Abstract
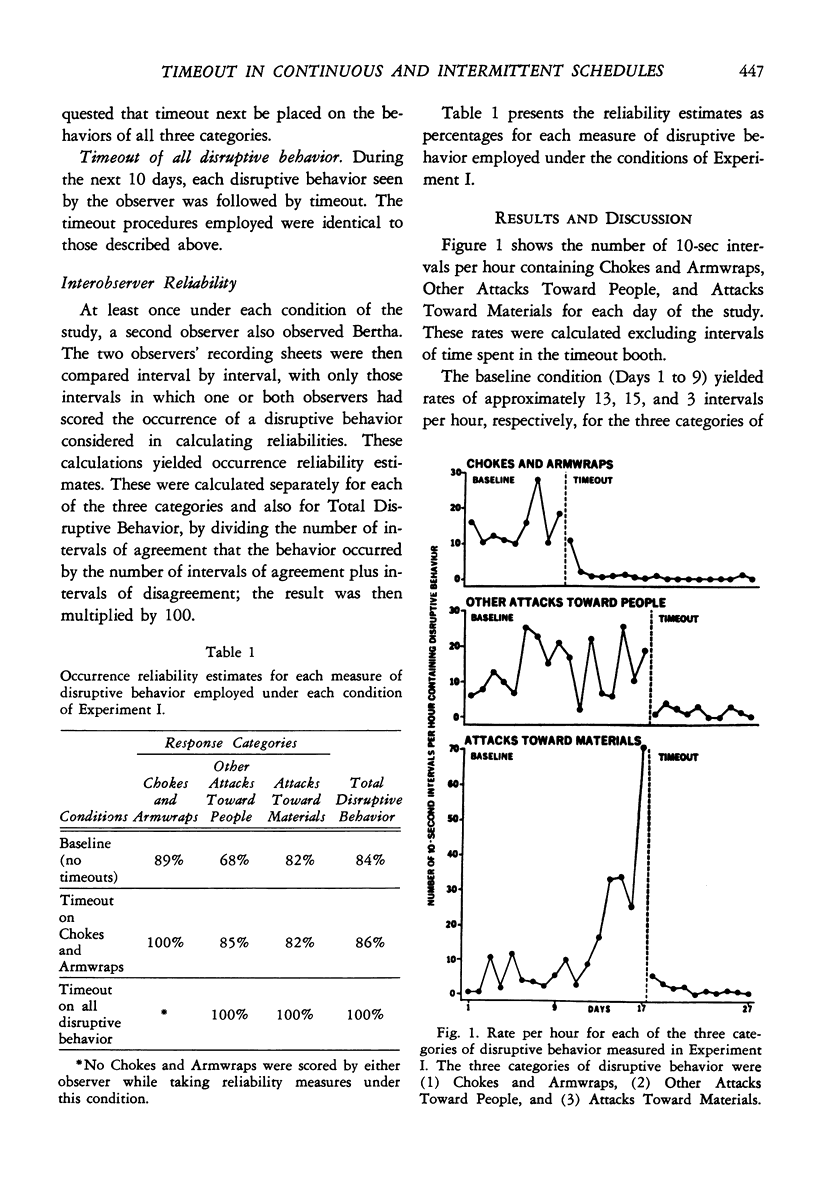
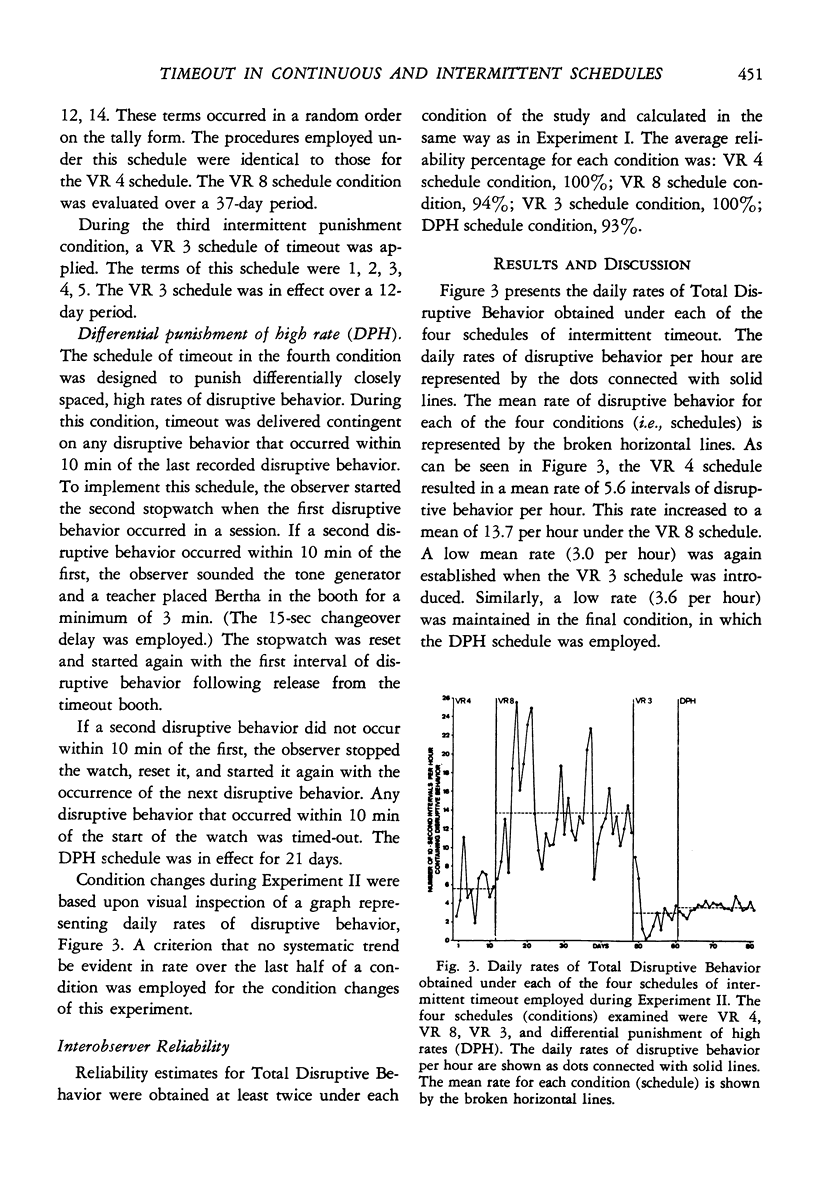
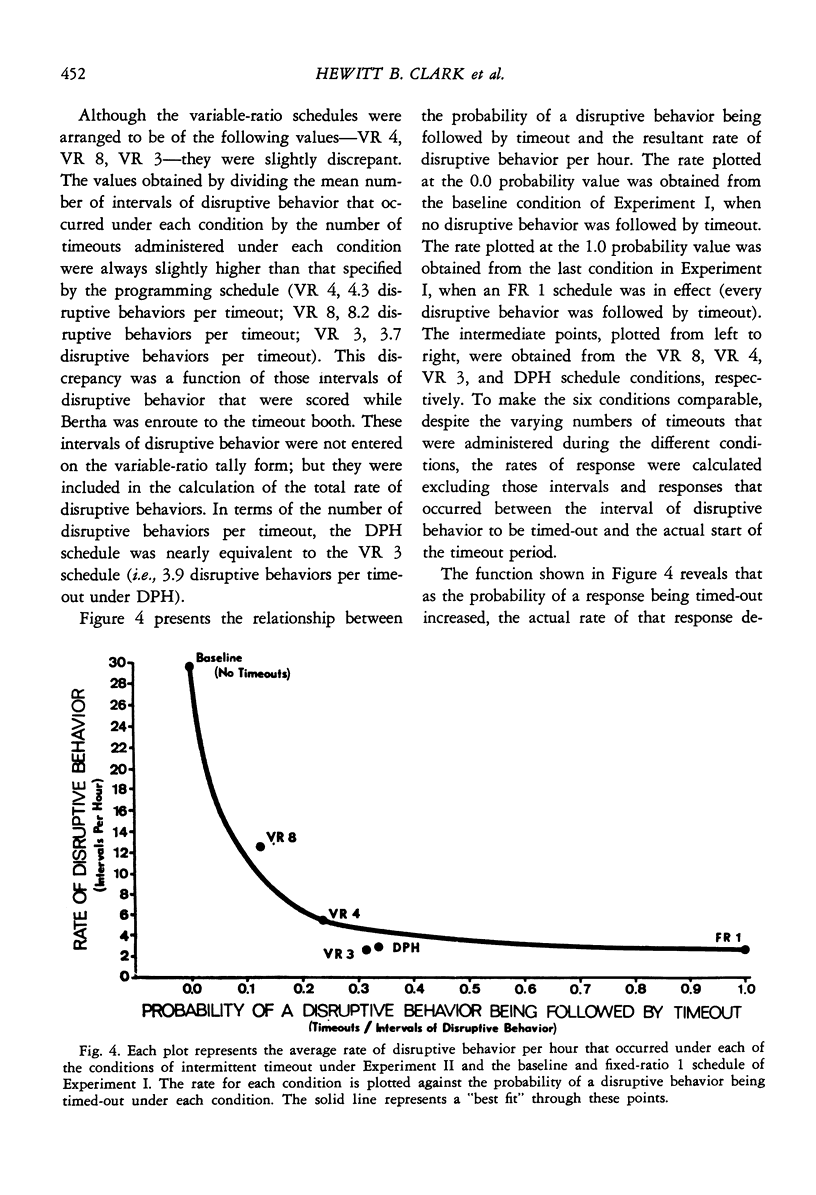
The effectiveness of a brief period of isolation (timeout) in the control of disruptive behavior emitted by a retarded child in a preschool classroom setting was examined. Timeout was shown to be an effective punishing stimulus, and its control of the child's disruptive behavior was investigated under four schedules of intermittent timeout. The results suggest that as a larger percentage of responses were punished, a greater decrease in the frequency of that response occurred. This inverse relationship between the percentage of responses punished and the frequency of the response did not appear to be linear, but rather a non-linear function. This function suggests that some schedules of intermittent punishment may be as effective as continuous punishment, at least in the case of the continued suppression of a response that has already been reduced to a low frequency.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C., HAKE D. F. Fixed-ratio punishment. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Apr;6:141–148. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAER D. M. Laboratory control of thumbsucking by withdrawal and re-presentation of reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Oct;5:525–528. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton E. S., Guess D., Garcia E., Baer D. M. Improvement of retardates' mealtime behaviors by timeout procedures using multiple baseline techniques. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Summer;3(2):77–84. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostow D. E., Bailey J. B. Modification of severe disruptive and aggressive behavior using brief timeout and reinforcement procedures. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Spring;2(1):31–37. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERSTER C. B., APPEL J. B. Punishment of S delta responding in matching to sample by time out from positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1961 Jan;4:45–56. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1961.4-45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filby Y., Appel J. B. Variable-interval punishment during variable-interval reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):521–527. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H., AYLLON T. Elimination of behavior of mental patients by response-produced extinction. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:407–412. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins R. P., Peterson R. F., Schweid E., Bijou S. W. Behavior therapy in the home: amelioration of problem parent-child relations with the parent in a therapeutic role. J Exp Child Psychol. 1966 Sep;4(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0022-0965(66)90054-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman A., Baron A. Suppression of behavior by timeout punishment when suppression results in loss of positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):595–607. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kircher A. S., Pear J. J., Martin G. L. Shock as punishment in a picture-naming task with retarded children. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Fall;4(3):227–233. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer T. J., Rilling M. Effects of timeout on spaced responding in pigeons. J Exp Anal Behav. 1969 Mar;12(2):283–288. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1969.12-283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillan D. E. A comparison of the punishing effects of response-produced shock and response-produced time out. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):439–449. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McReynolds L. V. Application of timeout from positive reinforcement for increasing the efficiency of speech training. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):199–205. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller N. B., Zimmerman J. The effects of a pre-time-out stimulus on matching-to-sample of humans. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):487–499. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro M. R. Punishment of an extinguishing shock-avoidance response by time-out from positive reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Jan;9(1):53–62. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T., Wolf M. Establishing functional speech in echolalic children. Behav Res Ther. 1967 May;5(2):73–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(67)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. R. Fixed-ratio punishment by timeout of concurrent variable-interval behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1968 Sep;11(5):609–616. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1968.11-609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler V. O., Jr, Brown D. The use of swift, brief isolation as a group control device for institutionalized delinquents. Behav Res Ther. 1967 Feb;5(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(67)90050-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahler R. G. Setting generality: some specific and general effects of child behavior therapy. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Winter;2(4):239–246. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., BAYDAN N. T. PUNISHMENT OF S-DELTA RESPONDING OF HUMANS IN CONDITIONAL MATCHING TO SAMPLE BY TIME-OUT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Oct;6:589–597. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIMMERMAN J., FERSTER C. B. Intermittent punishment of Sdelta responding in matching to sample. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:349–356. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilberger J., Sampen S. E., Sloane H. N. Modification of a child's problem behaviors in the home with the mother as therapist. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):47–53. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


