Abstract
1. Intracellular recordings of membrane potential and input resistance have been made in vivo and in vitro from the exocrine acinar cells of rat pancreas using indwelling glass micro-electrodes. 2. The resting cell membrane potential and input resistance in the in vivo experiments were not markedly different from the values obtained in the in vitro experiments. The effect of both acetylcholine (ACh) and pancreozymin (CCK-Pz) on the pancreas in vivo as well as in vitro was to reduce both the acinar cell membrane potential and the input resistance narkedly. The amplitude of the evoked depolarization and the change in input resistance evoked by supramaximal stimuli were of the same magnitude in both types of preparations. 3. Gastrin had an effect on the acinar cell potential and resistance which was indistinguishable from that of CCK-Pz or ACh. The effect of gastrin or CCK-Pz was, in contrast to that of ACh, not influenced by the presence of atropine. The reversal potential for the gastrin evoked potential change was about -20 mV. 4. Secretin in doses producing maximal volume secretion in vivo had no effect on acinar cell membrane potential and input resistance. 5. Dibutyryl cyclic AMP (5mM) and cyclic GMP (1mM) had no effect on cell membrane potential or resistance. 6. It is concluded that the in vitro superfused pancreas segment preparation is a useful model system in electrophysiological studies since it functions essentially as the in vivo preparation. In contrast to both gastrin and CCK-Pz, secretin has no effect on the bioelectrical properties of the acinar cells, indicating that there are no physiologically important secretin receptors in rat acinar cells.
Full text
PDF


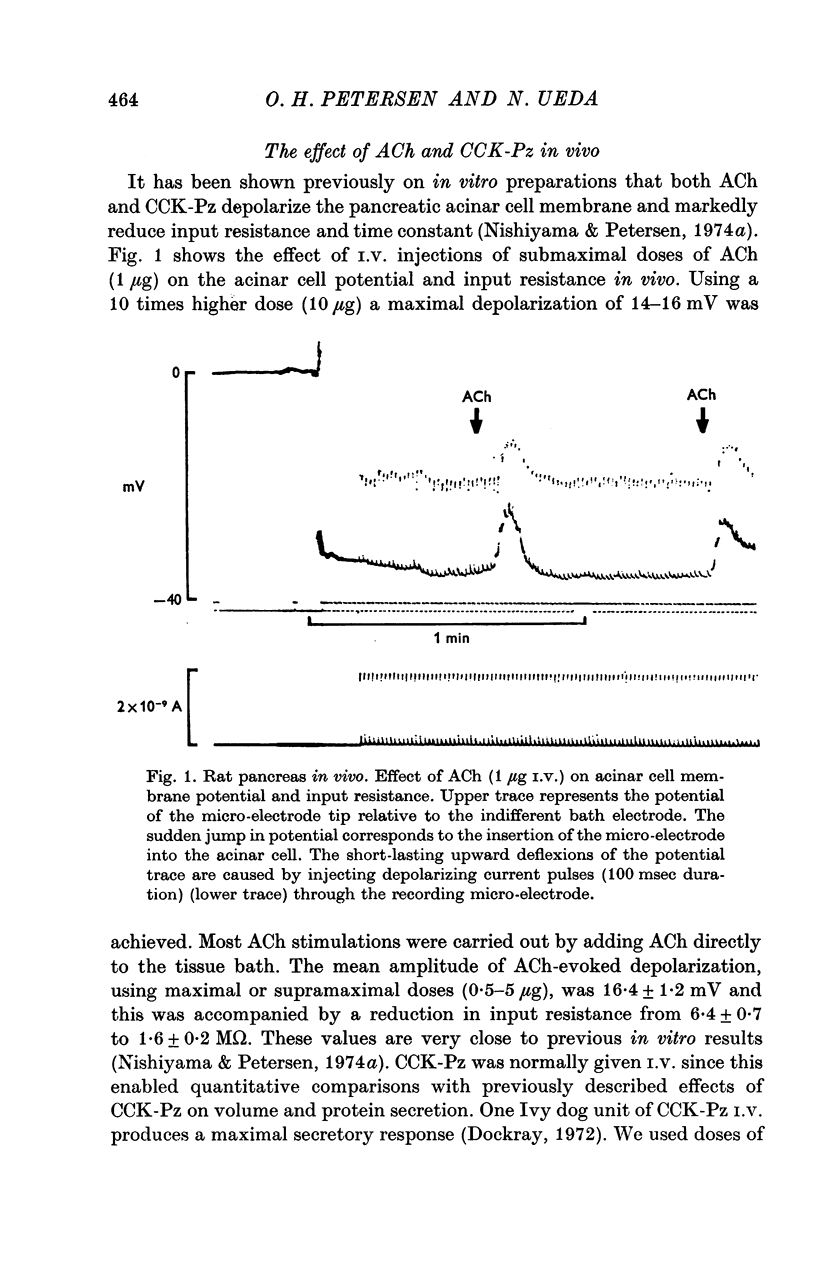
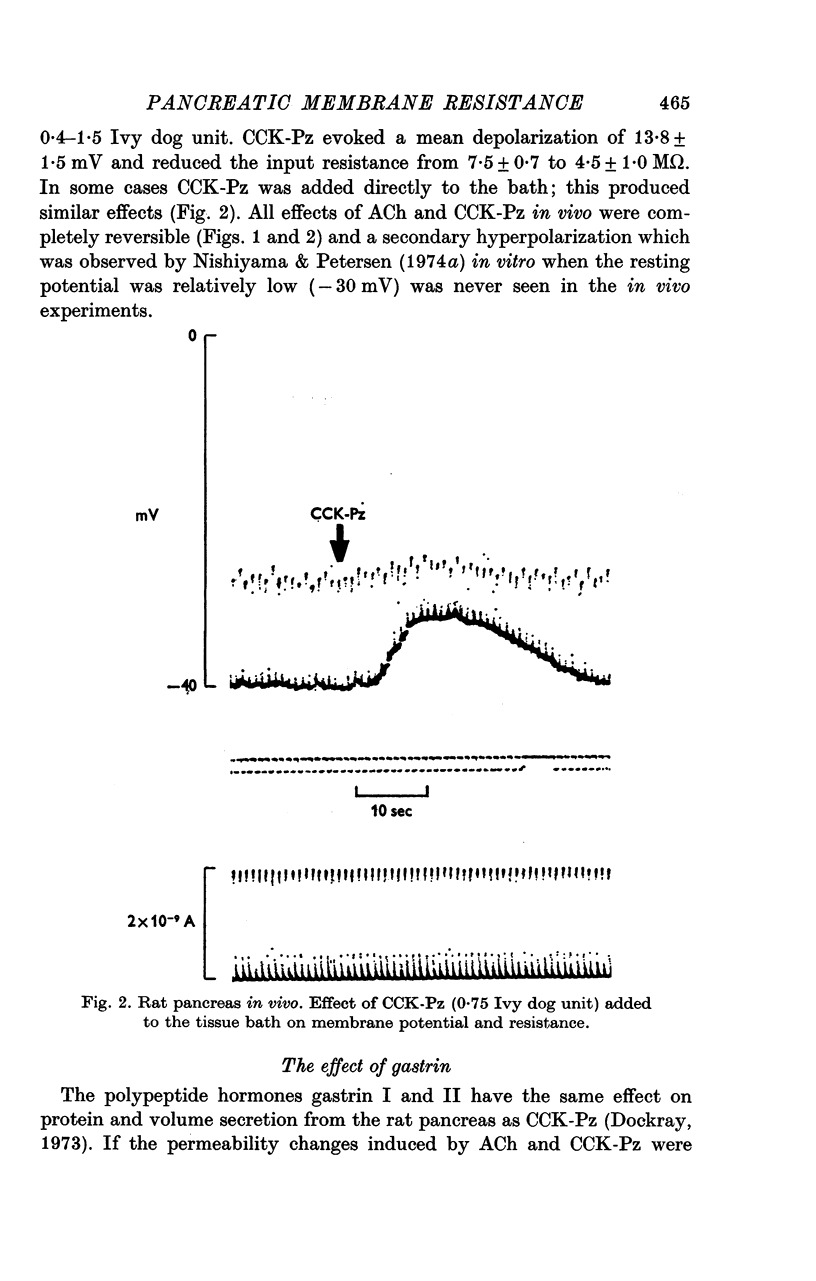
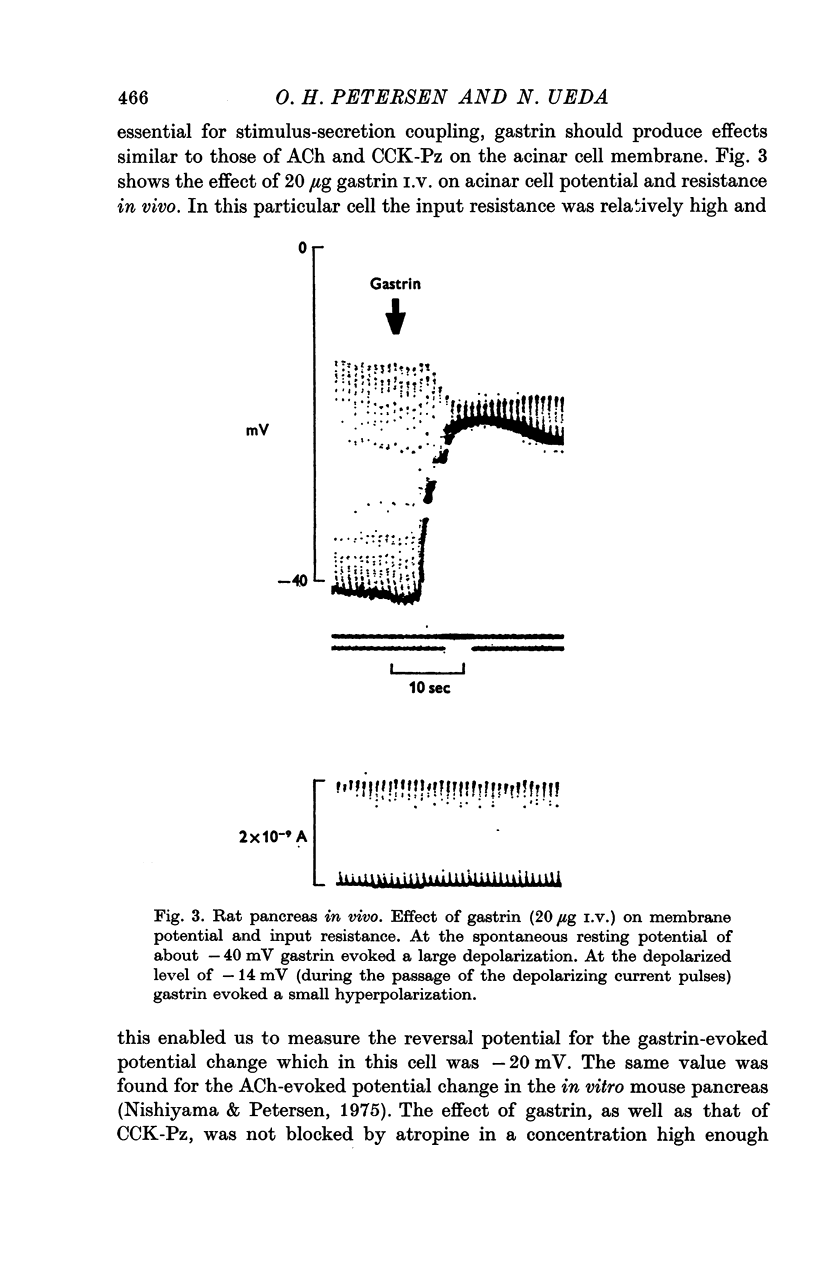
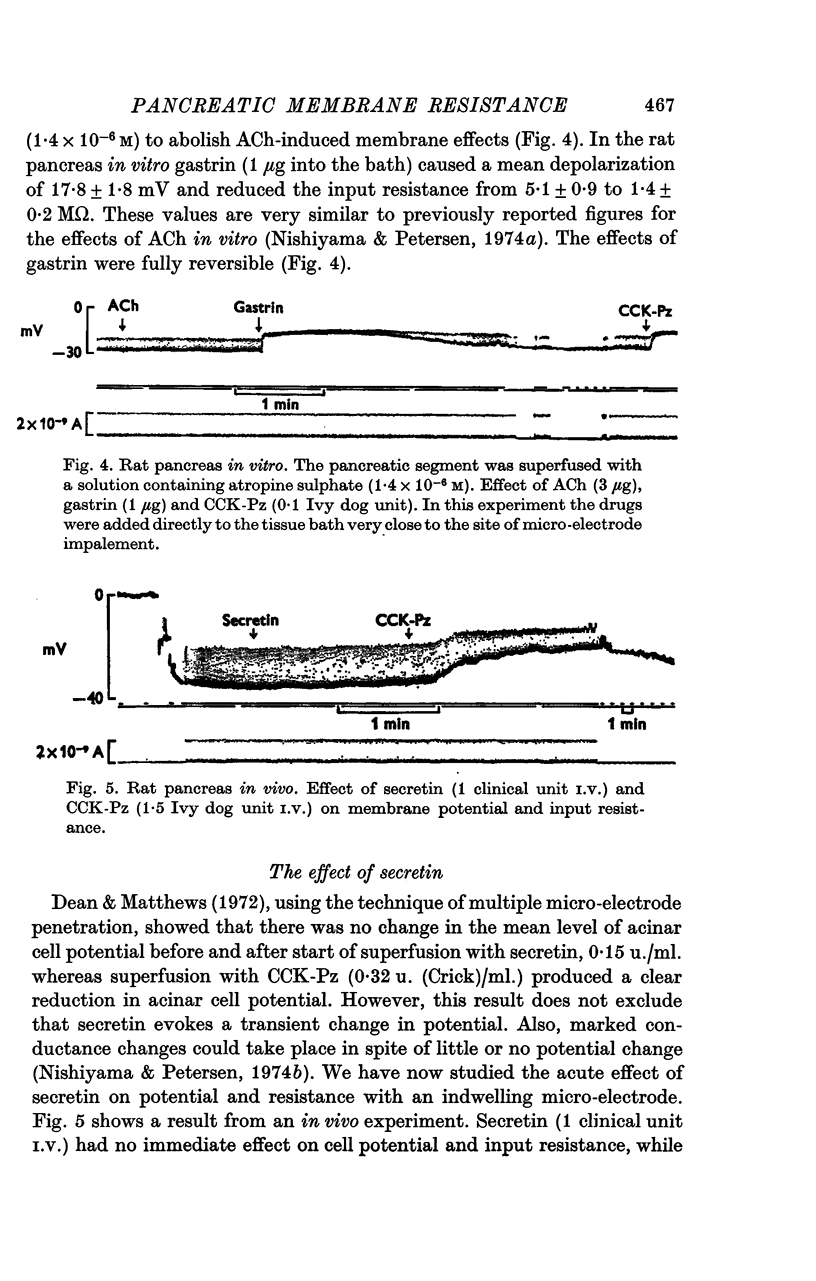




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argent B. E., Case R. M., Scratcherd T. Stimulation of amylase secretion from the perfused cat pancreas by potassium and other alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1971 Aug;216(3):611–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss W. M., Starling E. H. The mechanism of pancreatic secretion. J Physiol. 1902 Sep 12;28(5):325–353. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1902.sp000920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. L., Brown J. C., Harper A. A., Scratcherd T. A gastric phase of pancreatic secretion. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):812–824. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case R. M., Scratcherd T. The actions of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and methyl xanthines on pancreatic exocrine secretion. J Physiol. 1972 Jun;223(3):649–667. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Pancreatic acinar cells: measurement of membrane potential and miniature depolarization potentials. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;225(1):1–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. The action of gastrin and cholecystokinin-related peptides on pancreatic secretion in the rat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1973 Apr;58(2):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dockray G. J. The action of scretin, cholecystokinin-pancreozymin and caerulein on pancreatic secretion in the rat. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(3):679–692. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper A. A., Raper H. S. Pancreozymin, a stimulant of the secretion of pancreatic enzymes in extracts of the small intestine. J Physiol. 1943 Jun 30;102(1):115–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1943.sp004021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno T. Calcium-dependent amylase release and electrophysiological measurements in cells of the pancreas. J Physiol. 1972 Oct;226(2):353–371. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews E. K., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: ionic dependence of the membrane potential and acetycholine-induced depolarization. J Physiol. 1973 Jun;231(2):283–295. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Membrane potential and resistance measurement in acinar cells from salivary glands in vitro: effect of acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1974 Oct;242(1):173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: ionic dependence of acetylcholine-induced membrane potential and resistance change. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):431–465. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama A., Petersen O. H. Pancreatic acinar cells: membrane potential and resistance change evoked by acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1974 Apr;238(1):145–158. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. Cell membrane permeability change: an important step in hormone action. Experientia. 1974 Oct 15;30(10):1105–1108. doi: 10.1007/BF01923633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H., Pedersen G. L. Membrane effects mediated by alpha-and beta-adrenoceptors in mouse parotid acinar cells. J Membr Biol. 1974;16(4):353–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01872423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen O. H. The effect of glucagon on the liver cell membrane potential. J Physiol. 1974 Jun;239(3):647–656. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutten W. J., de Pont J. J., Bonting S. L. Adenylate cyclase in the rat pancreas properties and stimulation by hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 3;274(1):201–213. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz I., Yamagata A., Weske M. Micropuncture studies on the pancreas of the rabbit. Pflugers Arch. 1969;308(3):277–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00586559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


