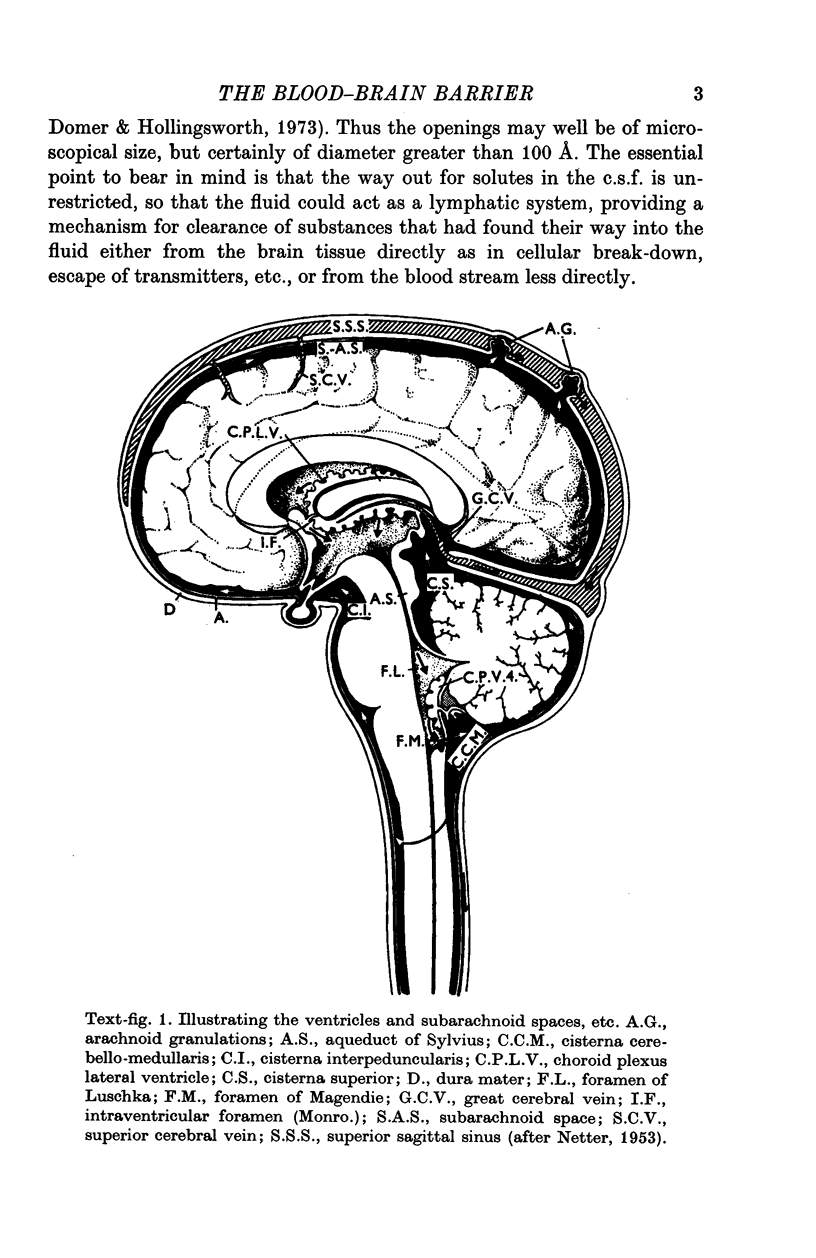
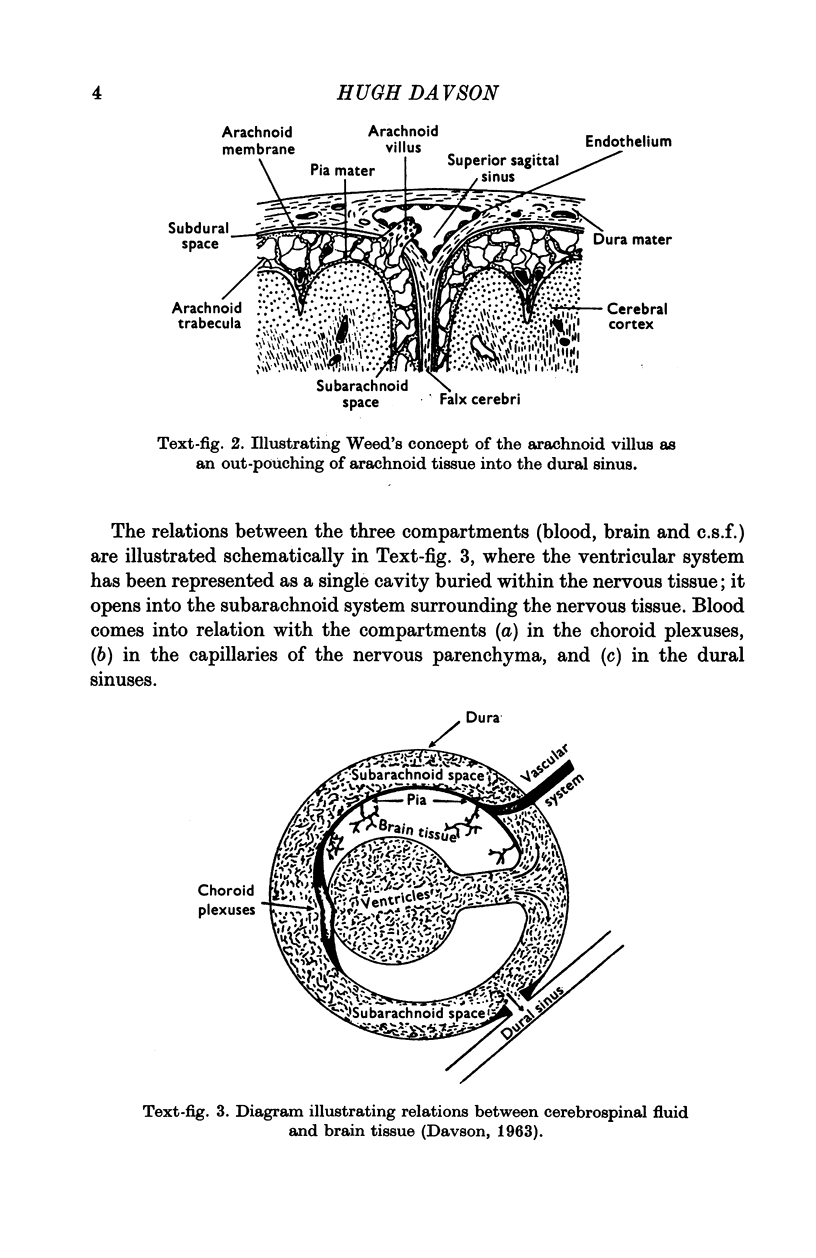
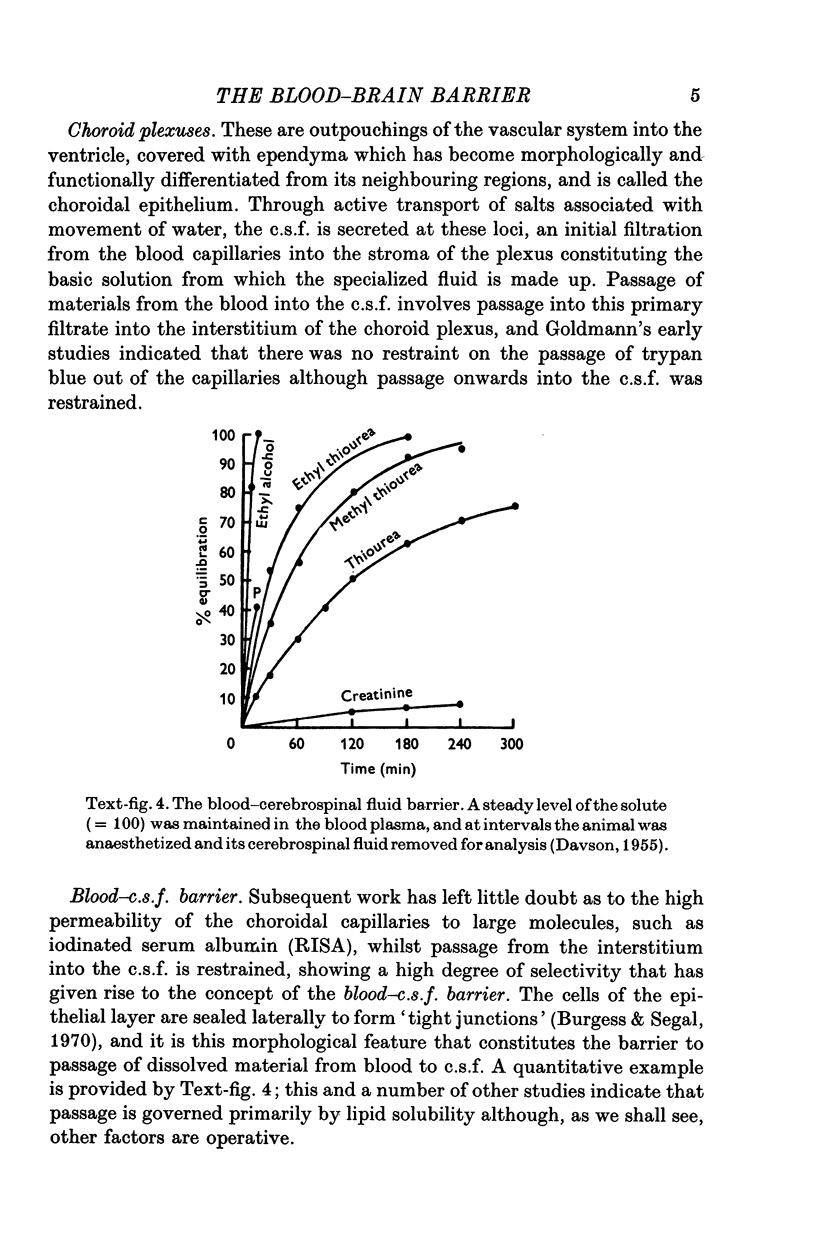
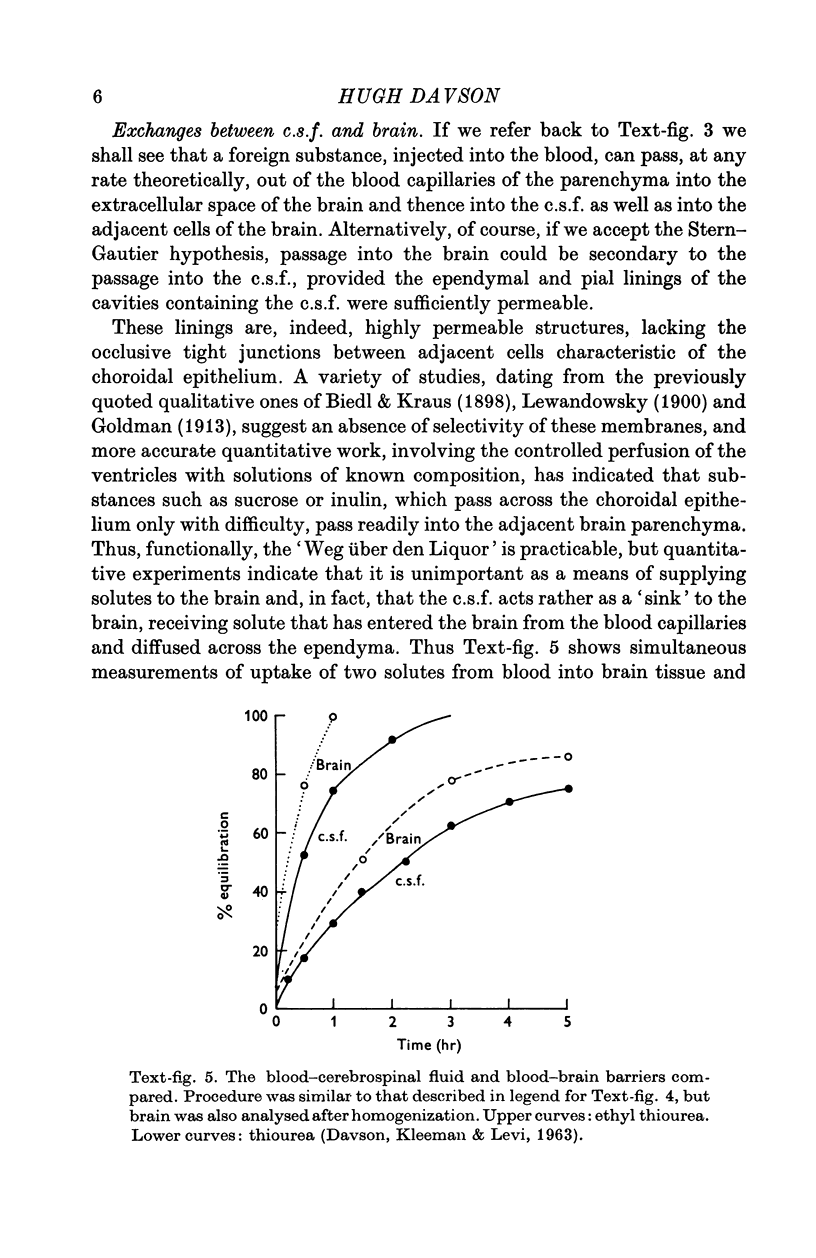
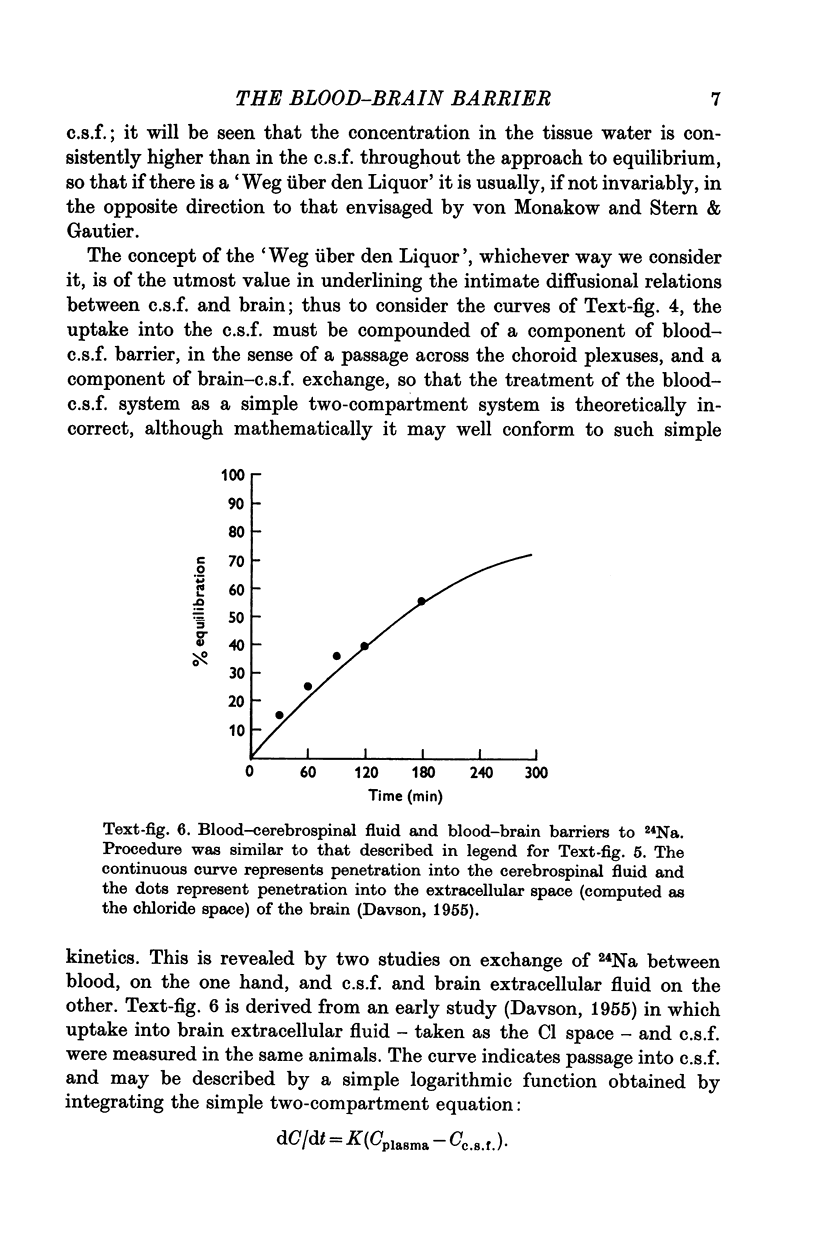
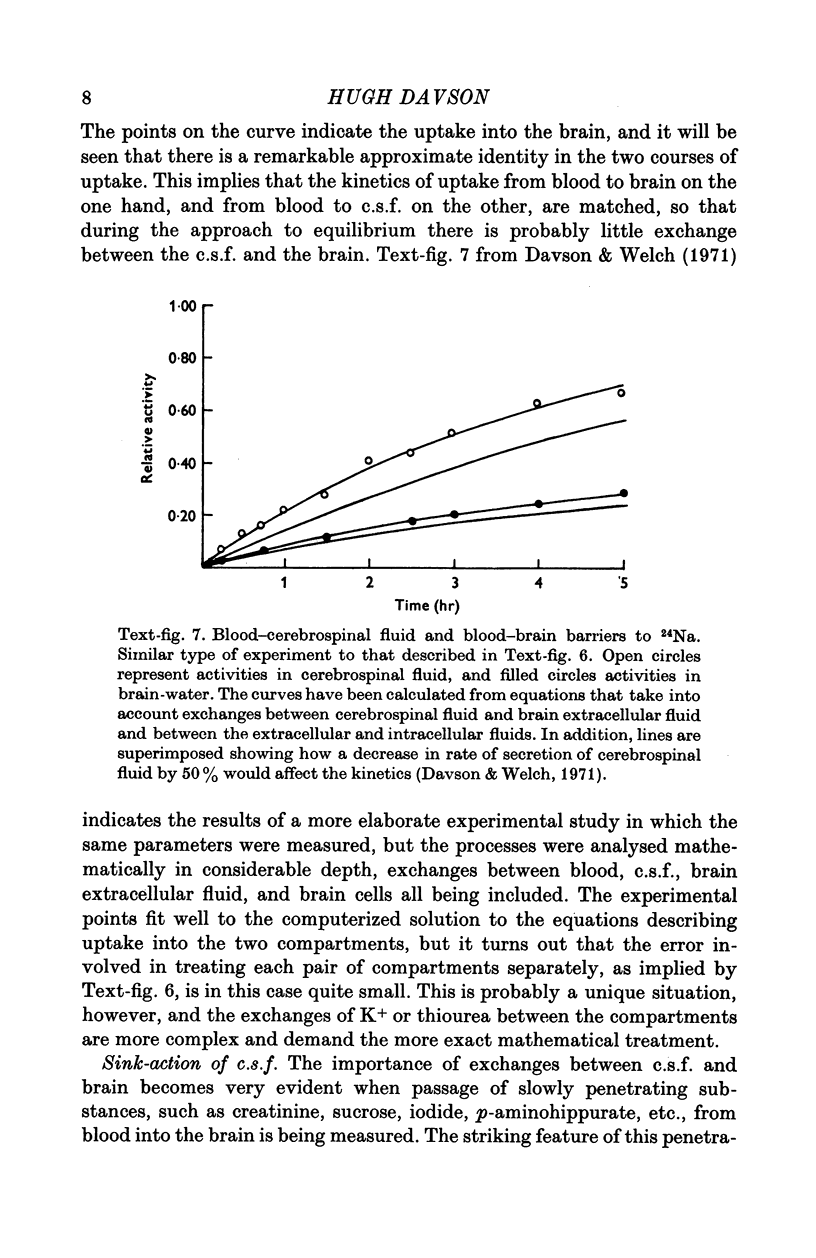
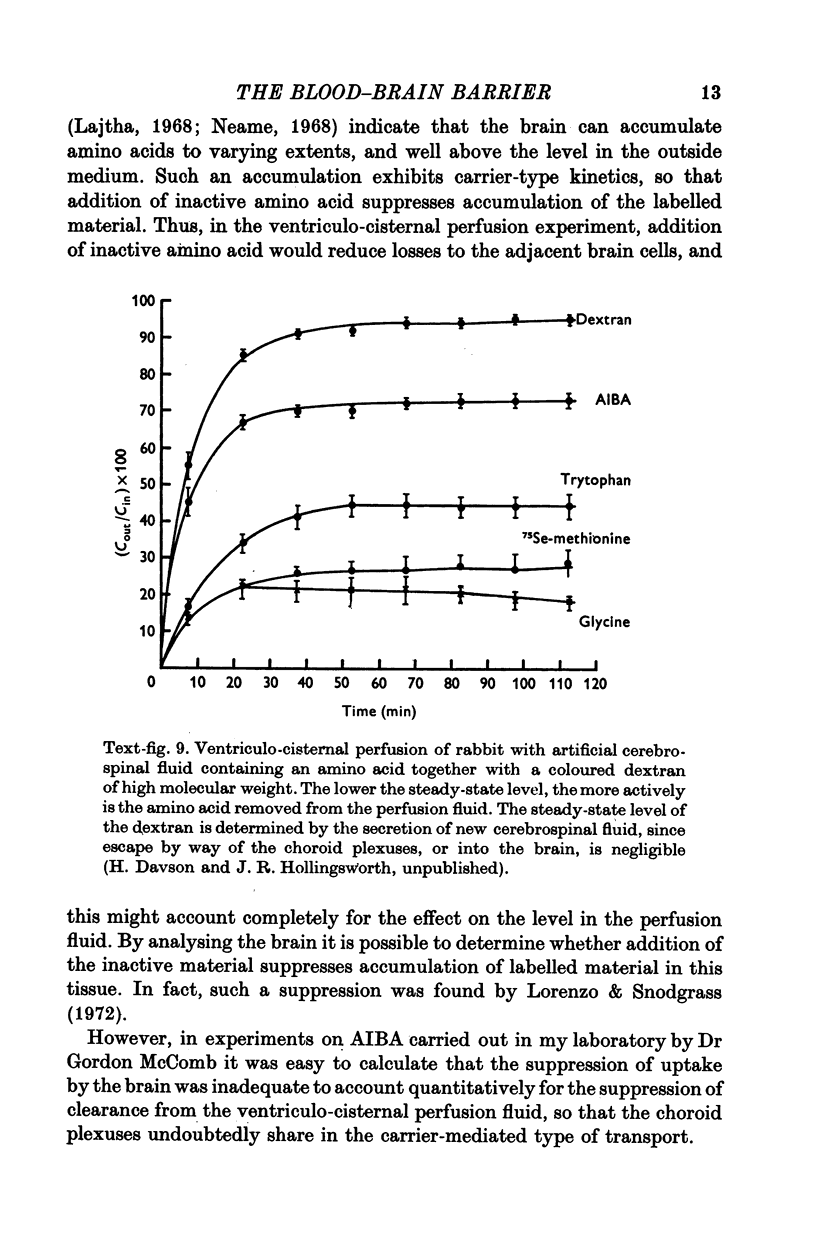
Full text
PDF






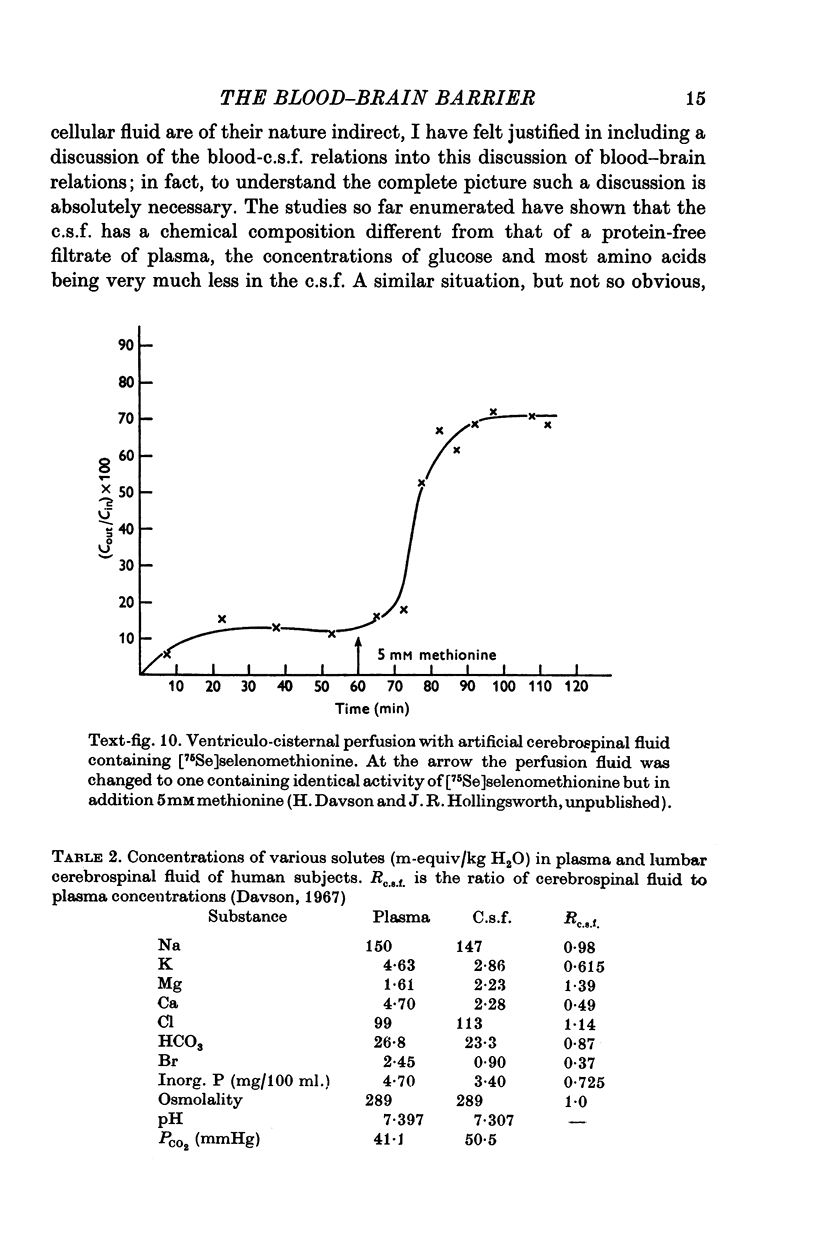
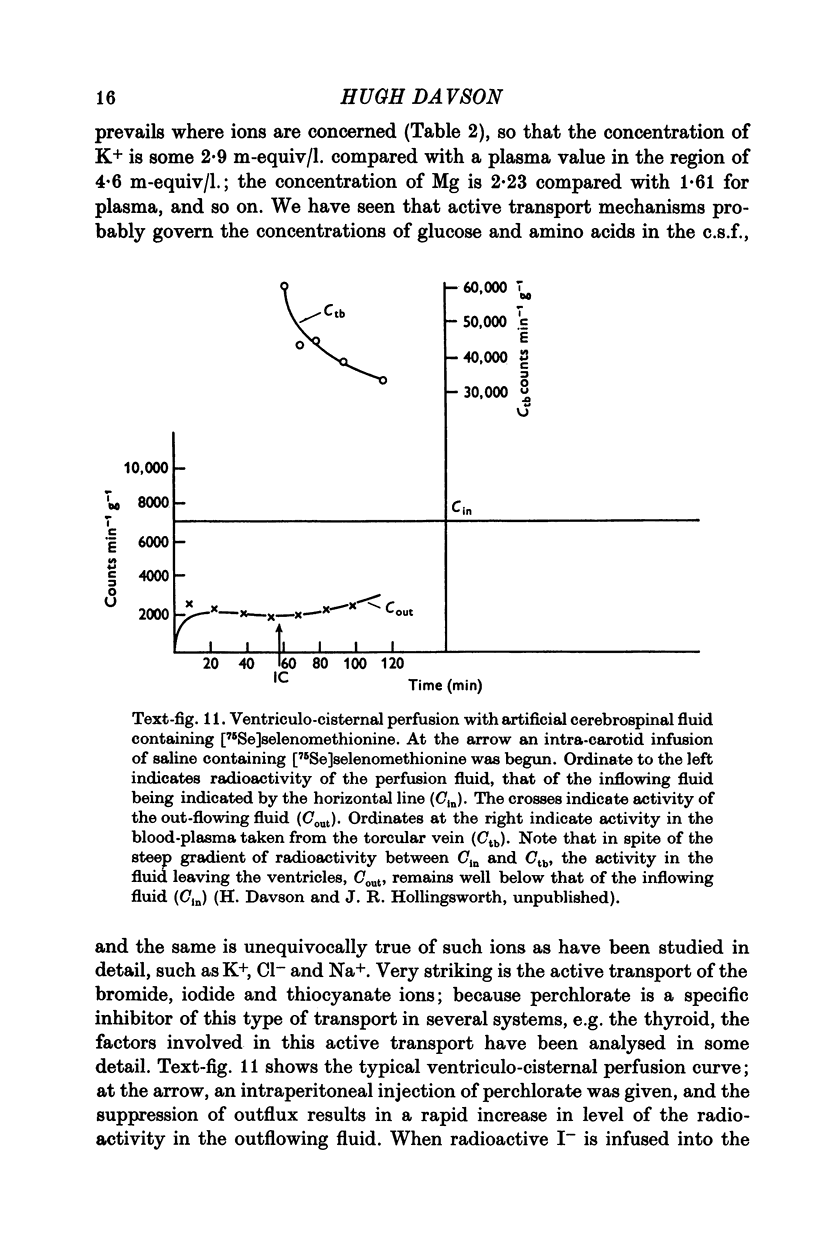
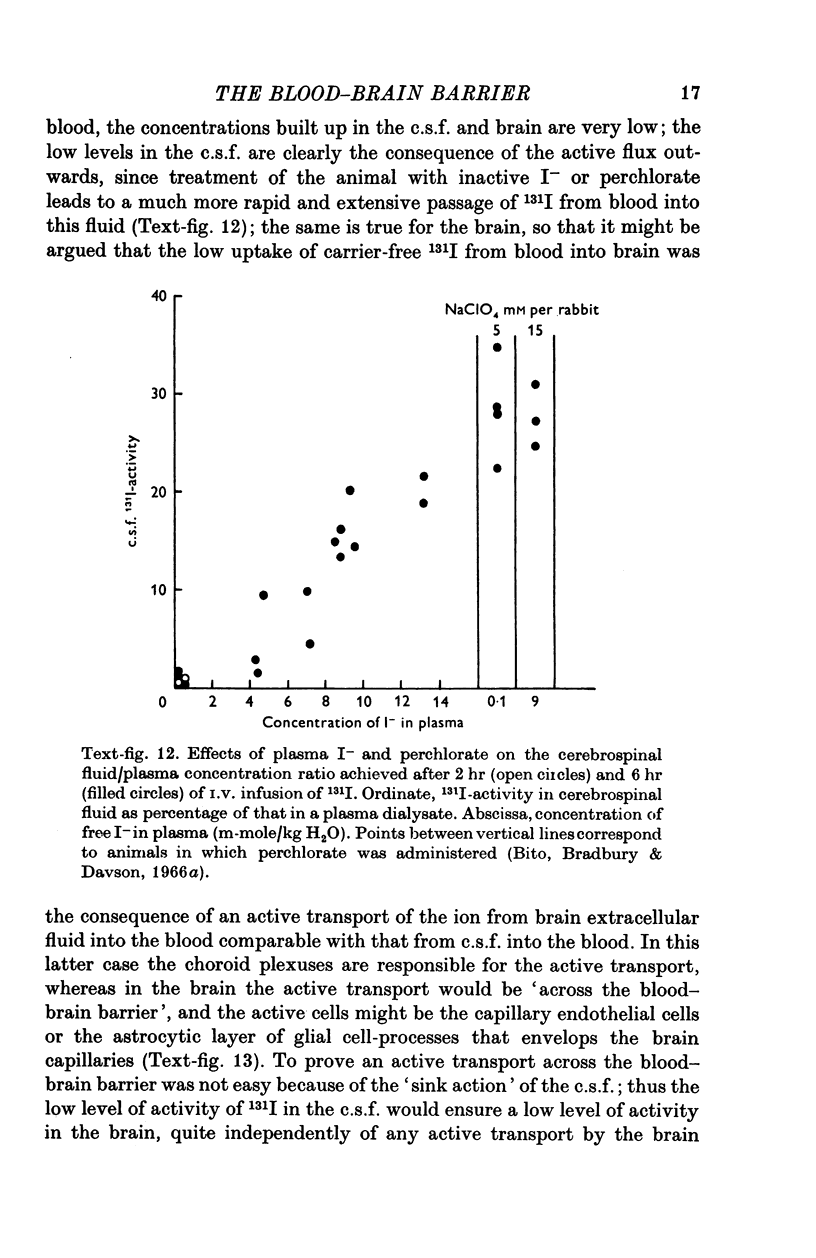








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed N., Van Harreveld A. The iodide space in rabbit brain. J Physiol. 1969 Sep;204(1):31–50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alksne J. F., Lovings E. T. Functional ultrastructure of the arachnoid villus. Arch Neurol. 1972 Nov;27(5):371–377. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490170003002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames A., 3rd, Higashi K., Nesbett F. B. Relation of potassium concentration in choroidplexus fluid to that in plasma. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):506–515. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEKAERT J., DEMEESTER G. The influence of glucose and insulin upon the potassium concentration of serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Arch Int Physiol. 1951 Jul;59(2):262–264. doi: 10.3109/13813455109145012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEKAERT J., DEMEESTER G. [The influence of dinitro-alpha-naphtol upon the potassium concentration of serum and cerebrospinal fluid]. Arch Int Physiol. 1952 Jun;60(2):172–175. doi: 10.3109/13813455209145055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADBURY M. W., DAVSON H. THE TRANSPORT OF UREA, CREATININE AND CERTAIN MONOSACCHARIDES BETWEEN BLOOD AND FLUID PERFUSING THE CEREBRAL VENTRICULAR SYSTEM OF RABBITS. J Physiol. 1964 Jan;170:195–211. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
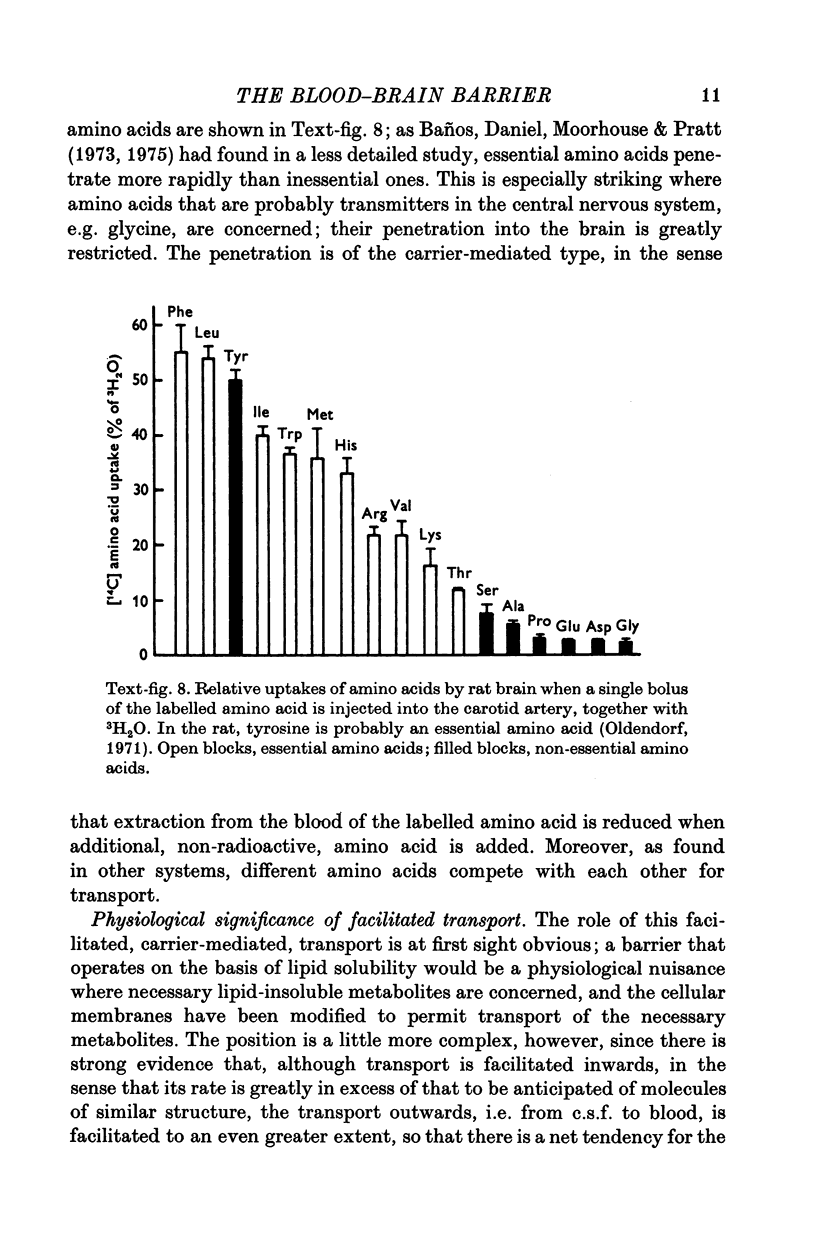
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The influx of amino acids into the brain of the rat in vivo: the essential compared with some non-essential amino acids. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Feb 27;183(1070):59–70. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1973.0004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baños G., Daniel P. M., Moorhouse S. R., Pratt O. E. The requirements of the brain for some amino acids. J Physiol. 1975 Apr;246(3):539–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Bradbury M. W., Davson H. Factors affecting the distribution of iodide and bromide in the central nervous system. J Physiol. 1966 Jul;185(2):323–354. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
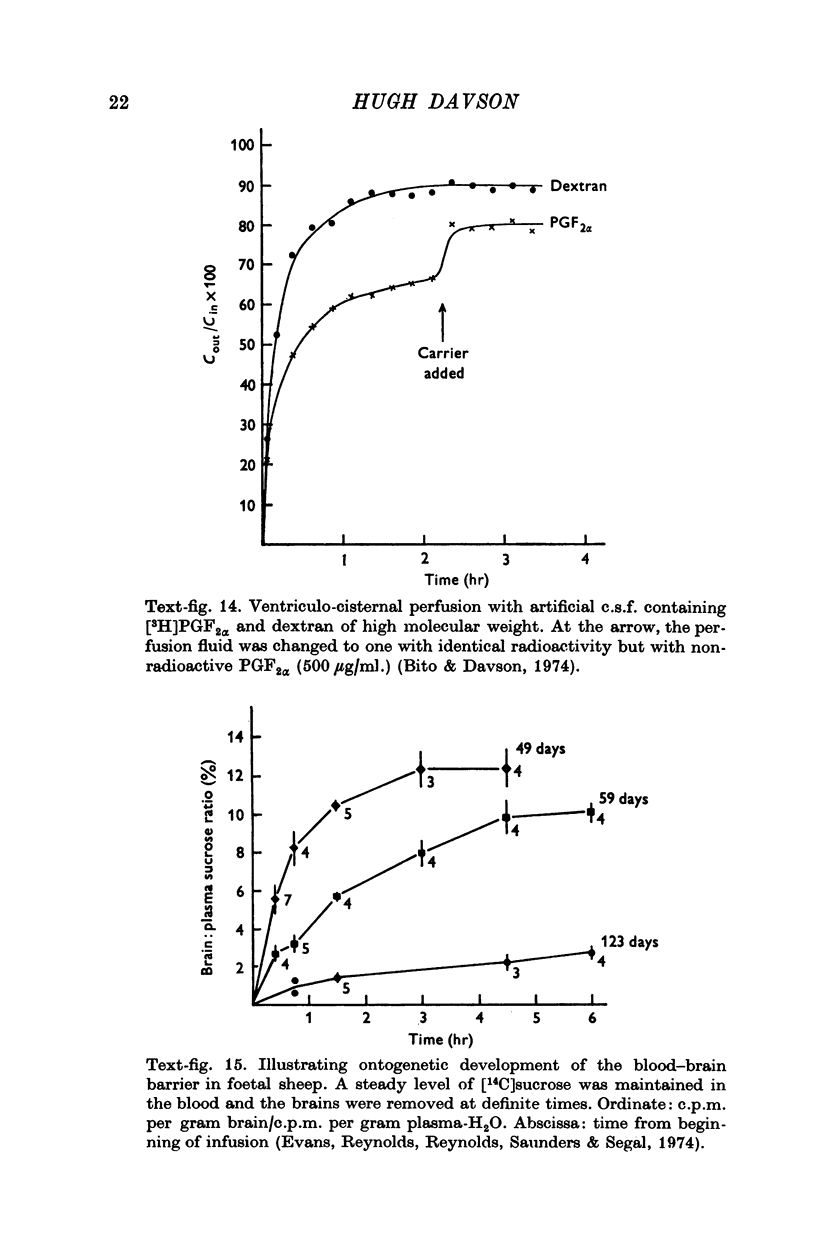
- Bito L. Z., Davson H. Proceedings: Carrier-mediated removal of prostaglandins from cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1974 Jan;236(1):39P–40P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Salvador E. V. Intraocular fluid dynamics. 3. The site and mechanism of prostaglandin transfer across the blood intraocular fluid barriers. Exp Eye Res. 1972 Nov;14(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(72)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L. Z., Spellane P. J. Saturable, "carrier-mediated", absorption of prostaglandin F2 alpha from the in vivo rabbit vagina and its inhibition by prostaglandin F2 beta. Prostaglandins. 1974 Nov 25;8(4):345–352. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(74)80100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bito L., Davson H., Levin E., Murray M., Snider N. The concentrations of free amino acids and other electrolytes in cerebrospinal fluid, in vivo dialysate of brain, and blood plasma of the dog. J Neurochem. 1966 Nov;13(11):1057–1067. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Kleeman C. R. Stability of the potassium content of cerebrospinal fluid and brain. Am J Physiol. 1967 Aug;213(2):519–528. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.2.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
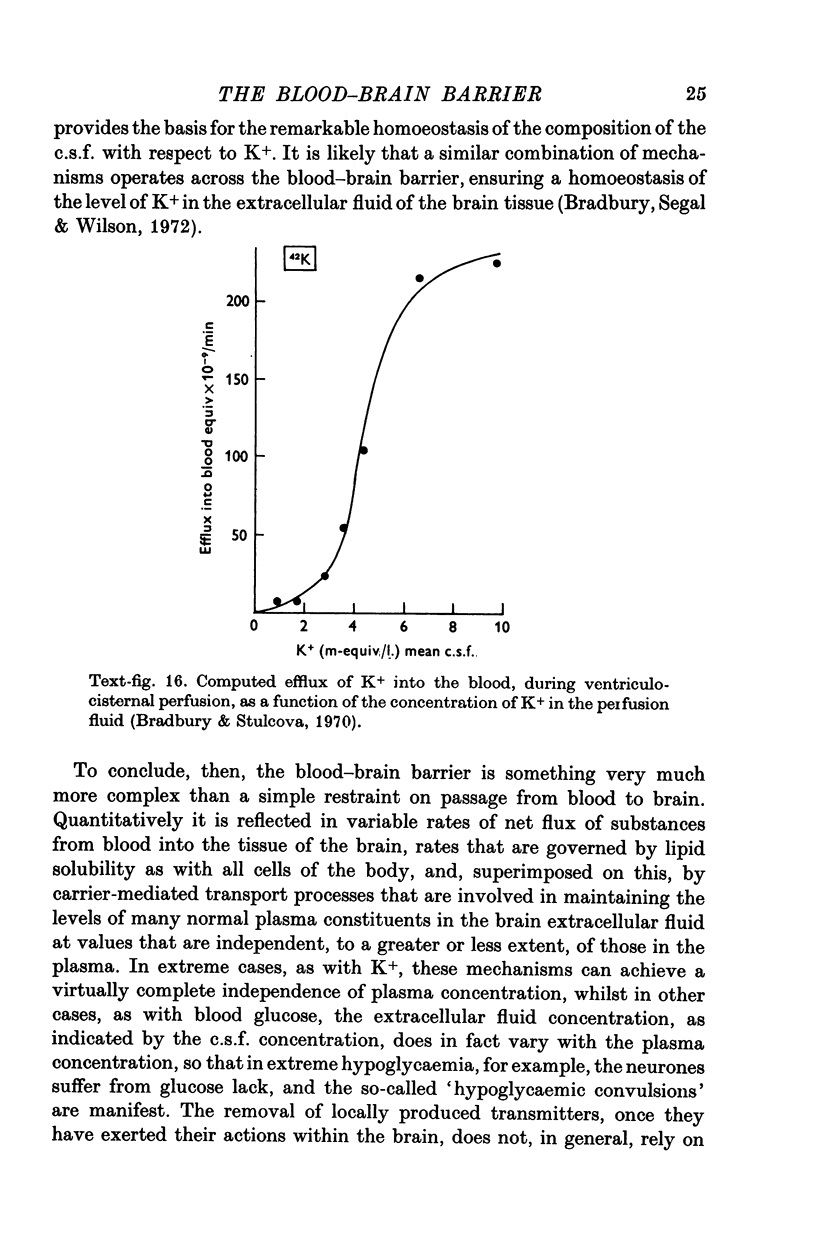
- Bradbury M. W., Segal M. B., Wilson J. Transport of potassium at the blood-brain barrier. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(3):617–632. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W., Stulcová B. Efflux mechanism contributing to the stability of the potassium concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1970 Jun;208(2):415–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W. The distribution within the brain of ferritin injected into cerebrospinal fluid compartments. II. Parenchymal distribution. Am J Anat. 1965 Sep;117(2):193–219. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001170204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coben L. A., Smith K. R. Iodide transfer at four cerebrospinal fluid sites in the dog: evidence for spinal iodide carrier transport. Exp Neurol. 1969 Jan;23(1):76–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. Facilitated transfer of glucose from blood into brain tissue. J Physiol. 1965 Nov;181(1):103–113. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csáky T. Z., Rigor B. M. The choroid plexus as a glucose barrier. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:147–158. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVSON H. A comparative study of the aqueous humour and cerebrospinal fluid in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1955 Jul 28;129(1):111–133. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Domer F. R., Hollingsworth J. R. The mechanism of drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain. 1973 Jun;96(2):329–336. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Hollingsworth G., Segal M. B. The mechanism of drainage of the cerebrospinal fluid. Brain. 1970;93(4):665–678. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Hollingsworth J. R. Active transport of 131-I across the blood-brain barrier. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(2):327–347. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davson H., Welch K. The permeation of several materials into the fluids of the rabbit's brain. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(2):337–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond I., Schmid R. Experimental bilirubin encephalopathy. The mode of entry of bilirubin-14C into the central nervous system. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):678–689. doi: 10.1172/JCI105383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. A., Reynolds J. M., Reynolds M. L., Saunders N. R., Segal M. B. The development of a blood-brain barrier mechanism in foetal sheep. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(2):371–386. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson R. K., Woodbury D. M. Penetration of 14C-inulin and 14C-sucrose into brain, cerebrospinal fluid, and skeletal muscle of developing rats. Exp Brain Res. 1969;7(3):181–194. doi: 10.1007/BF00239028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lajtha A. Transport as control mechanism of cerebral metabolite levels. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:201–218. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64157-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Snodgrass S. R. Leucine transport from the ventricles and the cranial subarachnoid space in the cat. J Neurochem. 1972 May;19(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01454.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame K. D. A comparison of the transport systems for amino acids in brain, intestine, kidney and tumour. Prog Brain Res. 1968;29:185–199. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Brain uptake of radiolabeled amino acids, amines, and hexoses after arterial injection. Am J Physiol. 1971 Dec;221(6):1629–1639. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.6.1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H. Stereospecificity of blood-brain barrier permeability to amino acids. Am J Physiol. 1973 Apr;224(4):967–969. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.224.4.967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., HEISEY S. R., JORDAN E. F. Active transport of Diodrast and phenolsulfonphthalein from cerebrospinal fluid to blood. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jan;200:1–10. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer J. R., Setchell B. P. Cerebral glucose transport and oxygen consumption in sheep and rabbits. J Physiol. 1973 Sep;233(3):529–551. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plum C. M. Free amino acid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of normal humans and their variation in cases of epilepsy and Spielmeyer-Vogt-Batten disease. J Neurochem. 1974 Sep;23(3):595–600. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1974.tb06064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi B. J., Tripathi R. C. Vacuolar transcellular channels as a drainage pathway for cerebrospinal fluid. J Physiol. 1974 May;239(1):195–206. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yudilevich D. L., De Rose N. Blood-brain transfer of glucose and other molecules measured by rapid indicator dilution. Am J Physiol. 1971 Mar;220(3):841–846. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.3.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





