Abstract
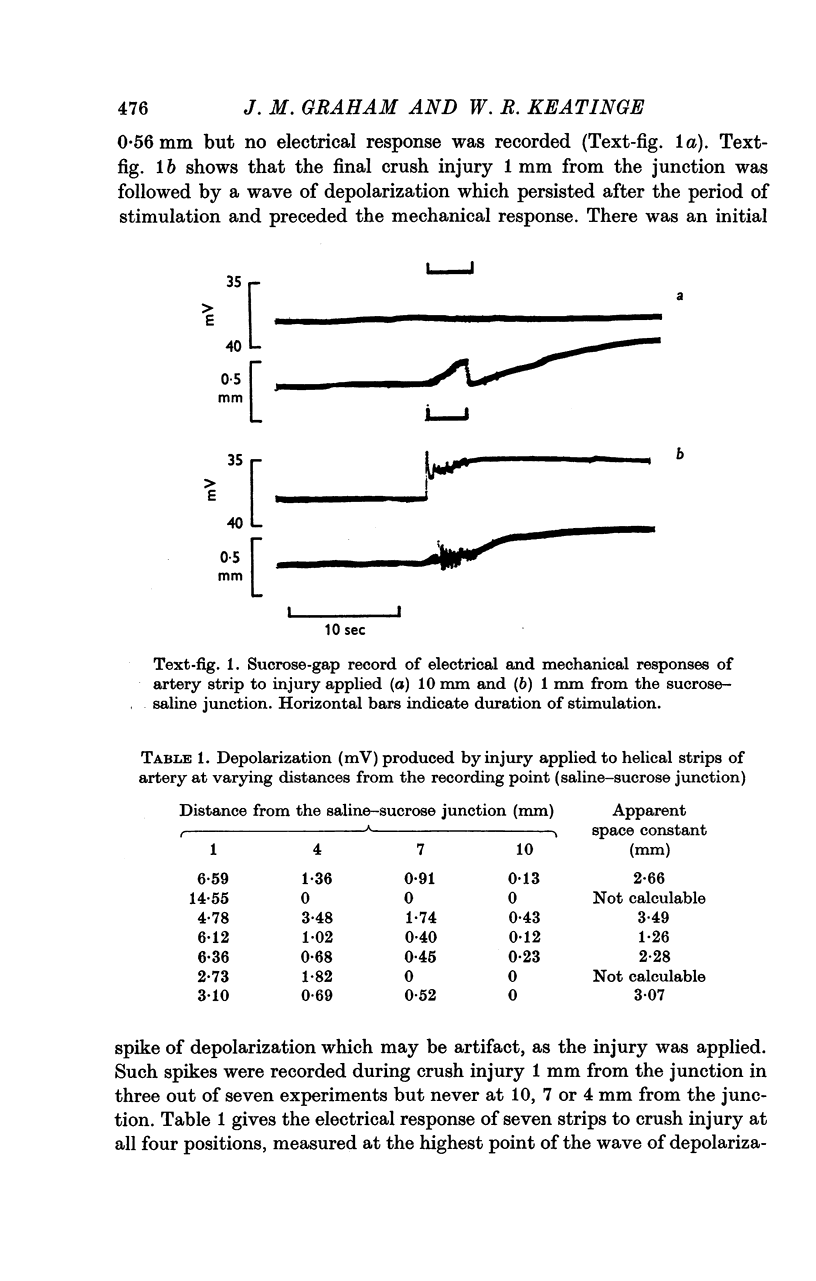
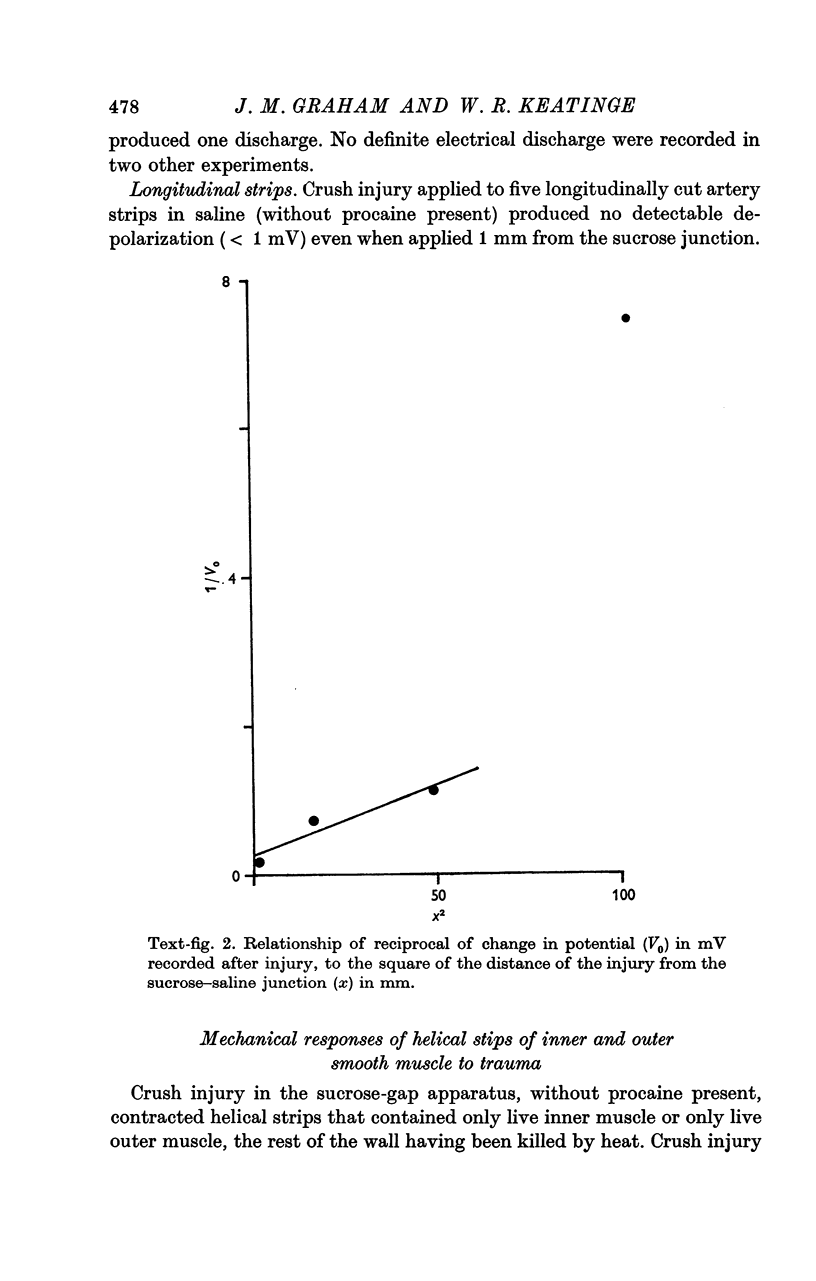
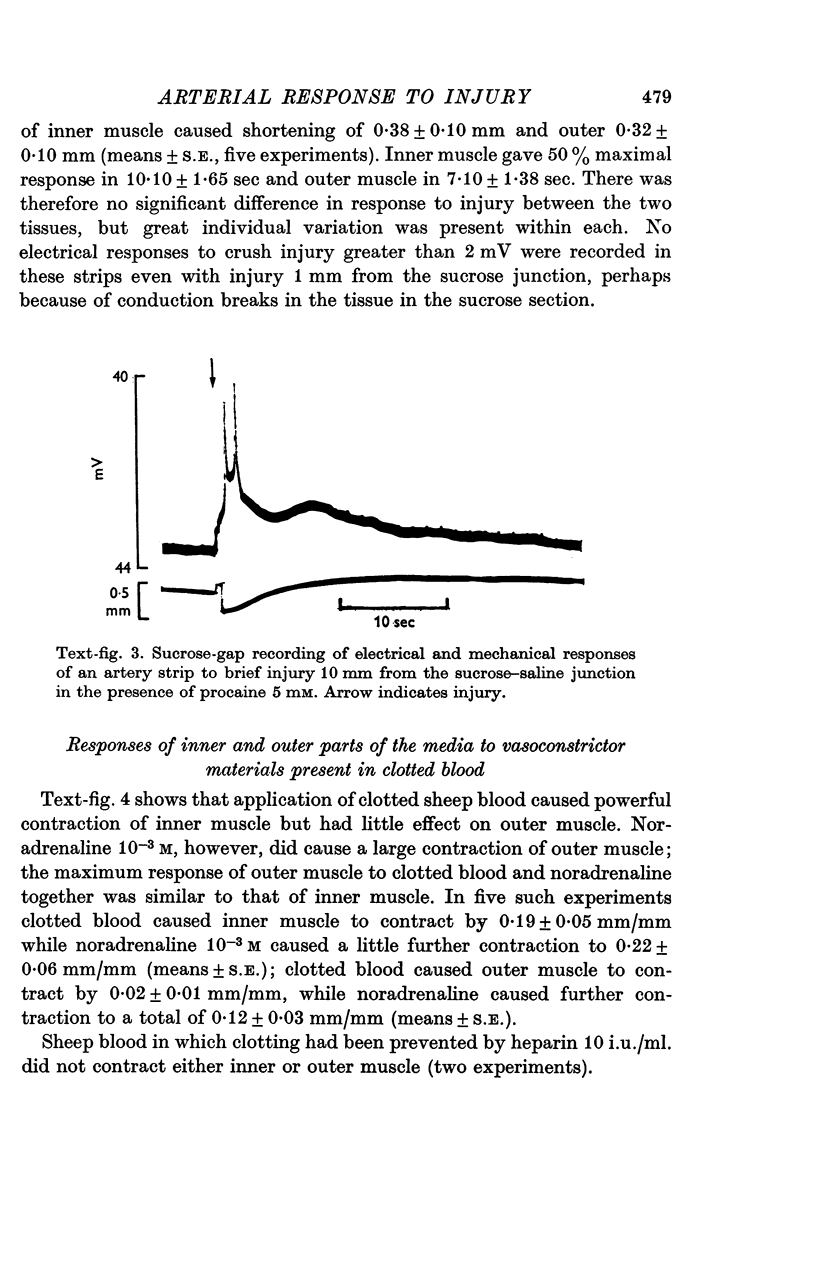
1. Direct injury to the smooth muscle of the sheep carotid artery in vivo caused large, persistent and sharply limited annular contraction, even with tetrodotoxin 10(-5)M present to block nerves. 2. Surcose gap records from artery strips showed that mechanical injury caused slow, prolonged depolarization of the smooth muscle that spread for a few millimetres in a circular direction in relation to the intact artery wall with an apparent space constant of 1-26--3.49 mm. In the longitudinal direction, no depolarization was recorded 1 mm from the site of injury. No spikes were recorded more than 1 mm in either direction from the site of injury except when procaine, which facilitates electrical activity in the smooth muscle, was present. 3. When responses of inner and outer muscle were recorded separately, injury caused comparable contraction of both parts. 4. Clotted blood caused large contractions of intact artery strips; it contracted inner much more than outer muscle. 5. The main factors in the intact vessel's response to injury therefore seem to be inner and outer muscles' direct response to injury, reinforced by spread of depolarization round the vessel wall, and inner muscle's response to vasoconstrictor agents released by clotting blood.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., BRICKNELL J. The uptake of 5-hydroxytryptamine by blood platelets in the cold. J Physiol. 1959 Jun 23;147(1):153–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. I., Tsai C. The mechanism of haemostasis in peripheral vessels. J Physiol. 1948 Jun 25;107(3):280–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1948.sp004272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. M., Keatinge W. R. Differences in sensitivity to vasoconstrictor drugs within the wall of the sheep carotid artery. J Physiol. 1972 Mar;221(2):477–492. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMPHREY J. H., JAQUES R. The histamine and serotonin content of the platelets and polymorphonuclear leucocytes of various species. J Physiol. 1954 May 28;124(2):305–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEATINGE W. R. MECHANISM OF ADRENERGIC STIMULATION OF MAMMALIAN ARTERIES AND ITS FAILURE AT LOW TEMPERATURES. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:184–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J., Mahaley M. S., Jr, Odom G. L. Cerebral arterial spasm. 2. Experimental evaluation of mechanical and humoral factors in pathogenesis. J Neurosurg. 1968 Oct;29(4):339–349. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.29.4.0339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keatinge W. R. Electrical and mechanical response of arteries to stimulation of sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1966 Aug;185(3):701–715. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletka P., Kenyon J. R., Snell M., Cohen S. L., Owen K., Mowbray J. F., Hulme B., Thompson A. E., Porter K. A., Leigh D. A. Cadaveric renal transplantation. An analysis of 65 cases. Lancet. 1969 Jan 4;1(7584):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90981-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND M., REID G. Source of 'serotonin' in serum. Nature. 1951 Sep 1;168(4270):385–385. doi: 10.1038/168385b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANO I., KAKIMOTO Y., TANIGUCHI K., TAKESADA M. Active transport of epinephrine into blood platelets. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jul;197(1):81–84. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH H., BOGDANSKI D. F., UDENFRIEND S. Binding of serotonin and other amines by blood platelets. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Feb;73(2):492–499. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



