Abstract
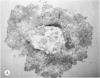
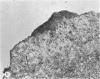
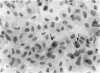
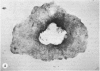
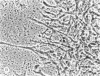
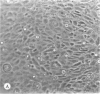
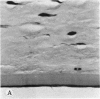
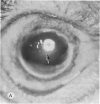
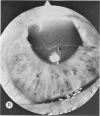
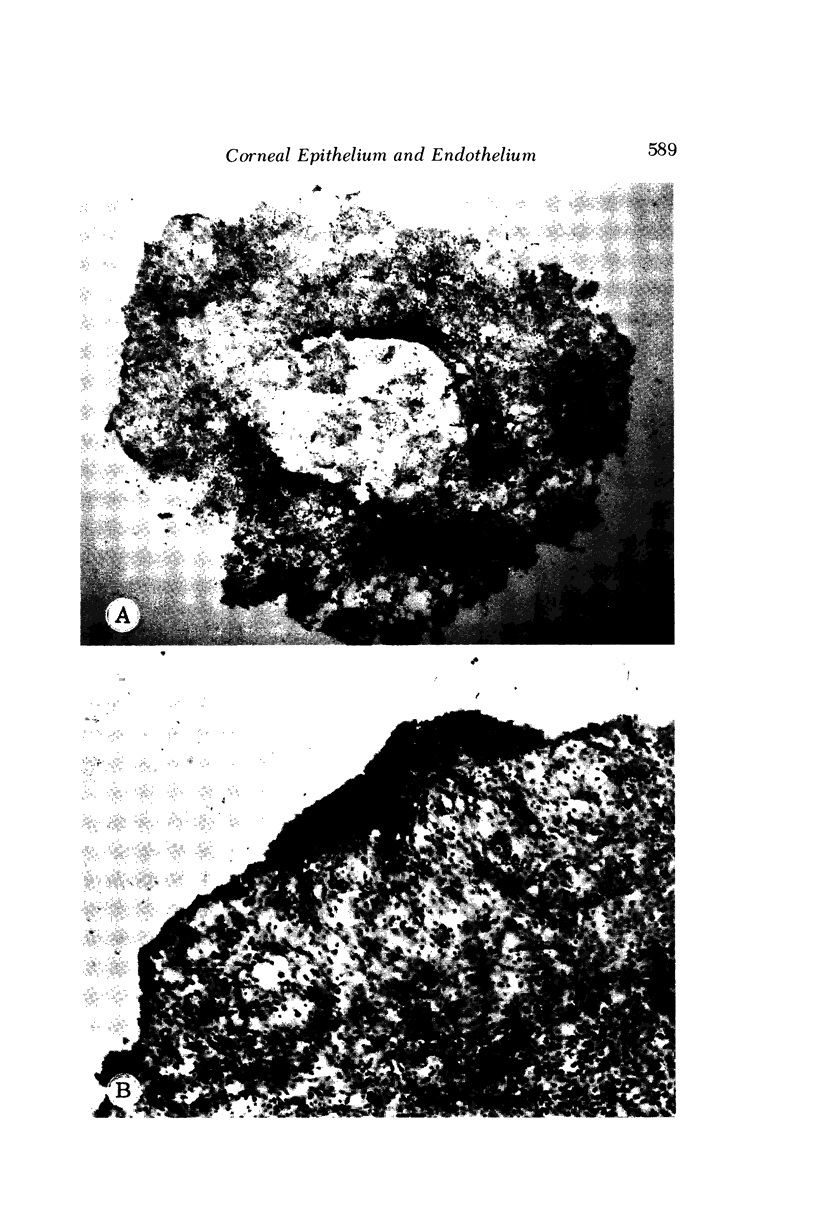
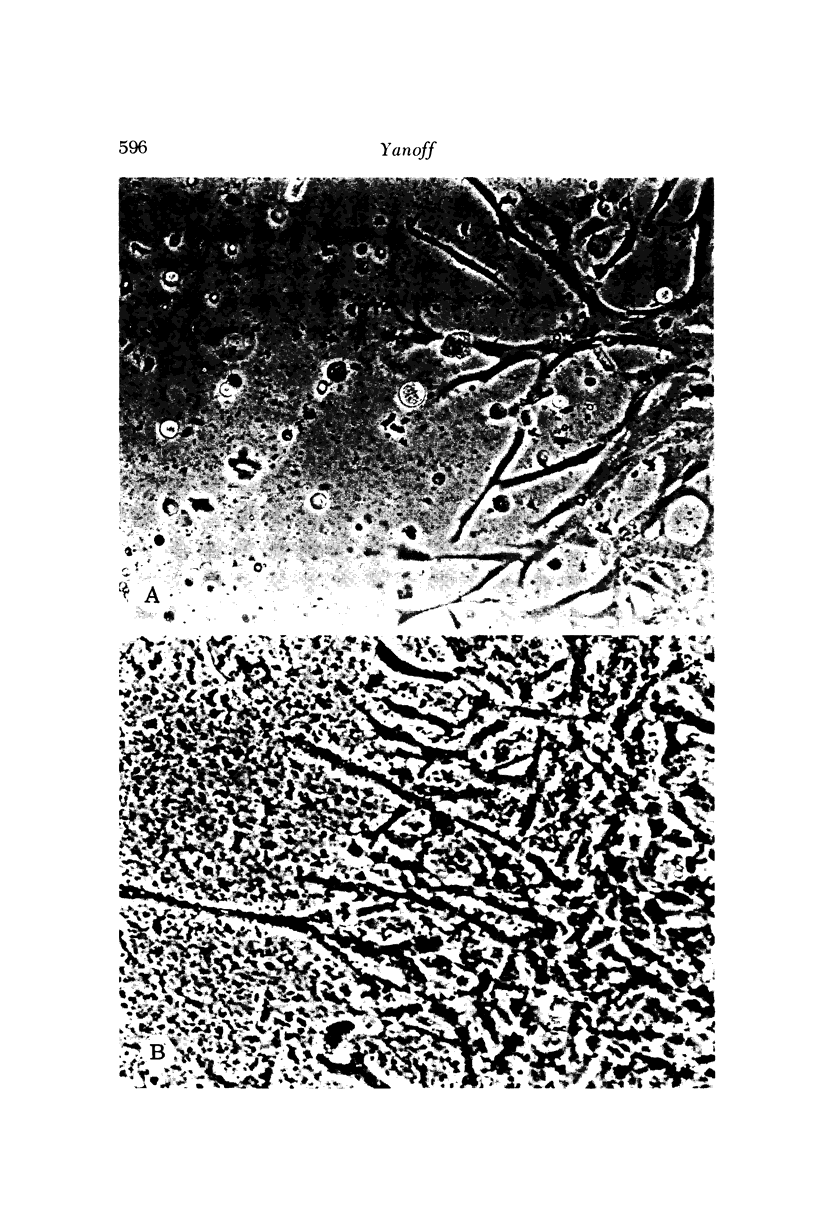
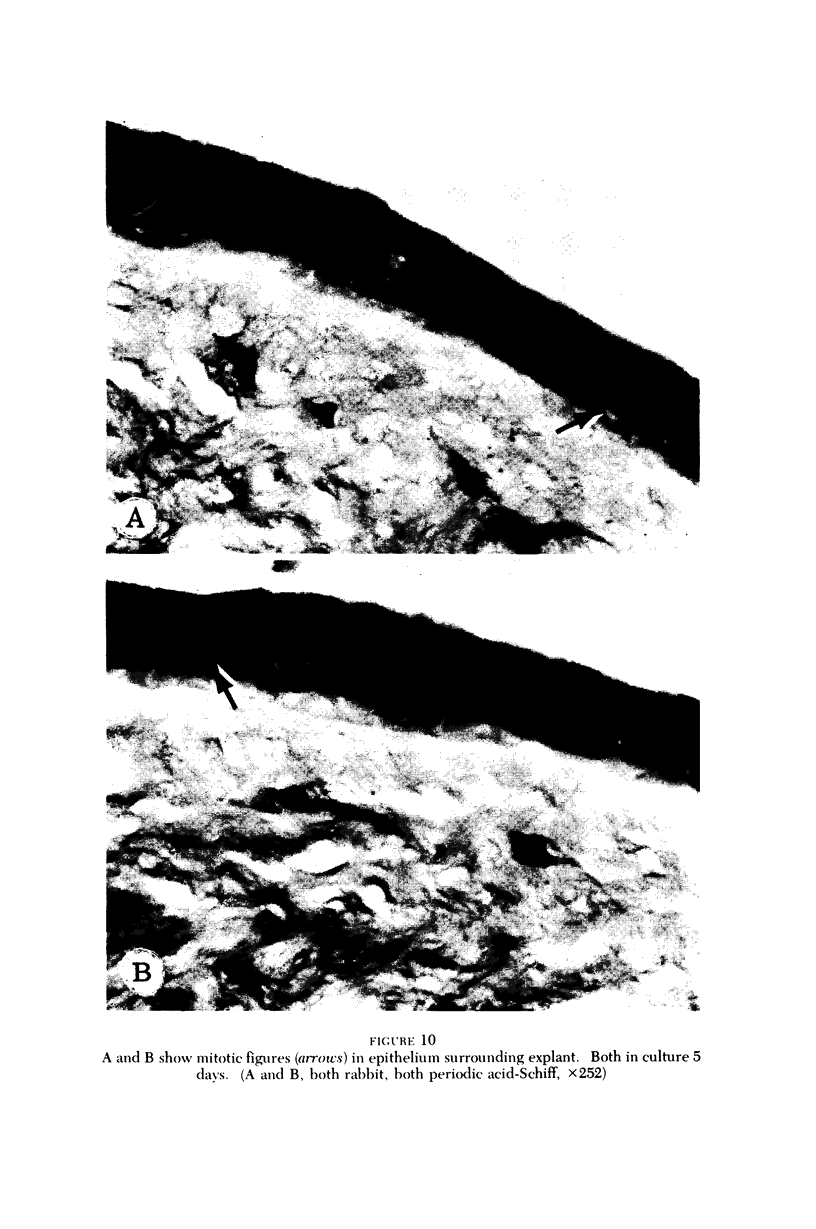
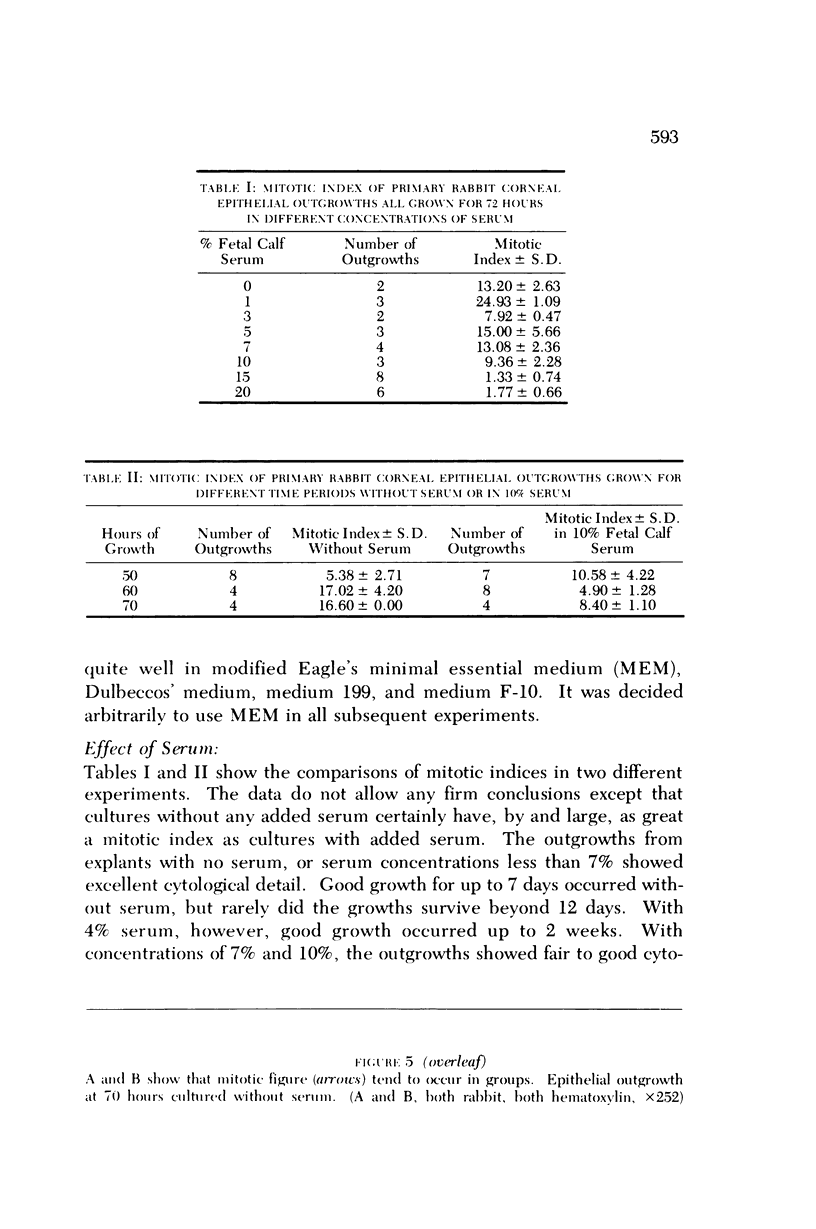
Four main areas are explored: (1) the proper culture medium for corneal tissue; (2) the effect of serum on in vitro tissue growth; (3) the in vitro interrelationships between corneal epithelium and endothelium; and (4) the biology of cultures of whole corneas (organ cultures). Modified Eagle's minimal essential medium (MEM) proved to be an excellent culture fluid. Corneal tissue could be grown in MEM without serum or clot, thus providing a defined culture medium. The in vitro biology of outgrowths of multilayered corneal epithelium and monolayered corneal endothelium are discussed. Contact inhibition between epithelium and endothelium is demonstrated in whole corneal (organ) cultures.
Full text
PDF

















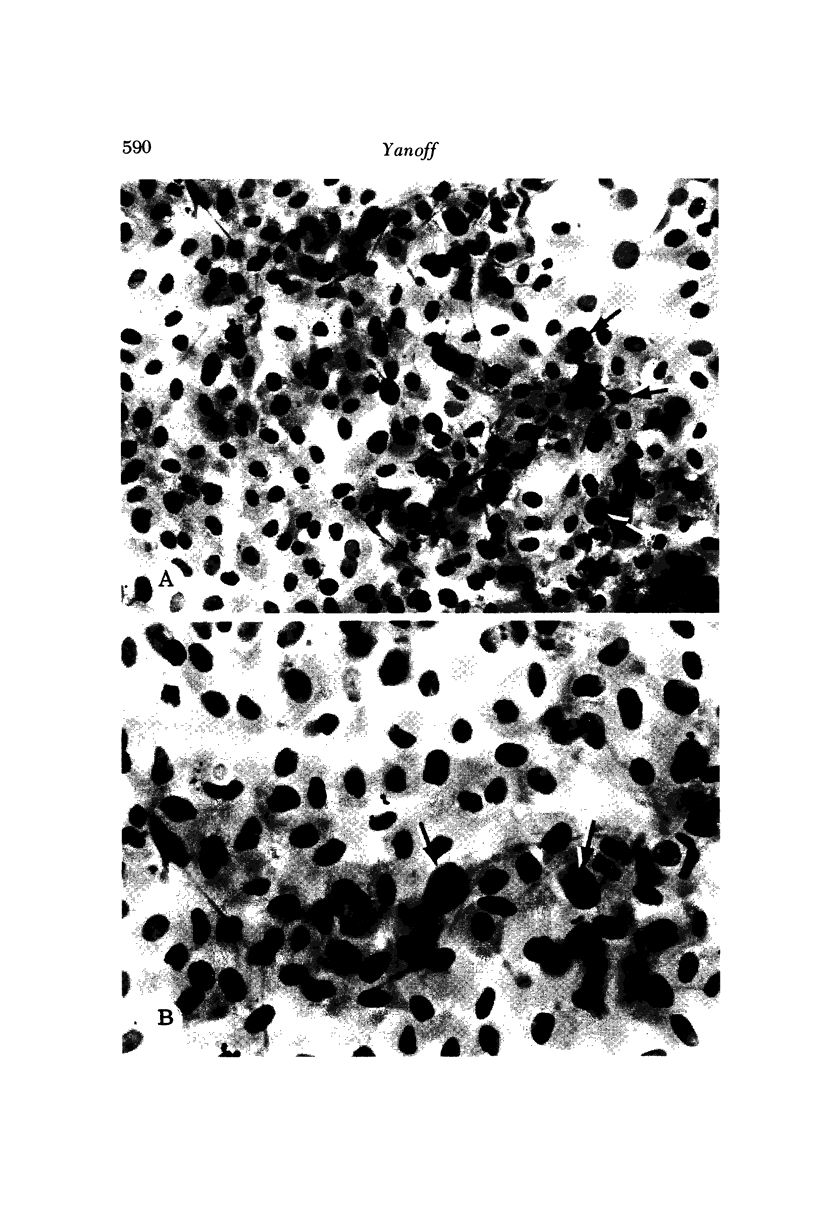
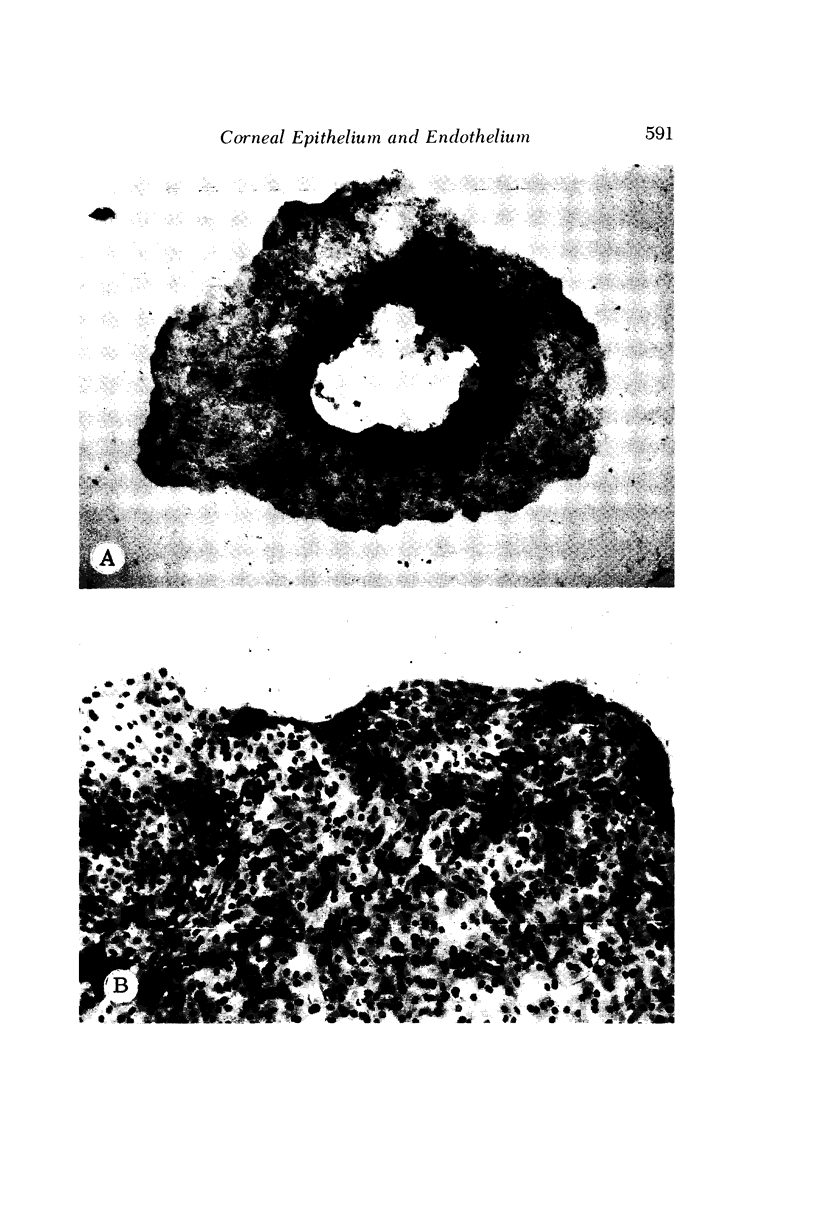

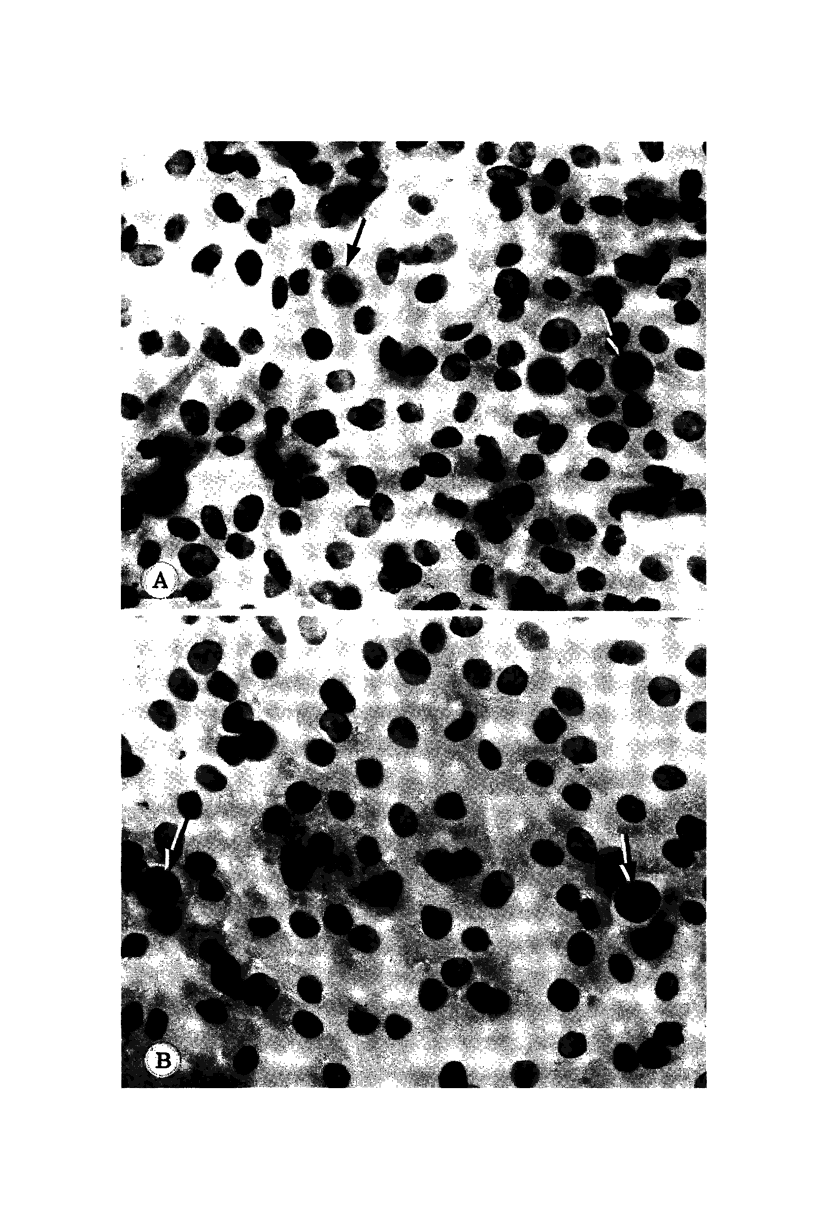


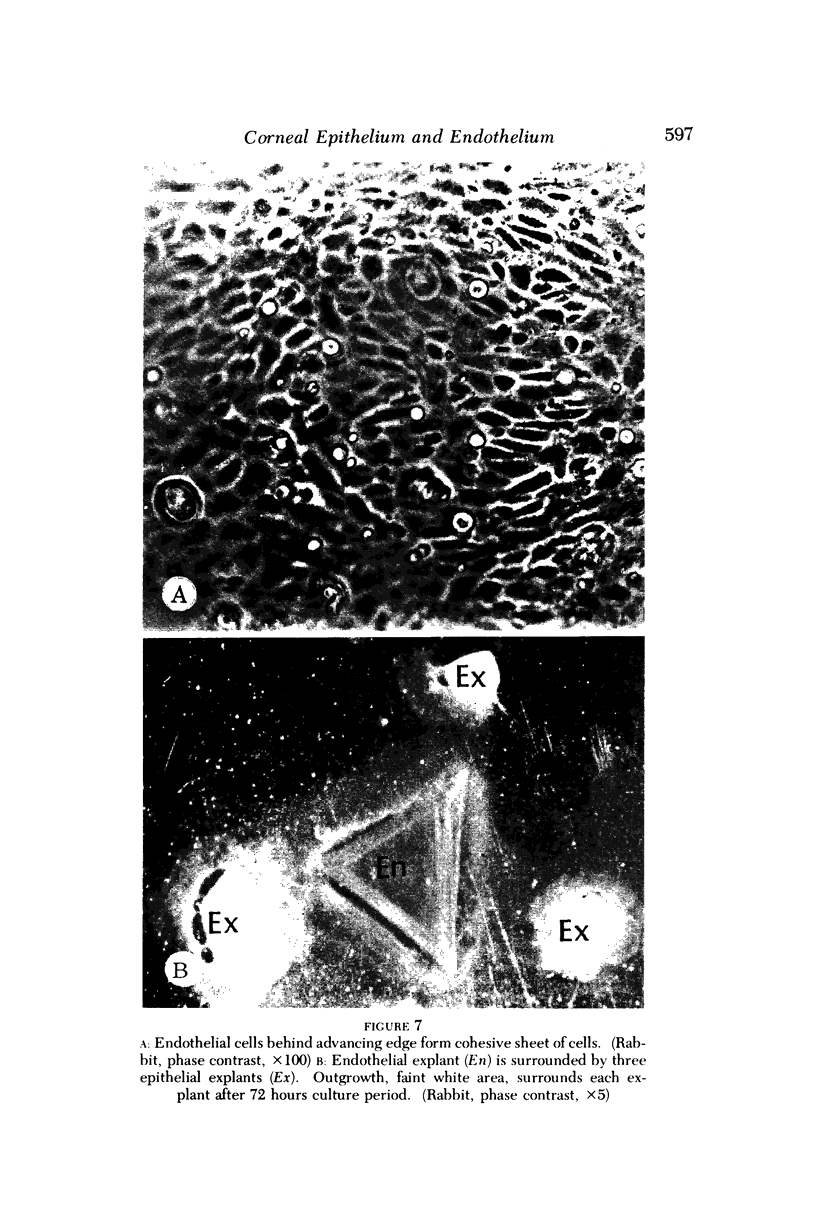
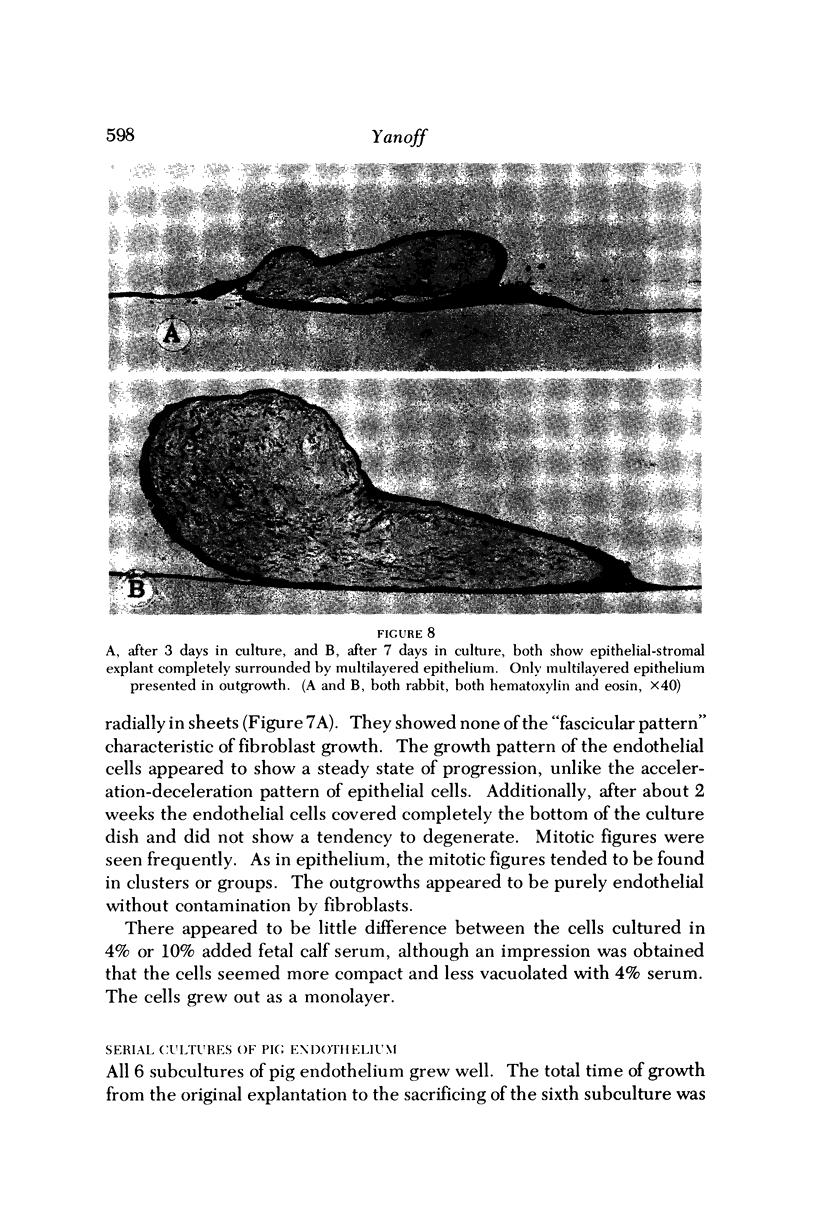
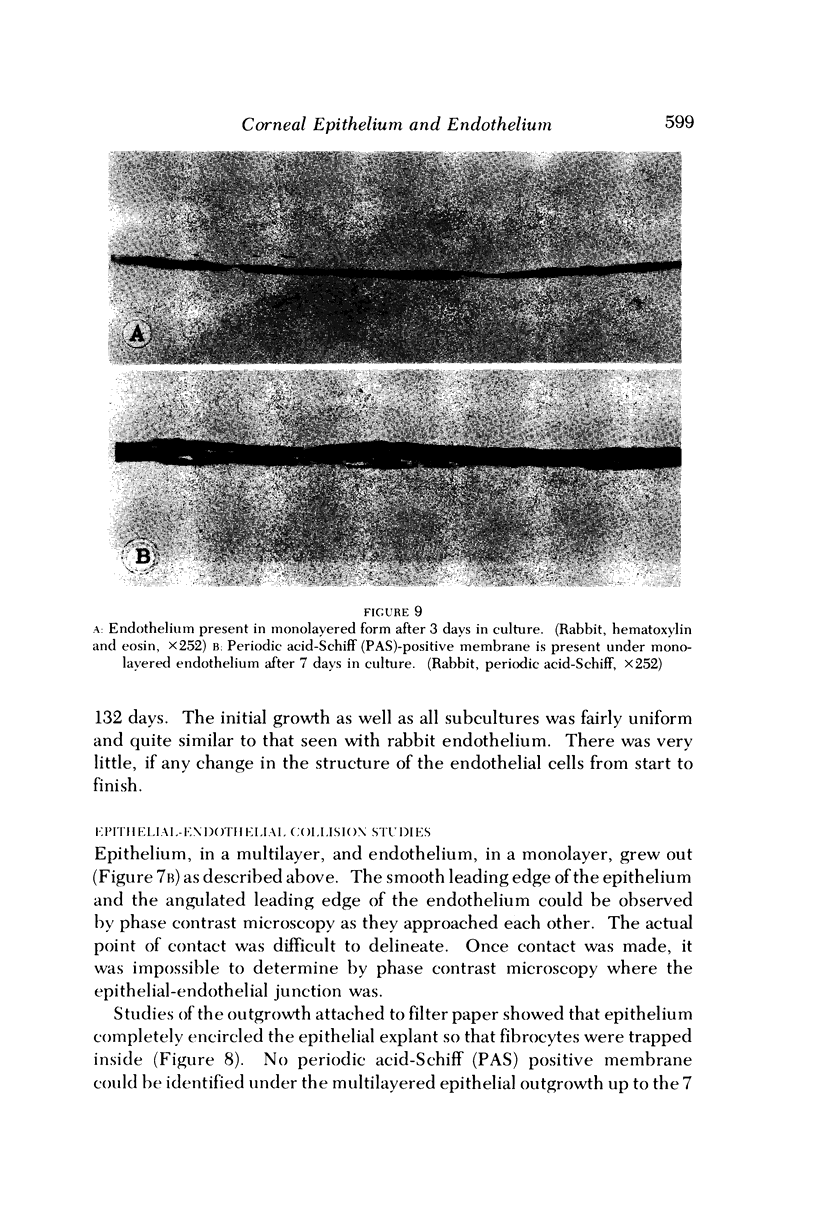

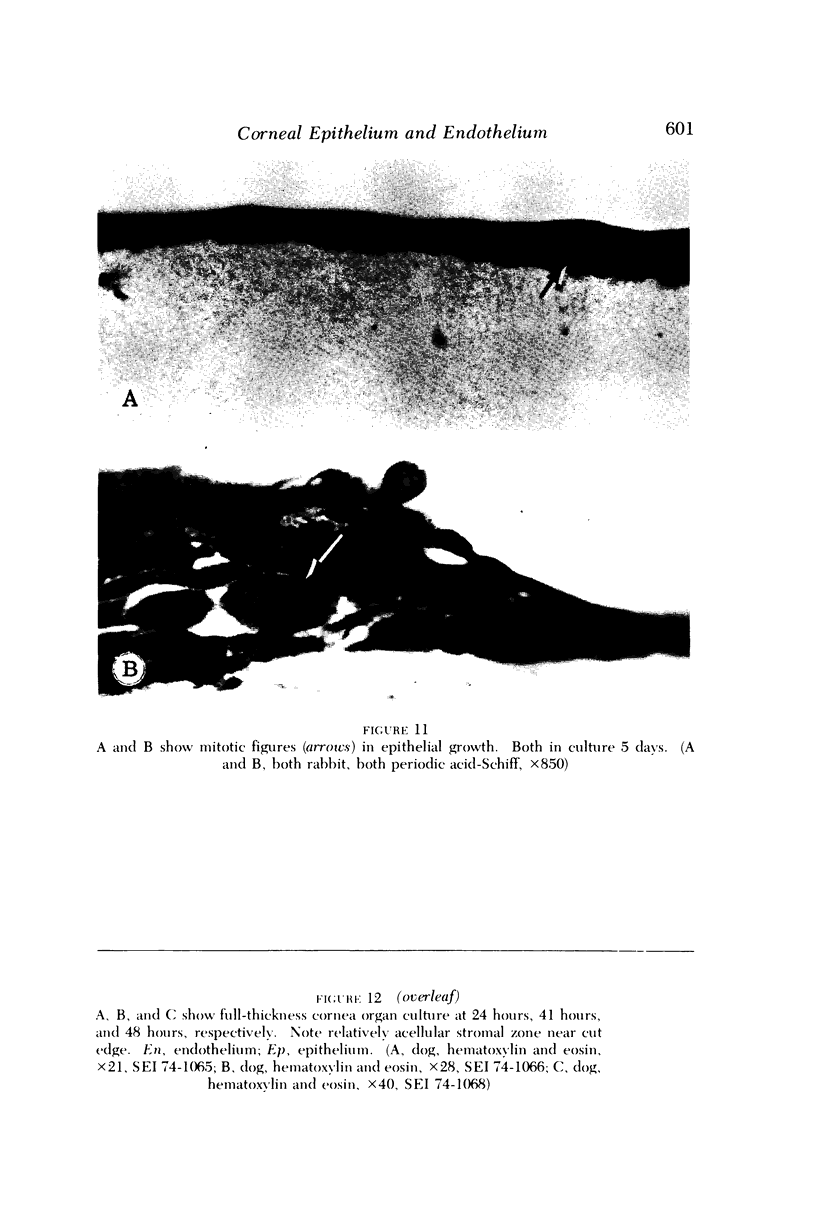













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABERCROMBIE M., AMBROSE E. J. Interference microscope studies of cell contacts in tissue culture. Exp Cell Res. 1958 Oct;15(2):332–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(58)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABERCROMBIE M., HEAYSMAN J. E. Invasiveness of sarcoma cells. Nature. 1954 Oct 9;174(4432):697–698. doi: 10.1038/174697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABERCROMBIE M., HEAYSMAN J. E., KARTHAUSER H. M. Social behaviour of cells in tissue culture. III. Mutual influence of sarcoma cells and fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Oct;13(2):276–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABERCROMBIE M., HEAYSMAN J. E. Observations on the social behaviour of cells in tissue culture. I. Speed of movement of chick heart fibroblasts in relation to their mutual contacts. Exp Cell Res. 1953 Sep;5(1):111–131. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(53)90098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ABERCROMBIE M., HEAYSMAN J. E. Observations on the social behaviour of cells in tissue culture. II. Monolayering of fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1954 May;6(2):293–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(54)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abercrombie M. Contact inhibition in tissue culture. In Vitro. 1970 Sep-Oct;6(2):128–142. doi: 10.1007/BF02616114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi M., Pollak O. J. Rabbits' corneal cells studied in tissue cultures. I. Morphologic and quantitative aspects. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;70(3):279–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00336495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi M., Pollak O. J. Rabbits' corneal cells studied in tissue cultures. II. Enzyme reactions. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1966;70(3):284–289. doi: 10.1007/BF00336496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya D. V., Mannagh J., Irvine A. R., Jr Effect of lysosomes on cultured rabbit corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Aug;11(8):662–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARSKI G., BELEHRADEK J., Jr ETUDE MICROCIN'EMATOGRAPHIQUE DU M'ECANISME D'INVASION CANC'EREUSE EN CULTURES DE TISSU NORMAL ASSOCI'E AUX CELLULES MALIGNES. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Feb;37:464–480. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAVEN E. P., COX A. J., Jr ORGAN CULTURE OF HUMAN SKIN. J Invest Dermatol. 1965 Mar;44:151–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BINDER H. F., BINDER R. F. Regenerative processes in the endothelium of the cornea. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1957 Jan;57(1):11–13. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1957.00930050013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benezra D., Sachs U. Growth and transplantation of organ-cultured corneas. Invest Ophthalmol. 1975 Jan;14(1):24–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Hook C. W., Tragakis M. P. Presence, significance, and inhibition of lysosomal proteoglycanases. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Mar;11(3):149–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Kitano S. Pathogenesis of the retrocorneal membrane. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Apr;75(4):518–525. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.00970050520016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A., Akiya S. Pathogenesis of ulcers of the alkali-burned cornea. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Feb;83(2):205–208. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030207014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A. Cell origin of collagenase in normal and wounded corneas. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Jan;83(1):74–77. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030076014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A. Collagenase inhibitors in prevention of ulcers of alkali-burned cornea. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Mar;83(3):352–353. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030352013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A. The pathogenesis and treatment of collagenase-induced diseases of the cornea. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1970 Mar-Apr;74(2):375–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A., Vidrich A. M. Effect of corticosteroids on corneal collagenase of rabbits. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970 Nov;70(5):744–747. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(70)90494-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. I., Weller C. A., Wassermann H. E. Collagenolytic activity of alkali-burned corneas. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Mar;81(3):370–373. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990010372015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow N., Ehlers N. Morphology and DOPA reaction of cultivated corneal epithelial cells. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1968;46(4):749–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1968.tb02873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COGAN D. G. Applied anatomy and physiology of the cornea. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1951 Mar-Apr;55:329–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS A. S. Cell contact and adhesion. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1962 Feb;37:82–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1962.tb01605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron J. D., Flaxman B. A., Yanoff M. In vitro studies of corneal wound healing: epithelial-endothelial interactions. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Aug;13(8):575–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron G. A. Organ culture of normal and psoriatic skin. Arch Dermatol. 1968 May;97(5):575–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Principles of cell motility: the direction of cell movement and cancer invasion. Nature. 1965 Dec 18;208(5016):1183–1187. doi: 10.1038/2081183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavoto F. V., Flaxman B. A. Low-resistance pathways between mitotic and interphase epidermal cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):223–225. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarini C., Eagle H. Induction and reversal of contact inhibition of growth by pH modification. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):271–273. doi: 10.1038/newbio233271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra D. P., Yu R. J., Flaxman B. A. Demonstration of a tissue specific inhibitor of mitosis of human epidermal cells in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1972 Sep;59(3):207–210. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12626986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cintron C. Organ culture of chick embryonic cornea. Dev Biol. 1972 Jan;27(1):100–115. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(72)90115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Berman M. Corneal collagenase: specific cleavage of types (alpha 1)2 alpha 2 and (alpha 1)3 collagens. Connect Tissue Res. 1973;2(1):57–64. doi: 10.3109/03008207309152600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPasquale A., Bell P. B., Jr The upper cell surface: its inability to support active cell movement in culture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):198–214. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson J. W., Hay E. D. Secretion of collagenous stroma by isolated epithelium grown in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):215–220. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman C. H. The function of the corneal epithelium in health and disease. The Jonas S. Friedenwald Memorial Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol. 1971 Jun;10(6):383–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donoff R. B., McLennan J. E., Grillo H. C. Preparation and properties of collagenases from epithelium and mesenchyme of healing mammalian wounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 10;227(3):639–653. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90014-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doughman D. J., Van Horn D., Harris J. E., Miller G. E., Lindstrom R., Summerlin W., Good R. A. Endothelium of the human organ cultured cornea: an electron microscopic study. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1973;71:304–328. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlers N. Some comparative studies on the mammalian corneal epithelium. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1970;48(4):821–828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellingson D. J., Yao K. T. Separation and in vitro growth of mammalian corneal epithelial and endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):478–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90703-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAVATA B. V. THE GROWTH ND BEHAVIOR OF GUINEA PIG IRIS, RETINA AND CORNEA IN VITRO. Am J Ophthalmol. 1964 Oct;58:651–663. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(64)91384-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Chopra D. P., Harper R. A. Autoradiographic analysis of hormone-independent development of the mouse vaginal epithelium in organ culture. In Vitro. 1974 Jul-Aug;10:42–50. doi: 10.1007/BF02615337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Harper R. A. Organ culture of human skin in chemically defined medium. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Feb;64(2):96–99. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12510310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Lasfargues E. Y. Hormone-independent DNA synthesis by epithelial cells of adult human mammary gland in organ culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jun;143(2):371–374. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Lutzner M. A., Van Scott E. J. Ultrastructure of cell attachment to substratum in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1968 Feb;36(2):406–410. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Nelson B. K. Ultrastructural studies of the early junctional zone formed by keratinocytes showing contact inhibition of movement in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1974 Oct;63(4):326–330. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12680297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaxman B. A., Revel J. P., Hay E. D. Tight junctions between contact-inhibited cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Dec;58(2):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90528-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J., Cambie E., Feher J. Collagenase inhibition with penicillamine. Case report. Ophthalmologica. 1973;166(3):222–225. doi: 10.1159/000306814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gail M. H., Boone C. W. Effect of colcemid on fibroblast motility. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):221–227. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Reeves O. R., Steinbach A. Metabolic coupling, ionic coupling and cell contacts. Nature. 1972 Feb 4;235(5336):262–265. doi: 10.1038/235262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnädinger M. C., Itoi M., Slansky H. H., Dohlman C. H. The role of collagenase in the alkali-burned cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969 Sep;68(3):478–483. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(69)90718-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnädinger M., Walz D., von Hahn H. P., Grün F. Acetylcholine-splitting activity of abraded and cultivated corneal epithelial cells. Exp Eye Res. 1967 Jul;6(3):239–242. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(67)80037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillo H. C., Gross J. Collagenolytic activity during mammalian wound repair. Dev Biol. 1967 Apr;15(4):300–317. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(67)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambrick G. W., Jr, Handwerger R. L. The behavior of explants of psoriasis in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 Feb;52(2):126–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambrick G. W., Jr, Lamberg S. I., Bloomberg R. Observations on keratinization of human skin in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1966 Dec;47(6):541–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. Behavior of cultured cells on substrata of variable adhesiveness. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Mar 15;77(1):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. Collagenases (third of three parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Sep 26;291(13):652–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197409262911305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho P. C., Davis W. H., Elliott J. H., Cohen S. Kinetics of corneal epithelial regeneration and epidermal growth factor. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;13(10):804–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoi M., Gnädinger M. C., Slansky H. H., Freeman M. I., Dohlman C. H. Collagenase in the cornea. Exp Eye Res. 1969 Jul;8(3):369–373. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(69)80050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. G., Sheridan J. D. Junctions between cancer cells in culture: ultrastructure and permeability. Science. 1971 Nov 12;174(4010):717–719. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4010.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A., Denduchis B. Structural components of epithelial and endothelial basement membranes. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4613–4621. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodadoust A. A., Silverstein A. M., Kenyon D. R., Dowling J. E. Adhesion of regenerating corneal epithelium. The role of basement membrane. Am J Ophthalmol. 1968 Mar;65(3):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(68)93082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodadoust A. A. Techniques for the preparation of sheets of pure corneal epithelium. Am J Ophthalmol. 1967 May;63(5):942–945. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(67)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejci L., Harrison R. Antiglaucoma drug effects on corneal epithelium. A comparative study in tissue culture. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Dec;84(6):766–769. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990040768015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejci L., Harrison R. Epinephrine effects on corneal cells in tissue culture. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Apr;83(4):451–454. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030451012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE E. M., BECKER Y., BOONE C. W., EAGLE H. CONTACT INHIBITION, MACROMOLECULAR SYNTHESIS, AND POLYRIBOSOMES IN CULTURED HUMAN DIPLOID FIBROBLASTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:350–356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leuenberger P. M., Gnädinger M. C., Cabernard E. Zur Frage der Kollagensynthese durch corneales Epithel. I. Elektronenmikroskopische Studie an regeneriertem Epithel der Kaninchenhornhaut. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol. 1973;187(3):171–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00531116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. The growth of adult human skin in vitro. Br J Dermatol. 1972 May;86(5):481–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb16100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry G. M. Corneal endothelium in vitro: characterization by ultrastructure and histochemistry. Invest Ophthalmol. 1966 Aug;5(4):355–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON P. L., ORMSBY H. L., BASU P. K. Healing of endothelium and Descemet's membrane of rabbit cornea. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Jul;46(1 Pt 2):62–67. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannagh J., Irving A. R., Jr Human corneal endothelium: growth in tissue cultures. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Dec;74(6):847–849. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970040849023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manski W., Whiteside T. L. Cell-surface receptors of normal, regenerating, and cultured corneal epithelial and endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Dec;13(12):935–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E., Steinberg M. S. Contact inhibition of what? An analytical review. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Feb;81(1):25–37. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda H., Smelser G. K. Electron microscopy of corneal wound healing. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Sep;16(6):427–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels R. G., Kenyon K. R., Maumence A. E. Retrocorneal fibrous membrane. Invest Ophthalmol. 1972 Oct;11(10):822–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton C. A. Contact inhibition of locomotion in cultures of pigmented retina epithelium. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Jan;70(1):91–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90185-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome D. A., Takasugi M., Kenyon K. R., Stark W. F., Opelz G. Human corneal cells in vitro: morphology and histocompatibility (HL-A) antigens of pure cell populations. Invest Ophthalmol. 1974 Jan;13(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Lague P., Dalen H., Rubin H., Tobias C. Electrical coupling: low resistance junctions between mitotic and interphase fibroblasts in tissue culture. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLDFIELD F. E. Orientation behavior of chick leucocytes in tissue culture and their interactions with fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Mar;30:125–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90219-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN R. A., LEE K. J., DONN A. ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE IN THE RABBIT CORNEA. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Mar;73:370–377. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970030372016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Baum J. L. Synthesis of a collagenous basal membrane by rabbit corneal endothelial cells in vitro. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974 Sep;92(3):238–239. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1974.01010010246015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman M., Baum J. L. The mass culture of rabbit corneal endothelial cells. Arch Ophthalmol. 1974 Sep;92(3):235–237. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1974.01010010243014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister R. R., McCulley J. P., Friend J., Dohlman C. H. Collagenase activity of intact corneal epithelium in peripheral alkali burns. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 Sep;86(3):308–313. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.01000010310014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINERTSON R. P. Stratum corneum formation in autoimplants and in explants of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1961 May;36:345–357. doi: 10.1038/jid.1961.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff E. C., Houck J. C. Migration and proliferation of diploid human fibroblasts following "wounding" of confluent monolayers. J Cell Physiol. 1969 Dec;74(3):235–244. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040740304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven E. P., Cox A. J. Behavior of adult human skin in organ culture. II. Effects of cellophane tape stripping, temperature, oxygen tension, pH and serum. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Feb;50(2):118–128. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Rubin H. Effects of local cell concentrations upon the growth of chick embryo cells in tissue culture. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Mar;49(3):666–678. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. A substance in conditioned medium which enhances the growth of small numbers of chick embryo cells. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Jan;41(1):138–148. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARKANY I., GRICE K., CARON G. A. ORGAN CULTURE OF ADULT HUMAN SKIN. Br J Dermatol. 1965 Feb;77:65–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1965.tb14602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARKAR P., BASU P. K., MILLER I. Karyologic studies on cells from rabbit cornea and other tissues grown in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol. 1962 Feb;1:33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLICK W. C., MANNAGH J., YUHASZ Z. ENZYMATIC REMOVAL AND PURE CULTURE OF RABBIT CORNEAL ENDOTHELIAL CELLS. Arch Ophthalmol. 1965 Feb;73:229–232. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1965.00970030231016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH A. U., ASHWOOD-SMITH M. J., YOUNG M. R. Some in vitro studies on rabbit corneal tissue. Exp Eye Res. 1963 Jan;2:71–87. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(63)80027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER F. W., EIRING A., GEORGIADE R., GEORGIADE N. A tissue culture technique for growing corneal epithelial, stromal, and endothelial tissues separately. Am J Ophthalmol. 1958 Nov;46(5 Pt 2):294–298. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(58)90811-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKER F. W., EIRING A., GEORGIADE R., GEORGIADE N. Evaluation of viability of donor tissue for corneal grafting. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1958;56:217–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar P., Basu P. K., Carré F. Bovine corneal epithelium in tissue culture. Chromosomal stability in a serially subcultured line. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 Mar;61(3):553–557. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)91068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Proliferation of corneal epithelium induced by epidermal growth factor. Exp Eye Res. 1973 Mar;15(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90151-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky H. H., Freeman M. I., Itoi M. Collagenolytic activity in bovine corneal epithelium. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968 Oct;80(4):496–498. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1968.00980050498018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky H. H., Gnädinger M. C., Itoi M., Dohlman C. H. Coagenase in corneal ulcerations. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Jul;82(1):108–111. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990020110026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M. G., Rubin H. Density dependent inhibition of cell growth in culture. Nature. 1967 Jul 8;215(5097):171–172. doi: 10.1038/215171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summerlin W. T., Miller G. E., Harris J. E., Good R. A. The organ-cultured cornea: an in vitro study. Invest Ophthalmol. 1973 Mar;12(3):176–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Lazar G. K., Green H. The initiation of cell division in a contact-inhibited mammalian cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):325–333. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkaus J. P., Betchaku T., Krulikowski L. S. Local inhibition of ruffling during contact inhibition of cell movement. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Feb;64(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90079-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON SALLMANN L., CARAVAGGIO L. L., GRIMES P. Studies on the corneal endothelium of the rabbit. I. Cell division and growth. Am J Ophthalmol. 1961 May;51:955–969. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(61)91782-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS L. Studies on cellular adhesion in tissue culture. II. The adhesion of cells to gel surfaces. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Jun;17(3):508–515. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS P. Perspectives in the field of morphogenesis. Q Rev Biol. 1950 Jun;25(2):177–198. doi: 10.1086/397540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar V. L., Haraguchi K. H. Growth stimulating effects of proteolytic enzymes on corneal tissues. Isr J Med Sci. 1972 Aug-Sep;8(8):1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar V. L., Haraguchi K. H. Neutral red uptake by corneal epithelial cells and by injury-activated corneal stromal cells. II. Competitive inhibition by riboflavin derivatives. Exp Eye Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(71)80066-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar V. L. Neutral red uptake by corneal epithelial cells and by injury-activated corneal stromal cells. I. A comparison of the effects of various metabolic inhibitors and lysosome labilizing and stabilizing agents. Exp Eye Res. 1971 Jan;11(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(71)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimar V., Fellman M. Connective tissue cell mobilization and migration following wounding. I. Inhibition of mobilization by chloroquine and inhibition of migration by colchicine. Exp Eye Res. 1970 Jan;9(1):12–21. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(70)80053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbanks G. D., Richart R. M. The in vitro interaction of intraepithelial neoplasia, normal epithelium, and fibroblasts from the adult human uterine cervix. Cancer Res. 1966 Aug;26(8):1641–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanoff M. Formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1973 Aug;76(2):303–304. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(73)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanoff M., Menocal N. G. Vacuum dehydration and paraffin embedding of eyes fixed in glutaraldehyde. Stain Technol. 1968 Sep;43(5):292–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]