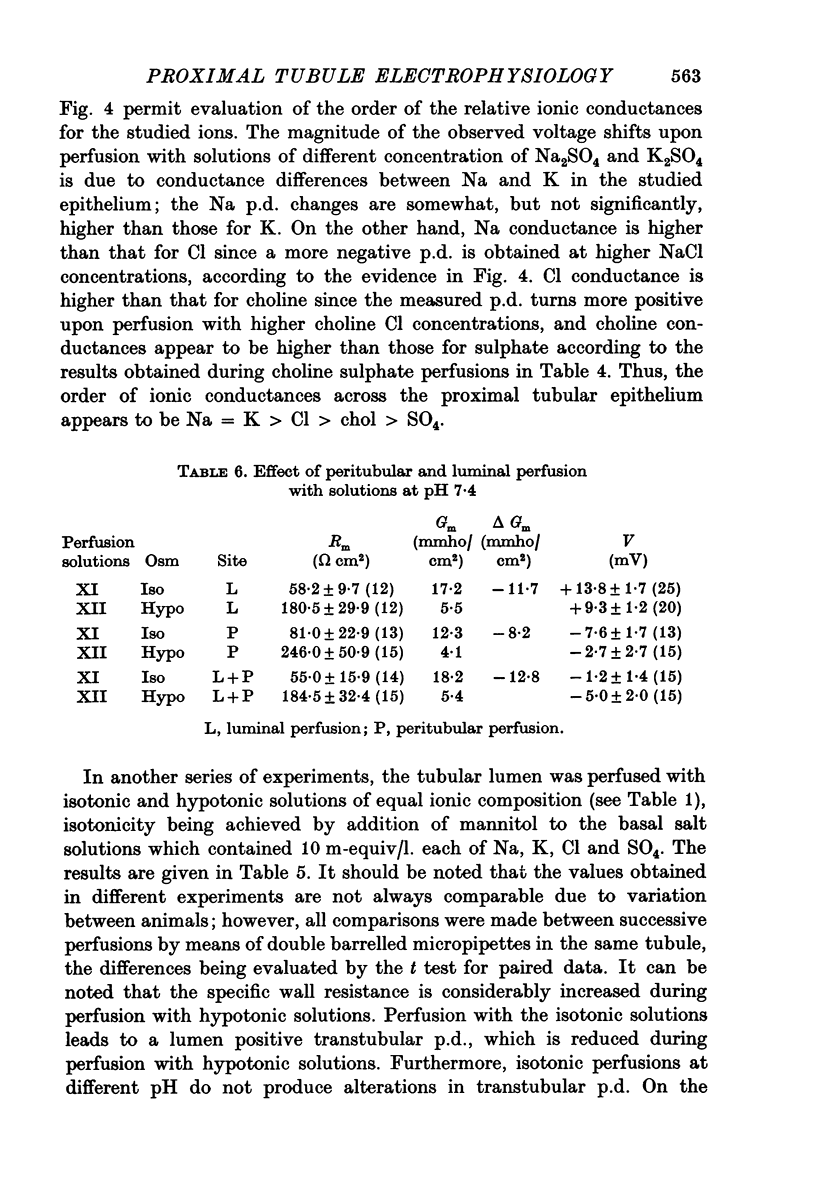






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos T. Biionic potentials in the proximal tubule of Necturus kidney. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):375–394. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos T. Letter: The partial conductances of limiting membranes in epithelial tissues. J Theor Biol. 1973 Nov 5;42(1):177–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barratt L. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Kokko J. P., Seldin D. W. Factors governing the transepithelial potential difference across the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):454–464. doi: 10.1172/JCI107579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulpaep E. L., Seely J. F. Electrophysiology of proximal and distal tubules in the autoperfused dog kidney. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1084–1096. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg M. B., Orloff J. Electrical potential difference across proximal convoluted tubules. Am J Physiol. 1970 Dec;219(6):1714–1716. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.6.1714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAPP J. R., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. Effect of unreabsorbed anions on proximal and distal transtubular potentials in rats. Am J Physiol. 1962 Apr;202:781–786. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., DiBona D. Pathways for movement of ions and water across toad urinary bladder. II. Site and mode of action of vasopressin. J Membr Biol. 1974;19(3):195–220. doi: 10.1007/BF01869978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGLER F. W. Short-circuit current measurements in proximal tubule of Necturus kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jul;201:157–163. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.1.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggena P. Osmotic regulation of toad bladder responsiveness to neurohypophyseal hormones. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Dec;60(6):665–678. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.6.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Gage P. W. Ionic conductances of the surface and transverse tubular membranes of frog sartorius fibers. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):279–297. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Active transport potentials, membrane diffusion potentials and streaming potentials across rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):85–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00603513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Effect of inhibitors and diuretics on electrical potential differences in rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Jun 26;357(3-4):209–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00585976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Gessner K. Free-flow potential profile along rat kidney proximal tubule. Pflugers Arch. 1974;351(1):69–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00603512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Hegel U. Transtubuläre Potentialdifferenzen an proximalen und distalen Tubuli der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;291(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G. Measurements of electrical potential differences on single nephrons of the perfused Necturus kidney. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Mar;44:659–678. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegel U., Frömter E. Erfahrungen mit der Oltropfenmethode zur Lokalisation der Mikroelektrodenspitze bei transtubulären Potentialmessungen an der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;291(1):121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegel U., Frömter E., Wick T. Der elektrische Wandwiderstand des proximalen Konvolutes der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;294(4):274–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kokko J. P. Proximal tubule potential difference. Dependence on glucose on glucose, HCO 3 , and amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1973 Jun;52(6):1362–1367. doi: 10.1172/JCI107308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutz M. D., Cardinal J., Burg M. B. Electrical resistance of renal proximal tubule perfused in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1973 Sep;225(3):729–734. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.3.729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALNIC G., KLOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF RENAL POTASSIUM EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:674–686. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Giebisch G. Some electrical properties of distal tubular epithelium in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1972 Oct;223(4):797–808. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins F. A., González E., Pérez-González M., Whittembury G. Effect of transtubular osmotic gradients on the paracellular pathway in toad kidney proximal tubule: electron microscopic observations. Pflugers Arch. 1975;353(4):287–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00587026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich G. T., Sha'afi I., Romualdez A., Solomon A. K. Effect of osmolality on the hydraulic permeability coefficient of red cells. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Dec;52(6):941–954. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.6.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. F. Effects of peritubular oncotic pressure on rat proximal tubule electrical resistance. Kidney Int. 1973 Jul;4(1):28–35. doi: 10.1038/ki.1973.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. F. Variation in electrical resistance along length of rat proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol. 1973 Jul;225(1):48–57. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring K. R. Current-induced voltage transients in Necturus proximal tubule. J Membr Biol. 1973 Nov 8;13(4):299–322. doi: 10.1007/BF01868234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring K. R., Paganelli C. V. Sodium flux in Necturus proximal tubule under voltage clamp. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Aug;60(2):181–201. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OSMOTIC REACTIONS AND ACTIVE SODIUM TRANSPORT IN THE FROG SKIN EPITHELIUM. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:141–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04052.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USSING H. H., WINDHAGER E. E. NATURE OF SHUNT PATH AND ACTIVE SODIUM TRANSPORT PATH THROUGH FROG SKIN EPITHELIUM. Acta Physiol Scand. 1964 Aug;61:484–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITTEMBURY G., SUGINO N., SOLOMON A. K. Ionic permeability and electrical potential differences in Necturus kidney cells. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Mar;44:689–712. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E., GIEBISCH G. ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY OF THE NEPHRON. Physiol Rev. 1965 Apr;45:214–244. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1965.45.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Diamond J. M. Effects of pH and polyvalent cations on the selective permeability of gall-bladder epithelium to monovalent ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Aug;163(1):57–74. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


