Abstract
Recent studies suggested a general behavioral engineering approach to behavioral disorders by portable operant treatment instruments. The approach was applied to the problem of poor posture, specifically rounding of the back or slouching. An apparatus was developed that provided a warning stimulus followed by an aversive tone for the duration of slouching. Slouching was thereby punished by onset of the tone, and non-slouching was reinforced by tone termination and postponement. Twenty-five adults wore the apparatus during their normal working day during alternate periods in which the aversive tone was connected and disconnected experimentally. A miniature time-meter recorded the duration of slouching. The results showed that slouching decreased for each subject during each period in which slouching produced the aversive tone. For two subjects, a second control procedure was applied in which slouching terminated the tone. The result was an increase of slouching, demonstrating that the postural changes were controlled by the scheduled relation between the aversive tone and the response, and not by other factors such as simple response feedback. The substantial changes in posture indicate that the present procedure may prove to be an effective treatment alternative and suggests the general value of the behavioral engineering approach.
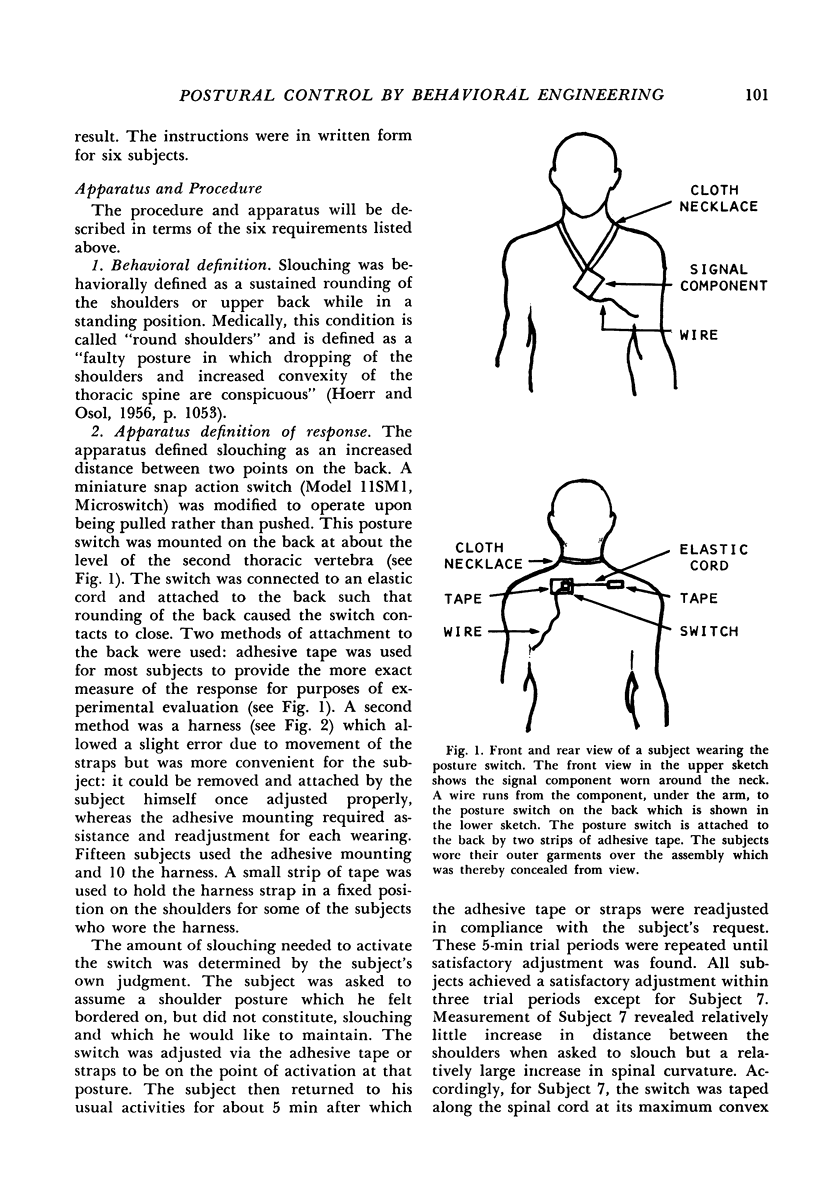
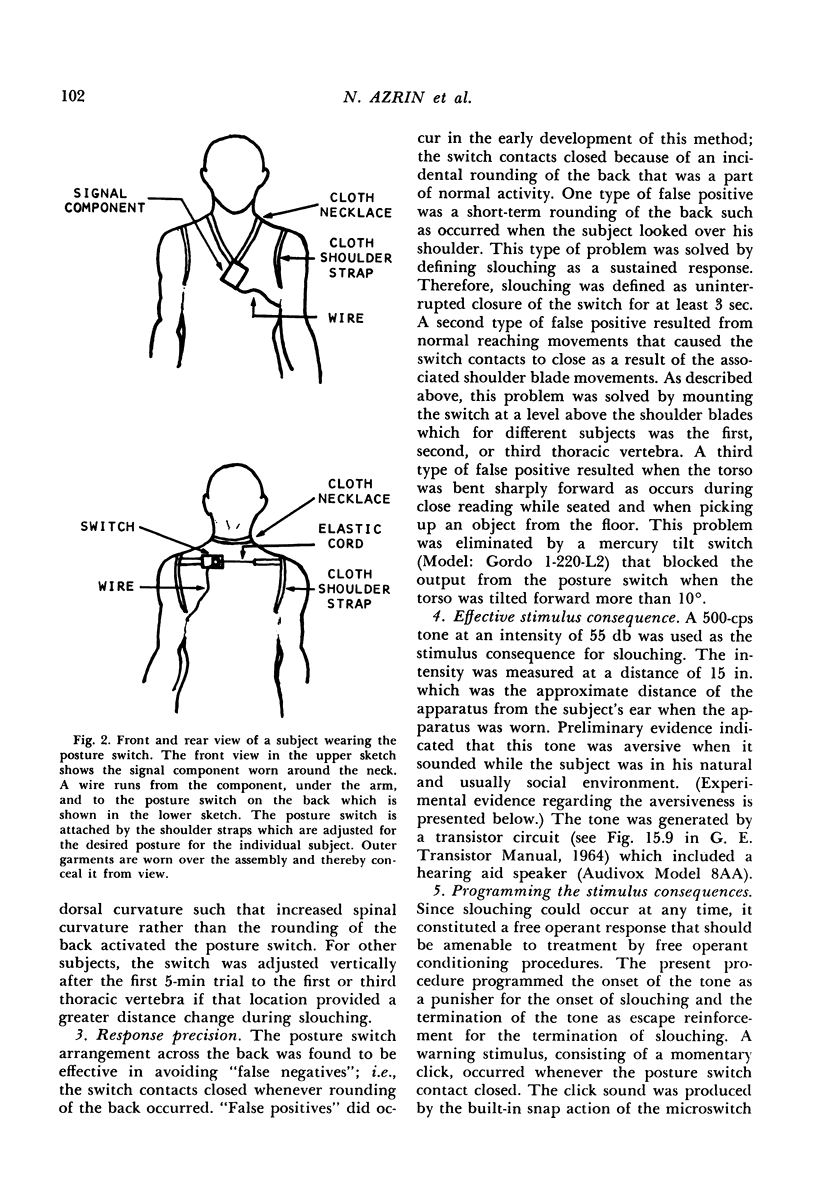
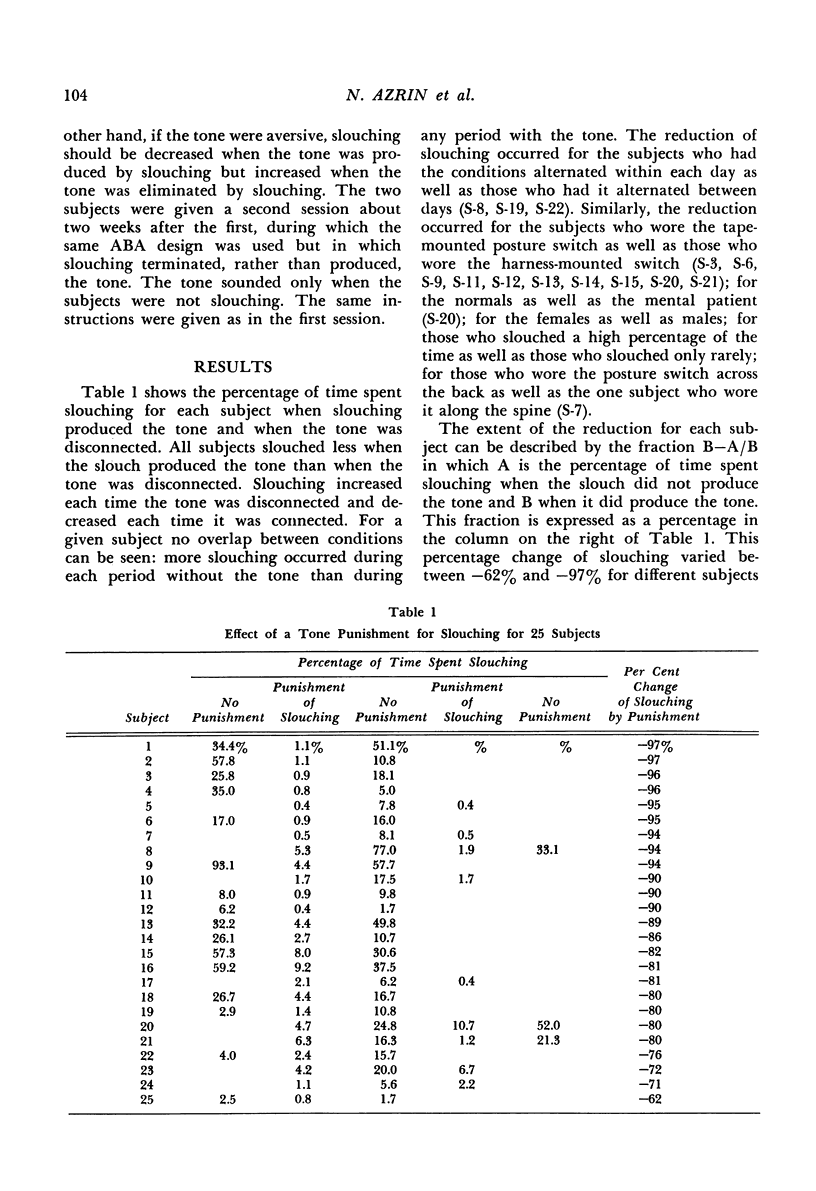
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AZRIN N. H., HOLZ W. C., HAKE D. F., AYLLON T. Fixed-ratio escape reinforcement. J Exp Anal Behav. 1963 Jul;6:449–456. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1963.6-449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayllon T., Azrin N. H. The measurement and reinforcement of behavior of psychotics. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Nov;8(6):357–383. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azrin N. H. Some Effects of Noise on Human Behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1958 Apr;1(2):183–200. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1958.1-183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRETHOWER D. M., REYNOLDS G. S. A facilitative effect of punishment on unpunished behavior. J Exp Anal Behav. 1962 Apr;5:191–199. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1962.5-191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURT H. A. Effects of faulty posture. Proc R Soc Med. 1950 Mar;43(3):187–194. doi: 10.1177/003591575004300315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church R. M., Raymond G. A., Beauchamp R. D. Response suppression as a function of intensity and duration of a punishment. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Feb;63(1):39–44. doi: 10.1037/h0024174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKE D. F., AZRIN N. H. CONDITIONED PUNISHMENT. J Exp Anal Behav. 1965 Sep;8:279–293. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1965.8-279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J., Azrin N. The effects of shock as a punisher for cigarette smoking. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):63–71. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIDMAN M. Some properties of the warning stimulus in avoidance behavior. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1955 Dec;48(6):444–450. doi: 10.1037/h0047481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULRICH R. E., HOLZ W. C., AZRIN N. H. STIMULUS CONTROL OF AVOIDANCE BEHAVIOR. J Exp Anal Behav. 1964 Mar;7:129–133. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1964.7-129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



