Abstract
1. Ionic currents of the egg membrane of a certain tunicate. Halocynthia roretzi Drashe, were studied by the voltage-clamp technique. 2. The membrane depolarization beyond -55mV in standard artificial sea water induced mainly transient inward current and slight outward currents, when the holding potential was kept at -99 mV. 3. The transient inward current was composed of two components; the major one showed a faster time course, a more negative critical level of about -55 mV, and a reversal potential around +60 mV and the minor one showed a slower time course, a less negative critical level o -10 mV, and no definite reversal potential. 4. The major component became maximum at about -25 mV with the peak time of 6-9 msec at 15 degrees C, and the maximum currents ranged from 0-5 to 1-5 X 10(-5) A/cm2. 5. The major component of the inward current was abolished by the replacement of Na with choline or Tris or Cs ions, while it was almost unaltered by the replacement with Li. The minor component was independent of Na concentration in the external solution. 6. The major component showed the activation and inactivation identical with those of Na current of other excitable membranes. A conditioning depolarization over -90 mV inactivated the Na current and the half inactivation of the major inward current was obtained by a conditioning pulse to -56 mV, when the pulse duration was 400 msec and the temperature was at 15 degrees C. 7. The time course of the Na current was formulated with m and h parameters in the following equations: (see article). 8. The kinetic parameters taum and tauh of egg Na current were calculated and compared with those of the squid axon. The potential dependence of taum and tauh was almost identical with that of the axon, but the absolute values of both taum and tauh were ten- to twentyfold larger than those of the axon in any range of the membrane potential. 9. The temperature depdence of the kinetic parameters taum, tauh and of the chord conductance gNa was studied. The Q10's for taum and tauh were both 4-0, while the Q10 for gNa was 2-0 in the temperature range from 5 to 20 degrees C. 10. The outward and inward rectifying conductances of egg membrane were remarkably activated at the potential level above +100 mV and below -70 mV respectively in standard artificial sea water. Both increased currents were subsequently subject to inactivation. 11. It was suggested that Na, Ca, K inward rectifying and K outward rectifying conductances all exist separately in the egg cell membrane and the Na current was essentially identical with that through the Na channel in other excitable membranes.
Full text
PDF


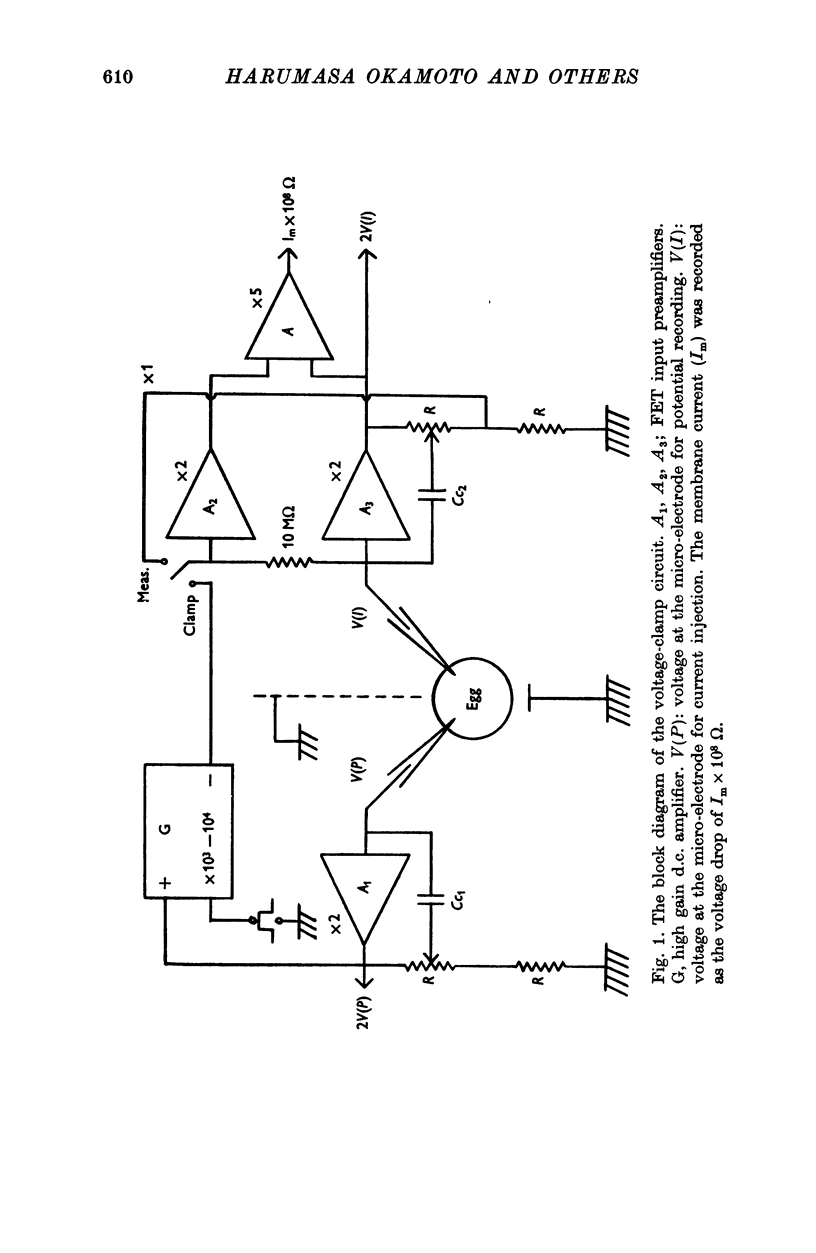

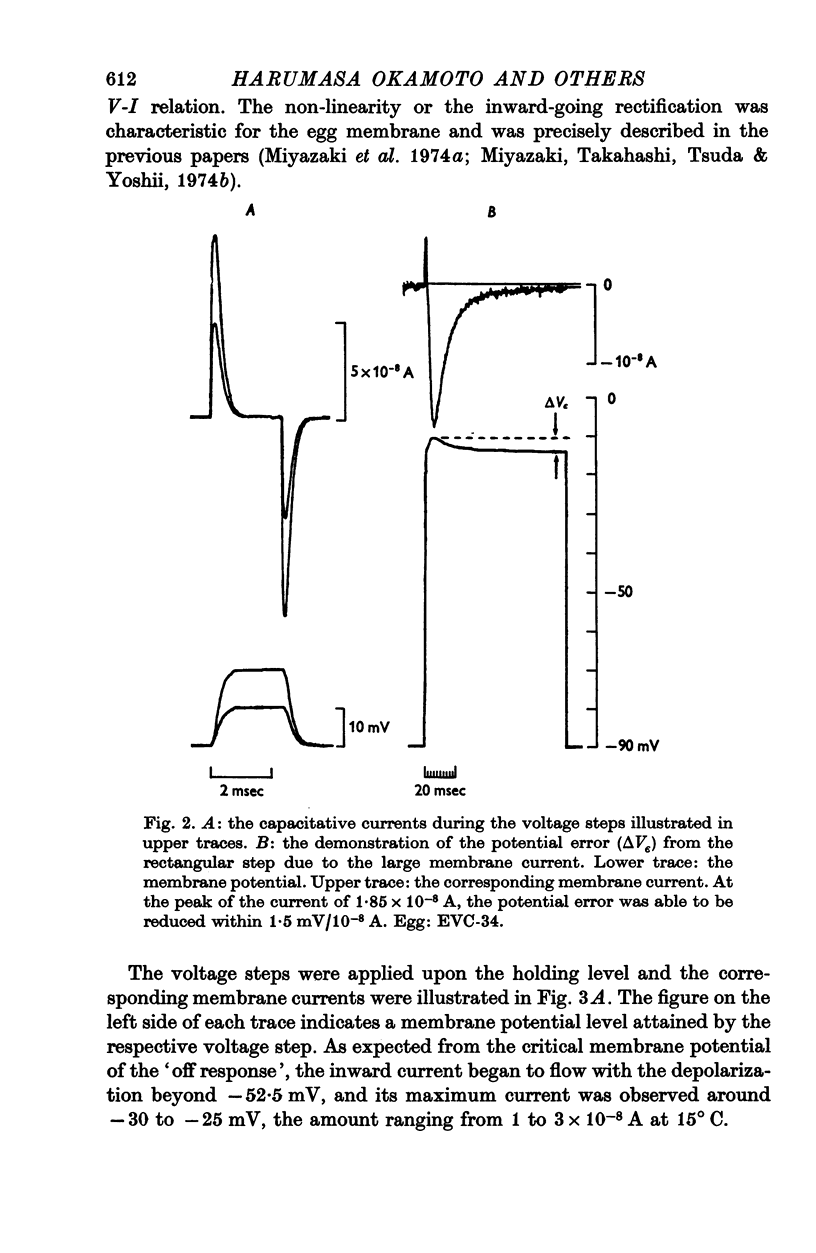
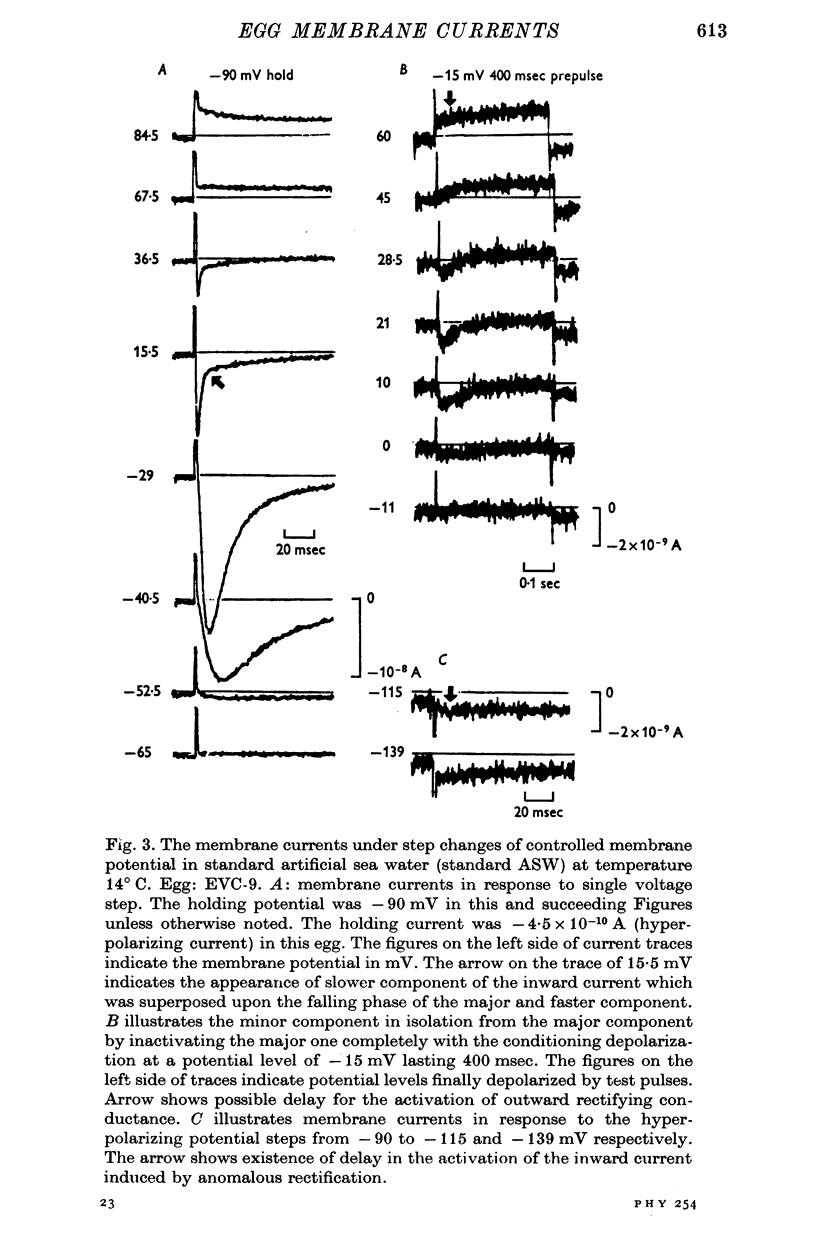

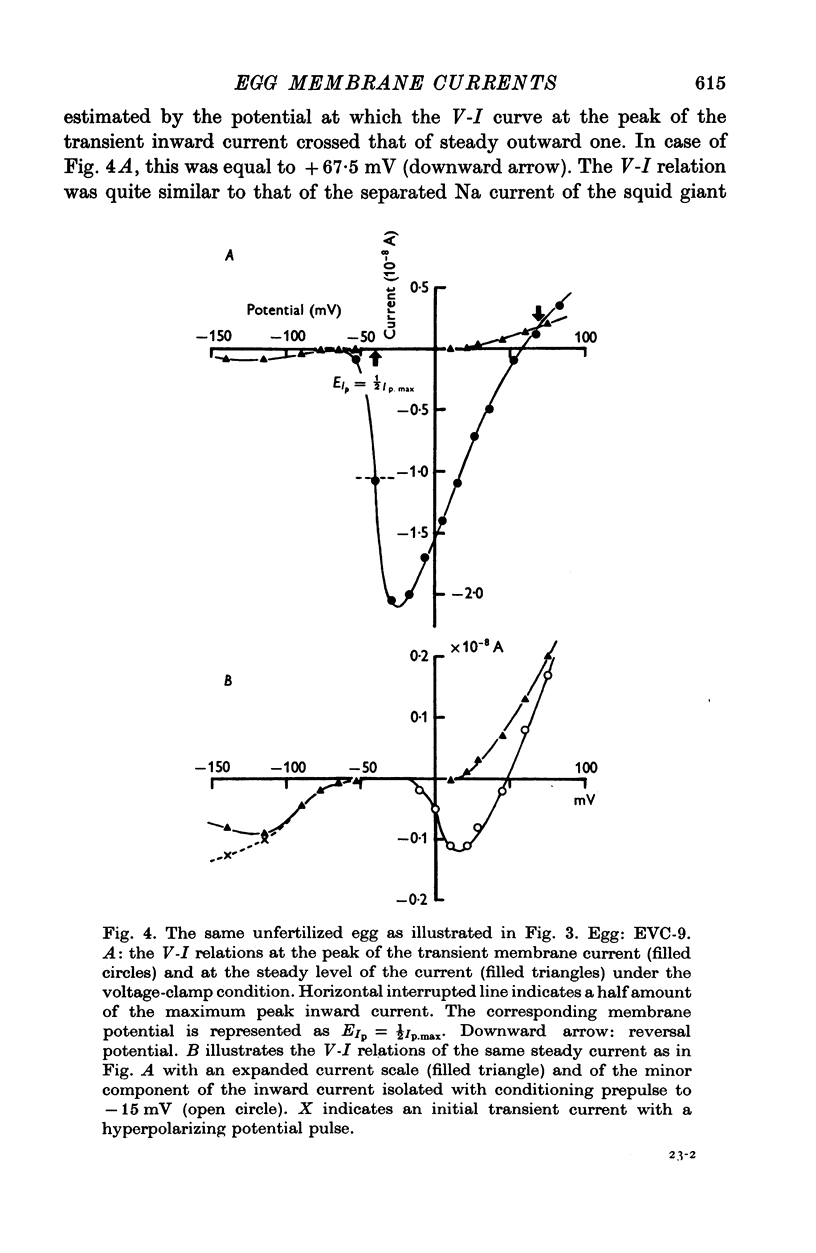
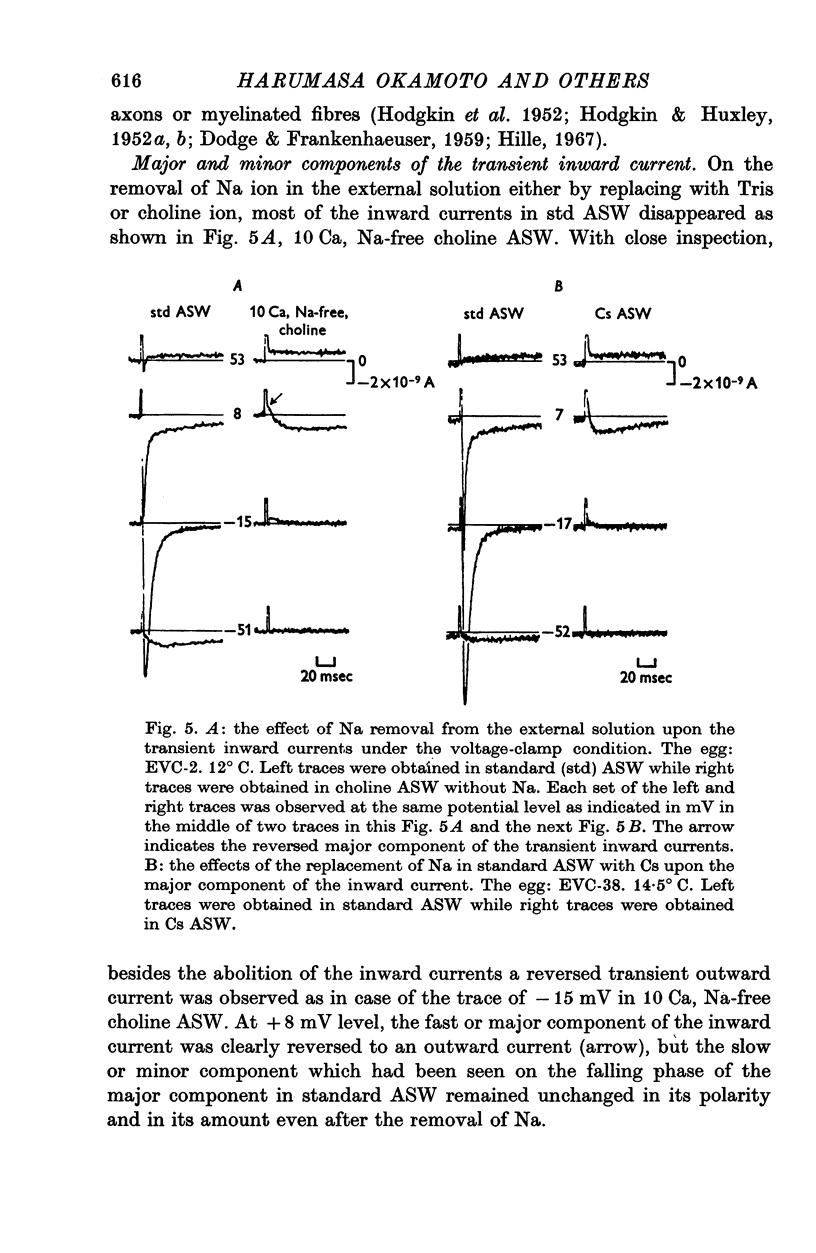
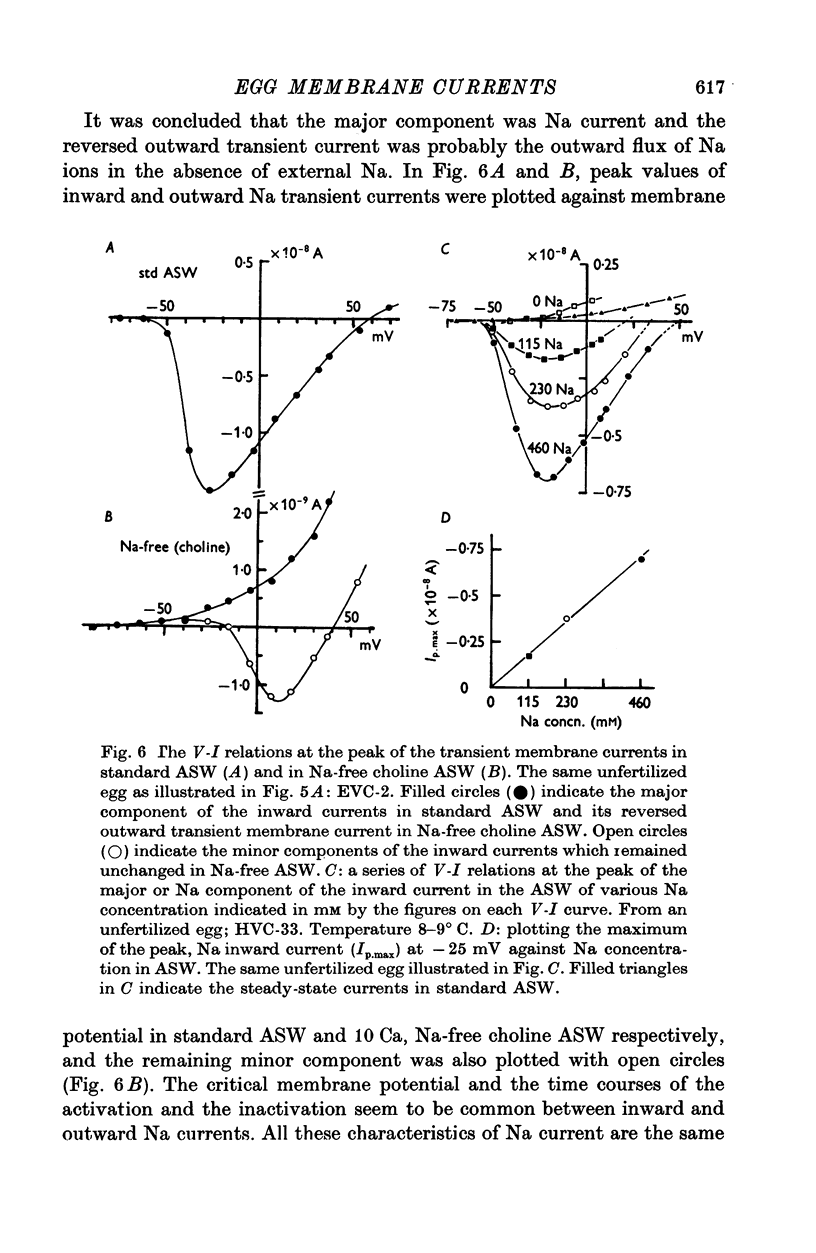

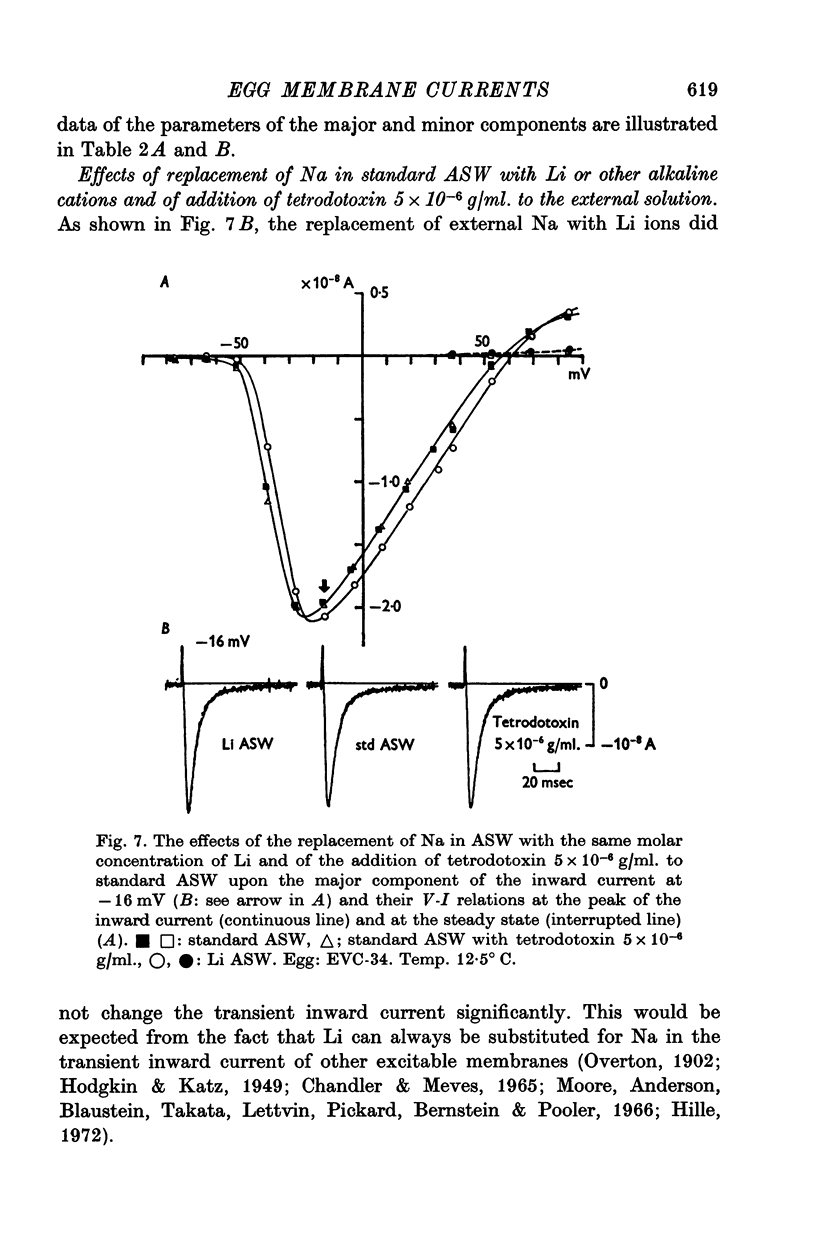
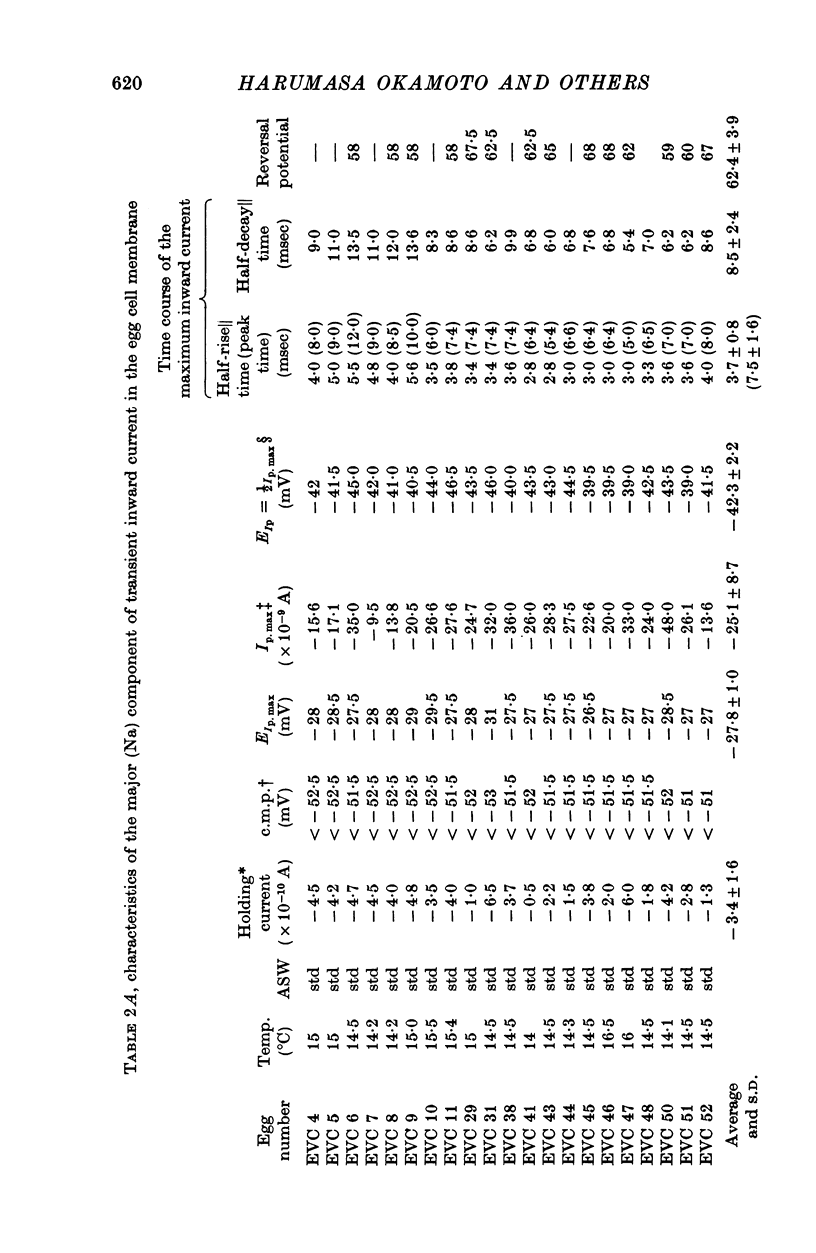
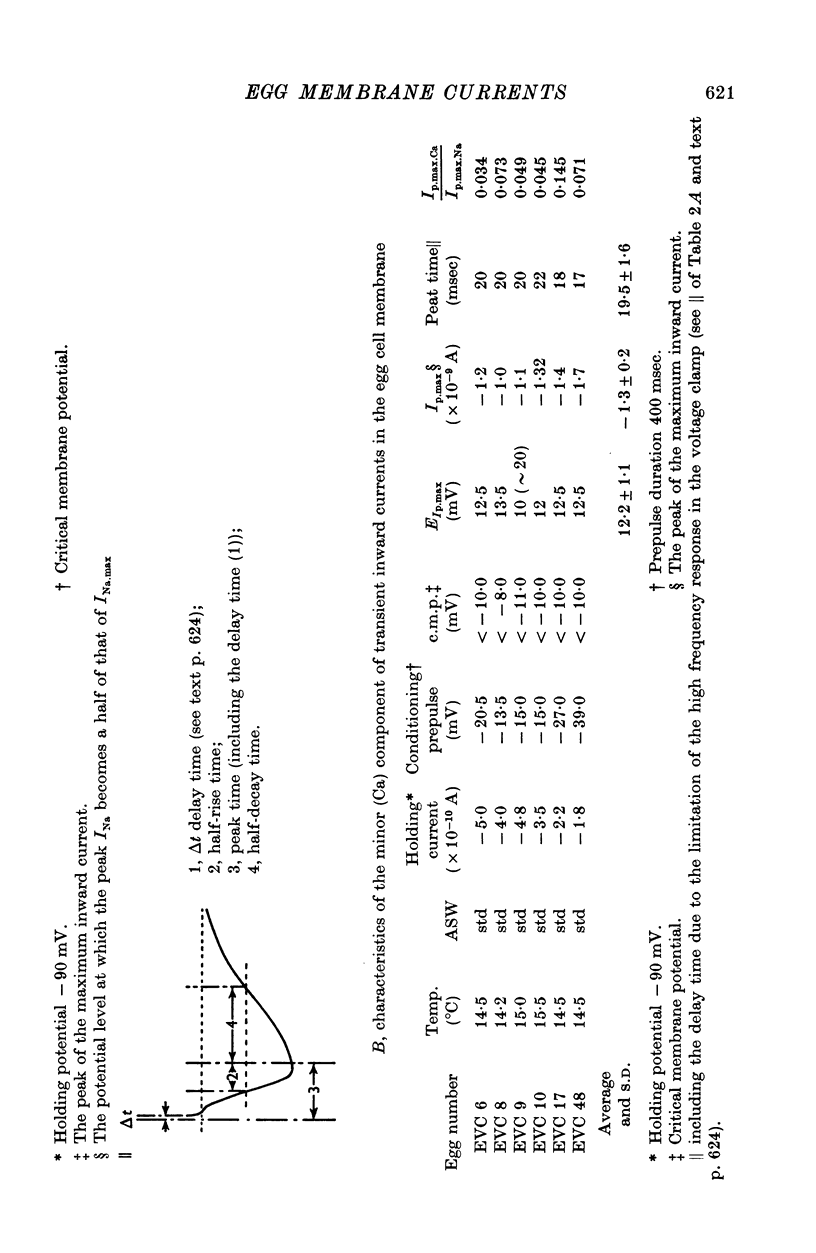

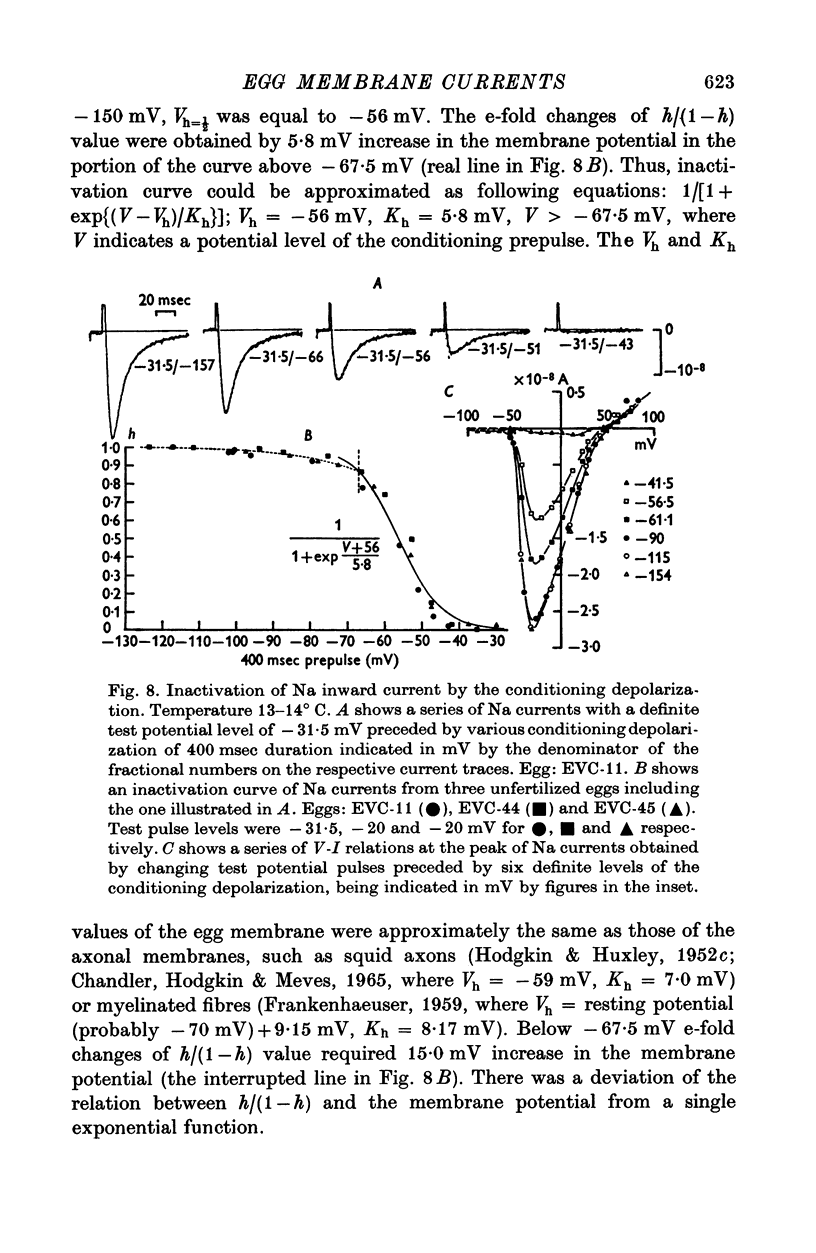

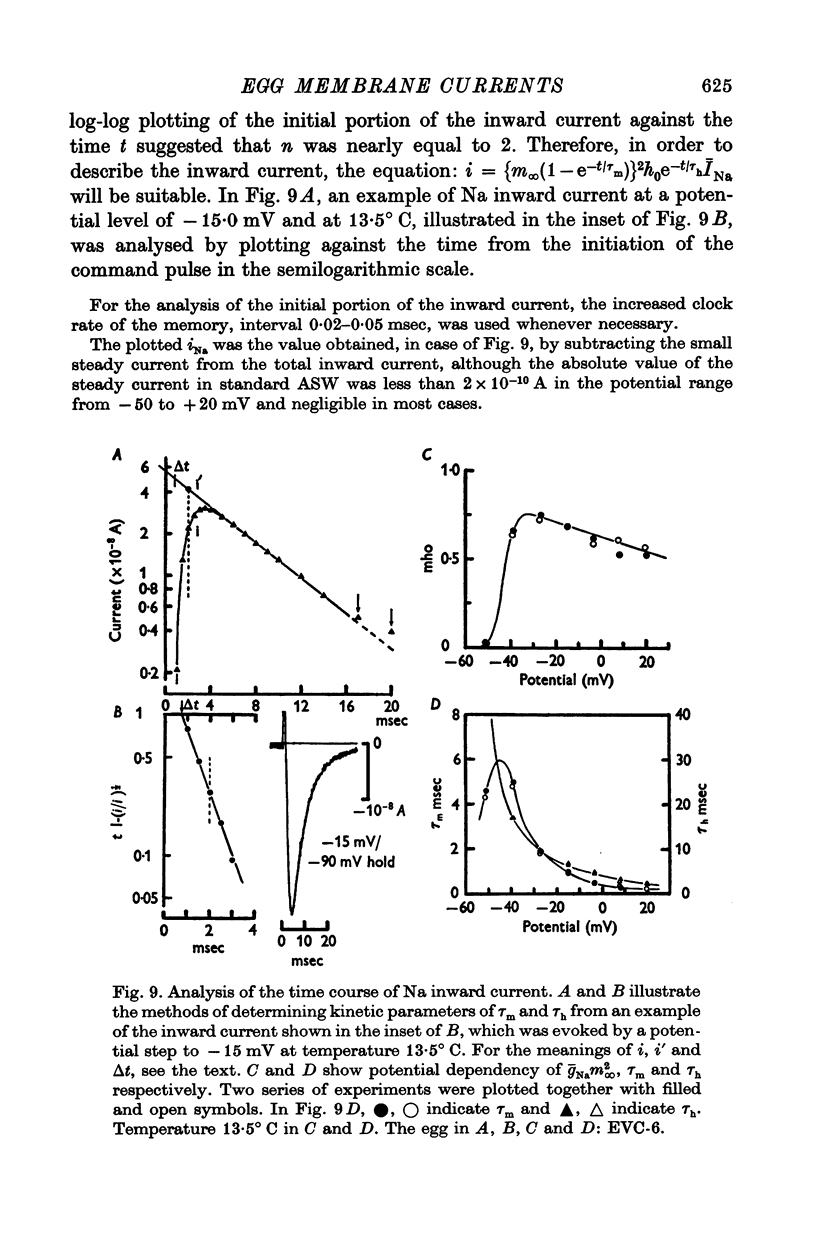

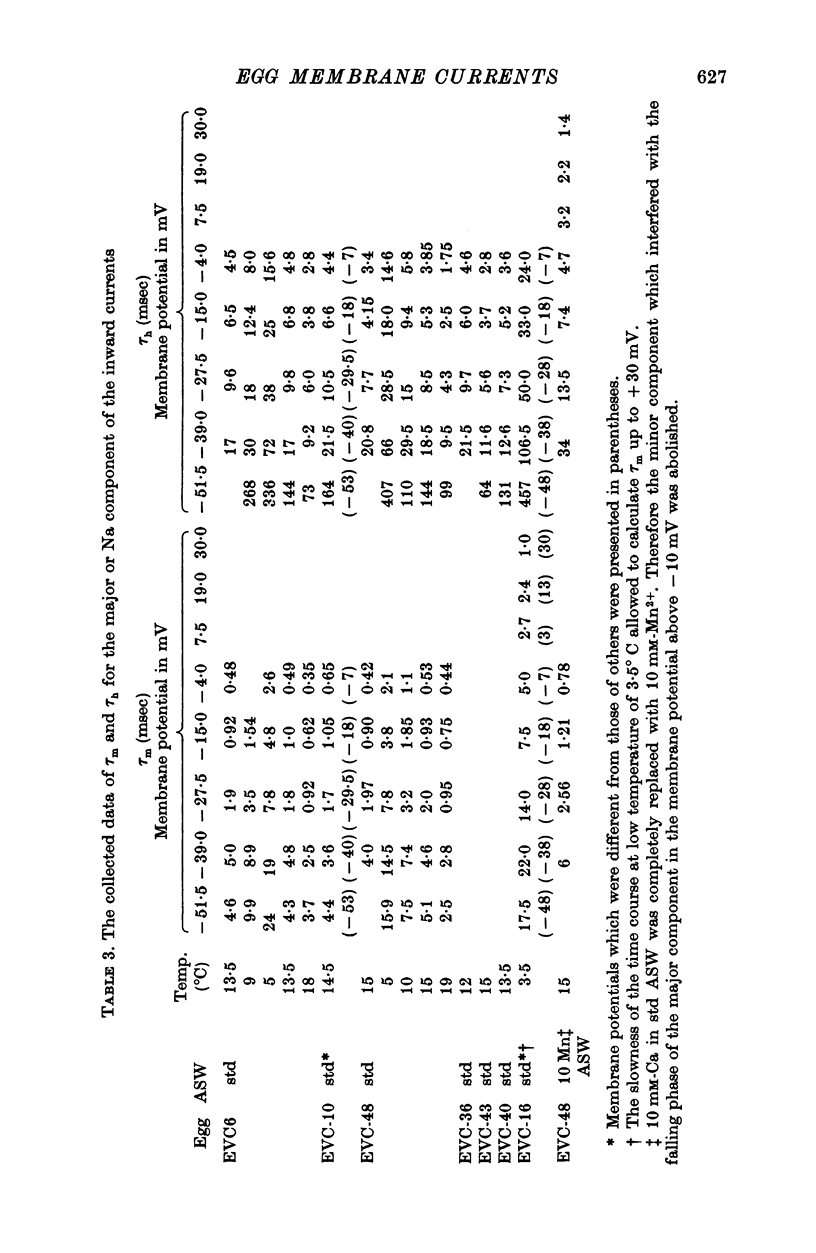








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG C. M., BINSTOCK L. ANOMALOUS RECTIFICATION IN THE SQUID GIANT AXON INJECTED WITH TETRAETHYLAMMONIUM CHLORIDE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:859–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Hodgkin A. L., Ridgway E. B. Depolarization and calcium entry in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1971 Nov;218(3):709–755. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
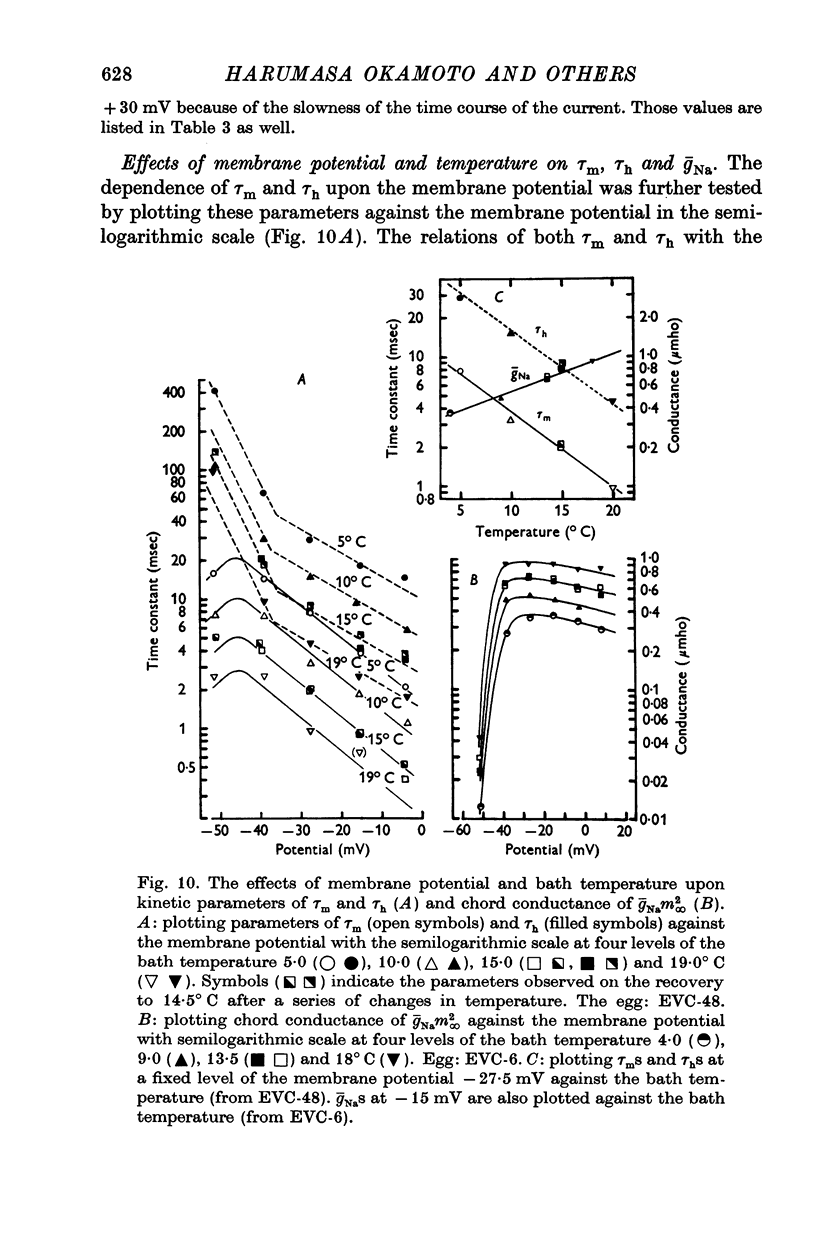
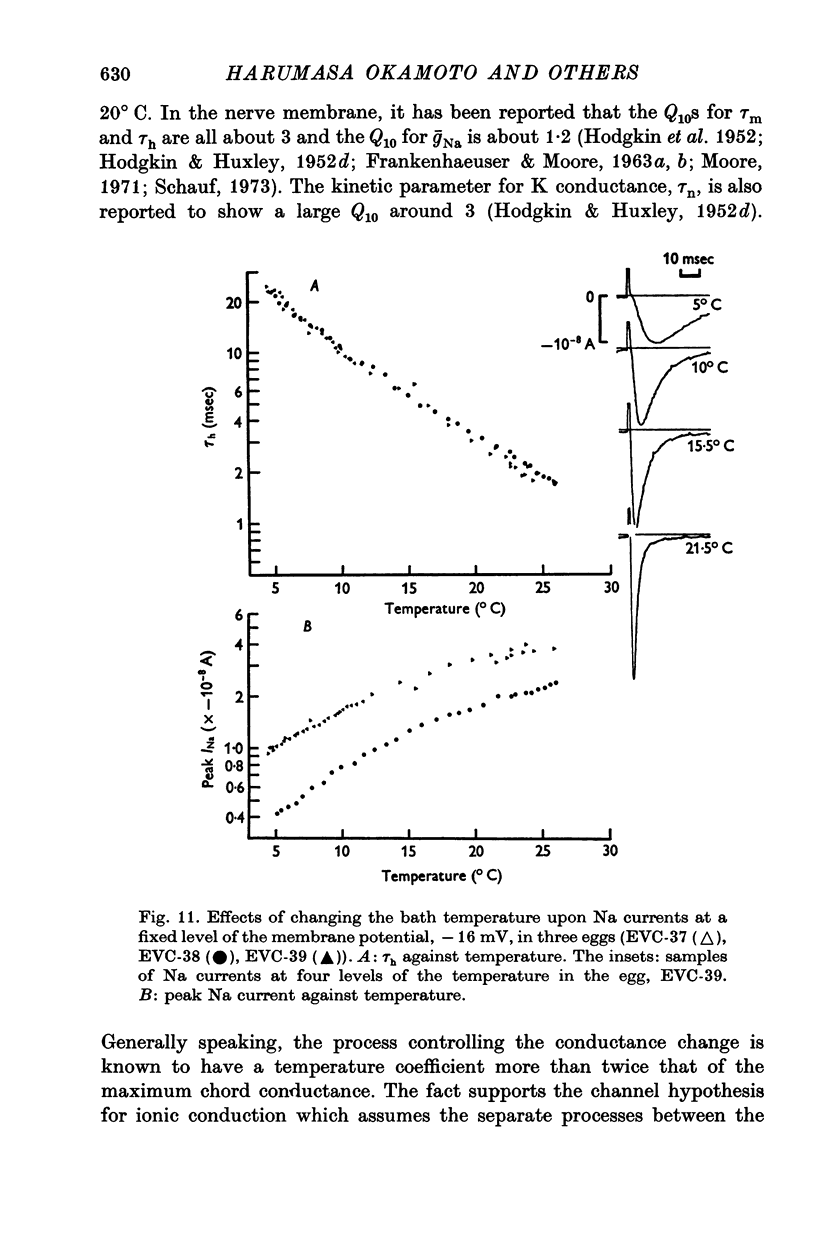
- Chandler W. K., Hodgkin A. L., Meves H. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):821–836. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
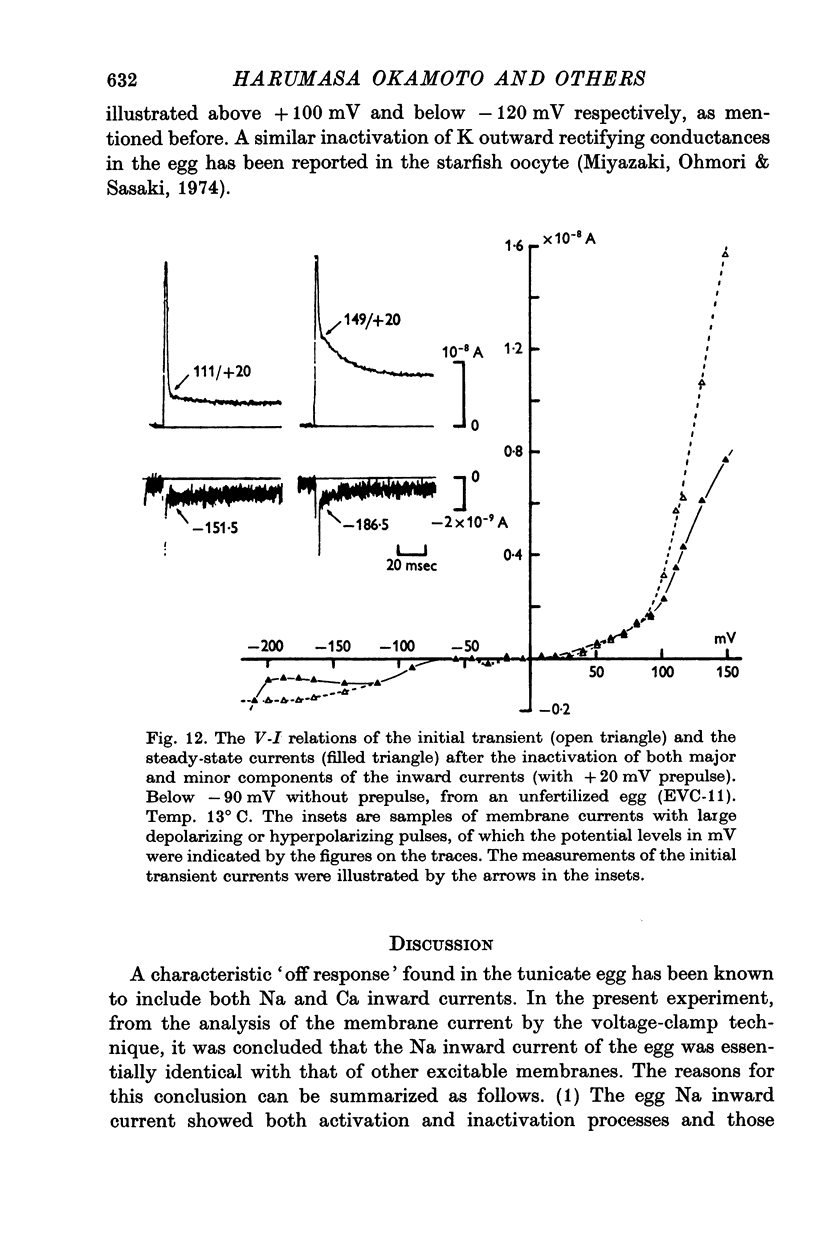
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Slow changes in membrane permeability and long-lasting action potentials in axons perfused with fluoride solutions. J Physiol. 1970 Dec;211(3):707–728. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE F. A., FRANKENHAEUSER B. Membrane currents in isolated frog nerve fibre under voltage clamp conditions. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):76–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE F. A., FRANKENHAEUSER B. Sodium currents in the myelinated nerve fibre of Xenopus laevis investigated with the voltage clamp technique. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:188–200. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. S., Engel E. The spatial variation of membrane potential near a small source of current in a spherical cell. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Jun;55(6):736–757. doi: 10.1085/jgp.55.6.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON THE SODIUM AND POTASSIUM PERMEABILITY CHANGES IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:431–437. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MOORE L. E. THE SPECIFICITY OF THE INITIAL CURRENT IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. VOLTAGE CLAMP EXPERIMENTS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:438–444. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. Quantitative description of sodium currents in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:491–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. Steady state inactivation of sodium permeability in myelinated nerve fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:671–676. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGIWARA S., NAKA K. I. THE INITIATION OF SPIKE POTENTIAL IN BARNACLE MUSCLE FIBERS UNDER LOW INTRACELLULAR CA++. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Sep;48:141–162. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.1.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F., KATZ B. Measurement of current-voltage relations in the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):424–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):1–37. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ion. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1287–1302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Discreteness of conductance change in bimolecular lipid membranes in the presence of certain antibiotics. Nature. 1970 Jan 31;225(5231):451–453. doi: 10.1038/225451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidokoro Y. Development of action potentials in a clonal rat skeletal muscle cell line. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 31;241(109):158–159. doi: 10.1038/newbio241158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhöfer E., Schmidt H. Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. I. Die Permeabilitäten PNa und PK. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(2):133–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00592631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasne S., Eisenman G., Szabo G. Freezing and melting of lipid bilayers and the mode of action of nonactin, valinomycin, and gramicidin. Science. 1971 Oct 22;174(4007):412–415. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4007.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald T. F., Sachs H. G., DeHaan R. L. Tetrodotoxin desensitization in aggregates of embryonic chick heart cells. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Sep;62(3):286–302. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.3.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meves H., Vogel W. Calcium inward currents in internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):225–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S. I., Ohmori H., Sasaki S. Potassium rectifications of the starfish oocyte membrane and their changes during oocyte maturation. J Physiol. 1975 Mar;246(1):55–78. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S. I., Takahashi K., Tsuda K. Electrical excitability in the egg cell membrane of the tunicate. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):37–54. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S. I., Takahashi K., Tsuda K., Yoshii M. Analysis of non-linearity observed in the current-voltage relation of the tunicate embryo. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):55–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Takahashi K., Tsuda K. Calcium and sodium contributions to regenerative responses in the embryonic excitable cell membrane. Science. 1972 Jun 30;176(4042):1441–1443. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Anderson N., Blaustein M., Takata M., Lettvin J. Y., Pickard W. F., Bernstein T., Pooler J. Alkali cation selectivity of squid axon membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):818–829. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50202.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Blaustein M. P., Anderson N. C., Narahashi T. Basis of tetrodotoxin's selectivity in blockage of squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1401–1411. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. E. Effect of temperature and calcium ions on rate constants of myelinated nerve. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jul;221(1):131–137. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Induced excitability in reconstituted cell membrane structure. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NARAHASHI T., MOORE J. W., SCOTT W. R. TETRODOTOXIN BLOCKAGE OF SODIUM CONDUCTANCE INCREASE IN LOBSTER GIANT AXONS. J Gen Physiol. 1964 May;47:965–974. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.5.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Nakajima S., Grundfest H. The action of tetrodotoxin on electrogenic components of squid giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jul;48(6):975–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfern P., Thesleff S. Action potential generation in denervated rat skeletal muscle. II. The action of tetrodotoxin. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 May;82(1):70–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04943.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Atwater I. Effect of tetrodotoxin on the early outward currents in perfused giant axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1350–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L. Temperature dependence of the ionic current kinetics of Myxicola giant axons. J Physiol. 1973 Nov;235(1):197–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigenobu K., Sperelakis N. Development of sensitivity to tetrodotoxin of chick embryonic hearts with age. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1971 Dec;3(3):271–286. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(71)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperelakis N., Shigenobu K. Changes in membrane properties of chick embryonic hearts during development. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Oct;60(4):430–453. doi: 10.1085/jgp.60.4.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., HAGIWAR A. S. Demonstration of two stable potential states in the squid giant axon under tetraethylammonium chloride. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Jul 20;40(6):859–885. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.6.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., TAKENAKA T. EFFECTS OF VARIOUS POTASSIUM SALTS AND PROTEASES UPON EXCITABILITY OF INTRACELLULARLY PERFUSED SQUID GIANT AXONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:804–810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Miyazaki S. I., Kidokoro Y. Development of excitability in embryonic muscle cell membranes in certain tunicates. Science. 1971 Jan 29;171(3969):415–418. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3969.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasaki I., Lerman L., Watanabe A. Analysis of excitation process in squid giant axons under bi-ionic conditions. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):130–138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W., Goodall M. C., Glickson J. D., Mayers D. F. The gramicidin A transmembrane channel: characteristics of head-to-head dimerized (L,D) helices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1907–1911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


