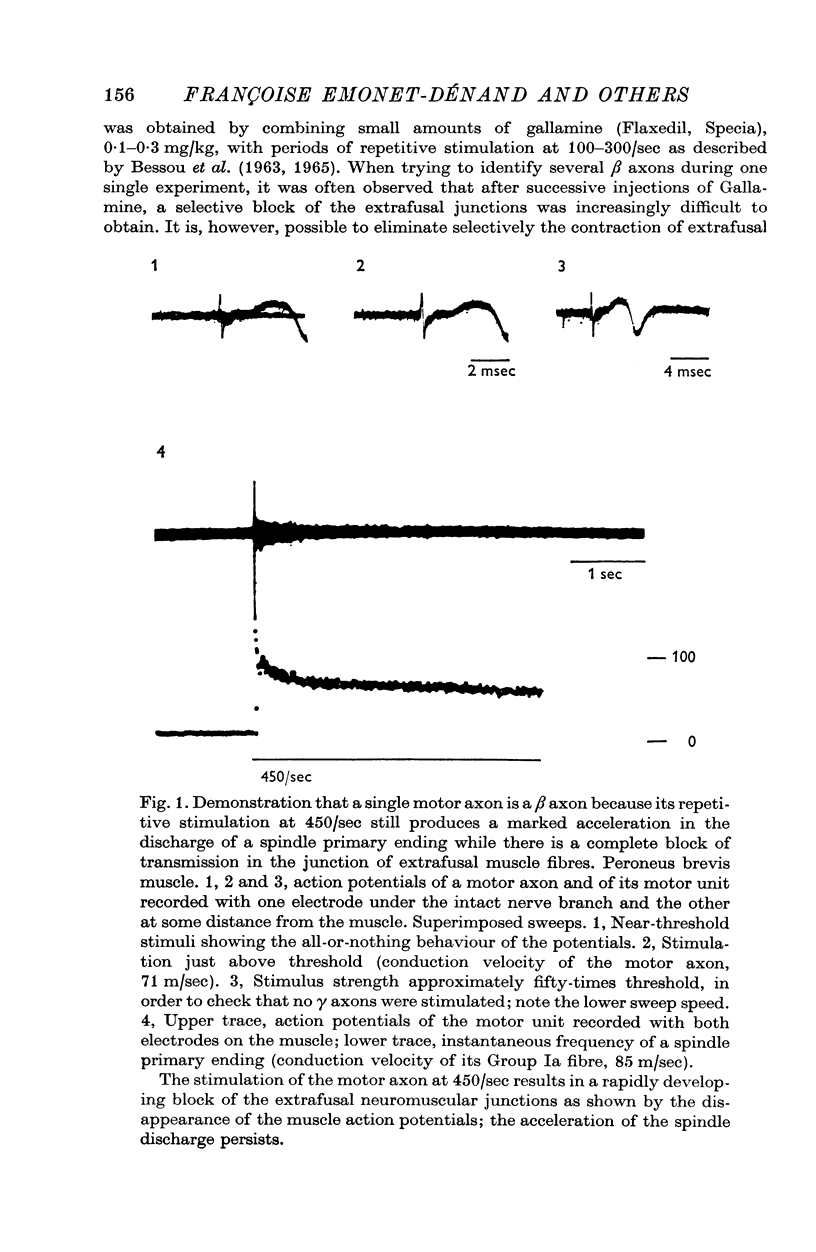
Abstract
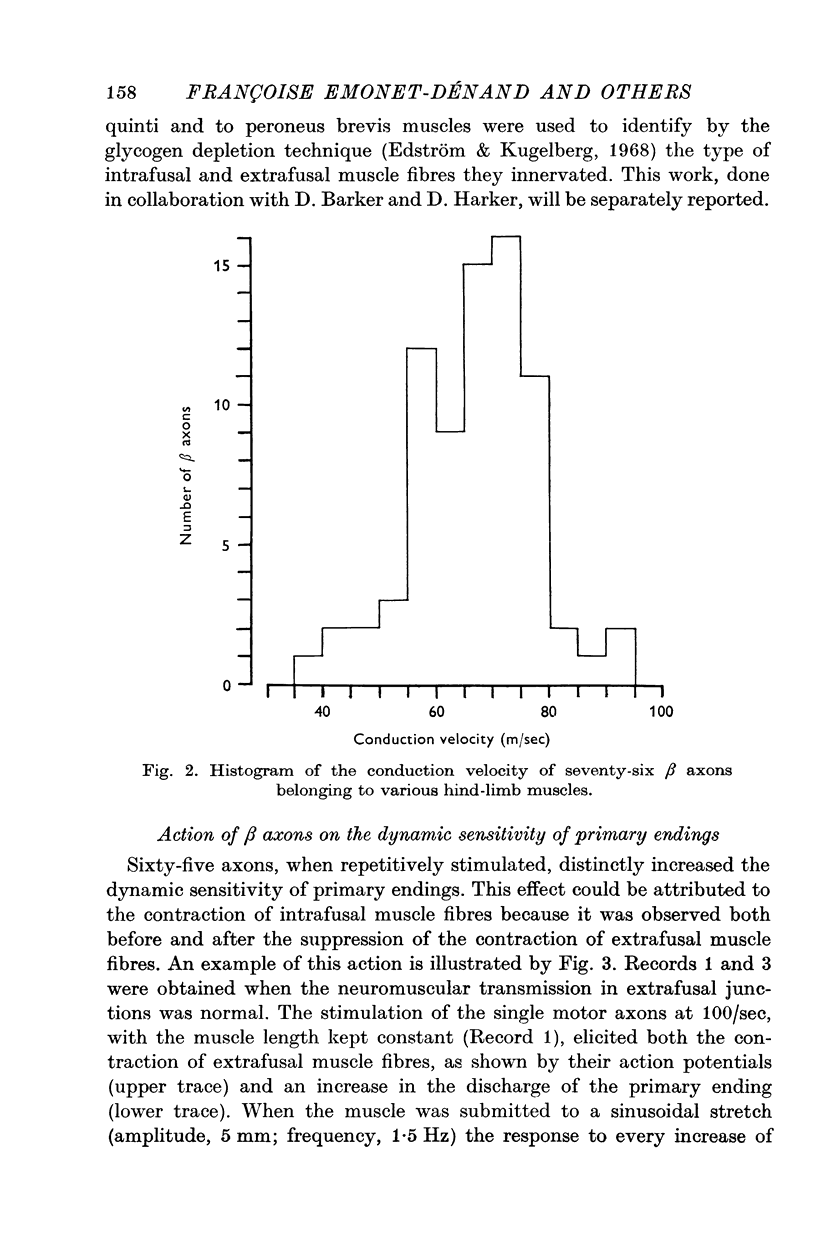
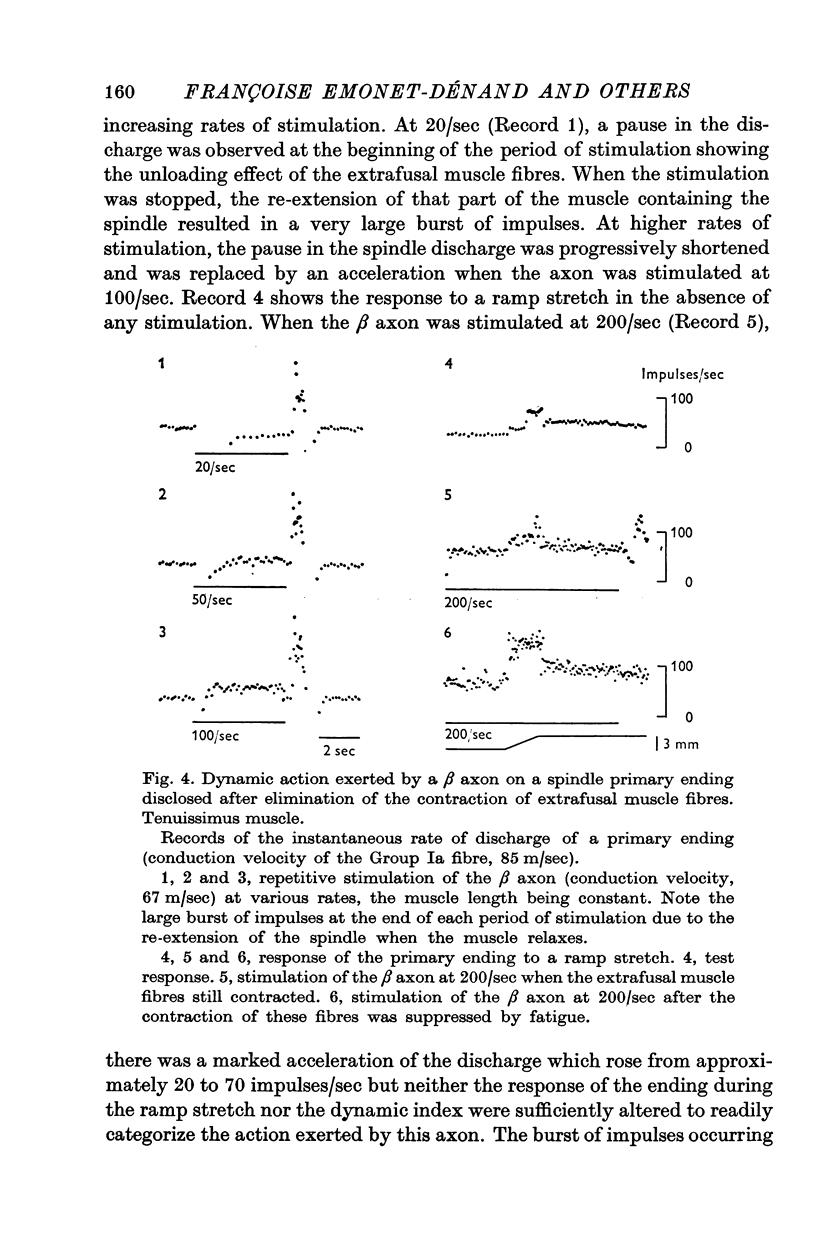
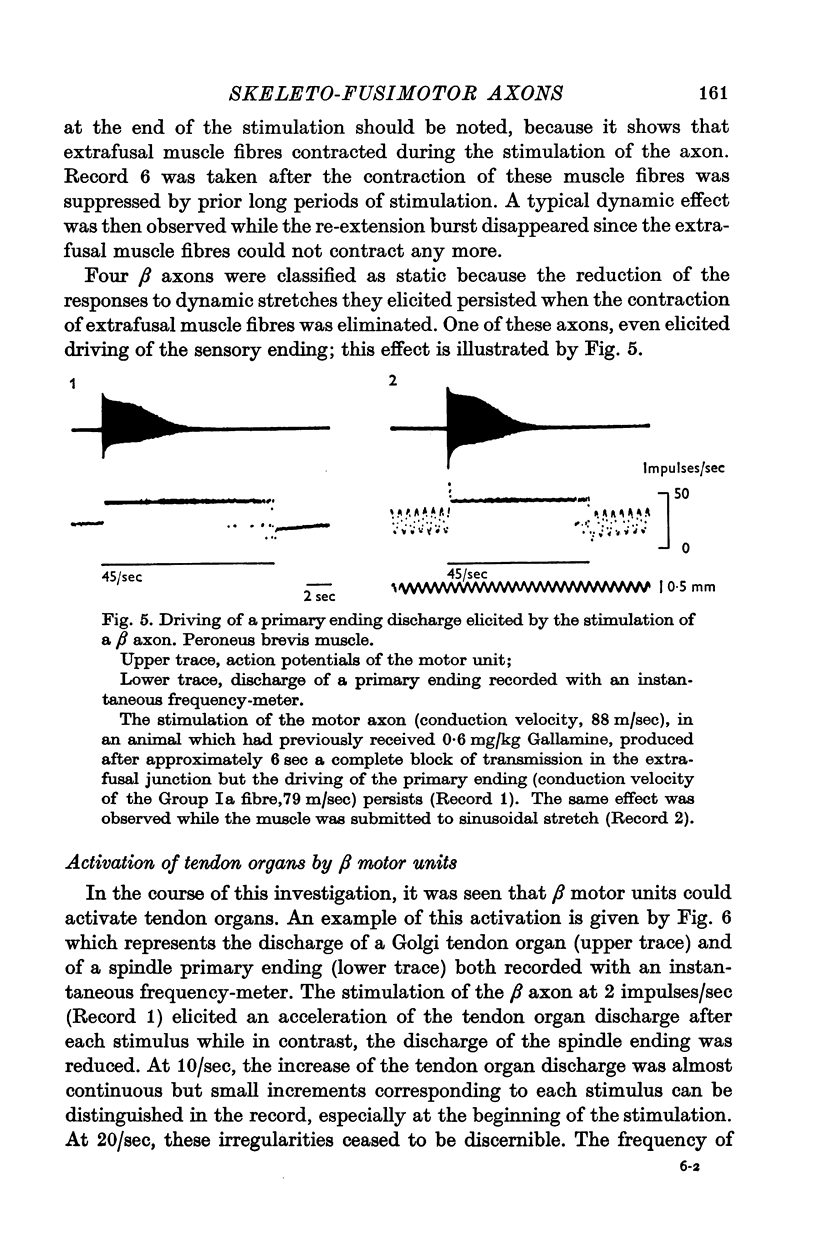
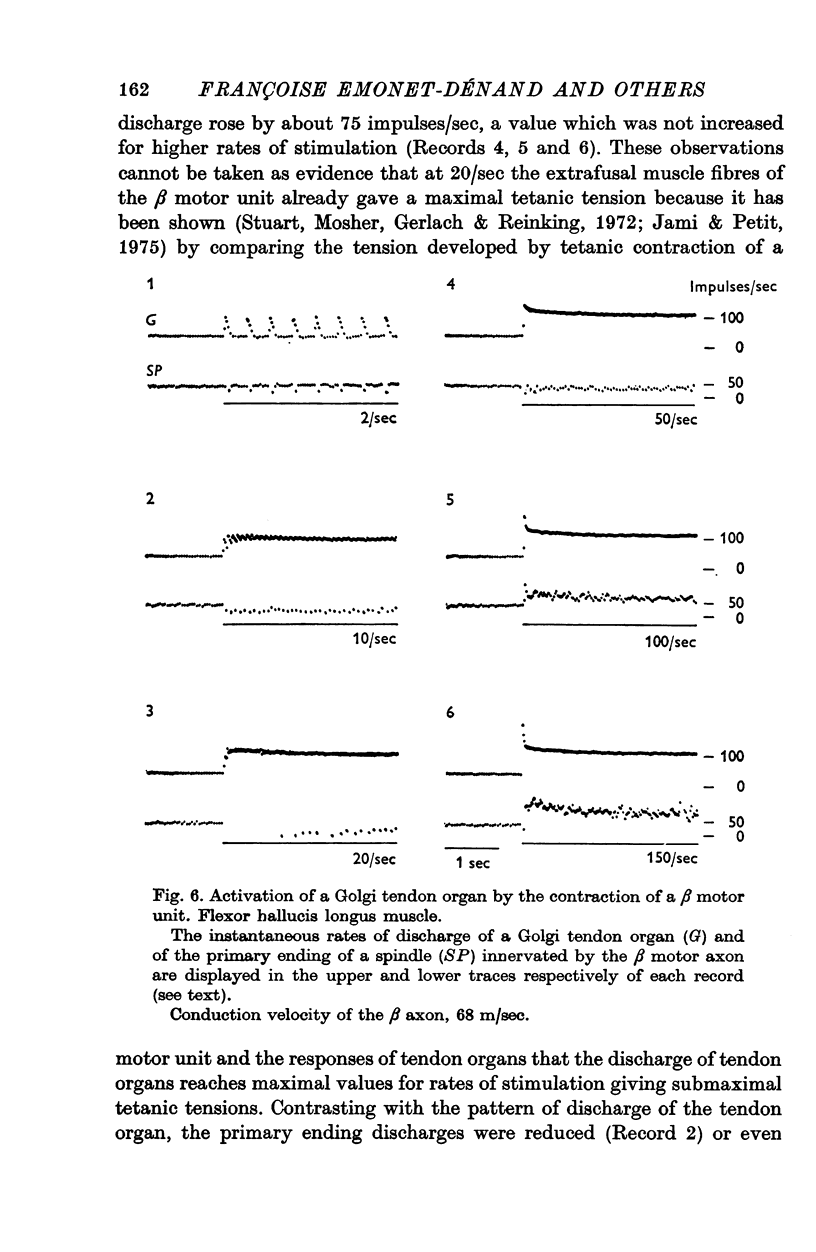
1. Motor axons supplying various hind-limb muscles of the cat (flexor hallucis lingus, peroneus brevis, peroneus digiti quinti, tibialis anterior, soleus and tenuissimus) were identified as skeleto-fusimotor or beta axons because their repetitive stimulation elicited both the contraction of extrafusal muscle fibres and an increase in the rate of discharge of spindle primary endings which perisited after selective blockade of extrafusal neuromuscular junctions. 2. The conduction velocity of these axons ranged from 39 to 92 m/sec. 3. Of seventy-six beta axons, seventy-two had a dynamic action on the sensitivity to velocity of stretching of primary endings, four had a static action. 4. The dynamic action of six beta axons was observed only after the contraction of extrafusal muscle fibres was selectively suppressed. 5. Tendon organs can be activated by beta motor units.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAL M. N., BARKER D. INTRAMUSCULAR BRANCHING OF FUSIMOTOR FIBRES. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:288–299. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN M. C., CROWE A., MATTHEWS P. B. OBSERVATIONS ON THE FUSIMOTOR FIBRES OF THE TIBIALIS POSTERIOR MUSCLE OF THE CAT. J Physiol. 1965 Mar;177:140–159. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y., Proske U., Stacey M. J. Morphological identification and intrafusal distribution of the endings of static fusimotor axons in the cat. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):405–427. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bessou P., Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Motor fibres innervating extrafusal and intrafusal muscle fibres in the cat. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(3):649–672. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L., Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. Anterior tibial muscle of the rat. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Oct;31(5):424–433. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.5.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Emonet-Denand F., Joffroy M., Laporte Y. Lack of exclusively fusimotor -axons in flexor and extensor leg muscles of the cat. J Neurophysiol. 1972 Jan;35(1):149–153. doi: 10.1152/jn.1972.35.1.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P. H., Emonet-Denand F., Joffroy M. Mise en évidence d'axones squeletto-fusimoteurs (axones) dans le muscle premier lombrical superficiel du chat. J Physiol (Paris) 1971;63(5):617–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellaway P., Emonet-Dénand F., Jami L., Joffroy M. Proportion des fibres fusimotrices statiques et dynamiques dans les muscles peroneus longus et flexor hallucis longus du chat. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Jun 26;274(26):3597–3600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Jami L., Laporte Y. Mise en évidence d'axones squeletto-fusimoteurs dans le muscle flexor hallucis longus, chez le chat. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1973 Jul 2;277(1):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonet-Dénand F., Laporte Y. Blocage neuromusculaire sélectif des jonctions extrafusales des axones squeletto-fusimoteurs produit par leur stimulation répétitive á fréquence élevée. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Dec 23;279(26):2083–2085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haase J., Meuser P., Tan U. Die Konvergenz fusimotorischer alpha-Impulse auf de-efferentierte Flexorspindeln der Katze. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;289(1):50–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. The efferent regulation of the muscle spindle in the frog. J Exp Biol. 1949 Aug;26(2):201–217. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTLEDGE L. T., HAASE J. Flexor muscle spindles and reflex firing of early discharging units. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Mar;24:182–192. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.2.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturart D. G., Mosher C. G., Gerlach R. I., Reinking R. M. Mechanical arrangement and transducing properties of Golgi tendon organs. Exp Brain Res. 1972;14(3):274–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00816163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



