Abstract
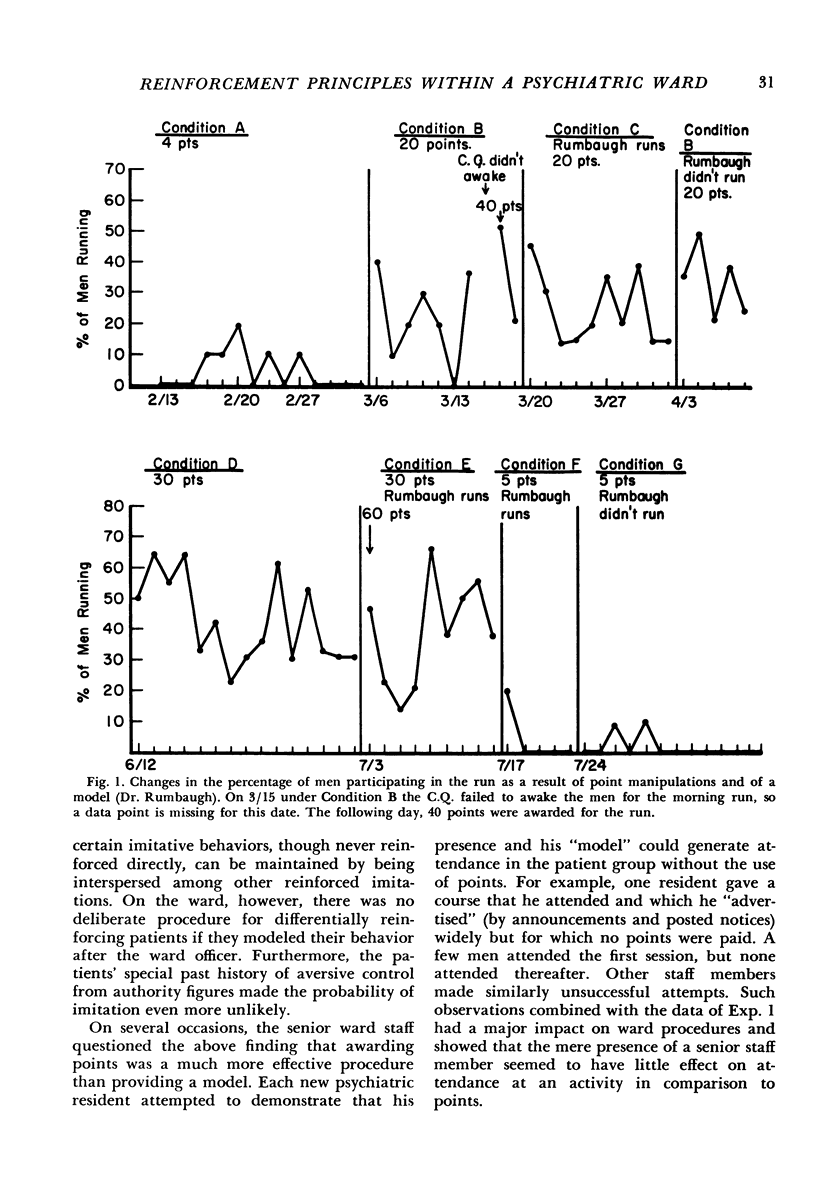
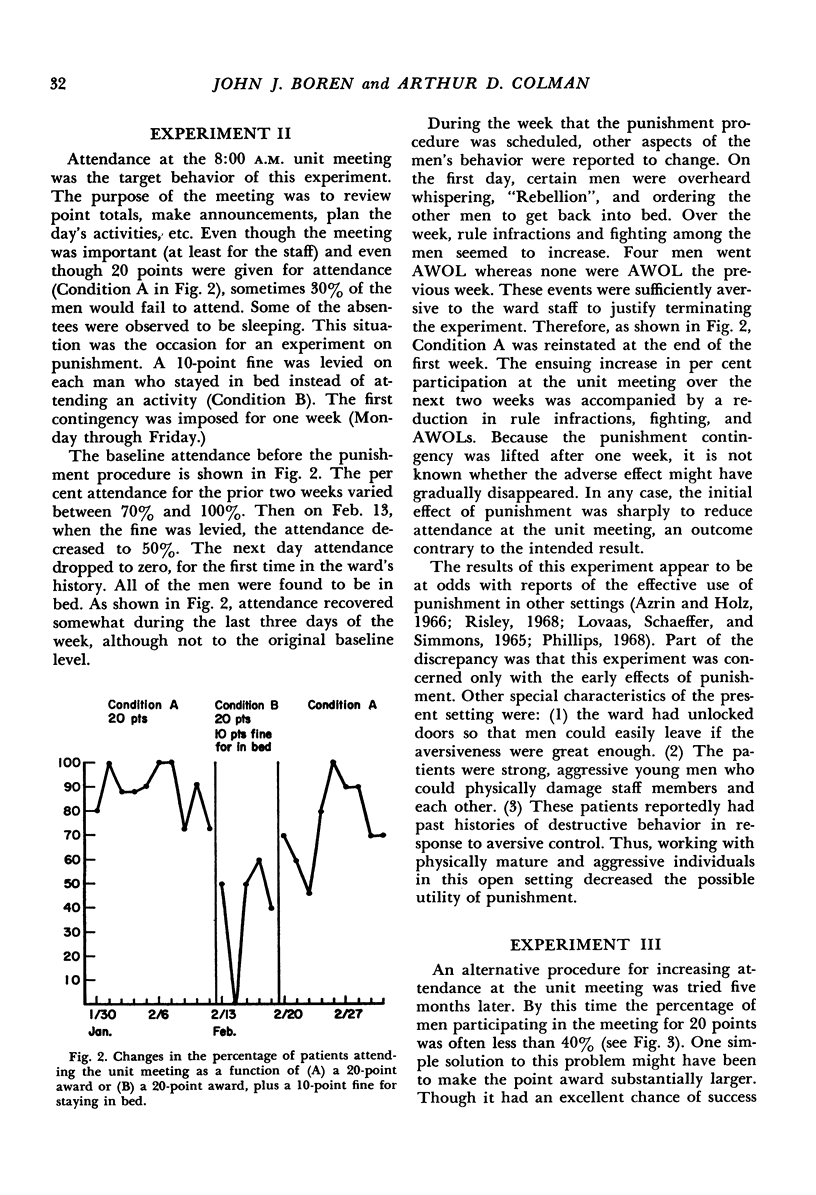
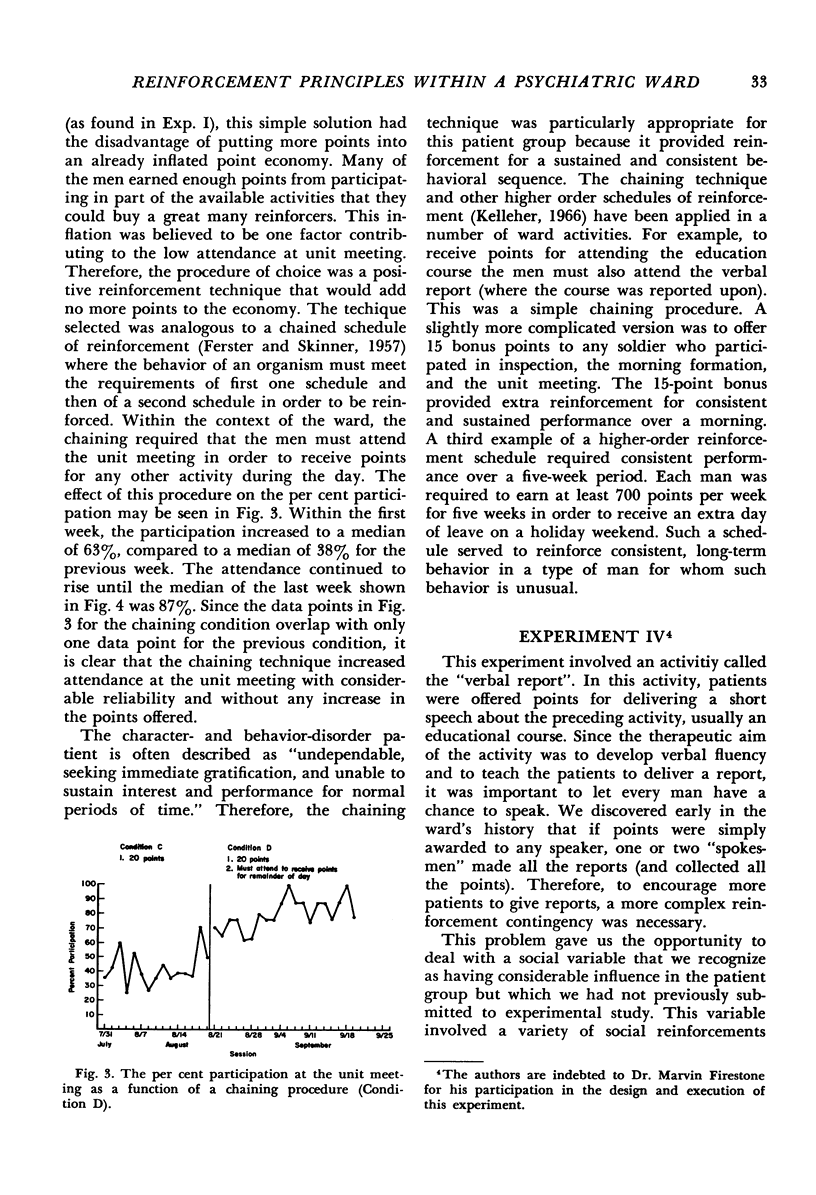
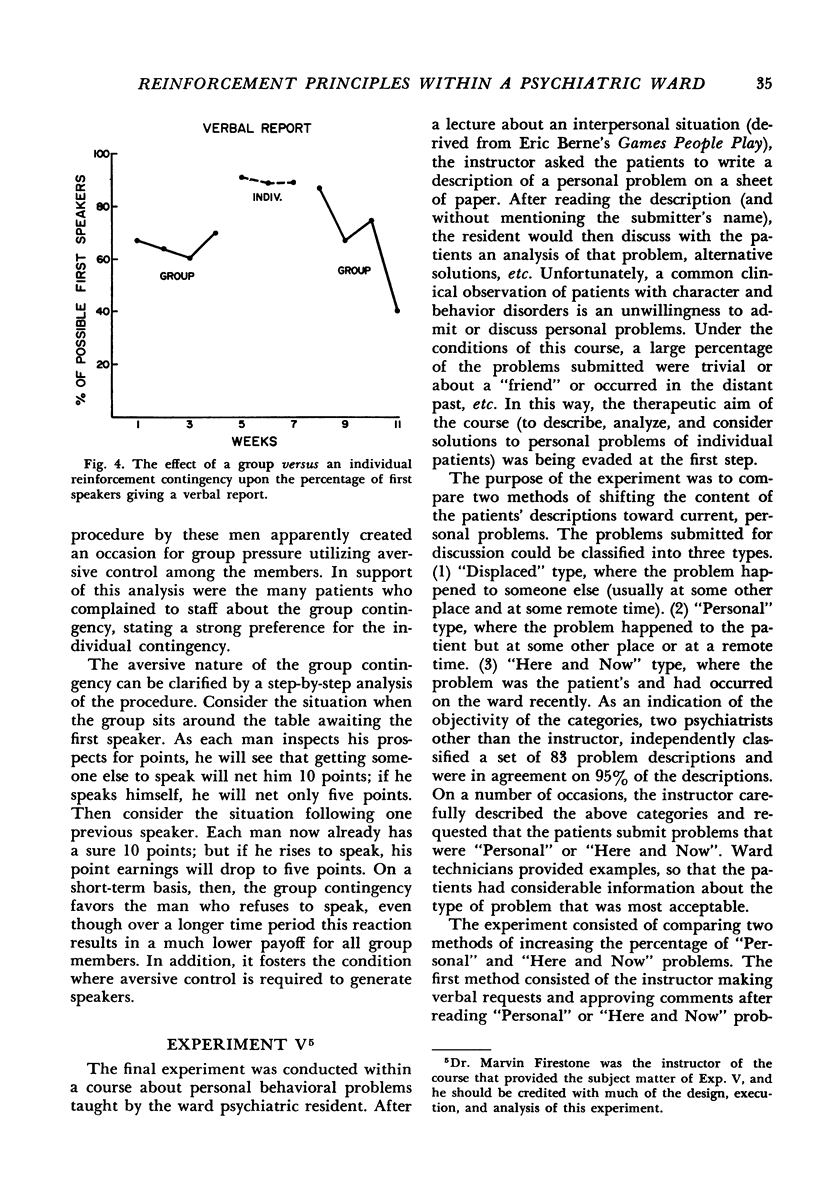
Several experiments exploring the effects of certain behavioral procedures were performed on a psychiatric ward for delinquent soldiers. Within the context of a point economy, the behavioral procedures were examined for their applicability to this patient group in a hospital-ward setting. The following procedures were studied: (1) use of points as consequences for specific behaviors compared with demonstration of “model” behavior by a ward officer; (2) punishment by a point-fine to control undesired behavior; (3) use of a chaining-type reinforcement contingency to increase desired behavior; (4) differential reinforcement of the individual versus the group to increase the frequency of a verbal performance; and (5) reinforcement of reports of personal problems versus impersonal problems.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURCHARD J., TYLER V., Jr THE MODIFICATION OF DELIQUENT BEHAVIOR THROUGH OPERANT CONDITIONING. Behav Res Ther. 1965 Apr;3:245–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-7967(65)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer D. M., Peterson R. F., Sherman J. A. The development of imitation by reinforcing behavioral similarity to a model. J Exp Anal Behav. 1967 Sep;10(5):405–416. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1967.10-405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A. D., Baker S. L., Jr Utilization of an operant conditioning model for the treatment of character and behavior disorders in a military setting. Am J Psychiatry. 1969 Apr;125(10):1395–1403. doi: 10.1176/ajp.125.10.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman A. D., Boren J. J. An information system for measuring patient behavior and its use by staff. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Fall;2(3):207–214. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. T. Conditioned reinforcement in second-order schedules. J Exp Anal Behav. 1966 Sep;9(5):475–485. doi: 10.1901/jeab.1966.9-475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. F. Some experiments on the organization of a class of imitative behaviors. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):225–235. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips E. L. Achievement Place: token reinforcement procedures in a home-style rehabilitation setting for "pre-delinquent" boys. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Fall;1(3):213–223. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quitkin F. M., Klein D. F. Follow-up of treatment failure: psychosis and character disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1967 Oct;124(4):499–505. doi: 10.1176/ajp.124.4.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risley T. R. The effects and side effects of punishing the autistic behaviors of a deviant child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):21–34. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


