Abstract
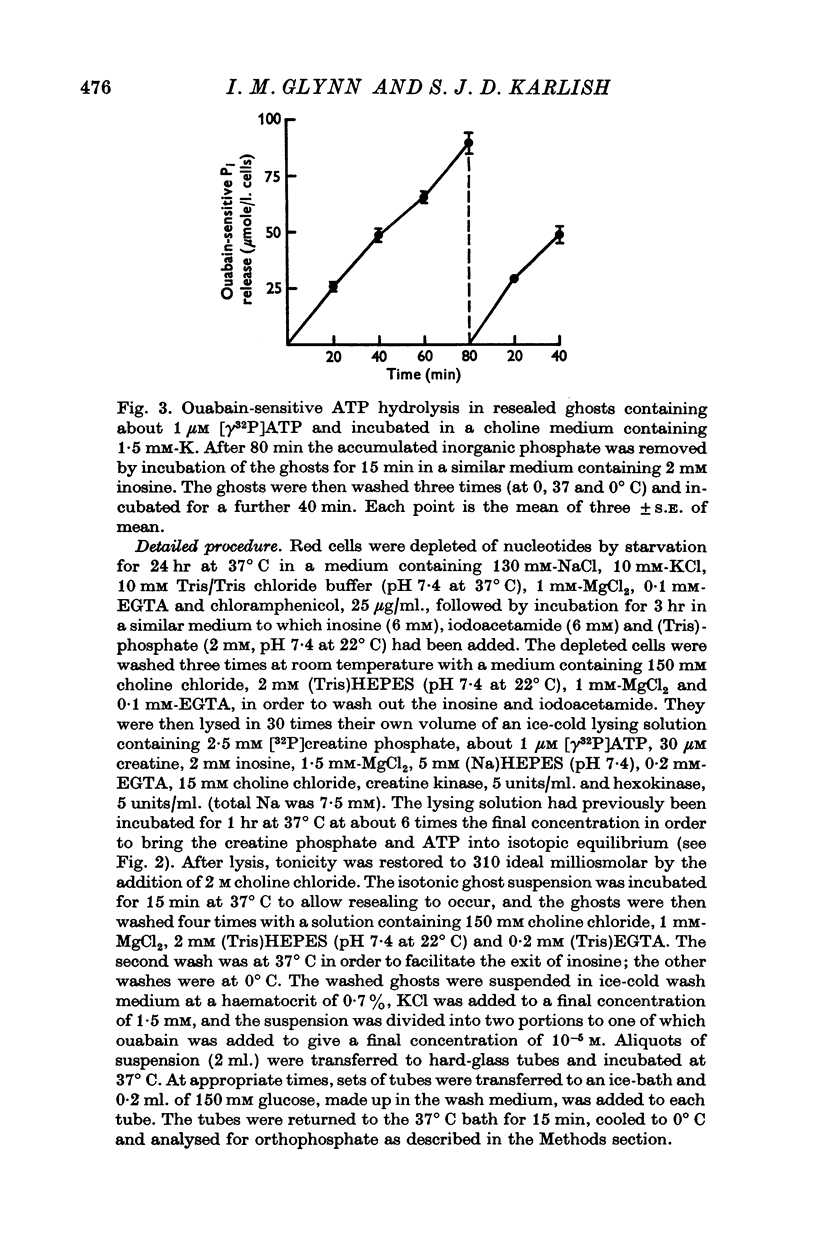
1. A method has been developed for regenerating [γ32P]ATP of constant specific activity within resealed red cell ghosts, and for measuring its hydrolysis. The method may be used to follow the hydrolysis of ATP at concentrations down to 1 μM, and for periods long enough for the ATP at these very low concentrations to turn over several hundred times.
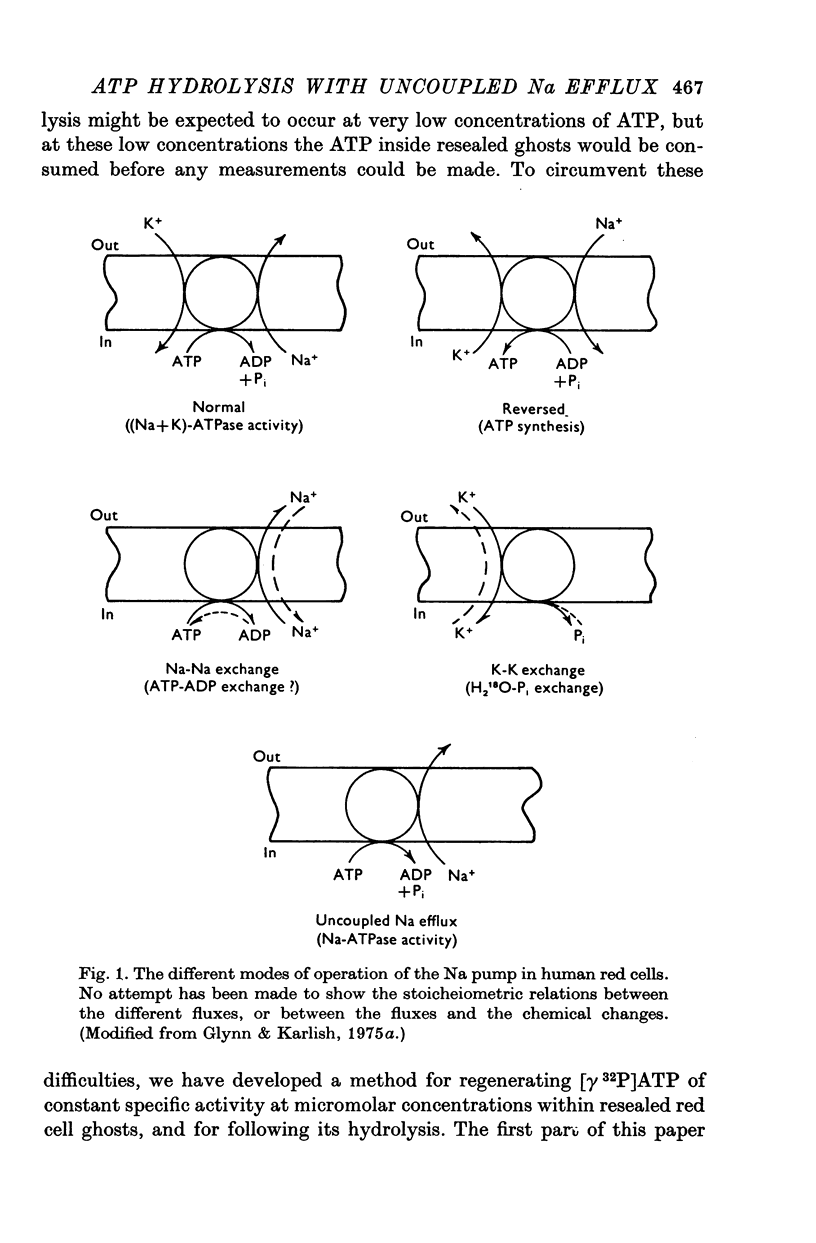
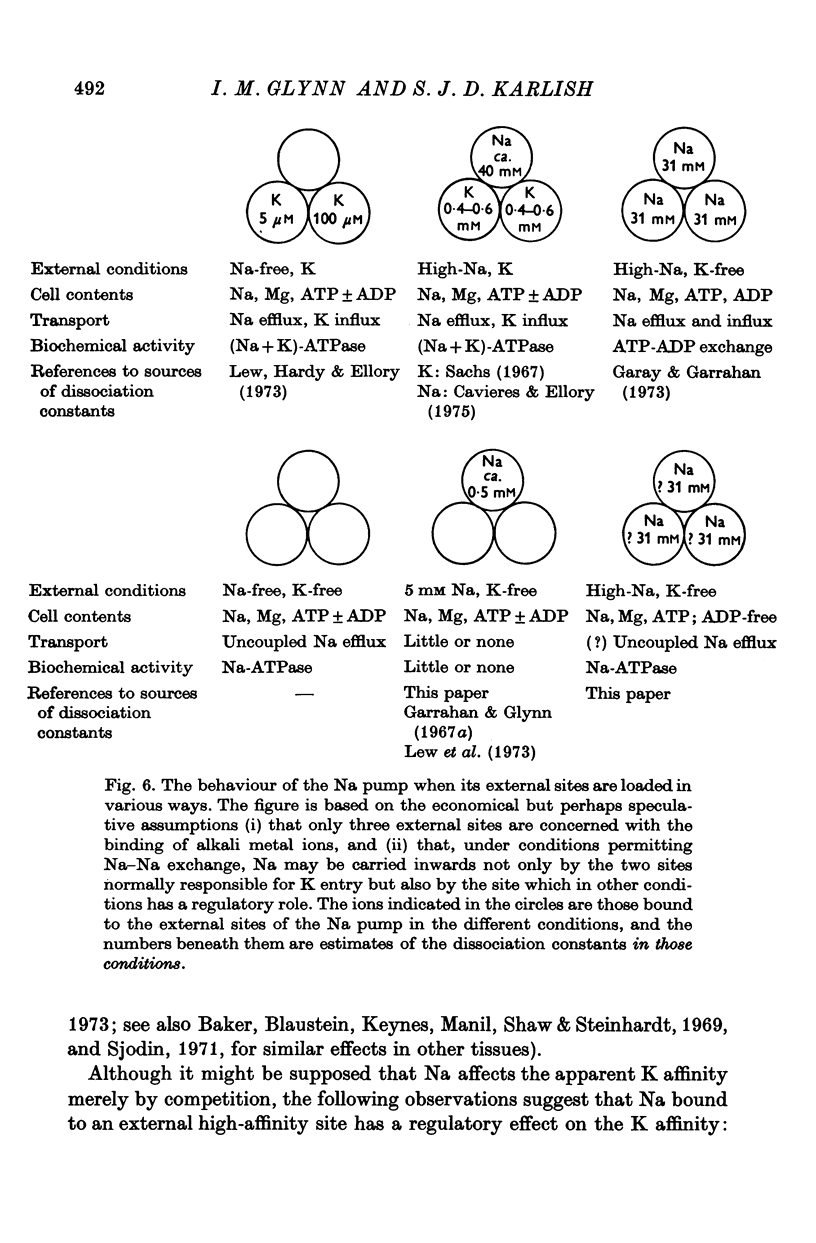
2. Using this method we have been able to show that the `uncoupled' efflux of Na caused by the Na pump when resealed red cell ghosts are incubated in (Na + K)-free media is associated with a hydrolysis of ATP. The stoicheiometry is roughly 2-3 Na ions expelled per molecule of ATP hydrolysed.
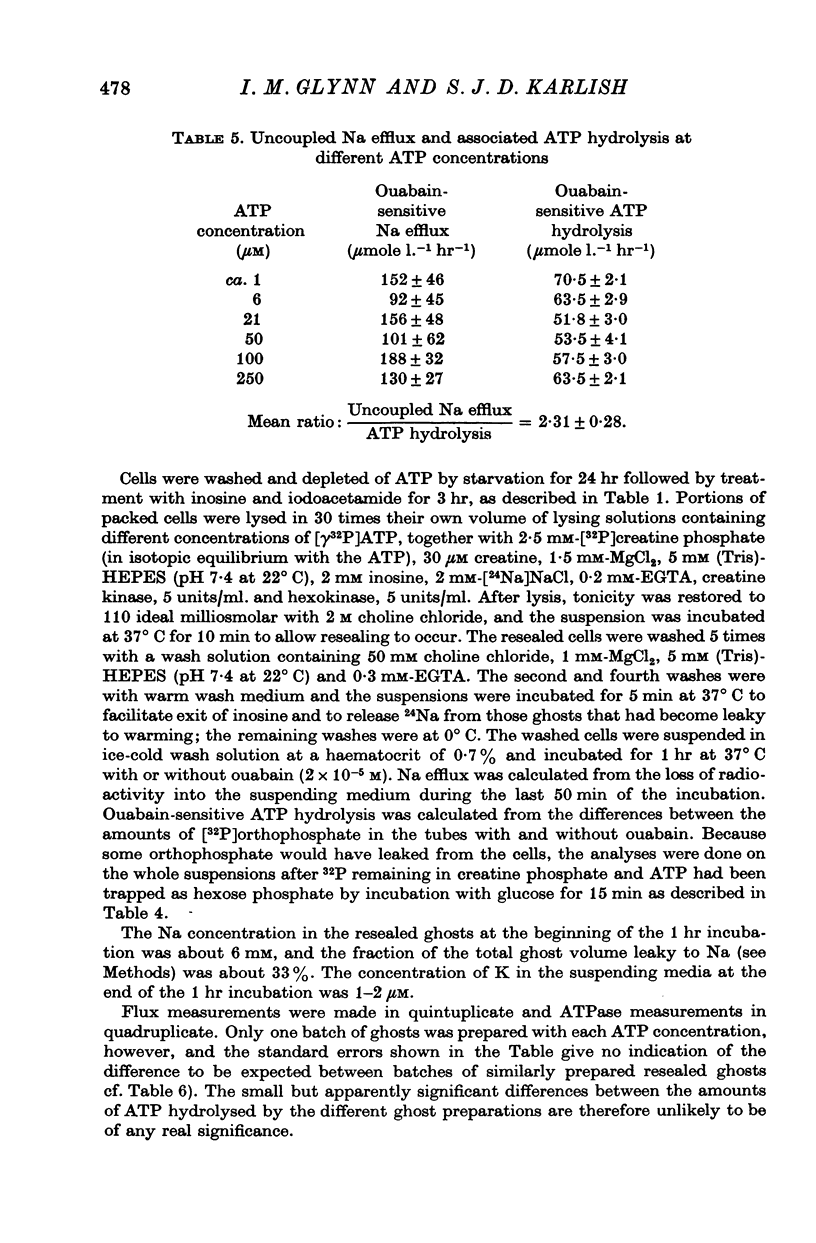
3. Measurements of ATP hydrolysis and Na efflux as functions of intracellular ATP concentration have shown that uncoupled Na efflux, and its associated ATP hydrolysis, are saturated at intracellular ATP concentrations in the region of 1 μM.
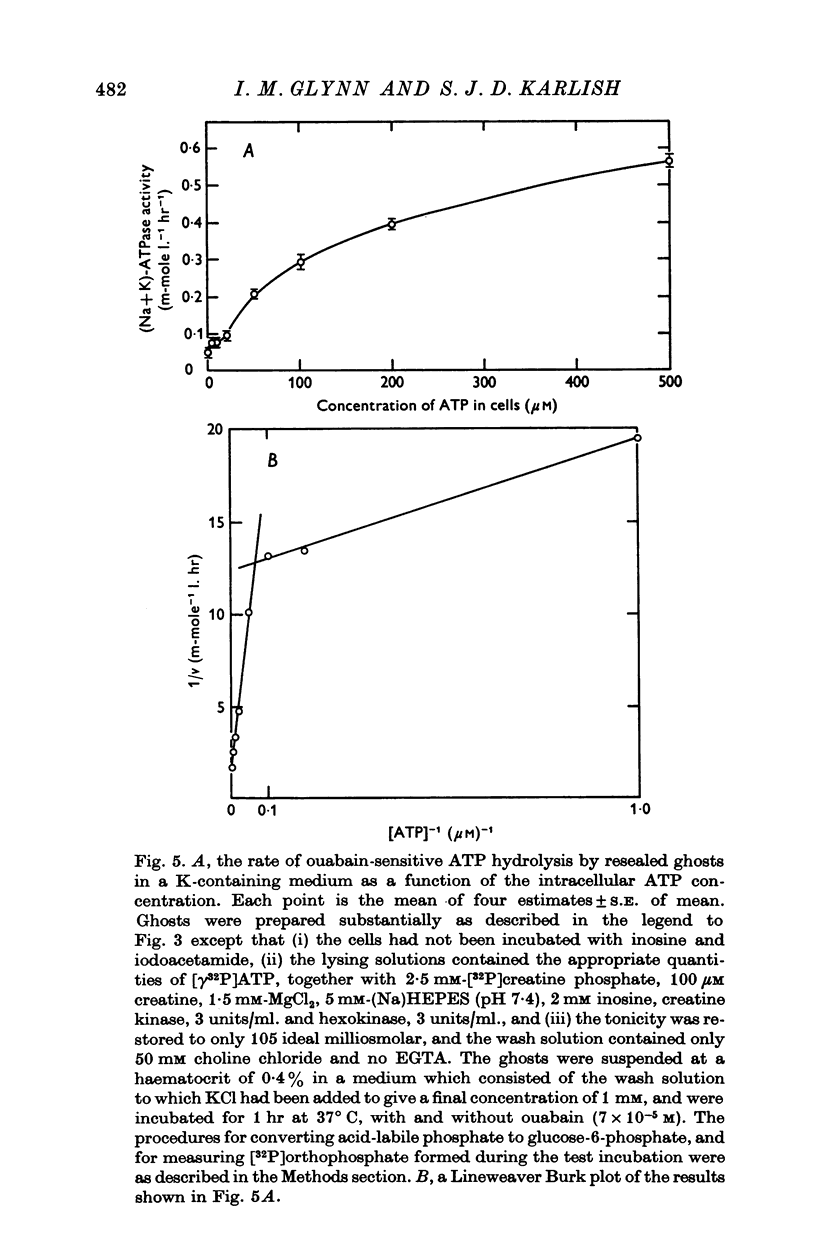
4. Measurement of ATP hydrolysis as a function of ATP concentration in resealed ghosts incubated in a K-containing medium gave a complicated activation curve suggesting the involvement of high-affinity (Km ca. 1 μM) and low-affinity (Km ca. 100 μM) sites.
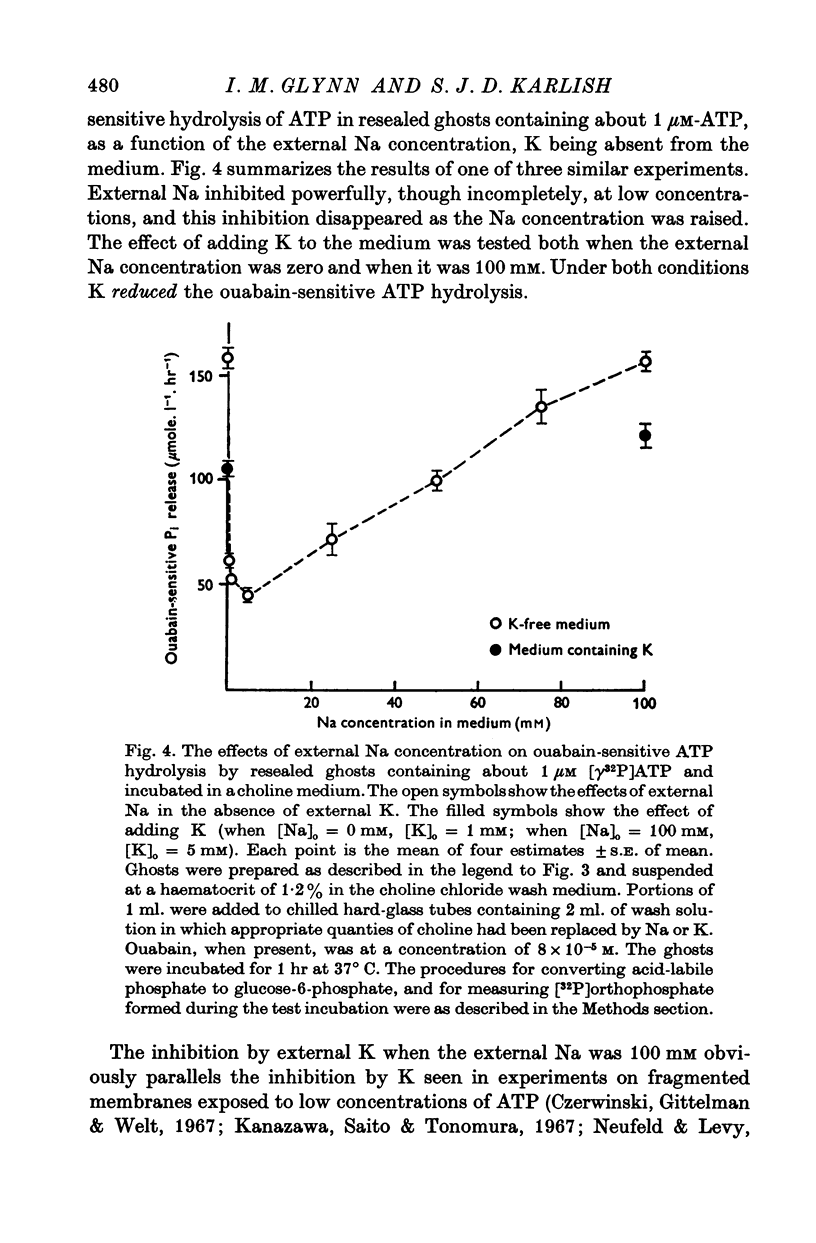
5. When resealed ghosts containing about 1 μM-ATP were incubated in a Na-free or in a high-Na medium, the addition of K to the medium reduced the rate of ouabain-sensitive ATP hydrolysis.
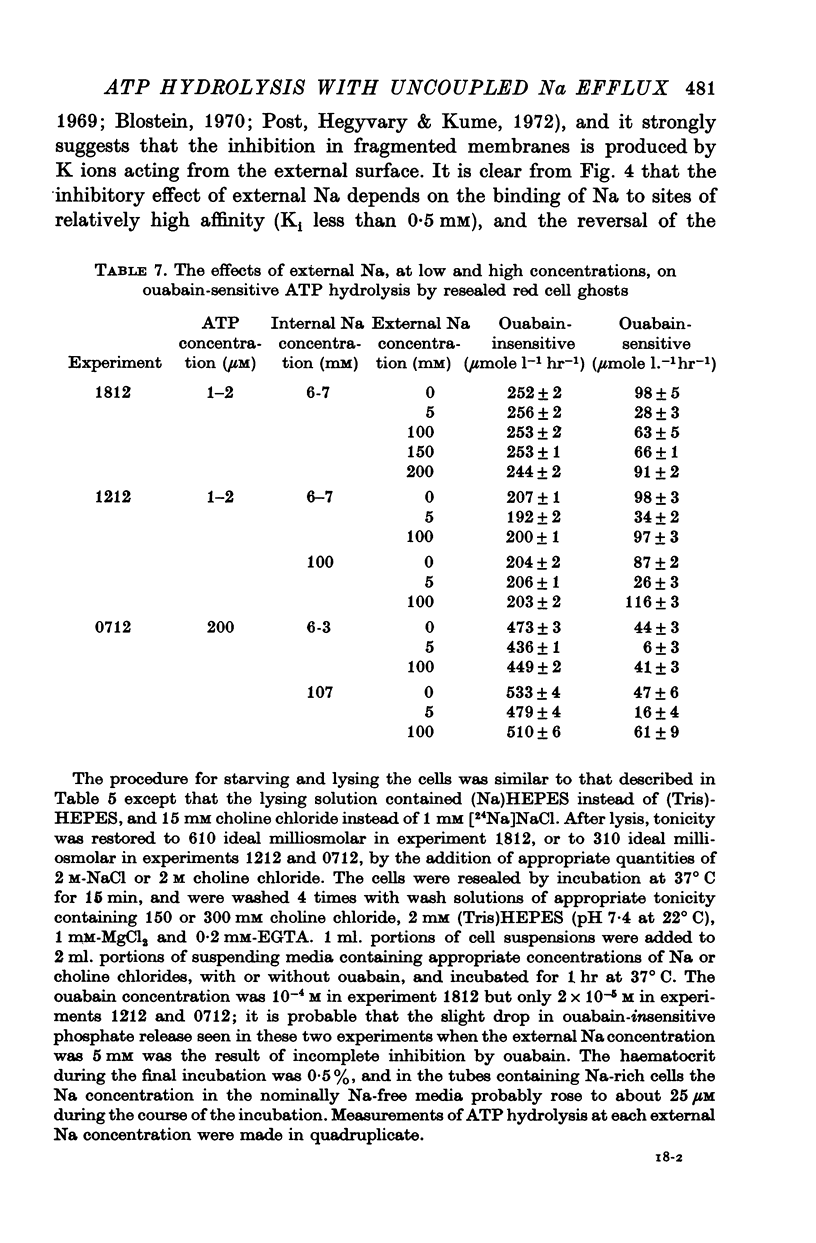
6. Ouabain-sensitive ATP hydrolysis in resealed ghosts incubated in K-free choline media was inhibited by external Na at low concentrations (Ki < 1 mM), but this inhibition was reversed as the external Na concentration was further increased.
7. The results show that uncoupled Na efflux may be thought of as the transport mode associated with Na-ATPase activity, just as Na-K exchange is the transport mode associated with (Na + K)-ATPase activity. The significance of the differences between uncoupled Na efflux and Na-ATPase activity, on the one hand, and Na—K exchange and (Na + K)-ATPase activity, on the other, is discussed.
Full text
PDF





















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Slayman C. L. Membrane potential and conductance during transport of sodium, potassium and rubidium in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):970–1014. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., CARAVAGGIO L. L. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. V. Correlation of enzyme activity with cation flux in six tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:37–46. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90531-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F., Blaustein M. P., Keynes R. D., Manil J., Shaw T. I., Steinhardt R. A. The ouabain-sensitive fluxes of sodium and potassium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(2):459–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker P. F. Phosphorus metabolism of intact crab nerve and its relation to the active transport of ions. J Physiol. 1965 Sep;180(2):383–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blostein R. Sodium-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity of the erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):270–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinley F. J., Jr, Mullins L. J. Effects of membrane potential on sodium and potassium fluxes in squid axons. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):406–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavieres J. D., Ellory J. C. Allosteric inhibition of the sodium pump by external sodium. Nature. 1975 May 22;255(5506):338–340. doi: 10.1038/255338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. B., Keynes R. D., Rybová R. The coupling of sodium efflux and potassium influx in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(4):865–880. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czerwinski A., Gitelman H. J., Welt L. G. A new member of the ATPase family. Am J Physiol. 1967 Sep;213(3):786–792. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.3.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dydynska M., Harris E. J. Consumption of high-energy phosphates during active sodium and potassium interchange in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jan;182(1):92–109. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Garrahan P. J. The interaction of sodium and potassium with the sodium pump in red cells. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):297–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The behaviour of the sodium pump in red cells in the absence of external potassium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):159–174. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Hoffman J. F. Nucleotide requirements for sodium-sodium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):239–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. ATP hydrolysis associated with an uncoupled efflux of Na through the Na pump. J Physiol. 1975 Aug;250(1):33P–34P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J., Cavieres J. D., Ellory J. C., Lew V. L., Jorgensen P. L. The effects of an antiserum to Na+, K+-ATPase on the ion-transporting and hydrolytic activities of the enzyme. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):357–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Lew V. L., Lüthi U. Reversal of the potassium entry mechanism in red cells, with and without reversal of the entire pump cycle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):371–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFMAN J. F. The active transport of sodium by ghosts of human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1962 May;45:837–859. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.5.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegyvary C., Post R. L. Binding of adenosine triphosphate to sodium and potassium ion-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5234–5240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J., Norby J. G. On the specificity of the ATP-binding site of (Na+ + K+)-activated ATPase from brain microsomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Apr 13;233(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa T., Saito M., Tonomura Y. Formation and decomposition of a phosphorylated intermediate in the reaction of Na plus-K plus dependent ATPase. J Biochem. 1970 May;67(5):693–711. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa T., Saito M., Tonomura Y. [Properties of a phosphorylated protein as a reaction intermediate of Na+-K+ sensitive ATPase]. J Biochem. 1967 May;61(5):555–566. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlish S. J., Glynn I. M. An uncoupled efflux of sodium ions from human red cells, probably associated with Na-dependent ATPase activity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974;242(0):461–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb19110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G., Krishtal O. A., Pidoplichko V. I. Potential-dependent membrane current during the active transport of ions in snail neurones. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):373–392. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L., Hardy M. A., Jr, Ellory J. C. The uncoupled extrusion of Na+ through the Na+ pump. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Oct 11;323(2):251–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90149-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew V. L. On the ATP dependence of the Ca 2+ -induced increase in K + permeability observed in human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins L. J., Brinley F. J., Jr Potassium fluxes in dialyzed squid axons. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Jun;53(6):704–740. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.6.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mårdh S., Zetterqvist O. Phosphorylation of bovine brain Na + , K + -stimulated ATP phosphohydrolase by adenosine ( 32 P)triphosphate studied by a rapid-mixing technique. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld A. H., Levy H. M. A second ouabain-sensitive sodium-dependent adenosine triphosphate in brain microsomes. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 10;244(23):6493–6497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norby J. G., Jensen J. Binding of ATP to brain microsomal ATPase. Determination of the ATP-binding capacity and the dissociation constant of the enzyme-ATP complex as a function of K+ concentration. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):104–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., SEN A. K., ROSENTHAL A. S. A PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATE IN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT ACROSS KIDNEY MEMBRANES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Toda G., Rogers F. N. Phosphorylation by inorganic phosphate of sodium plus potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. Four reactive states. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):691–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestland R. N., Whittam R. The influence of external sodium ions on the sodium pump in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):369–374. doi: 10.1042/bj1090369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repke K. R., Schön R. Flip-flop model of (NaK)-ATPase function. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1973;31(4 Suppl):K19–K30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEN A. K., POST R. L. STOICHIOMETRY AND LOCALIZATION OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT IN THE ERYTHROCYTE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:345–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Competitive effects of some cations on active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Sep;46(9):1433–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI105635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R. Interaction of external K, Na, and cardioactive steroids with the Na-K pump of the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1974 Feb;63(2):123–143. doi: 10.1085/jgp.63.2.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs J. R., Welt L. G. The concentration dependence of active potassium transport in the human red blood cell. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):65–76. doi: 10.1172/JCI105512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. The interaction of ATP-analogues possessing a blocked gamma-phosphate group with the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):731–739. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjodin R. A. The kinetics of sodium extrusion in striated muscle as functions of the external sodium and potassium ion concentrations. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Feb;57(2):164–187. doi: 10.1085/jgp.57.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein W. D., Lieb W. R., Karlish S. J., Eilam Y. A modle for active transport of sodium and potassium ions as mediated by a tetrameric enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):275–278. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Post R. L. Synthesis of adenosine triphosphate and exchange between inorganic phosphate and adenosine triphosphate in sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3010–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teipel J., Koshland D. E., Jr The significance of intermediary plateau regions in enzyme saturation curves. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4656–4663. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittam R., Ager M. E. The connexion between active cation transport and metabolism in erythrocytes. Biochem J. 1965 Oct;97(1):214–227. doi: 10.1042/bj0970214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



