Abstract
1. Sulphated glycoprotein output from the trachea, isolated in situ, has been measured in anaesthetized cats by a radio-isotopic method. The effects of irritation of various parts of the airway on this mucus output were studied. 2. Mechanical stimulation of the nose and nasopharynx increased tracheal mucus output by reflexes which involved parasympathetic and probably also sympathetic motor pathways. 3. Laryngeal stimulation had a similar through the same motor pathways. 4. Inhalation of ammonia vapour into the lower airways reflexly increased mucus output from the isolated trachea. The efferent pathway for this reflex was mainly or entirely parasympathetic. It is argued that the afferent pathway involved cough receptors. 5. Lung inflation, inhalation of histamine aerosol and intravenous injection of phenyl diguanide (which excite mainly lung stretch receptors, lung 'irritant' receptors and alveolar 'J-receptors' respectively) had no consistent effect on tracheal mucus secretion. 6. The afferent and efferent pathways of these reflexes are discussed.
Full text
PDF

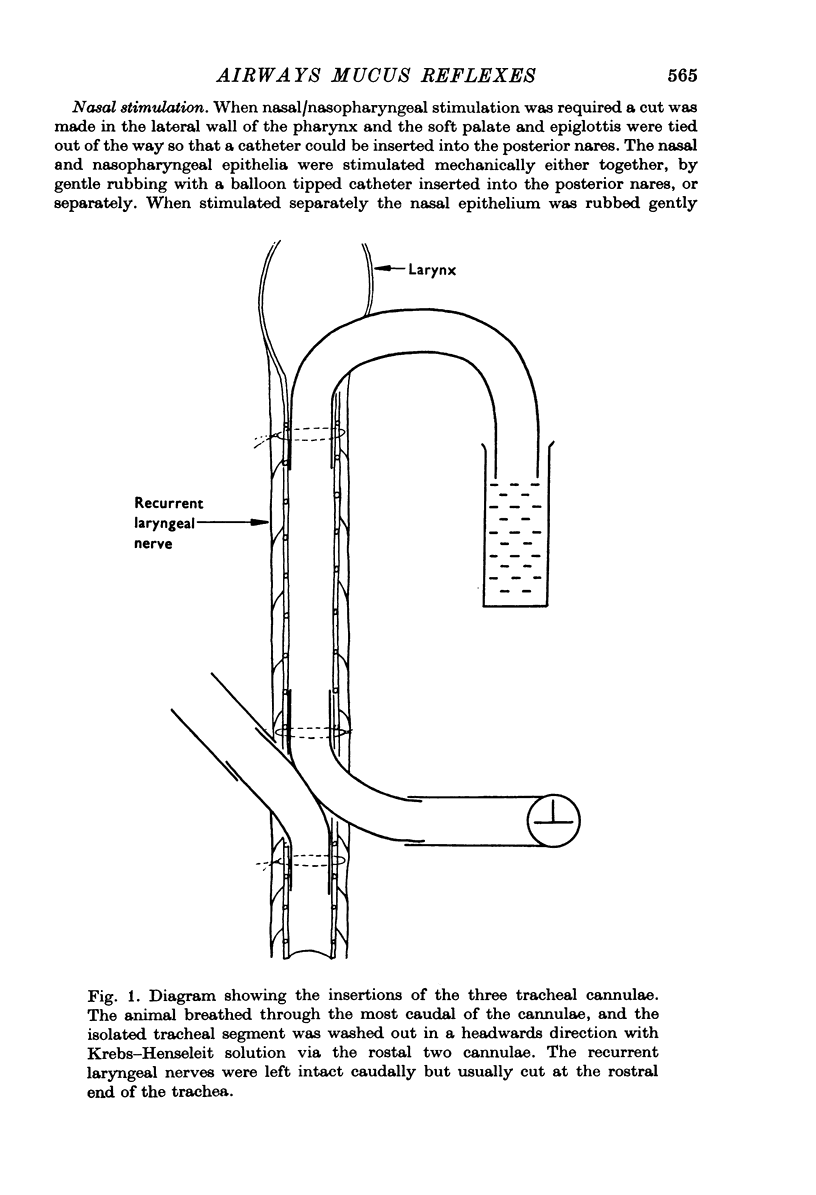





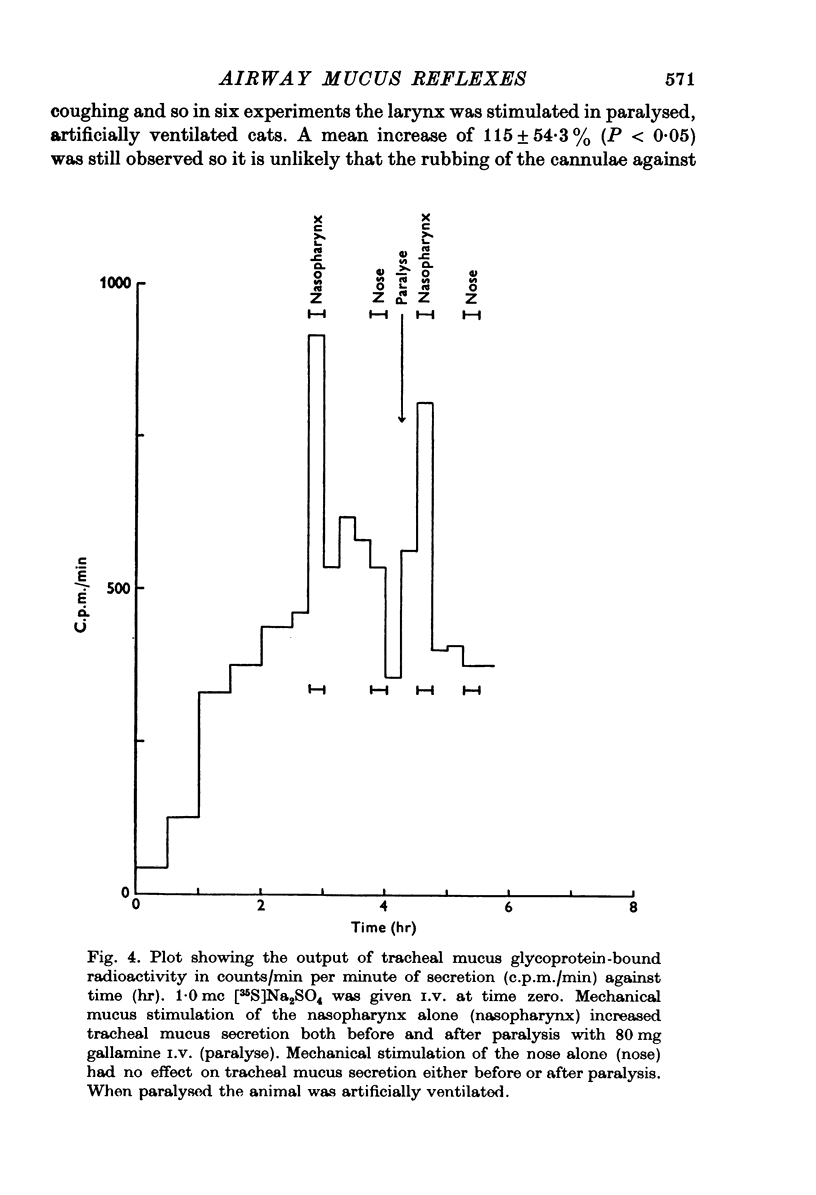










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D. Afferent impulses in the vagus and their effect on respiration. J Physiol. 1933 Oct 6;79(3):332–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1933.sp003053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison D. J., Clay T. P., Hughes J. M., Jones H. A., Shevis A. Effects of nasal stimulation on total respiratory resistance in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):23P–24P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D. J., Luck J. C. A comparative study of irritant and type J receptors in the cat. Respir Physiol. 1974 Jul;21(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(74)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushey H. A., Richardson P. S., Widdicombe J. G. Reflex effects of laryngeal irritation on the pattern of breathing and total lung resistance. J Physiol. 1972 Jul;224(2):501–513. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boushey H. A., Richardson P. S., Widdicombe J. G., Wise J. C. The response of laryngeal afferent fibres to mechanical and chemical stimuli. J Physiol. 1974 Jul;240(1):153–175. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody J. S., Klempfner G., Staum M. M., Vidyasagar D., Kuhl D. E., Waldhausen J. A. Mucociliary clearance after lung denervation and bronchial transection. J Appl Physiol. 1972 Feb;32(2):160–164. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1972.32.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher J. T., Kent P. W., Passatore M., Phipps R. J., Richardson P. S. The composition of tracheal mucus and the nervous control of its secretion in the cat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Dec 31;192(1106):49–76. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. EFFECT OF SUPERIOR LARYNGEAL NERVES ON TRACHEAL MUCUS: AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE RELATIONSHIP. Ann Surg. 1935 Jan;101(1):494–499. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193501000-00053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski W., Widdicombe J. G. The role of the vagus nerves in the respiratory and circulatory responses to intravenous histamine and phenyl diguanide in rabbits. J Physiol. 1969 Apr;201(2):271–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. E., Sellick H., Widdicombe J. G. Activity of lung irritant receptors in pulmonary microembolism, anaphylaxis and drug-induced bronchoconstrictions. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(2):337–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nail B. S., Sterling G. M., Widdicombe J. G. Epipharyngeal receptors responding to mechanical stimulation. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):91–98. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paintal A. S. Mechanism of stimulation of type J pulmonary receptors. J Physiol. 1969 Aug;203(3):511–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID L. Chronic bronchitis and hypersecretion of mucus. Lect Sci Basis Med. 1958 1959;8:235–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellick H., Widdicombe J. G. Stimulation of lung irritant receptors by cigarette smoke, carbon dust, and histamine aerosol. J Appl Physiol. 1971 Jul;31(1):15–19. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1971.31.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomori Z., Widdicombe J. G. Muscular, bronchomotor and cardiovascular reflexes elicited by mechanical stimulation of the respiratory tract. J Physiol. 1969 Jan;200(1):25–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. Receptors in the trachea and bronchi of the cat. J Physiol. 1954 Jan;123(1):71–104. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDDICOMBE J. G. The activity of pulmonary stretch receptors during bronchoconstriction, pulmonary oedema, atelectasis and breathing against a resistance. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:436–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widdicombe J. G. Action potentials in parasympathetic and sympathetic efferent fibres to the trachea and lungs of dogs and cats. J Physiol. 1966 Sep;186(1):56–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


