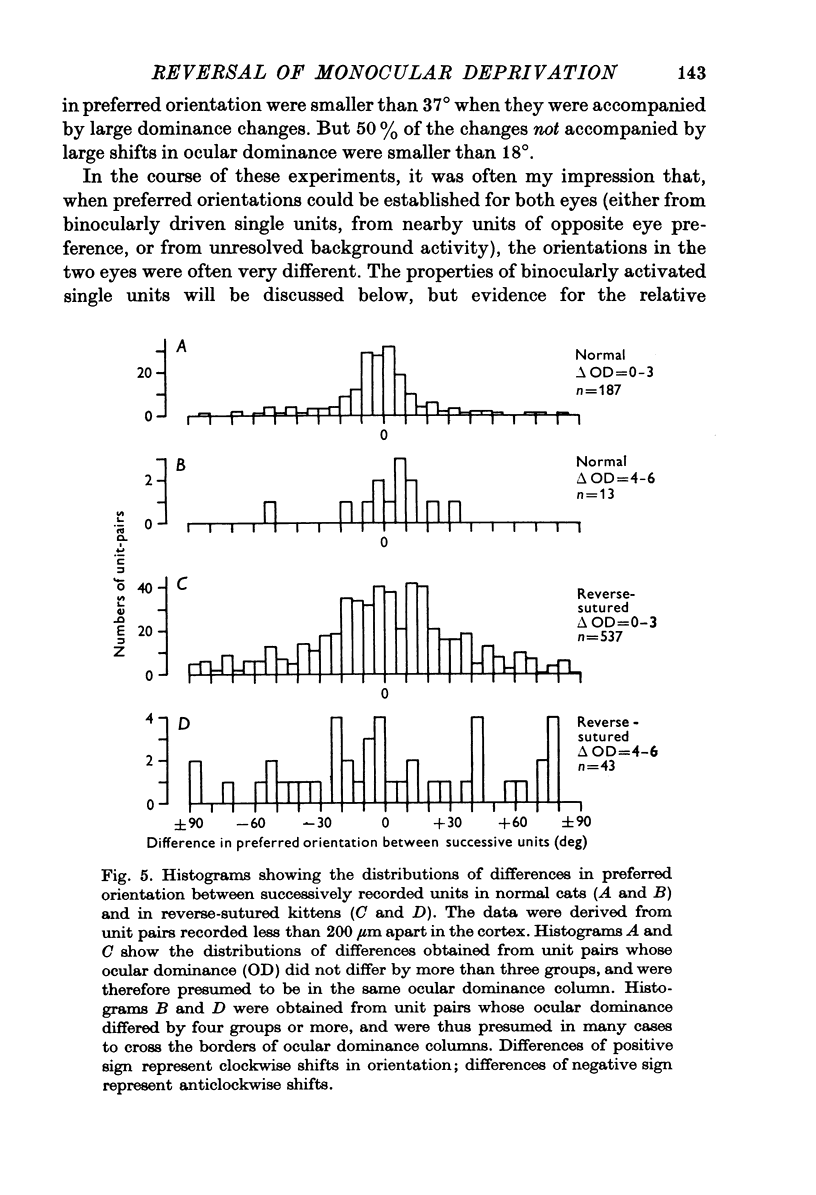
Abstract
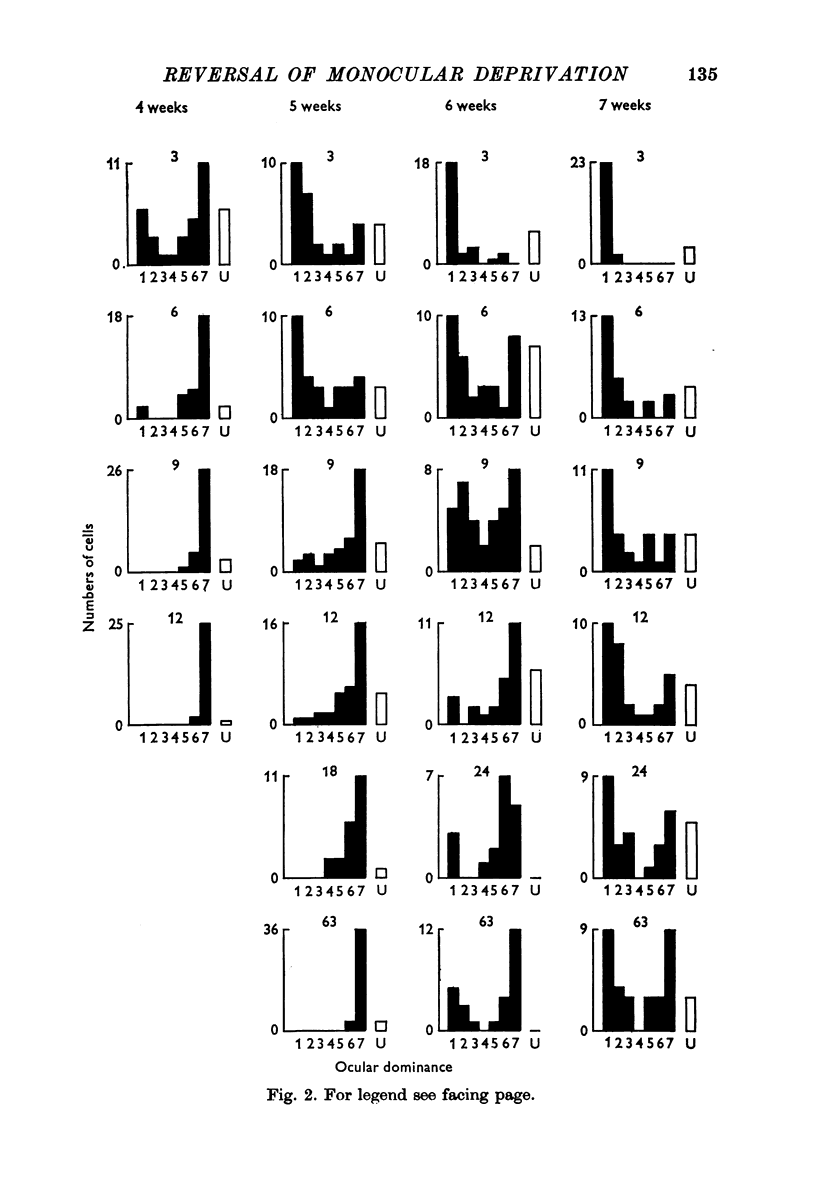
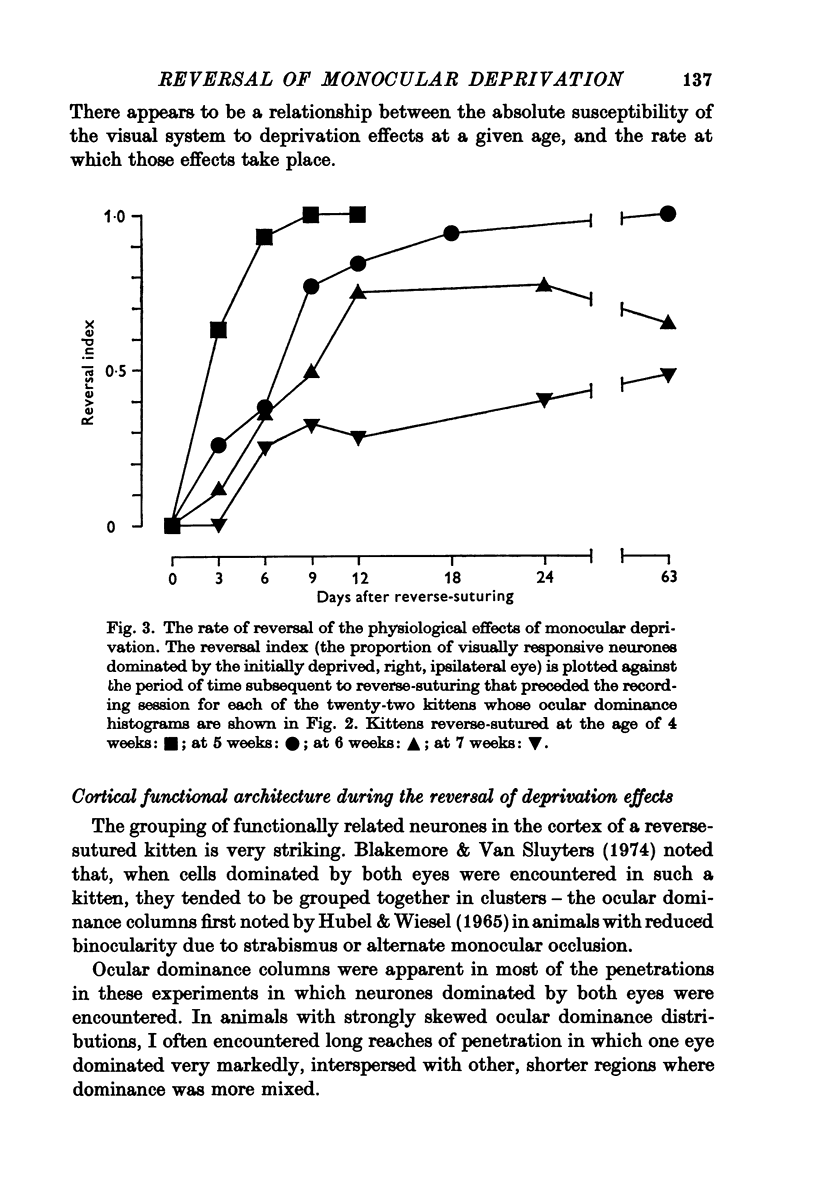
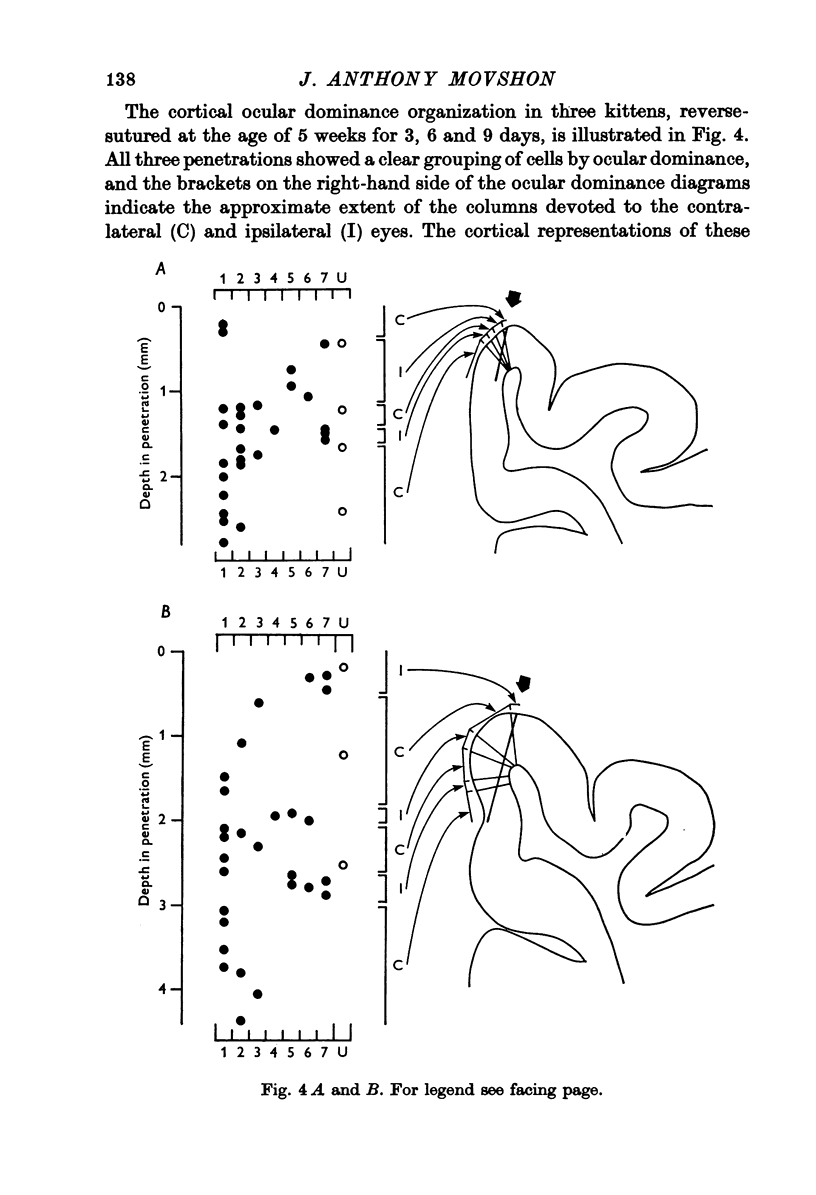
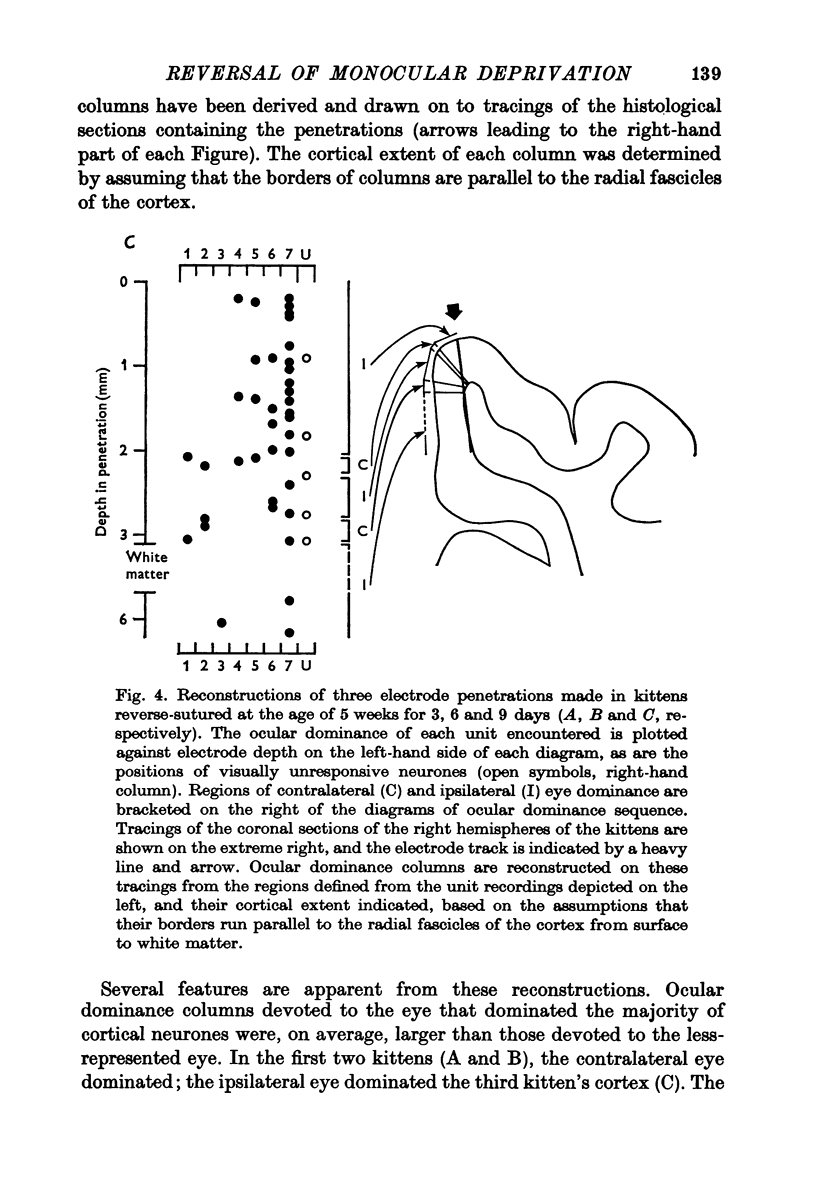
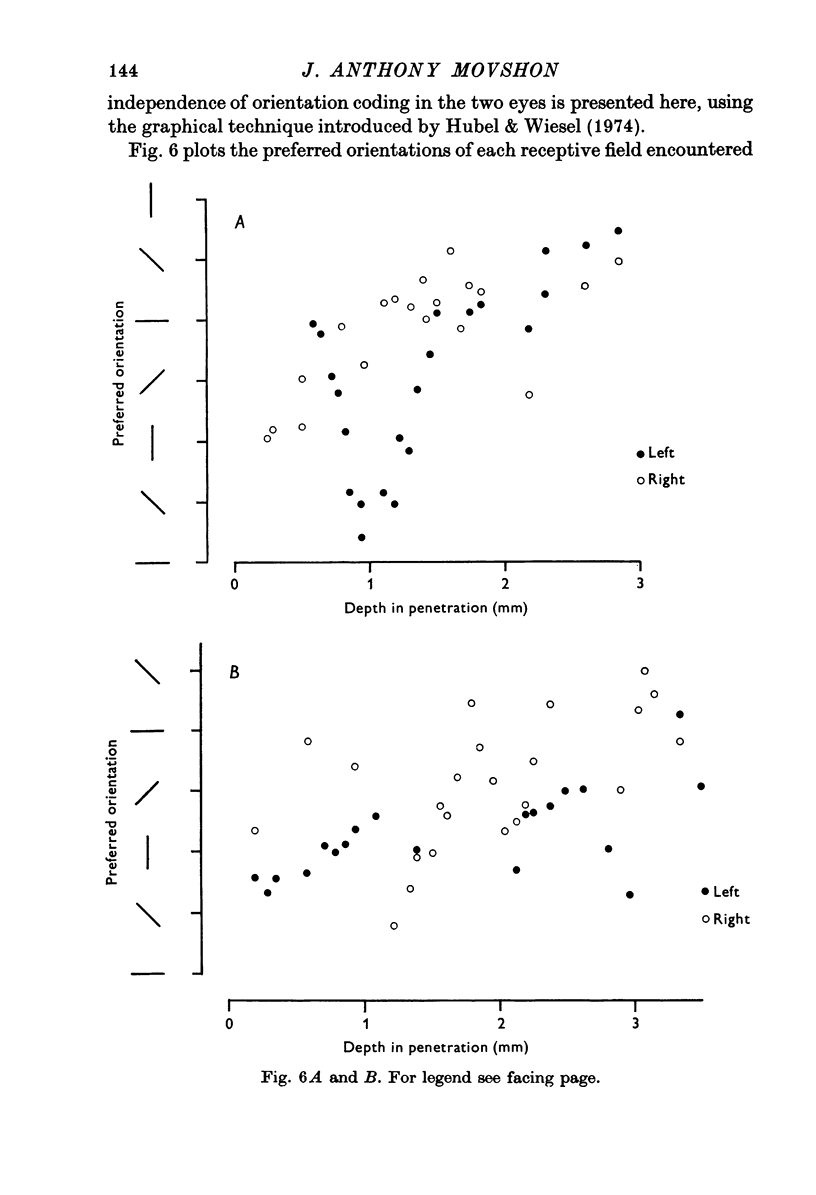
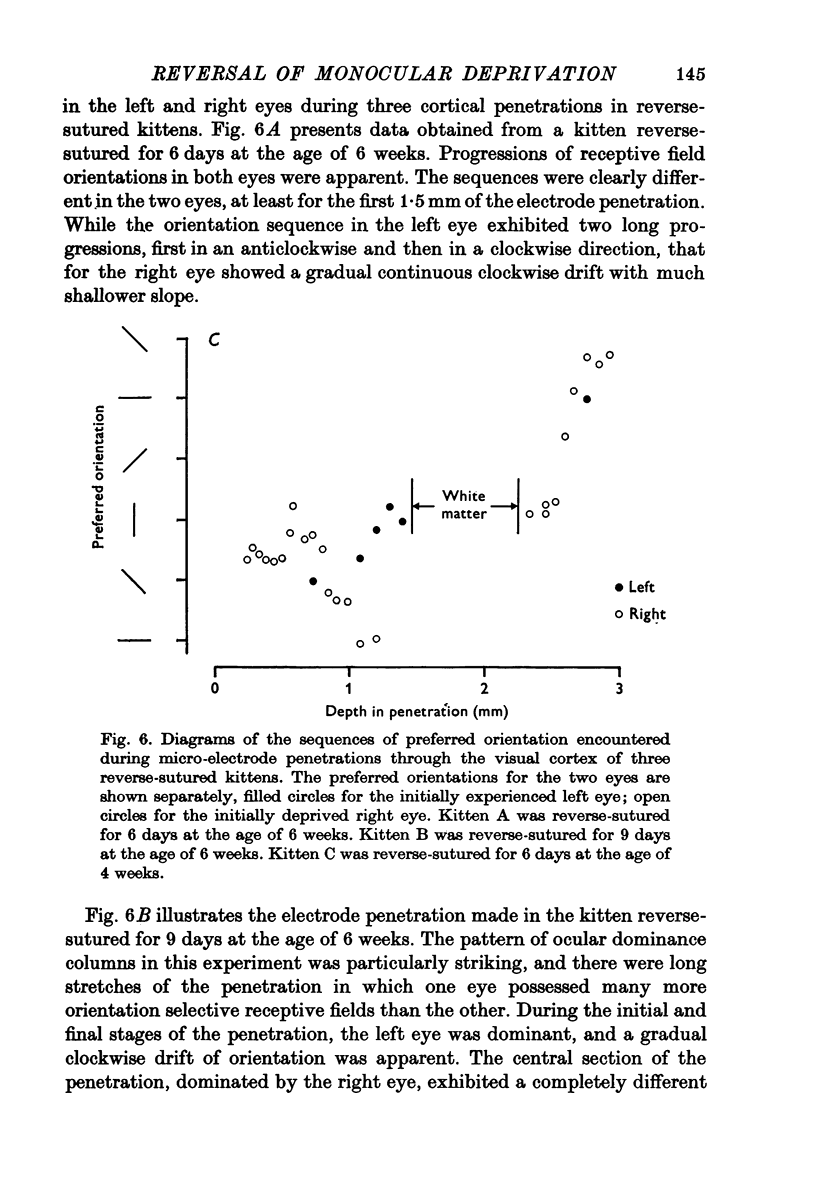
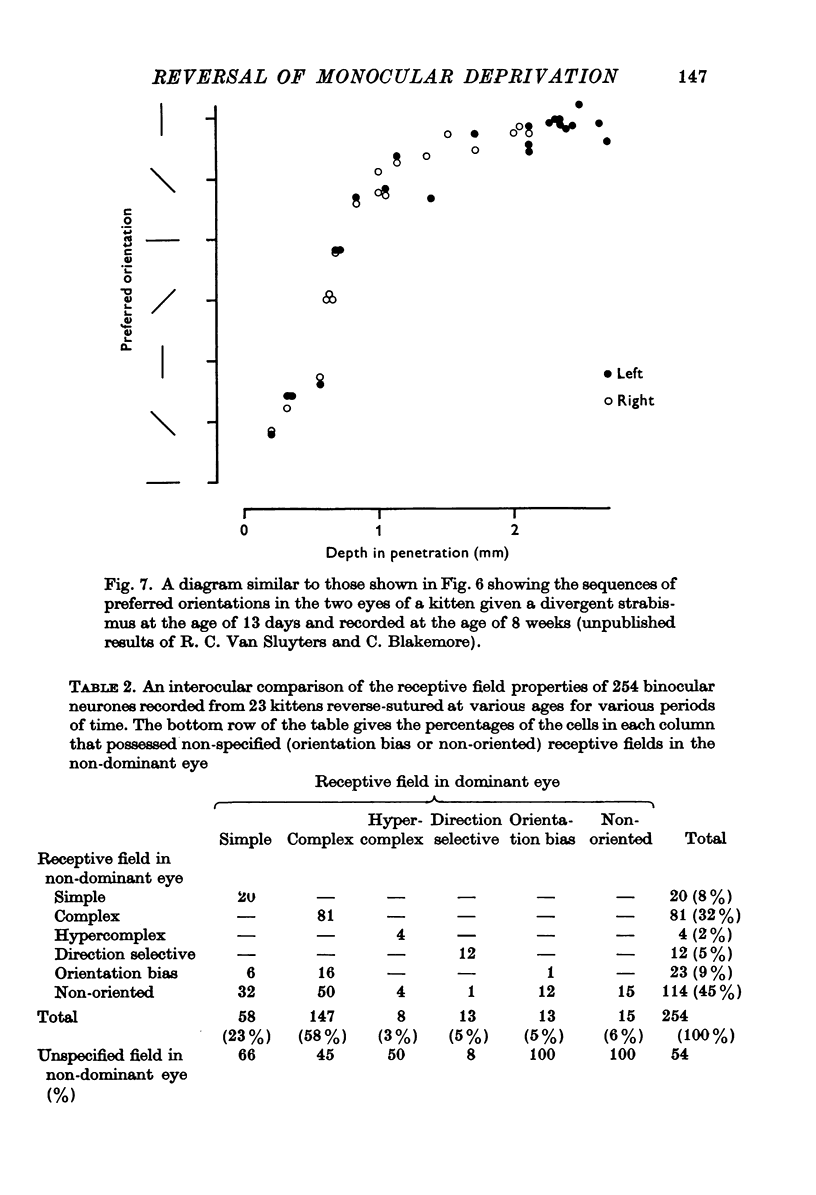
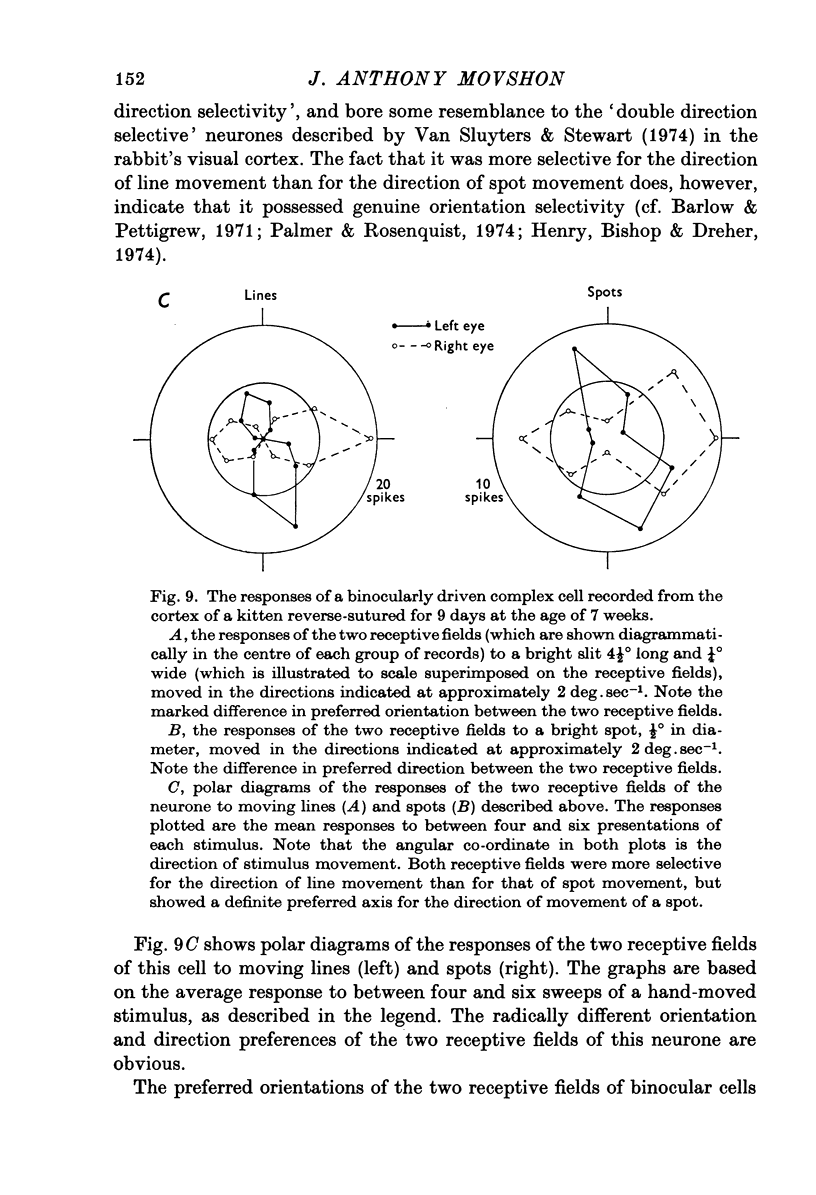
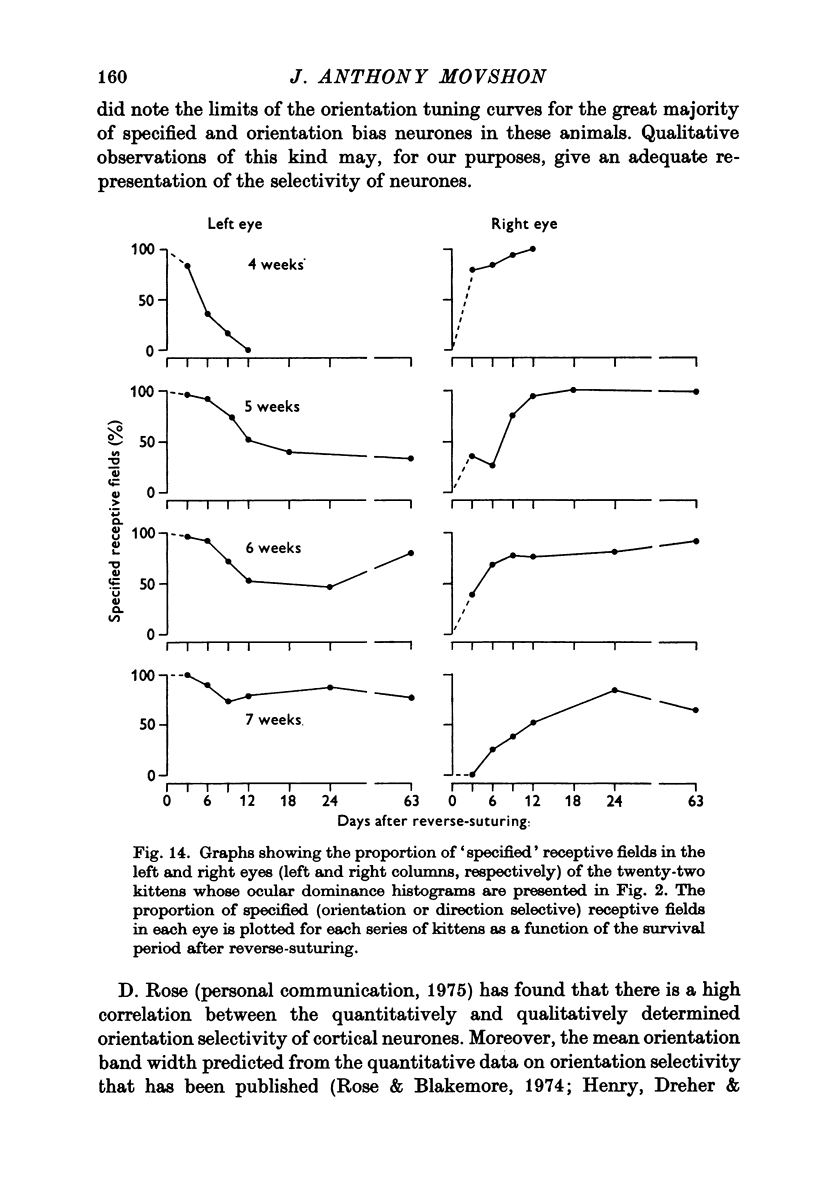
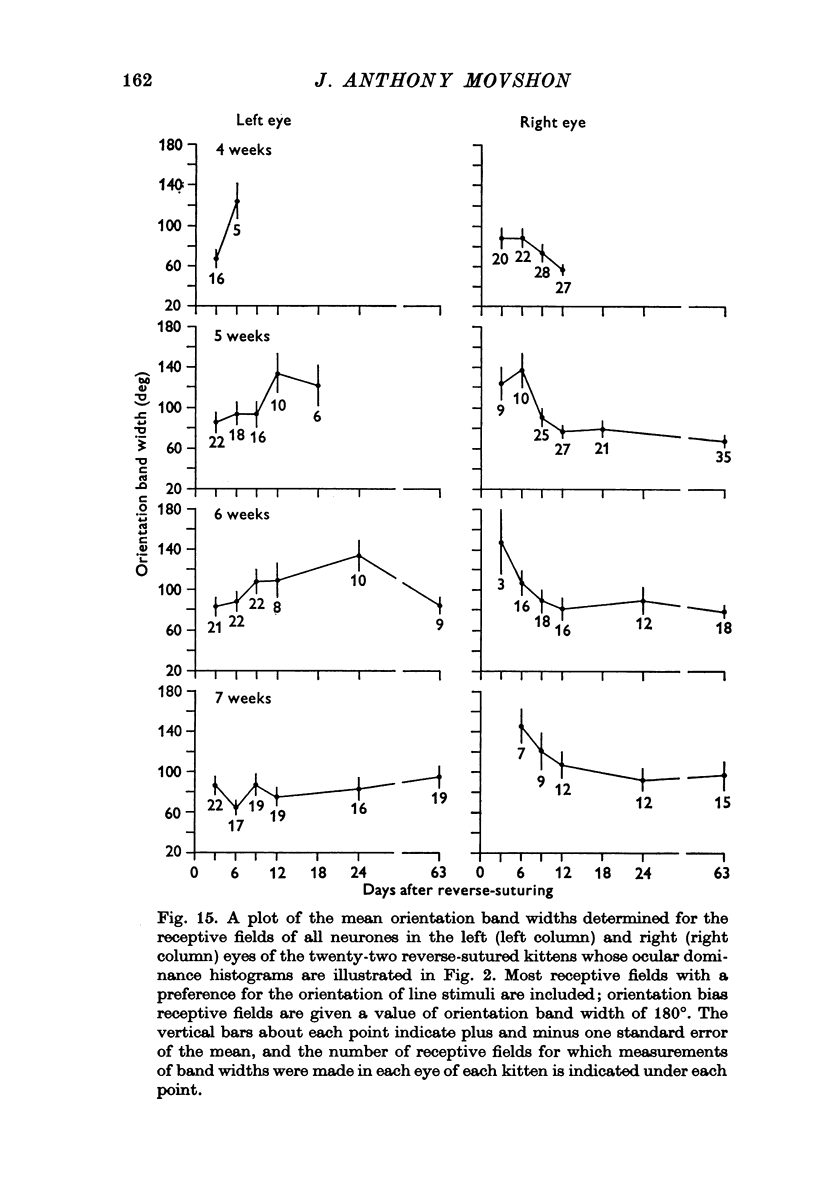
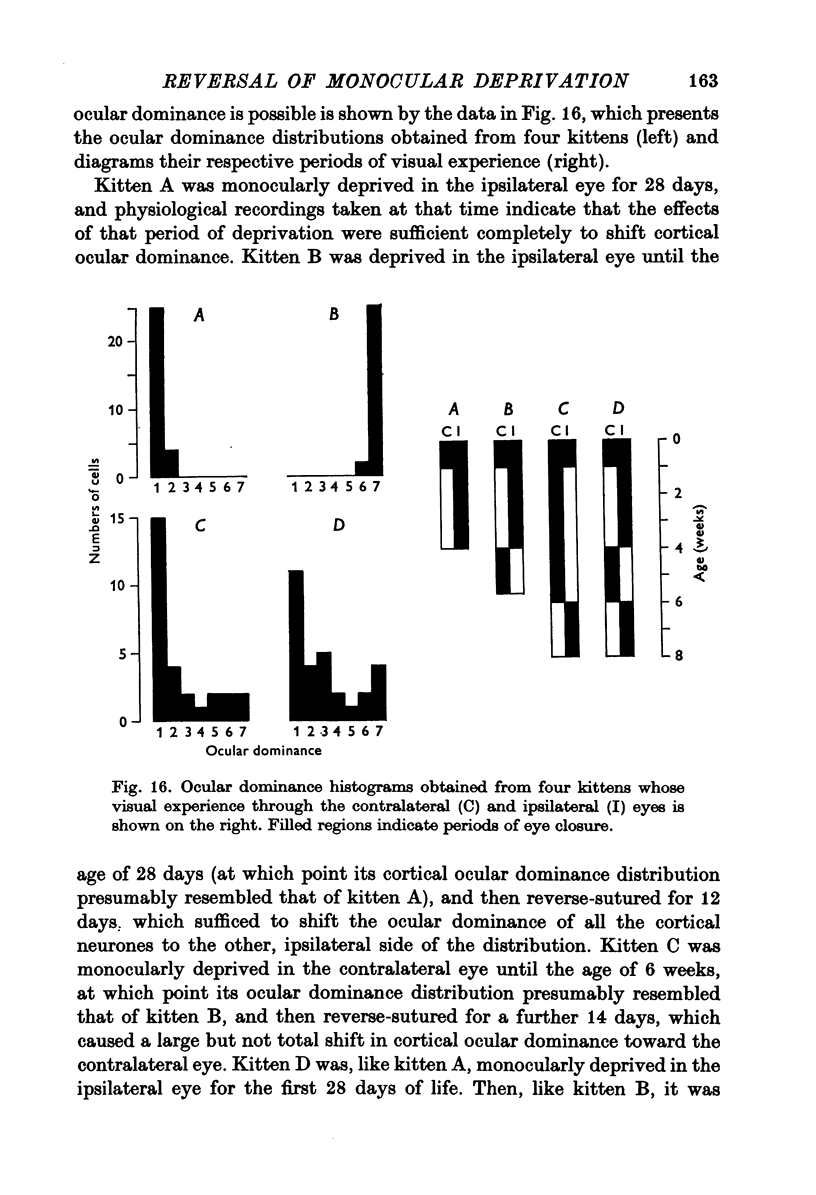
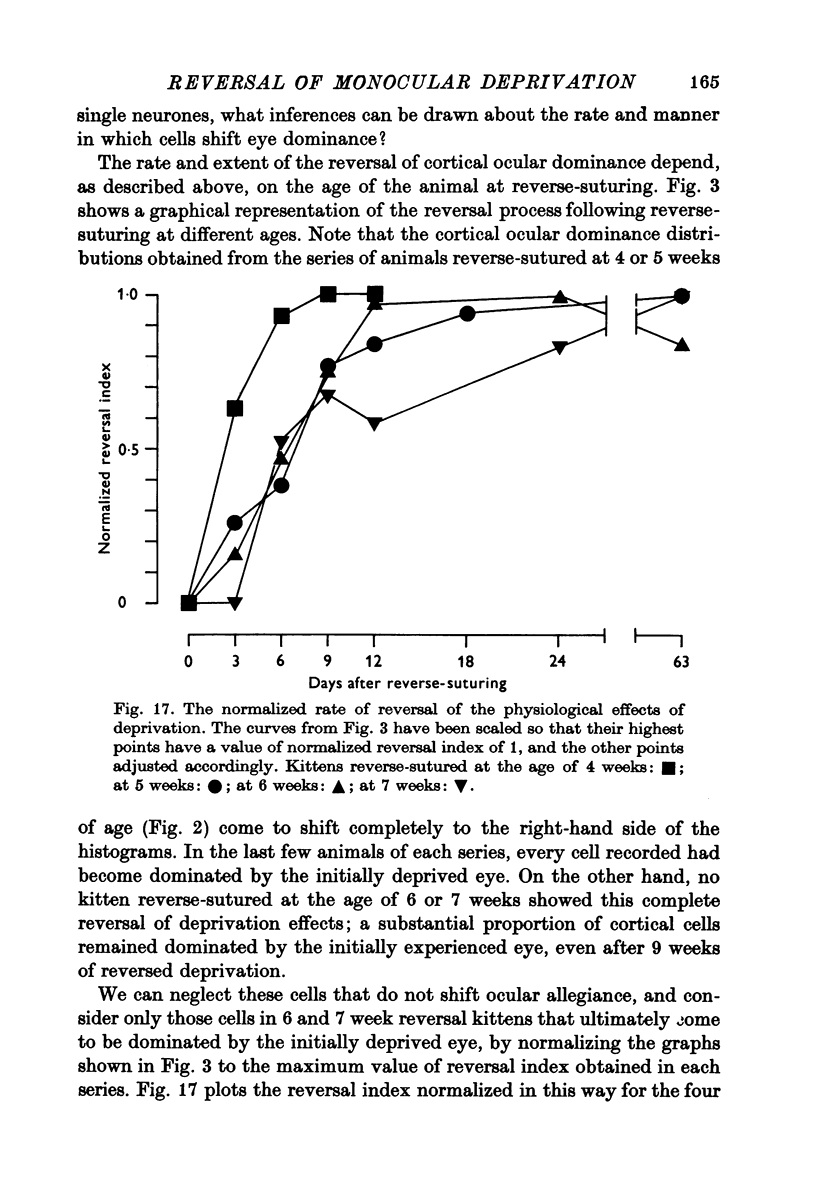
1. Twenty-three kittens were monocularly deprived of vision until the age of 4, 5, 6 or 7 weeks. Their deprived eyes were then opened, and their experienced eyes shut for a further 3-63 days. After this time physiological recordings were made in the visual cortex, area 17. Three control kittens, monocularly deprived for various periods, showed that at the time of reverse-suturing, few neurones could be influenced at all from the deprived eye. 2. Following reverse-suturing, the initially deprived eye regained control of cortical neurones. This switch of cortical ocular dominance was most rapid following reverse-suturing at the age of 4 weeks. Delaying the age of reverse-suturing reduced the rate and then the extent of the cortical ocular dominance changes. 3. The cortex of reverse-sutured kittens is divided into regions of cells dominated by one eye or the other. The relative sizes of these ocular dominance columns changed during reversed deprivation. The columns devoted to the initially deprived eye were very small in animals reverse-sutured for brief periods, but in animals that underwent longer periods of reversed deprivation, the columns driven by that eye were larger, while those devoted to the initially open eye were smaller. 4. Clear progressions of orientation columns across the cortex were apparent in many of the kittens, but, in contrast to the situation in normal or strabismic kittens, these sequences were disrupted at the borders of eye dominance columns: the cortical representations of orientation and ocular dominance were not independent. 5. Binocular units in these kittens were rather rare, but those that could be found often had dissimilar receptive field properties in the two eyes. Commonly, a cell would have a normal orientation selective receptive field in one eye, and an immature, unselective receptive field in the other. Cells that had orientation selective receptive fields in both eyes often had greatly differing orientation preferences in the two eyes, occasionally by nearly 90 degrees. 6. During the reversal of deprivation effects, the proportion of receptive fields exhibiting mature properties declined in the initially experienced eye, while the proportion increased in the initially deprived eye. Similarly, the average band width of orientation tuning of receptive fields in the initially deprived eye decreased, while that of receptive fields in the initially experienced eye increased. 7. One kitten was reverse-sutured twice, to demonstrate that cortical ocular dominance may be reversed a second time, even after one reversal of ocular dominance. 8. It is suggested that the sensitive period for cortical binocular development consists of two phases. In the first phase, all cortical neurones may be modified by experience, but the rate at which they may be modified decreases with age. In the second phase, an increasing number of cortical neurones becomes fixed in their properties, while those that remain modifiable are as modifiable as they were at the end of the first phase. 9...
Full text
PDF















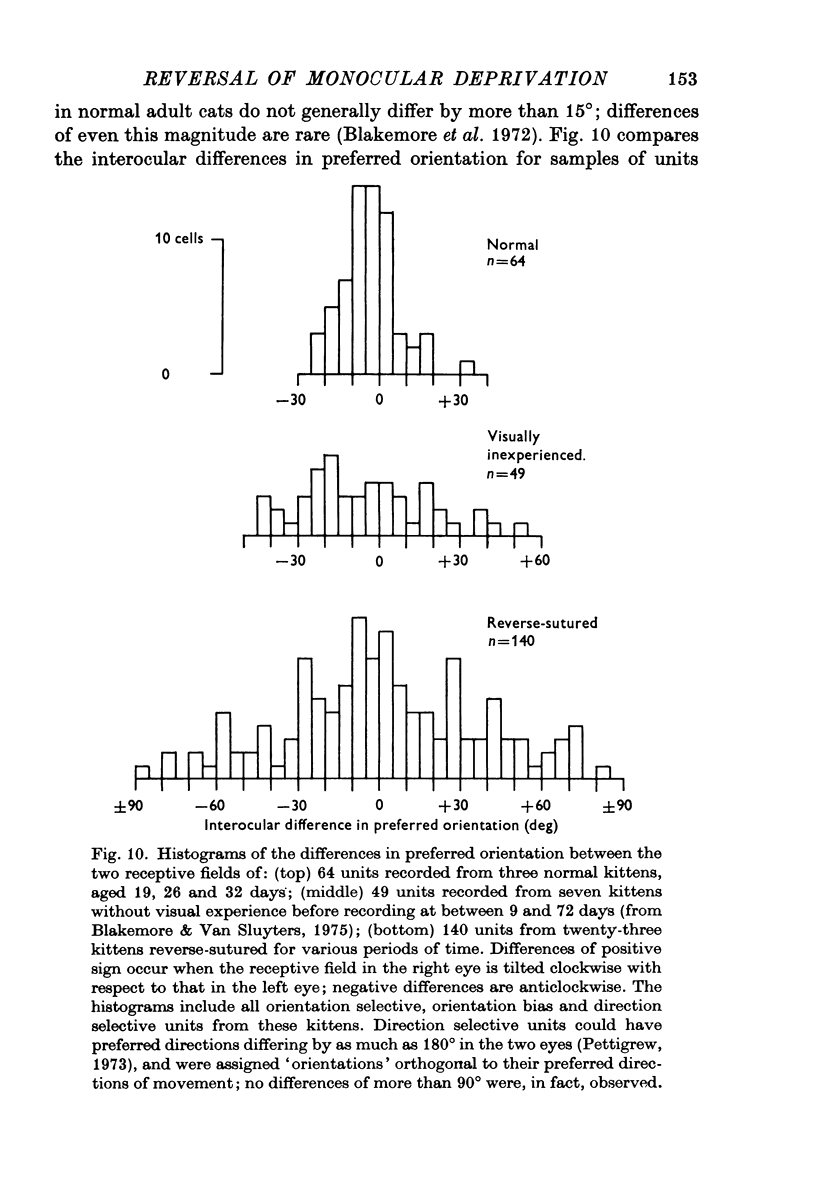

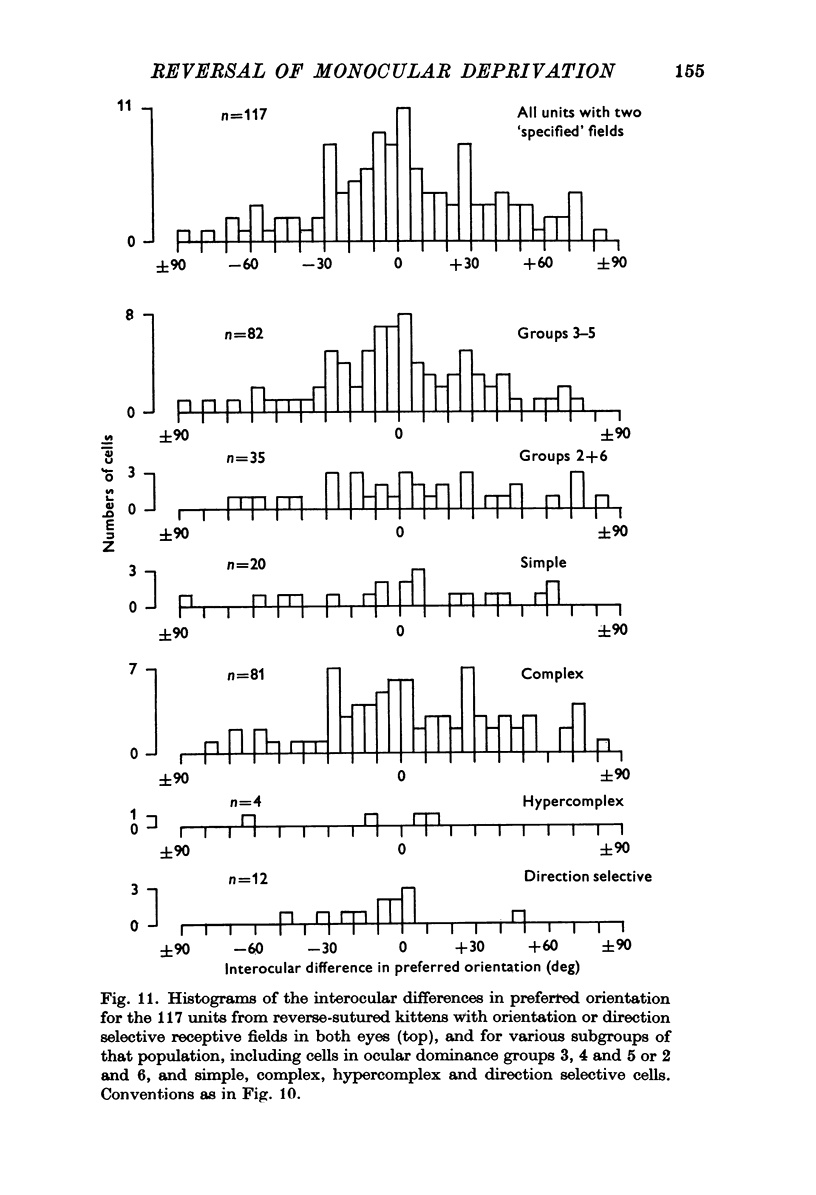
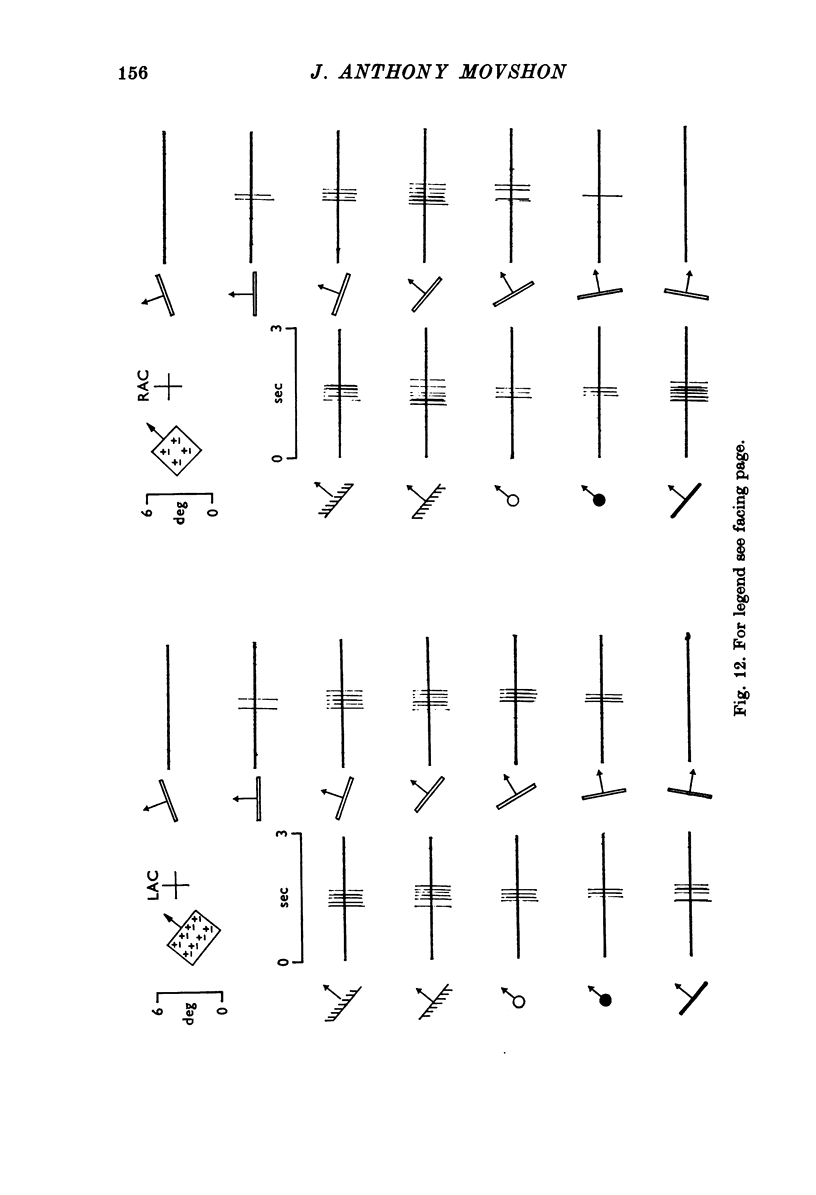

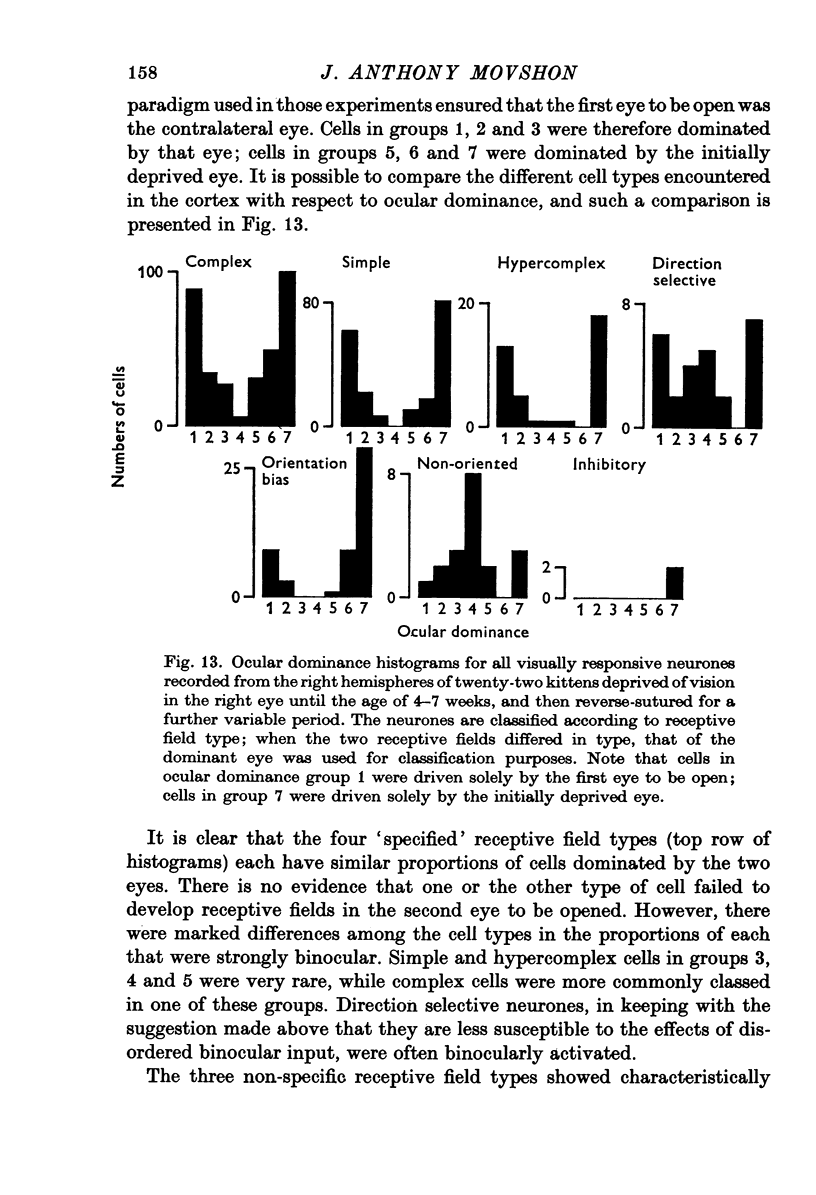












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARLOW H. B., HILL R. M., LEVICK W. R. RETINAL GANGLION CELLS RESPONDING SELECTIVELY TO DIRECTION AND SPEED OF IMAGE MOTION IN THE RABBIT. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;173:377–407. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow H. B., Blakemore C., Pettigrew J. D. The neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):327–342. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow H. B., Pettigrew J. D. Lack of specificity of neurones in the visual cortex of young kittens. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218 (Suppl):98P–100P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. O., Coombs J. S., Henry G. H. Interaction effects of visual contours on the discharge frequency of simple striate neurones. J Physiol. 1971 Dec;219(3):659–687. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop P. O., Coombs J. S., Henry G. H. Receptive fields of simple cells in the cat striate cortex. J Physiol. 1973 May;231(1):31–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Cooper G. F. Development of the brain depends on the visual environment. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):477–478. doi: 10.1038/228477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Donaghy M. J., Maffei L., Movshon J. A., Rose D., Van Sluyters R. C. Evidence that nitrous oxide can maintain anaesthesia after induction with barbiturates. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):39P–41P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Fiorentini A., Maffei L. A second neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. J Physiol. 1972 Nov;226(3):725–749. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Tobin E. A. Lateral inhibition between orientation detectors in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1972;15(4):439–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00234129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Van Sluyters C. V., Movshon J. A. Synaptic competition in the kitten's visual cortex. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:601–609. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Van Sluyters R. C. Innate and environmental factors in the development of the kitten's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;248(3):663–716. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore C., Van Sluyters R. C. Reversal of the physiological effects of monocular deprivation in kittens: further evidence for a sensitive period. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):195–216. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow K. L., Stewart D. L. Reversal of structural and functional effects of long-term visual deprivation in cats. Exp Neurol. 1972 Mar;34(3):409–433. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(72)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland B. G., Levick W. R. Brisk and sluggish concentrically organized ganglion cells in the cat's retina. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(2):421–456. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cragg B. G. The development of synapses in the visual system of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Mar 15;160(2):147–166. doi: 10.1002/cne.901600202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutzfeldt O. D., Kuhnt U., Benevento L. A. An intracellular analysis of visual cortical neurones to moving stimuli: response in a co-operative neuronal network. Exp Brain Res. 1974;21(3):251–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00235746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürsteler M. R., Garey L. J., Movshon J. A. Reversal of the morphological effects of monocular deprivation in the kittens's lateral geniculate nucleus. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):189–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enroth-Cugell C., Robson J. G. Proceedings: Direct measurement of image quality in the cat eyes. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):30P–31P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon B., Gummow L. Effects of extraocular muscle section on receptive fields in cat superior colliculus. Vision Res. 1975 Aug-Sep;15:1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(75)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. RECEPTIVE FIELDS OF CELLS IN STRIATE CORTEX OF VERY YOUNG, VISUALLY INEXPERIENCED KITTENS. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:994–1002. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Jan;160:106–154. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBEL D. H., WIESEL T. N. Shape and arrangement of columns in cat's striate cortex. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165:559–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. H., Bishop P. O., Dreher B. Orientation, axis and direction as stimulus parameters for striate cells. Vision Res. 1974 Sep;14(9):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(74)90141-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry G. H., Dreher B., Bishop P. O. Orientation specificity of cells in cat striate cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1974 Nov;37(6):1394–1409. doi: 10.1152/jn.1974.37.6.1394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess R., Murata K. Effects of glutamate and GABA on specific response properties of neurones in the visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1974;21(3):285–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00235748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Binocular interaction in striate cortex of kittens reared with artificial squint. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Nov;28(6):1041–1059. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.6.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Laminar and columnar distribution of geniculo-cortical fibers in the macaque monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Dec;146(4):421–450. doi: 10.1002/cne.901460402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N., LeVay S. Functional architecture of area 17 in normal and monocularly deprived macaque monkeys. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:581–589. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):215–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Sequence regularity and geometry of orientation columns in the monkey striate cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Dec 1;158(3):267–293. doi: 10.1002/cne.901580304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. The period of susceptibility to the physiological effects of unilateral eye closure in kittens. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):419–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. Development of specific neuronal connections. Science. 1969 Feb 7;163(3867):543–547. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3867.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeVay S., Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. The pattern of ocular dominance columns in macaque visual cortex revealed by a reduced silver stain. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Feb 15;159(4):559–576. doi: 10.1002/cne.901590408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick W. R. Another tungsten microelectrode. Med Biol Eng. 1972 Jul;10(4):510–515. doi: 10.1007/BF02474199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levick W. R. Receptive fields and trigger features of ganglion cells in the visual streak of the rabbits retina. J Physiol. 1967 Feb;188(3):285–307. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotte L. R., Mark R. F. The mechanism of selective reinnervation of fish eye muscle. I. Evidence from muscle function during recovery. Brain Res. 1970 Apr 1;19(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotte L. R., Mark R. P. The mechanism of selective reinnervation of fish eye muscle. II. Evidence from electronmicroscopy of nerve endings. Brain Res. 1970 Apr 1;19(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(70)90236-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movshon J. A., Blakemore C. Functional reinnervation in kitten visual cortex. Nature. 1974 Oct 11;251(5475):504–505. doi: 10.1038/251504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movshon J. A. Reversal of the behavioural effects of monocular deprivation in the kitten. J Physiol. 1976 Sep;261(1):175–187. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTSUKA R., HASSLER R. [On the structure and segmentation of the cortical center of vision in the cat]. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1962;203:212–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00352744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer L. A., Rosenquist A. C. Visual receptive fields of single striate corical units projecting to the superior colliculus in the cat. Brain Res. 1974 Feb 15;67(1):27–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90295-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D. Binocular neurons which signal change of disparity in area 18 of cat visual cortex. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 24;241(108):123–124. doi: 10.1038/newbio241123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D., Nikara T., Bishop P. O. Binocular interaction on single units in cat striate cortex: simultaneous stimulation by single moving slit with receptive fields in correspondence. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(4):391–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00233186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D., Olson C., Hirsch H. V. Cortical effect of selective visual experience: degeneration or reorganization? Brain Res. 1973 Mar 15;51:345–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90387-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Blakemore C. An analysis of orientation selectivity in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Apr 30;20(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00239014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stent G. S. A physiological mechanism for Hebb's postulate of learning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Sluyters R. C., Stewart D. L. Binocular neurons of the rabbit's visual cortex: receptive field characteristics. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Jan 31;19(2):166–195. doi: 10.1007/BF00238533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESEL T. N., HUBEL D. H. EFFECTS OF VISUAL DEPRIVATION ON MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF CELLS IN THE CATS LATERAL GENICULATE BODY. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:978–993. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIESEL T. N., HUBEL D. H. SINGLE-CELL RESPONSES IN STRIATE CORTEX OF KITTENS DEPRIVED OF VISION IN ONE EYE. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Nov;26:1003–1017. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.6.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins D. W., Berkley M. A. The orientation selectivity of single neurons in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1974 Feb 28;19(4):433–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00234465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickelgren-Gordon B. Some effects of visual deprivation on the cat superior colliculus. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Jun;11(6):460–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel T. N., Hubel D. H. Comparison of the effects of unilateral and bilateral eye closure on cortical unit responses in kittens. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Nov;28(6):1029–1040. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.6.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel T. N., Hubel D. H. Extent of recovery from the effects of visual deprivation in kittens. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Nov;28(6):1060–1072. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.6.1060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel T. N., Hubel D. H., Lam D. M. Autoradiographic demonstration of ocular-dominance columns in the monkey striate cortex by means of transneuronal transport. Brain Res. 1974 Oct 18;79(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(74)90416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesel T. N., Hubel D. H. Ordered arrangement of orientation columns in monkeys lacking visual experience. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Dec 1;158(3):307–318. doi: 10.1002/cne.901580306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


