Abstract
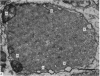
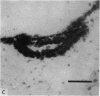
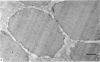
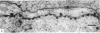
1. The localization of Ca-accumulating structures in the anterior byssal retractor muscle (ABRM) of Mytilus edulis and their role in the contraction-relaxation cycle were studied by fixing the ABRM at rest or during various phases of mechanical activity with a 1% osmium tetroxide solution containing 2% potassium pyroantimonate. 2. In the resting ABRM, electron-opaque pyroantimonate precipitate was observed at the inner surface of the plasma membrane, the vesicles and the mitochondria. 3. Electron X-ray microanalysis showed the presence of Ca in the precipitate, indicating that the precipitate provides a valid measure for Ca localization. 4. In the ABRM fixed at the peak of mechanical response to the Ca-removal or to acetylcholine, the precipitate was found to be diffusely distributed in the myoplasm in the form of a number of particles. At the completion of spontaneous relaxation, the precipitate was again seen at the inner surface of the plasma membrane. 5. During the catch state, the precipitate was found to be re-accumulated in the peripheral structures with a corresponding decrease of the precipitate in the myoplasm. 6. These results not only provide evidence for the involvement of the Ca-accumulating structures in the contraction-relaxation cycle in the ABRM, but also suggest that the transition from active to catch contractions is related to a decrease in myoplasmic free Ca ion concentration.
Full text
PDF
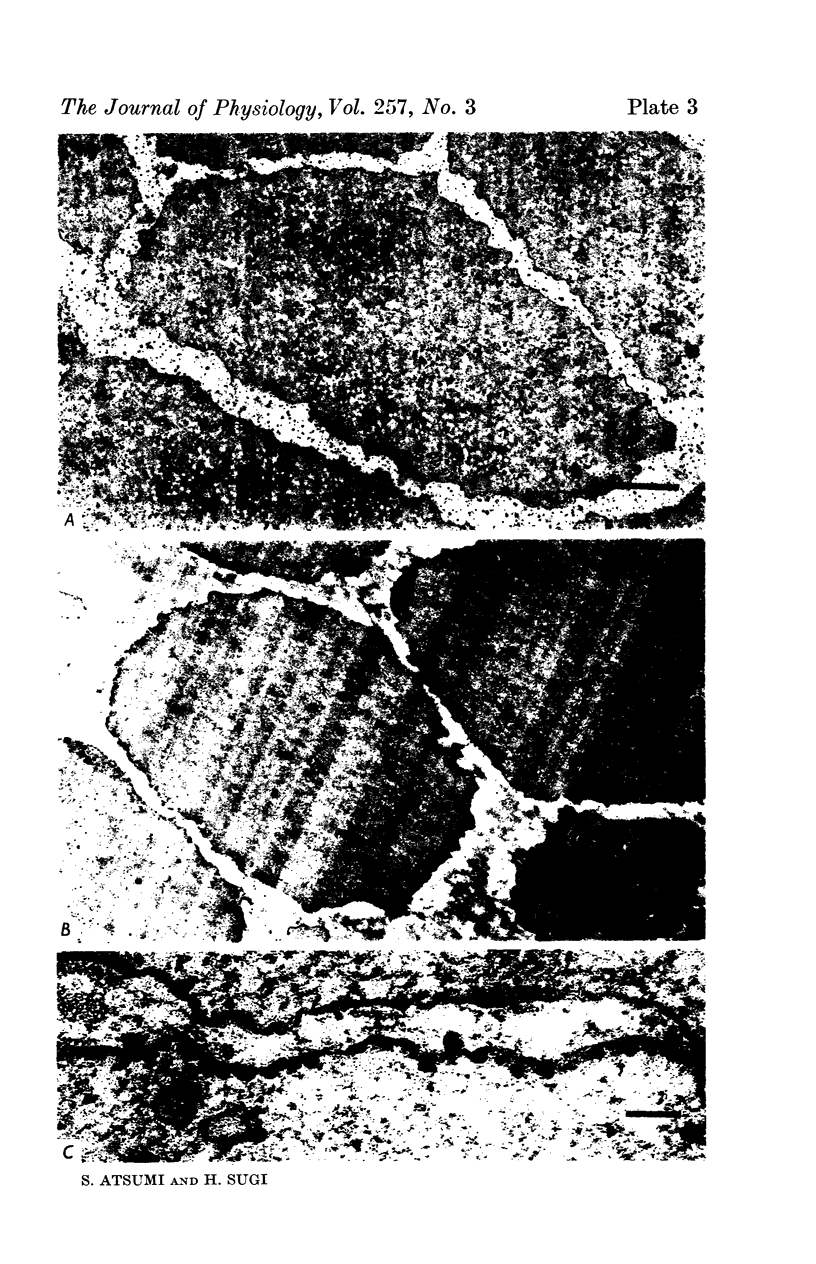











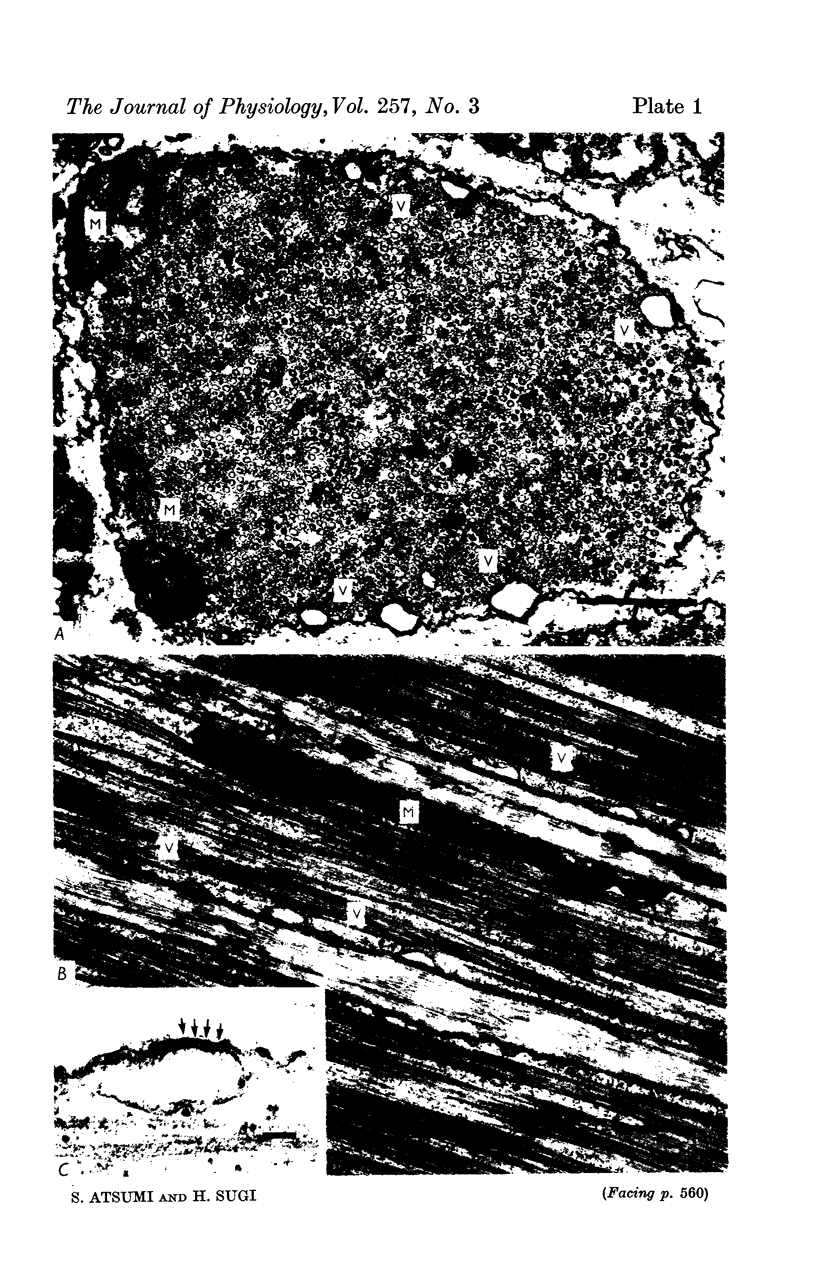
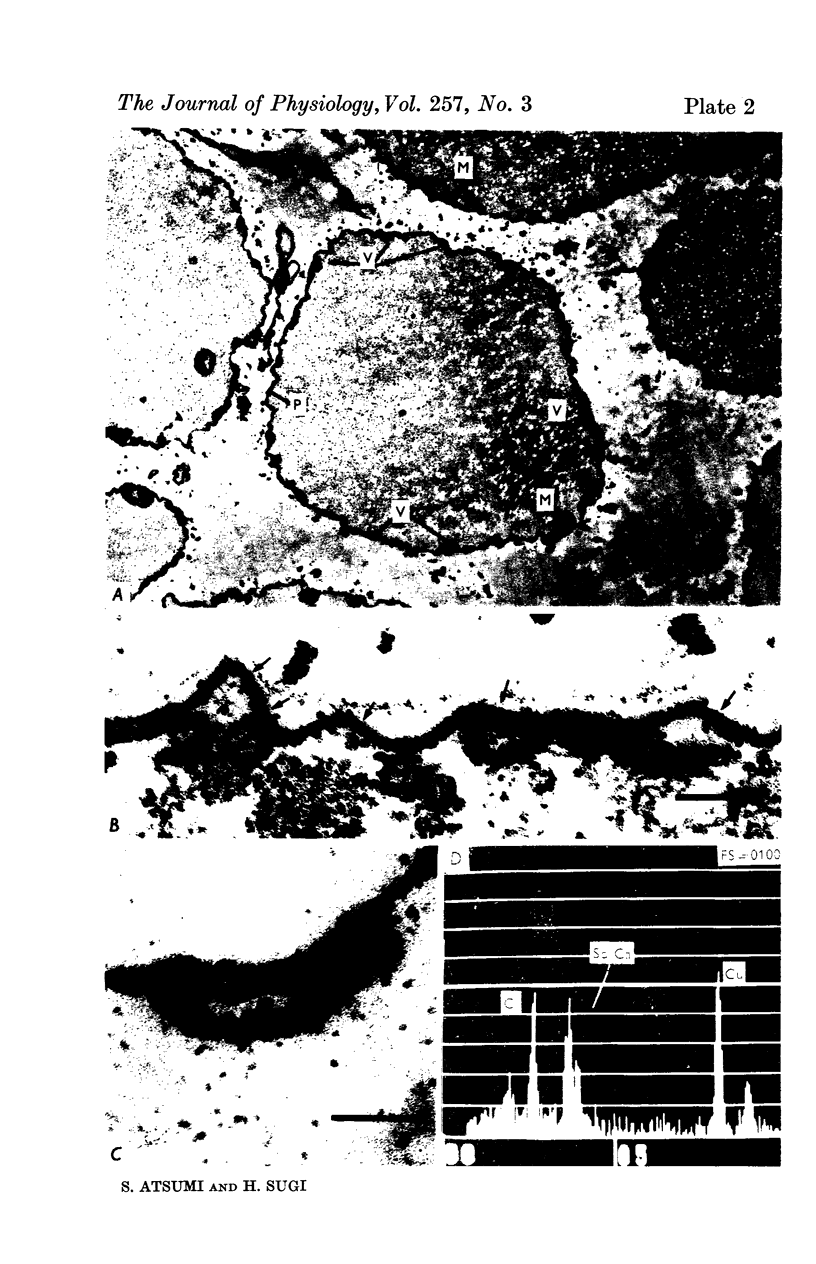

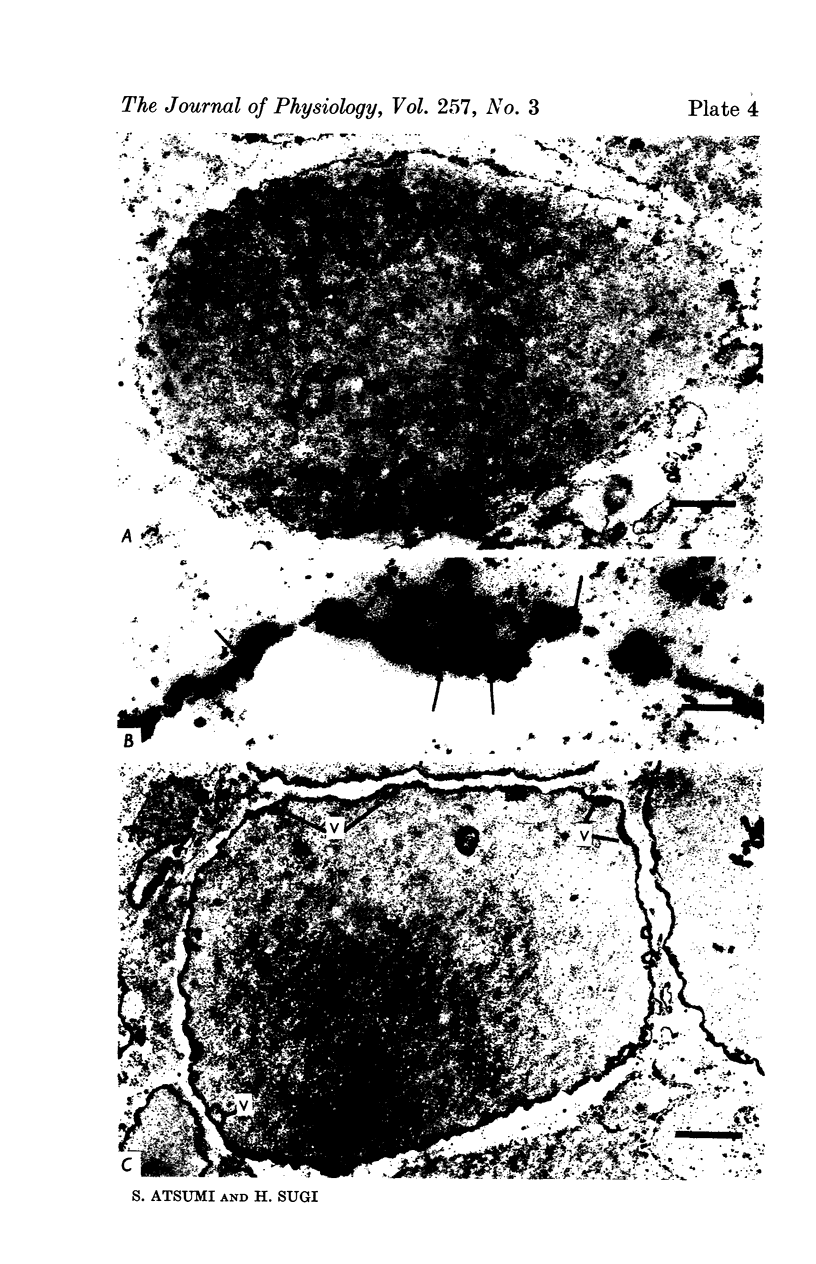
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABBOTT B. C., LOWY J. Contraction in mulluscan smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):385–397. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baguet F., Gillis J. M. Energy cost of tonic contraction in a lamellibranch catch muscle. J Physiol. 1968 Sep;198(1):127–143. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baguet F. The catch-state in glycerol extracted fibres from a lamellibranch smooth muscle (ABRM). Pflugers Arch. 1973;340(1):19–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00592194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batra S. C., Daniel E. E. Effect of multivalent cations and drugs on Ca uptake by the rat myometrial microsomes. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1971 Feb 1;38(2):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(71)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMBRIDGE G. W., HOLGATE J. A., SHARP J. A. A pharmacological analysis of the contractile mechanism of Mytilus muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:451–464. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carsten M. E. Role of calcium binding by sarcoplasmic reticulum in the contraction and relaxation of uterine smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Apr;53(4):414–426. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.4.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine C. E., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Sarcoplasmic reticulum and excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian smooth muscles. J Cell Biol. 1972 Mar;52(3):690–718. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine C. E., Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria as cation accumulation sites in smooth muscle. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1973 Mar 15;265(867):17–23. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1973.0005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M. Calcium ion and muscle contraction. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1968;18:123–183. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(68)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodford P. J., Wolowyk M. W. Localization of cation interactions in the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig taenia coli. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):521–535. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann H. G. Calciumakkumulierende Strukturen in einem glatten Wirbellosenmuskel. Protoplasma. 1969;67(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01256771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann H. G., Zebe E. Uber die Funktionsweise glatter Muskelfasern. Elektronemikroskopische Untersuchungen am Byssjstretraktor (ABRM) von Mytilus edulise. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;85(4):534–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka T., Osa T., Twarog B. M. The action of 5-hydroxytryptamine on Mytilus smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):869–877. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz L., Fitzpatrick D. F., Debbas G., Landon E. J. Localization of calcium pump activity in smooth muscle. Science. 1973 Jan 26;179(4071):384–386. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4071.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON W. H. Tonic mechanisms in smooth muscles. Physiol Rev Suppl. 1962 Jul;5:113–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legato M. J., Langer G. A. The subcellular localization of calcium ion in mammalian myocardium. J Cell Biol. 1969 May;41(2):401–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEEGG J. C., STRAUB R. W., TWAROG B. M. INHIBITION OF CONTRACTION IN A MOLLUSCAN SMOOTH MUSCLE BY THIOUREA, AN INHIBITOR OF THE ACTOMYOSIN CONTRACTILE MECHANISM. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Sep 17;158:156–176. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg J. C. Smooth muscle tone. Physiol Rev. 1971 Jan;51(1):201–248. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1971.51.1.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Devine C. E., Somlyo A. V., North S. R. Sarcoplasmic reticulum and the temperature-dependent contraction of smooth muscle in calcium-free solutions. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):722–741. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. P., Somlyo A. V., Devine C. E., Peters P. D., Hall T. A. Electron microscopy and electron probe analysis of mitochondrial cation accumulation in smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jun;61(3):723–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stössel W., Zebe E. Zur intracellulären Regulation der Kontraktionsaktivität. Vergleichende Untersuchungen an verscheidenen Muskeltypen. Pflugers Arch. 1968;302(1):38–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00586781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugi H., Yamaguchi T. Activation of the contractile mechanism in the anterior byssal retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. J Physiol. 1976 Jun;257(3):531–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulakhe P. V., Drummond G. I., Ng D. C. Calcium binding by skeletal muscle sarcolemma. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 25;248(12):4150–4157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWAROG B. M. Effects of acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine on the contraction of a molluscan smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:236–242. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TWAROG B. M. Responses of a molluscan smooth muscle to acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Cell Physiol. 1954 Aug;44(1):141–163. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030440112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twarog B. M., Dewey M. M., Hidaka T. The structure of Mytilus smooth muscle and the electrical constants of the resting muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Feb;61(2):207–221. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twarog B. M. Excitation of Mytilus smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Oct;192(3):857–868. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twarog B. M. The regulation of catch in molluscan muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):157–169. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. Connections between the T system and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Anat Rec. 1966 May;155(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091550102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Schrodt G. R. T system connexions with the sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):935–938. doi: 10.1038/211935a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelck U., Jonas L., Wiegershausen B. Ultrahistochemischer Nachweis von Calcium in glatten Muskelzellen der Arteria coronaria sinistra des Schweins. Acta Histochem. 1972;44(1):180–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]