Abstract
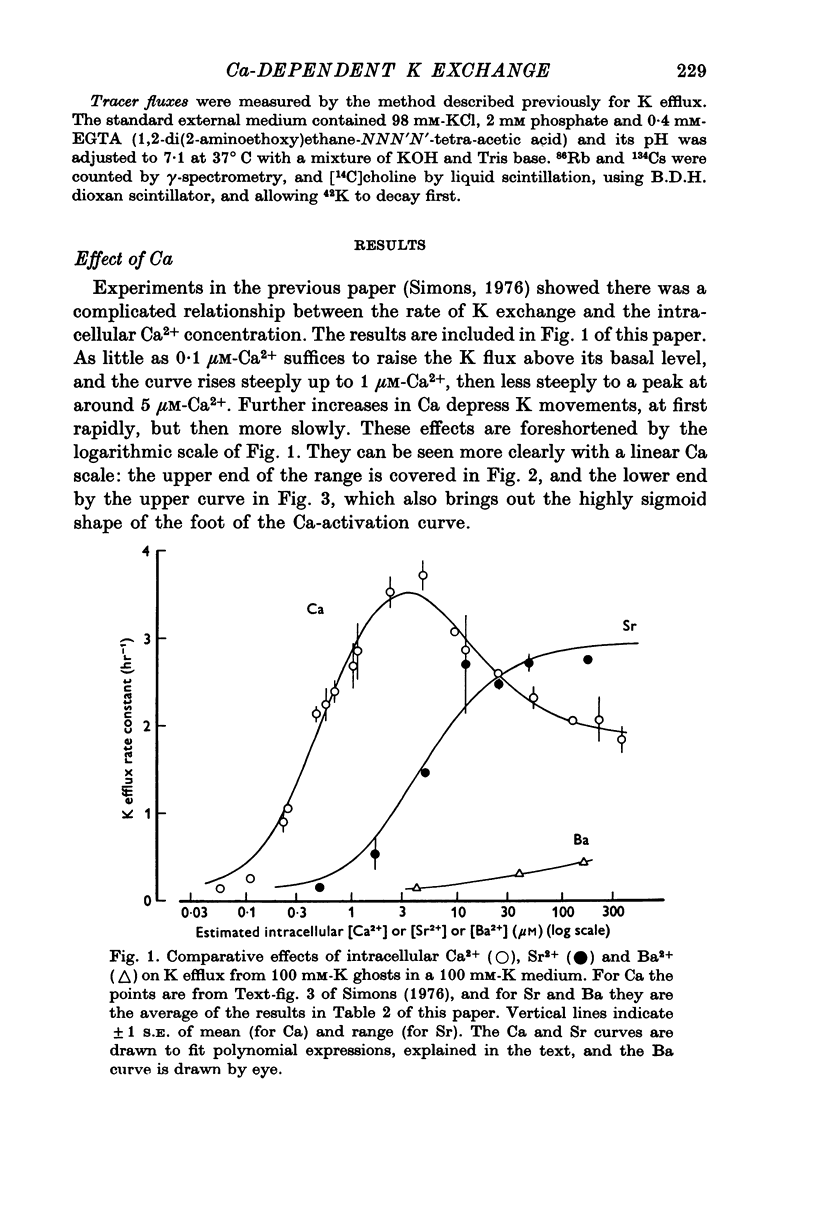
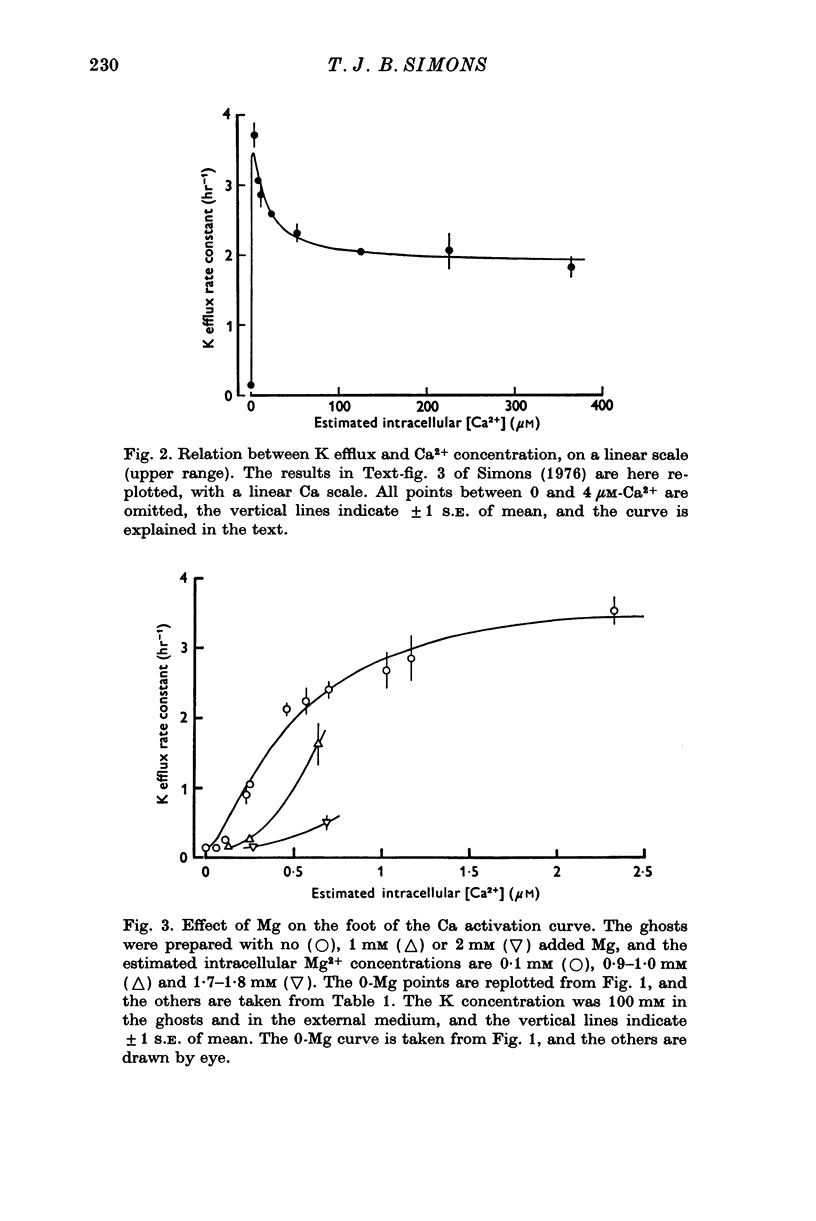
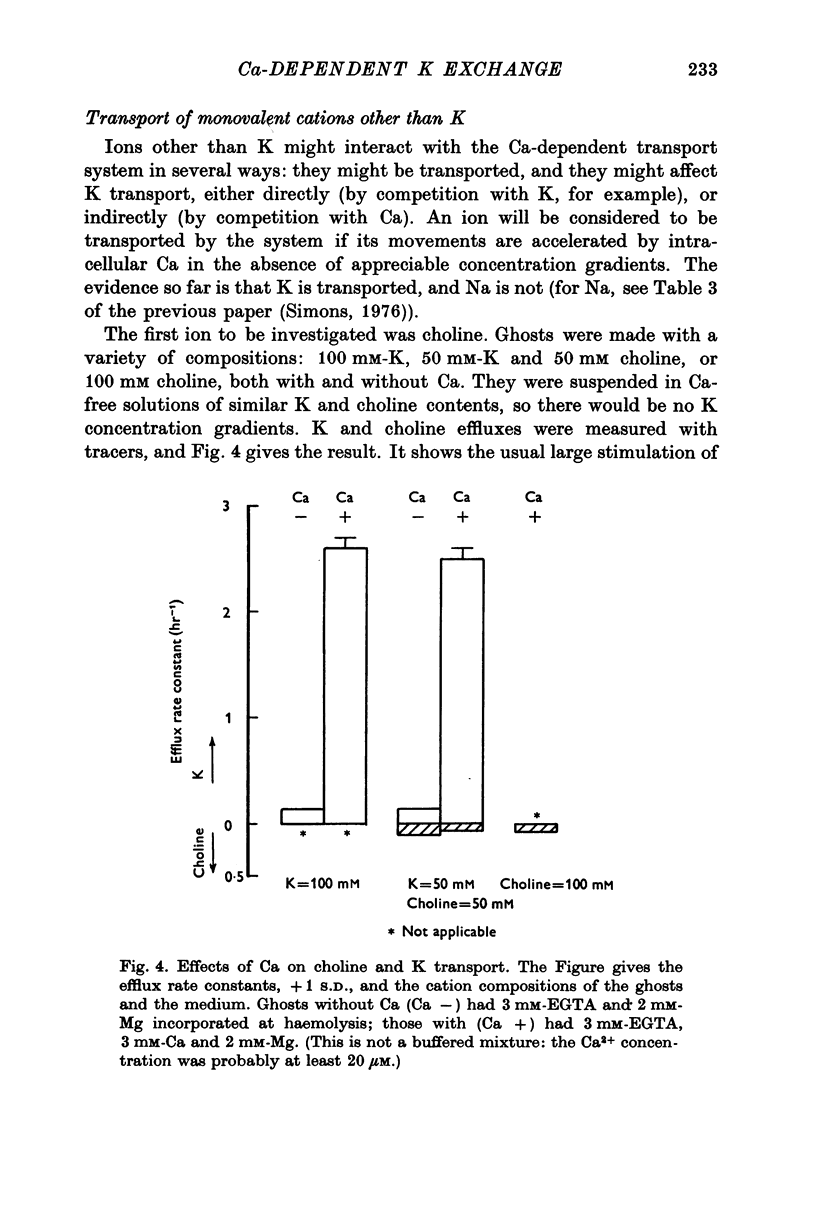
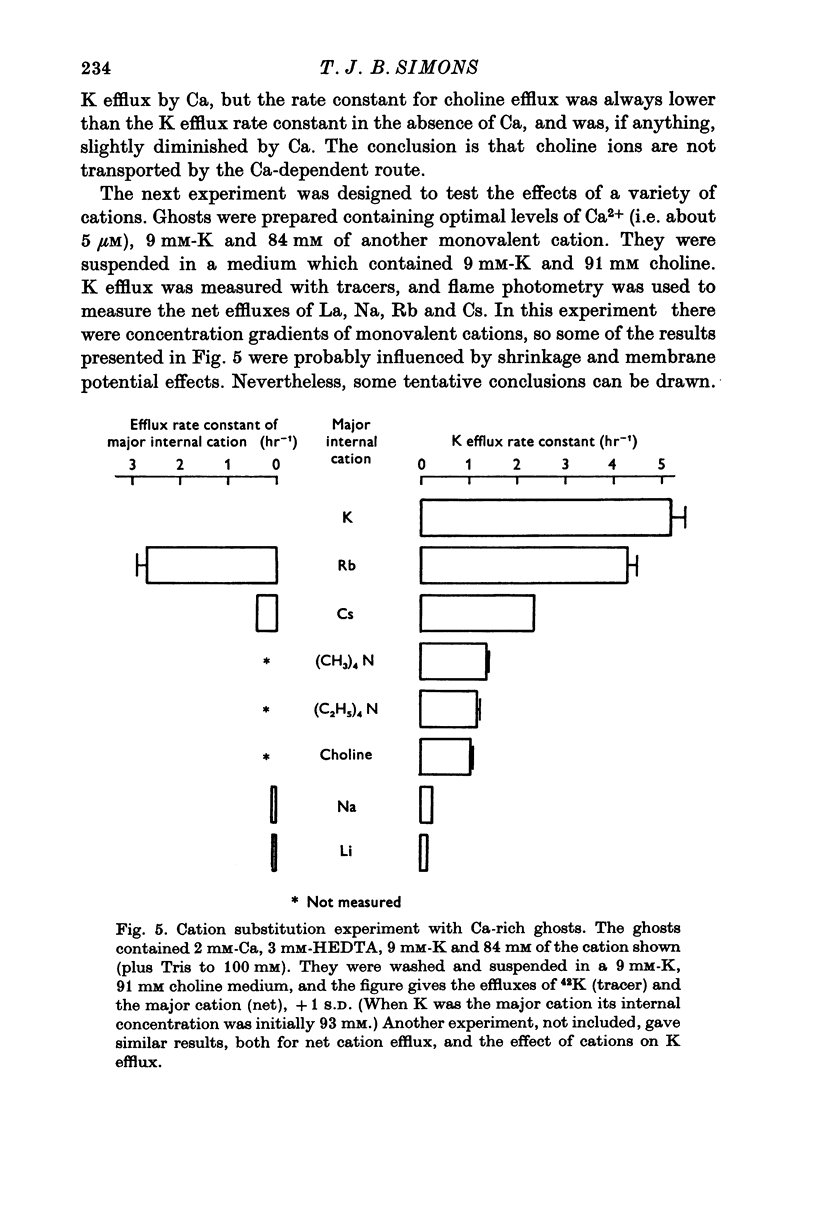
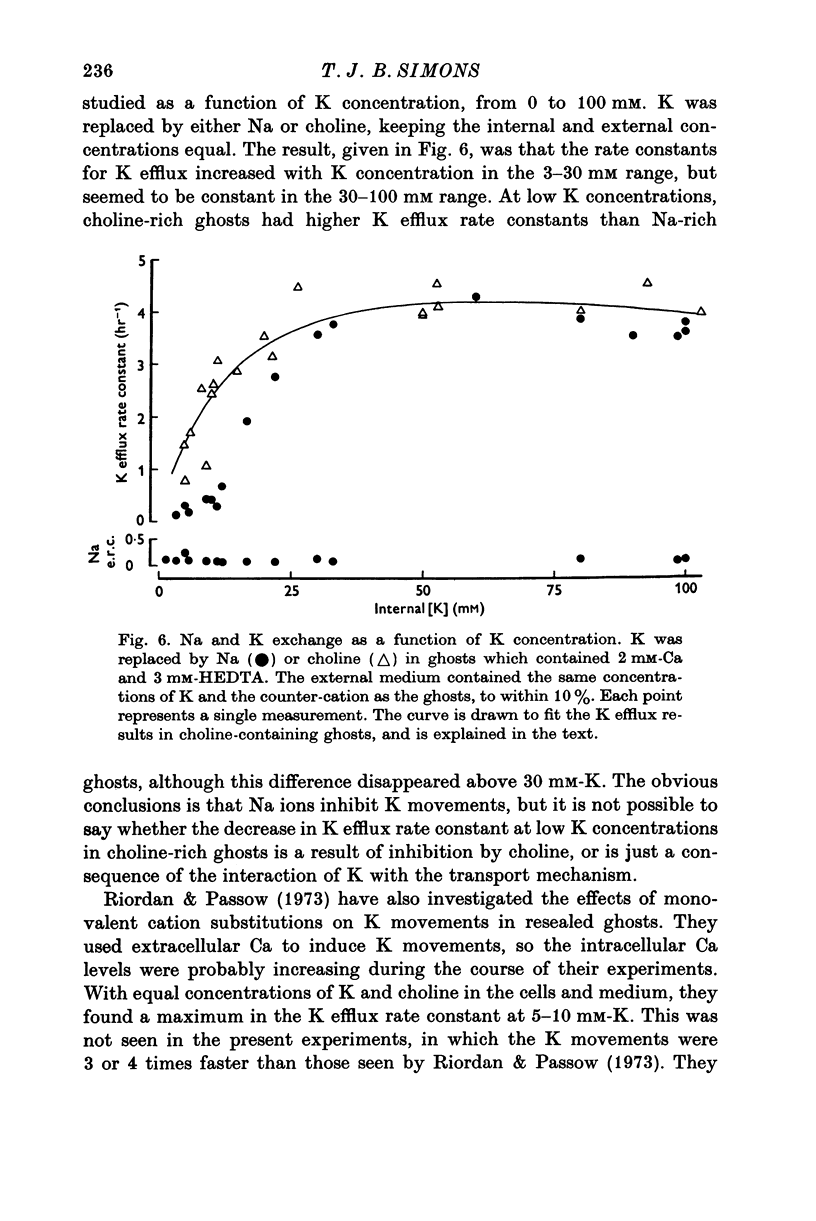
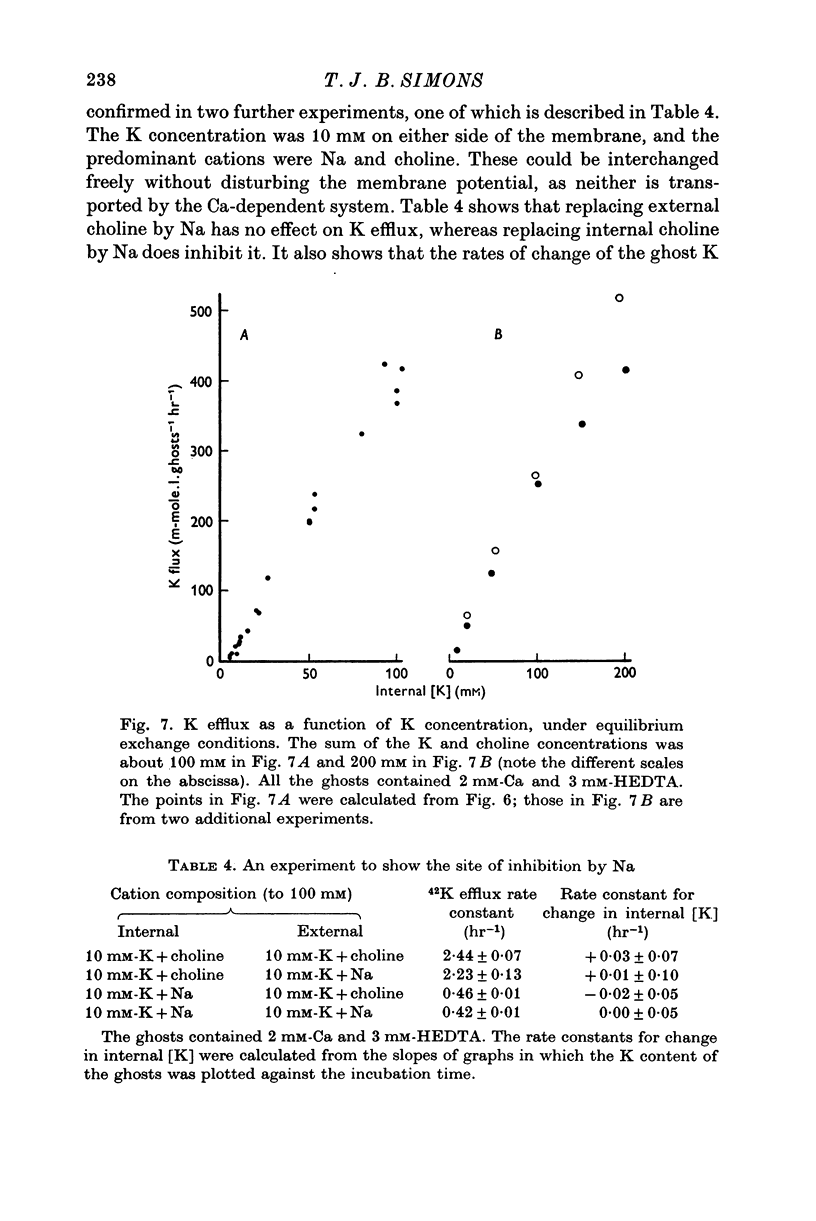
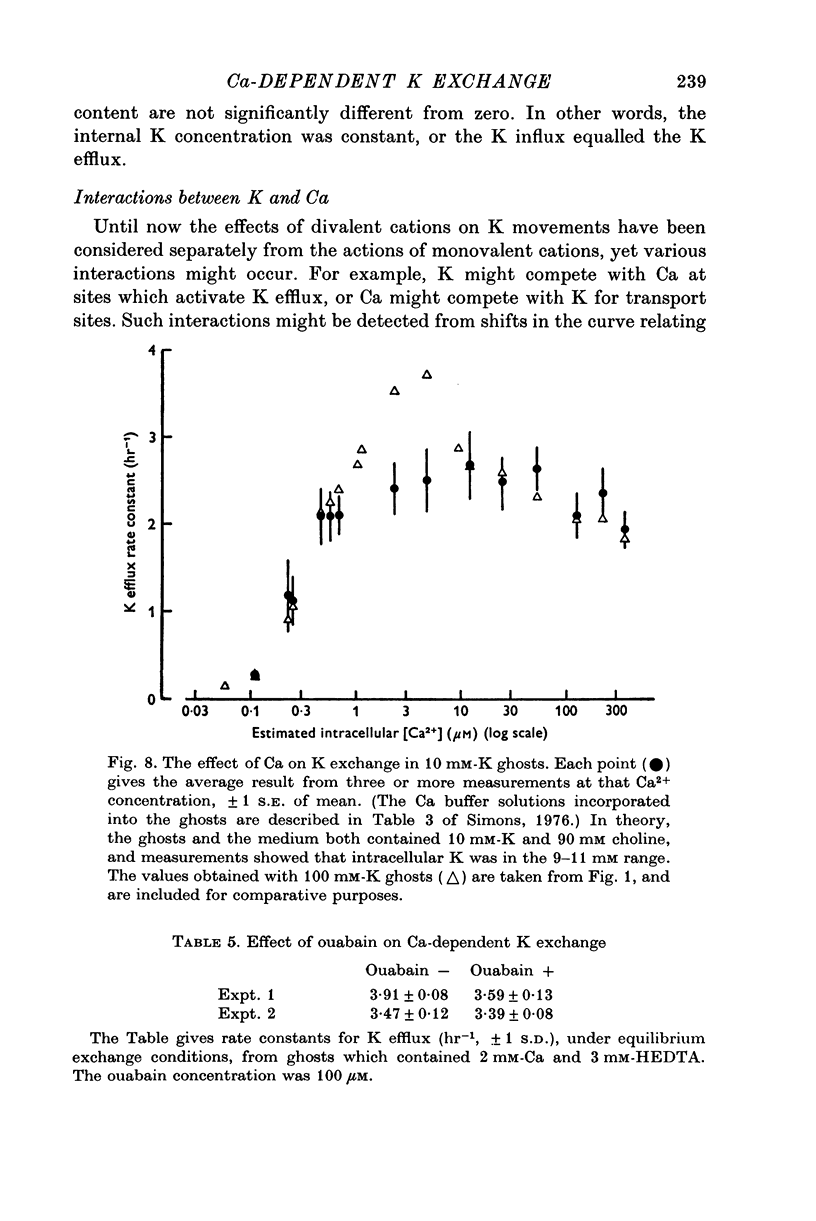
1. The properties of the Ca-dependent K transport system of human red cell ghosts have been examined under equilibrium exchange conditions. 2. K transport is stimulated half-maximally by about 0-4muM-Ca2i+ or 5muM-Sr2i+, but much higher concentrations of Ba2i+ give only slight stimulation. Mg is a weak antagonist to Ca. 3. The free Ca2+ concentration in human red cells is estimated to be below 0-25muM. 4. The curve relating the rate of K transport to the intracellular Ca2+ concentration is complicated and suggests that internal Ca acts at three or more sites. 5. K, Rb and possibly Cs ions are transported by the Ca-dependent system. Under comparable conditions the relative rates are 1(K):1-5(Rb): less than 0-05(Cs). 6. No Ca-dependent transport of Na, Li or choline could be detected. If Na is transported, it must be at less than 1/40 of the rate of K. 7. The rate of K transport is almost linearly related to the K concentration in the 0-200 mM range, but the curve is sigmoid close to the origin. 8. Intracellular, but not extracellular Na inhibits K transport, in a way that suggests competition with K at more than one site. 9. These results suggest that the transport system has a complex mechanism.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger H., Jänig G. R., Gerber G., Ruckpaul K., Rapoport S. M. Interaction of haemoglobin with ions. Interactions among magnesium, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate, and oxygenated and deoxygenated human haemoglobin under simulated intracellular conditions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 18;38(3):553–562. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03090.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. The permeability of human erythrocytes to potassium. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1956;10(2-4):185–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isnberg G. Is potassium conductance of cardiac Purkinje fibres controlled by (Ca2+)? Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):273–274. doi: 10.1038/253273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. On the ATP dependence of the Ca 2+ -induced increase in K + permeability observed in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb W. R., Stein W. D. Testing and characterizing the simple carrier. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 10;373(2):178–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb W. R., Stein W. D. Testing and characterizing the simple pore. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 10;373(2):165–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porzig H. Comparative study of the effects of propranolol and tetracaine on cation movements in resealed human red cell ghosts. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(1):27–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. J., Whittam R. The control by internal calcium of membrane permeability to sodium and potassium. J Physiol. 1971 May;214(3):481–507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzmann H. J. Dependence on calcium concentration and stoichiometry of the calcium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(2):551–569. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. The preparation of human red cell ghosts containing calcium buffers. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;256(1):209–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



