Abstract
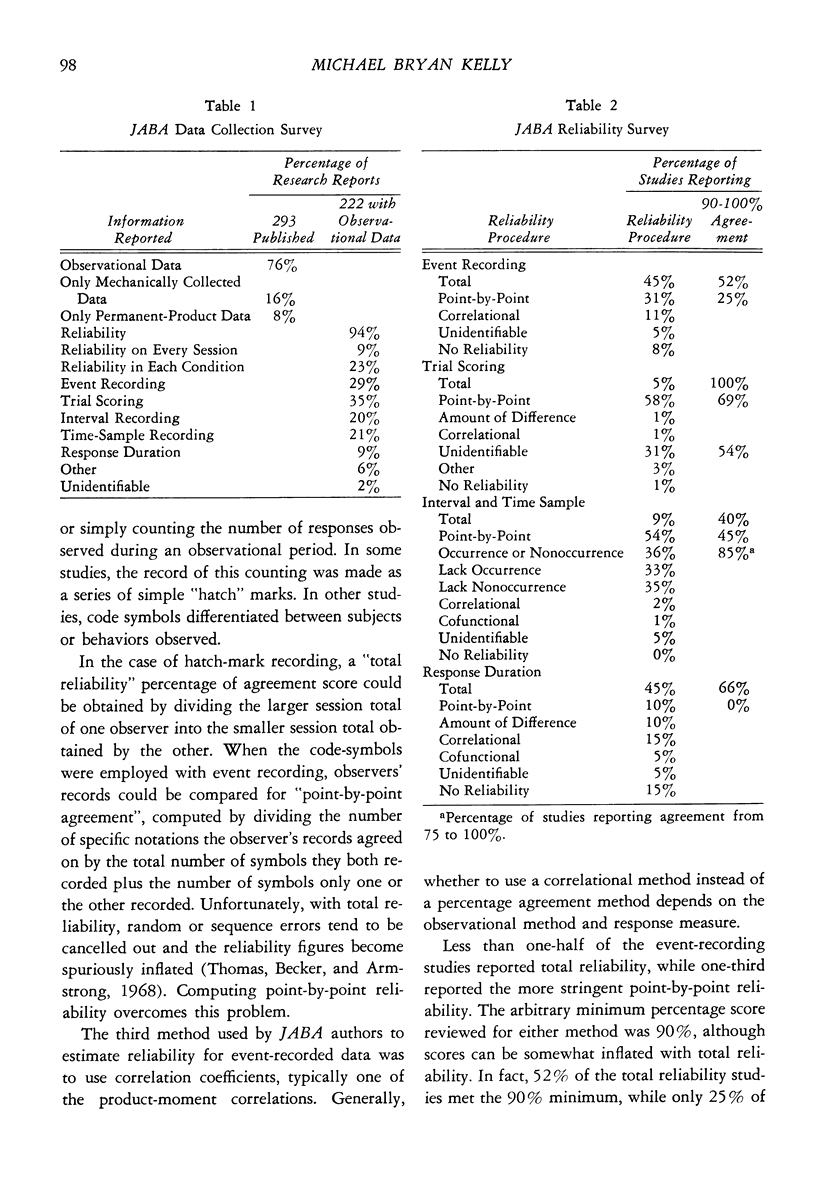
The research published in the Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis (1968 to 1975) was surveyed for three basic elements: data-collection methods, reliability procedures, and reliability scores. Three-quarters of the studies reported observational data. Most of these studies' observational methods were variations of event recording, trial scoring, interval recording, or time-sample recording. Almost all studies reported assessment of observer reliability, usually total or point-by-point percentage agreement scores. About half the agreement scores were consistently above 90%. Less than one-quarter of the studies reported that reliability was assessed at least once per condition.
Keywords: behavioral recording in JABA, observational data, observational technology, observer agreement, reliability
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. S., Wolf M. M., Phillips E. L. Home-based reinforcement and the modification of pre-delinquents' classroom behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Fall;3(3):223–233. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijou S. W., Peterson R. F., Ault M. H. A method to integrate descriptive and experimental field studies at the level of data and empirical concepts. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):175–191. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins B. L., Schutte R. C., Garton K. L. The effects of access to a playroom on the rate and quality of printing and writing of first and second-grade students. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Summer;4(2):77–87. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pendergrass V. E. Timeout from positive reinforcement following persistent, high-rate behavior in retardates. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):85–91. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. R., Becker W. C., Armstrong M. Production and elimination of disruptive classroom behavior by systematically varying teacher's behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):35–45. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward M. H., Baker B. L. Reinforcement therapy in the classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Winter;1(4):323–328. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


