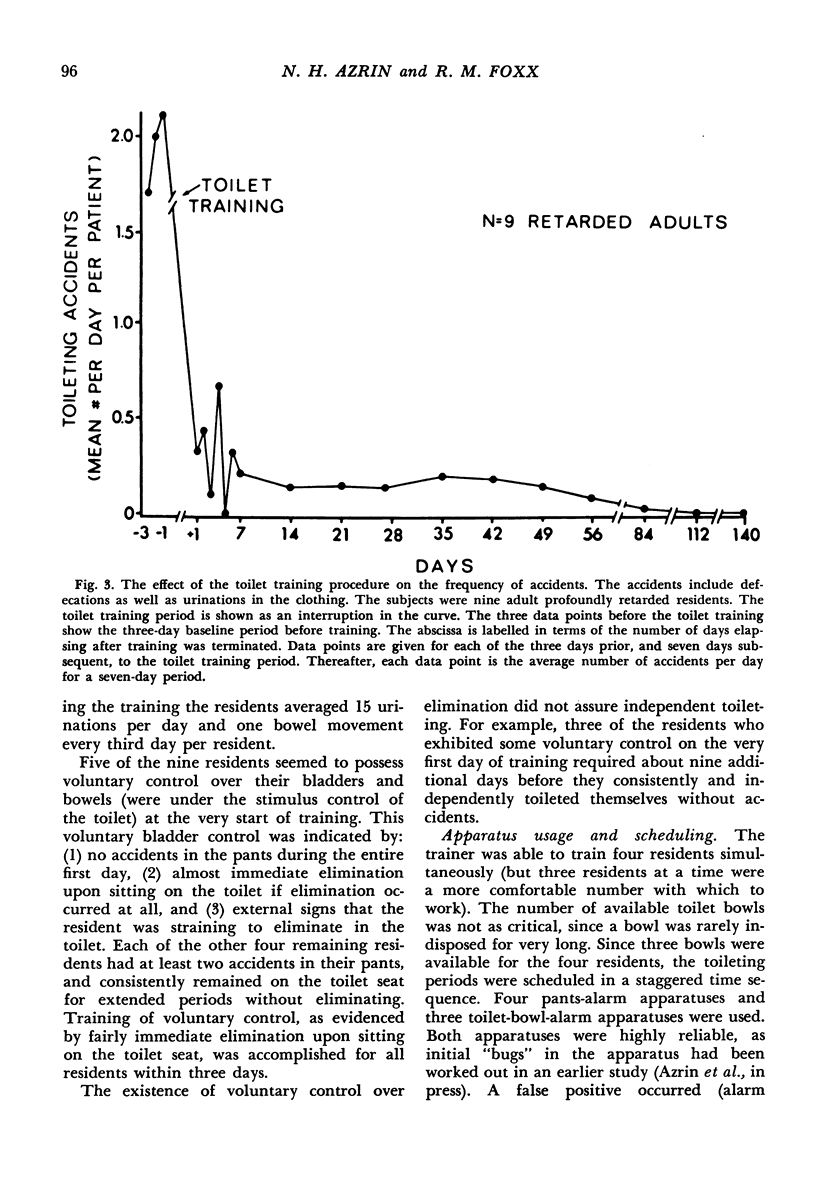
Abstract
Incontinence is a major unsolved problem in the institutional care of the profoundly retarded. A reinforcement and social analysis of incontinence was used to develop a procedure that would rapidly toilet train retardates and motivate them to remain continent during the day in their ward setting. Nine profoundly retarded adults were given intensive training (median of four days per patient), the distinctive features of which were artificially increasing the frequency of urinations, positive reinforcement of correct toileting but a delay for “accidents”, use of new automatic apparatus for signalling elimination, shaping of independent toileting, cleanliness training, and staff reinforcement procedures. Incontinence was reduced immediately by about 90% and eventually decreased to near-zero. These results indicate the present procedure is an effective, rapid, enduring, and administratively feasible solution to the problem of incontinence of the institutionalized retarded.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENSBERG G. J., COLWELL C. N., CASSEL R. H. TEACHING THE PROFOUNDLY RETARDED SELF-HELP ACTIVITIES BY BEHAVIOR SHAPING TECHNIQUES. Am J Ment Defic. 1965 Mar;69:674–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister A., Klosowski R. An attempt to group toilet train severely retarded patients. Ment Retard. 1965 Dec;3(6):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAYAN M. TOILET TRAINING RETARDED CHILDREN IN A STATE RESIDENTIAL INSTITUTION. Ment Retard. 1964 Apr;2(2):116–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles D. K., Wolf M. M. Toilet training institutionalized, severe retardates: an application of operant behavior modification techniques. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 Mar;70(5):766–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundziak M., Maurer R. A., Watson L. S. Operant conditioning in toilet training of severely mentally retarded boys. Am J Ment Defic. 1965 Jul;70(1):120–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimbrell D. L., Luckey R. E., Barbuto P. F., Love J. G. Operation dry pants: an intensive habittraining program for severely and profoundly retarded. Ment Retard. 1967 Apr;5(2):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rentfrow R. K., Rentfrow D. K. Studies related to toilet training of the mentally retarded. Am J Occup Ther. 1969 Sep-Oct;23(5):425–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wagenen R. K., Meyerson L., Kerr N. J., Mahoney K. Field trials of a new procedure for toilet training. J Exp Child Psychol. 1969 Aug;8(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(69)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson L. S., Jr Applications of behavior-shaping devices to training severely and profoundly mentally retarded children in an institutional setting. Ment Retard. 1968 Dec;6(6):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


