Abstract
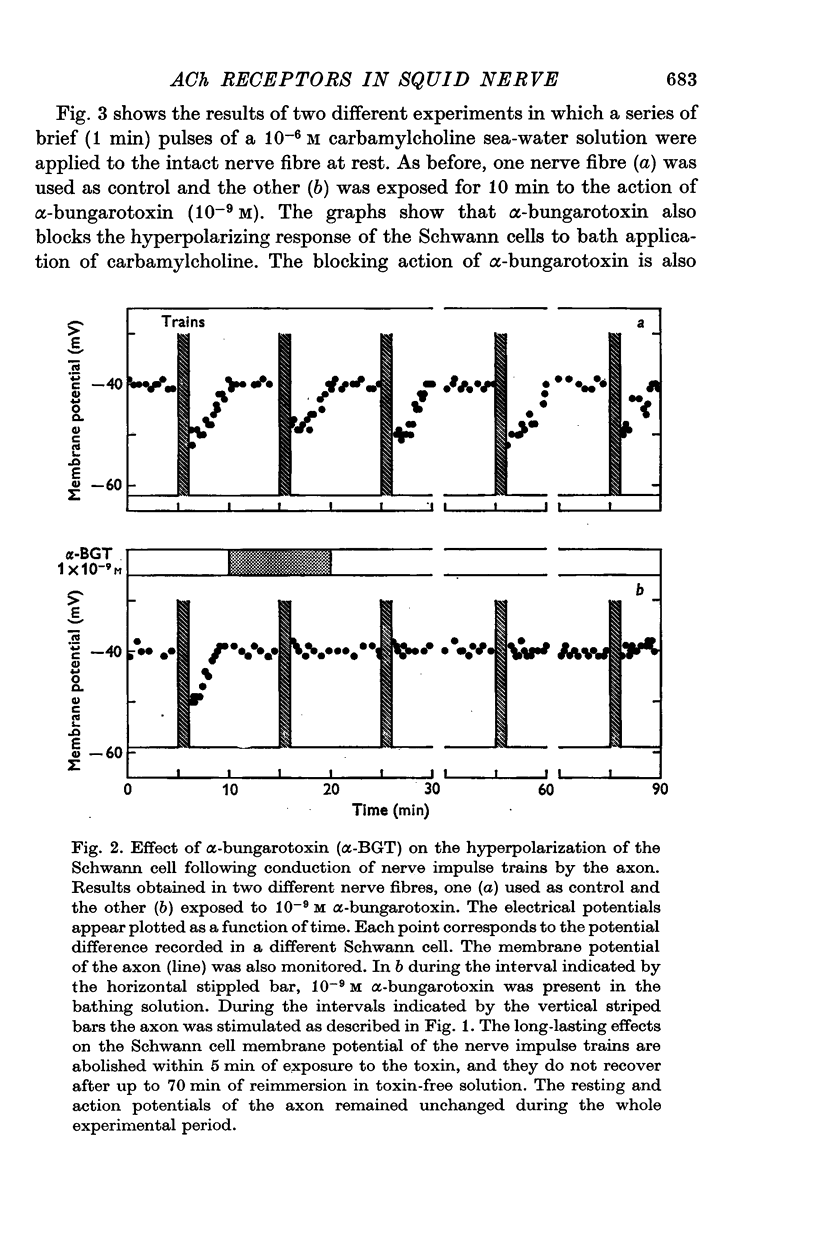
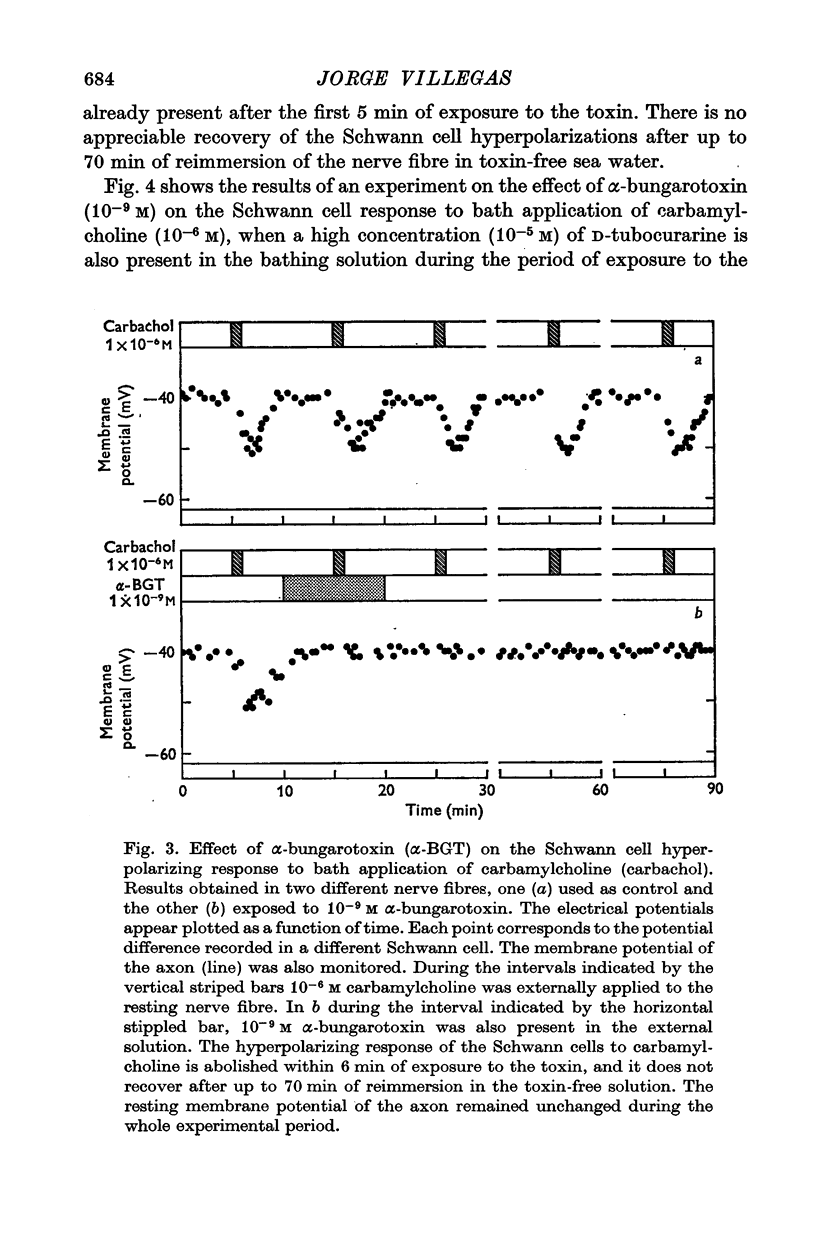
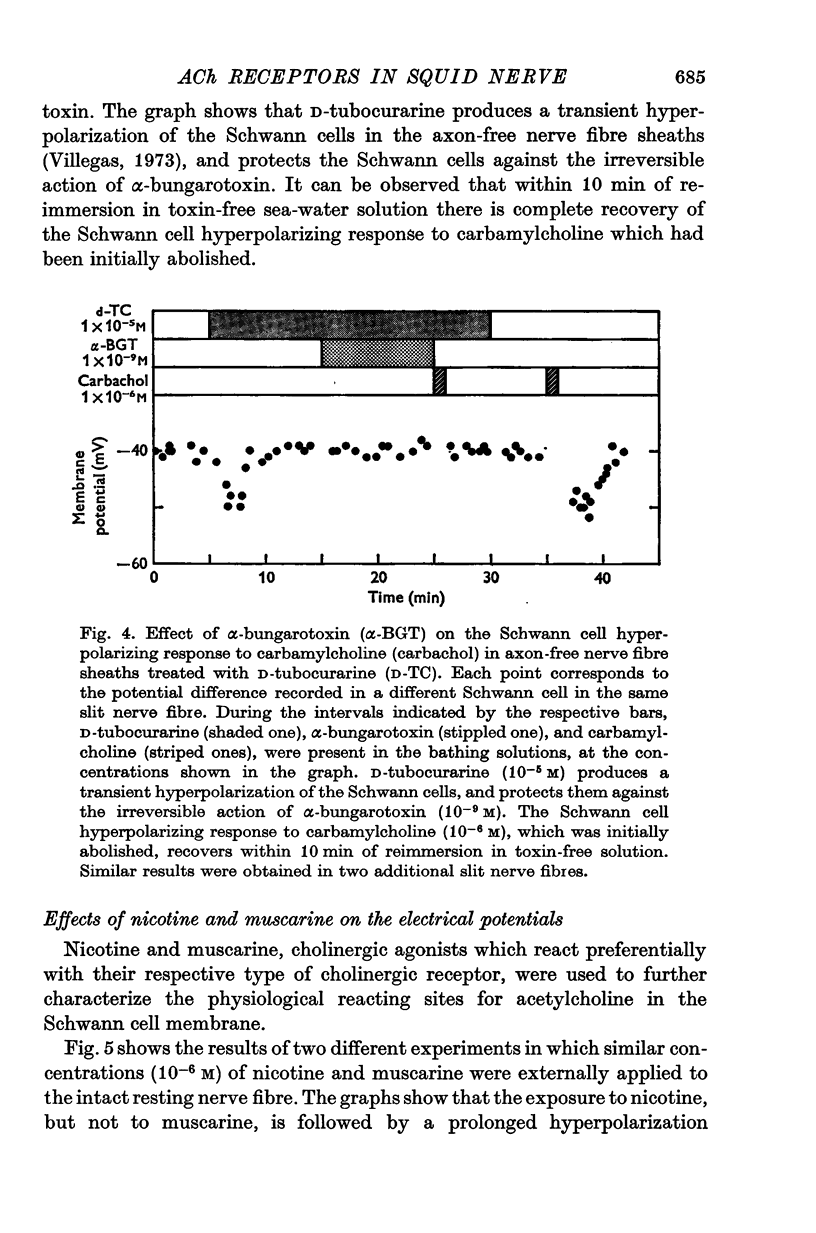
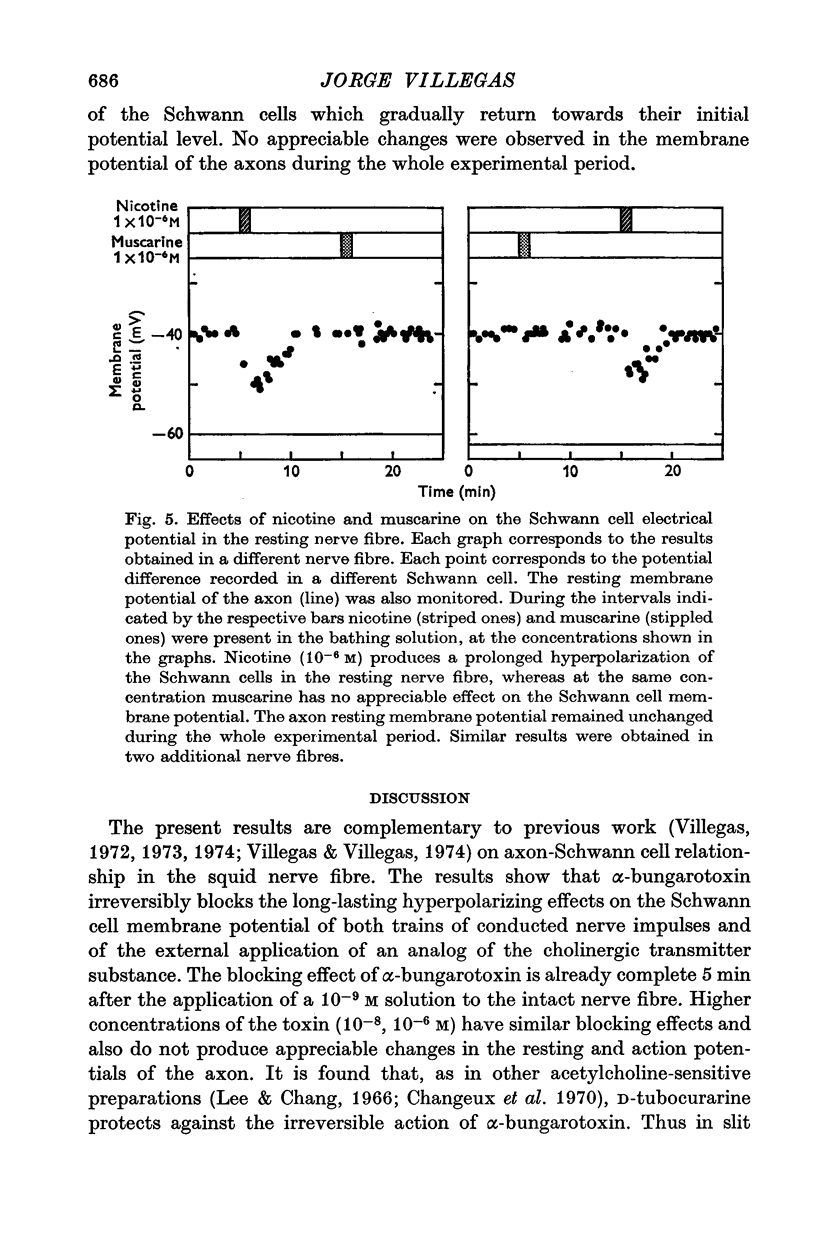
1. The effects of alpha-bungarotoxin, nicotine and muscarine on the Schwann cell membrane potential have been studied in the giant nerve fibre of the squid. The external application of alpha-bungarotoxin (10(-6), 10(-8), 10(-9) M) irreversibly blocks the long-lasting Schwann cell hyperpolarizations following the conduction of nerve impulse trains by the axon. It also blocks the Schwann cell hyperpolarizing response to the external application of carbamylcholine (10(-6)M) to the resting nerve fibre. 2. Externally applied D-tubocurarine (10(-5)M) protects against the irreversible action of alpha-bungarotoxin (10(-9)M) on the Schwann cell. Within 10 min of reimmersion in toxin-free sea water there is complete recovery of the Schwann cell hyperpolarizing response to carbamylcholine (10(-6)M) which had been initially abolished. 3. Nicotine (10(-6)M) induces a prolonged hyperpolarization of the Schwann cells in the resting nerve fibre, wheras at the same concentration, muscarine has no appreciable effect on the Schwann cell membrane potential. 4. None of these drugs, at the concnetrations utilized in the present study, had any appreciable effect on the resting and action potentials of the axon. 5. These findings show the presence of acetylcholine receptors of the nicotinic type in the Schwann cell membrane, and give further support to the hypothesis on the role of the acetylcholine system in the genesis of the long-lasting Schwann cell hyperpolarizations caused by the conduction of nerve impulse trains by the axon.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnola F. V., Villegas R., Camejo G. Tetrodotoxin receptors in plasma membranes isolated from lobster nerve fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camejo G., Villegas G. M., Barnola F. V., Villegas R. Characterization of two different membrane fractions isolated from the first stellar nerves of the squid Dosidicus gigas. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;193(2):247–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90186-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Kasai M., Lee C. Y. Use of a snake venom toxin to characterize the cholinergic receptor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1241–1247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell G. A., Pentreath V. W., Powell B. Is the Mya arenaria heart suitable for ACh bioassay? Comp Biochem Physiol. 1968 Dec;27(3):787–794. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90618-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. Y., Chang C. C. Modes of actions of purified toxins from elapid venoms on neuromuscular transmission. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(2):555–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Postsynaptic action of cobra toxin at the myoneural junction. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):727–728. doi: 10.1038/227727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., ARMETT C. J. The role of acetylcholine in conduction in mammalian nonmyelinated nerve fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Feb;139:201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas G. M., Villegas J. Acetylcholinesterase localization in the giant nerve fiber of the squid. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Jan;46(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)80028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J. Axon-Schwann cell interaction in the squid nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):275–296. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J. Effects of acetylcholine and carbamylcholine on the axon and Schwann cell electrical potentials in the squid nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1974 Nov;242(3):647–659. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villegas J. Effects of tubocurarine and eserine on the axon-Schwann cell relationship in the squid nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):193–208. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELSH J. H., TWAROG B. Measurement of smooth muscle activity in invertebrate animals. Methods Med Res. 1960;8:187–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


