Abstract
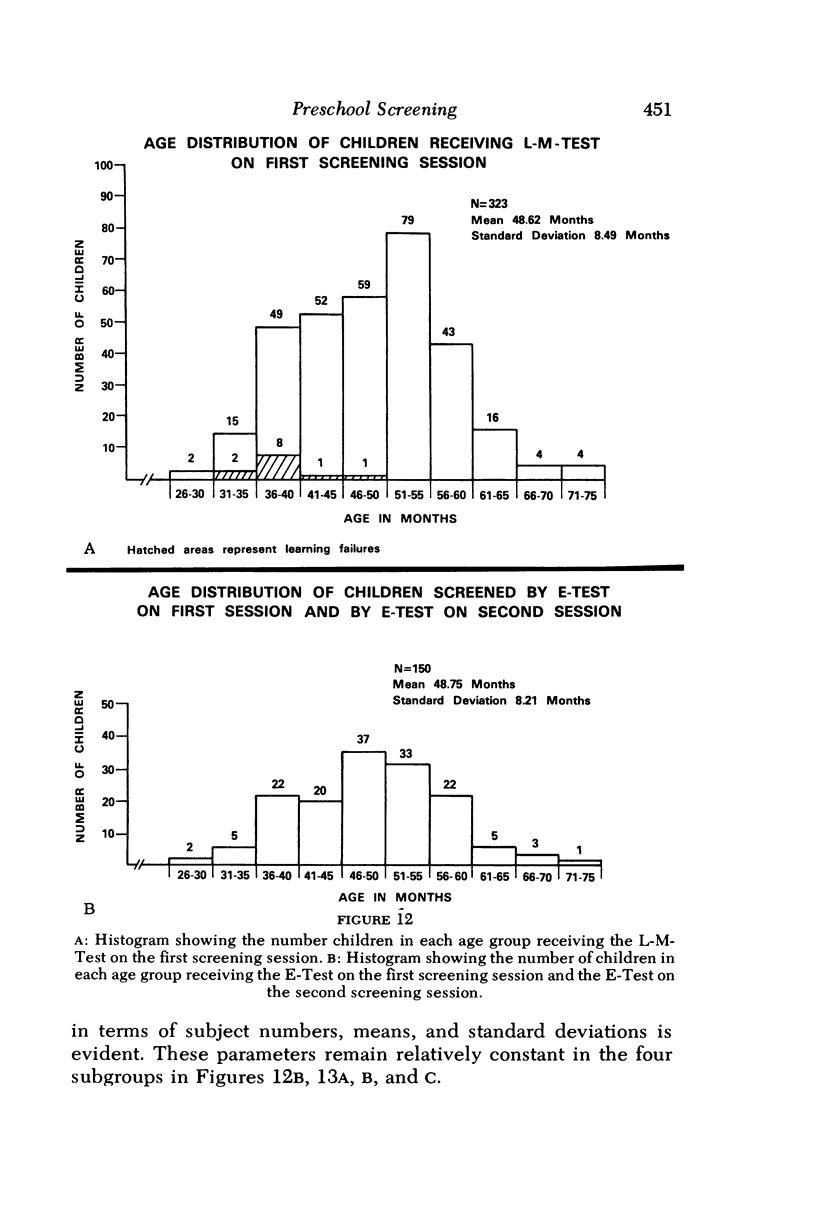
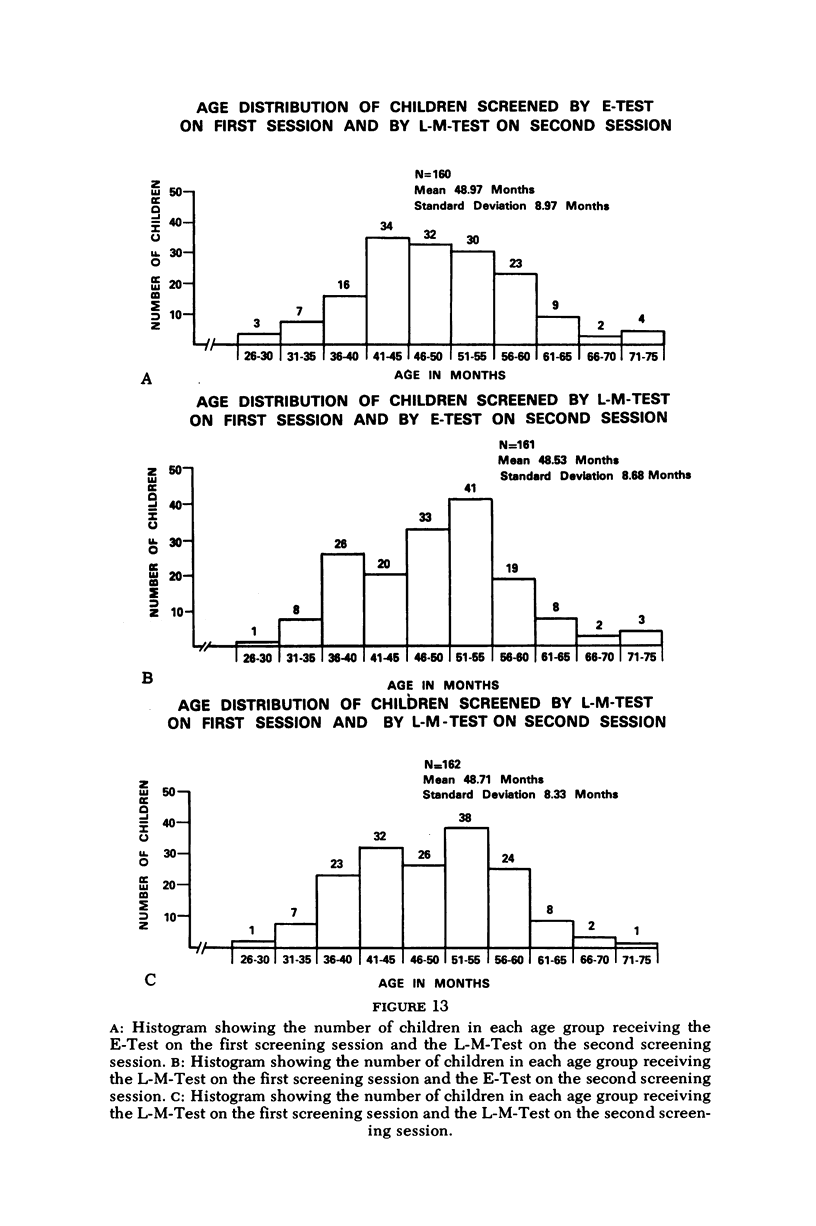
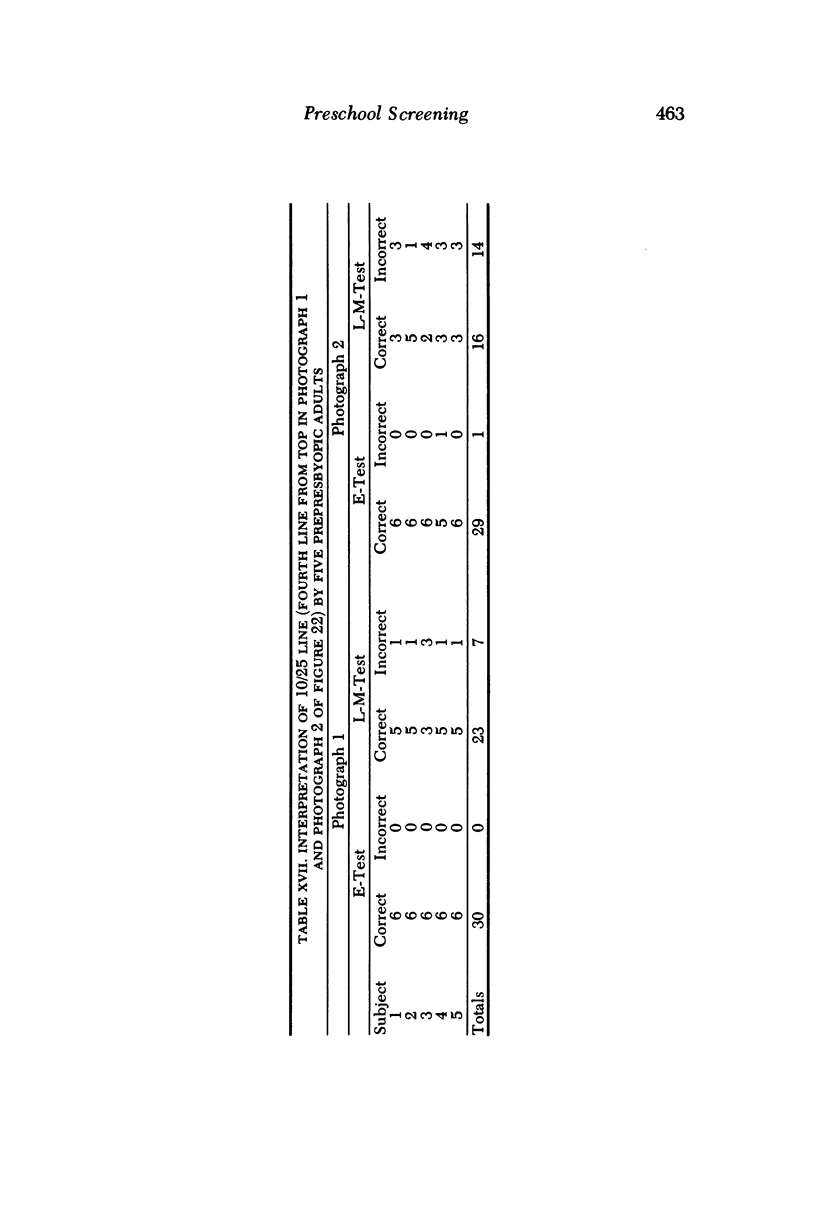
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the relative merits of two screening tests used for visual acuity assessment of preschool children. The tests that were compared were the Good-Lite Company versions of the E-Test and of the STYCAR (Screening Test for Young Children and Retardates). The former is the most popular method for evaluating central acuity in young children in this nation; the STYCAR is a relatively new letter-matching-test developed in England, where it is widely employed. The E-Test poses left-right orientation problems which are eliminated by the symmetrical letters H, T, O and V utilized in the Letter-Matching-Test. Both visual acuity tests were administered on two separate occasions by personnel from the Prevention of Blindness Society of Metropolitan Washington to 633 preschool children in Washington, D.C. By random selection, 150 of the children received the E-Test at both sessions, 162 children received the Letter-Matching-Test at both sessions, 160 chilt athe the second session, and 161 children received the Letter-Matching-Test at the first session and the E-Test at the second session. The author medically examined the eyes of 408 of the 633 children without knowledge of which test had been initially administered. Statistical analysis of the data obtained from the study indicated that the Letter-Matching-Test was significantly better in terms of testability rates, group and individual instruction time, and performance time. The E-Test was more reliable in terms of test-retest acuity scores and was also more valid in terms of agreement between pass-fail results obtained at the first screening session and two levels of pass-fail refraction criteria.
Full text
PDF






















































































Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN H. F. A new picture series for preschool vision testing. Am J Ophthalmol. 1957 Jul;44(1):38–41. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(57)91953-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLEN H. F. Testing of visual acuity in preschool children; norms, variables and a new picture test. Pediatrics. 1957 Jun;19(6):1093–1100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amigo G. Pre-school vision study. Br J Ophthalmol. 1973 Feb;57(2):125–132. doi: 10.1136/bjo.57.2.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKHURST R. T. Successful preschool vision screening in Michigan. J Mich State Med Soc. 1962 Sep;61:1124–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacharach J. A., Miller G., Gustafson V., Dernbach A., Lovlien A., Elliott M. Vision testing by parents of 3 and one-half-year-old children. Public Health Rep. 1970 May;85(5):426–432. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banister H. BLOCK CAPITAL LETTERS AS TESTS OF VISUAL ACUITY. Br J Ophthalmol. 1927 Feb;11(2):49–62. doi: 10.1136/bjo.11.2.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow H. B., Blakemore C., Pettigrew J. D. The neural mechanism of binocular depth discrimination. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):327–342. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bax M. C. Development of visual acuity. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Sep;48(9):746–746. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.9.746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A. G. Ophthalmic test types. A review of previous work and discussions on some controversial questions. Br J Physiol Opt. 1965;22(4):238–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg G., Sundmark E. A comparative study of visual acuity test for children. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1967;45(1):105–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1967.tb06483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyce V. S. The home eye test program. Sight Sav Rev. 1973 Spring;43(1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browder J. A., Levy W. J. Vision testing of young and retarded children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 1974 Nov;13(11):983–986. doi: 10.1177/000992287401301111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg A. Visual acuity as measured by dynamic and static tests: a comparative evaluation. J Appl Psychol. 1966 Dec;50(6):460–466. doi: 10.1037/h0023982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burian H. M. Pathophysiologic basis of amblyopia and of its treatment. Am J Ophthalmol. 1969 Jan;67(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(69)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman M. L. Vision screening of pre-school children in Prince George's County, Maryland, nursery schools. J Natl Med Assoc. 1969 Jul;61(4):352–passim. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLONNIER M. THE TANGENTIAL ORGANIZATION OF THE VISUAL CORTEX. J Anat. 1964 Jul;98:327–344. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. W., Green D. G. Optical and retinal factors affecting visual resolution. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(3):576–593. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell F. W., Kulikowski J. J., Levinson J. The effect of orientation on the visual resolution of gratings. J Physiol. 1966 Nov;187(2):427–436. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casellato L. Testing visual acuity. Br J Ophthalmol. 1971 Jan;55(1):44–47. doi: 10.1136/bjo.55.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catford G. V., Oliver A. Development of visual acuity. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Jan;48(1):47–50. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cibis L., Hurtt J., Rasicovich A. A clinical study of separation difficulty in organic and in functional amblyopia. Am Orthopt J. 1968;18:66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DREYER V. ON THE EXACTNESS OF VISUAL ACUITY DETERMINATION CHARTS WITH DECIMAL, SNELLEN, AND LOGARITHMIC NOTATION. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1964;42:295–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1964.tb03609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davens E. The nationwide alert to preschool vision screening. Sight Sav Rev. 1966 Spring;36(1):13–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FFOOKS O. VISION TEST FOR CHILDREN: USE OF SYMBOLS. Br J Ophthalmol. 1965 Jun;49:312–314. doi: 10.1136/bjo.49.6.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINK W. H. Testing visual acuity of the pre-school child. Minn Med. 1959 Jan;42(1):23–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLOM M. C., WEYMOUTH F. W., KAHNEMAN D. VISUAL RESOLUTION AND CONTOUR INTERACTION. J Opt Soc Am. 1963 Sep;53:1026–1032. doi: 10.1364/josa.53.001026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREY R. G. Die Beziehung zwischen Sehschärfe und Tiefensehschärfe. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1953 Jun 13;103(24):436–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flom M. C., Neumaier R. W. Prevalence of amblyopia. Public Health Rep. 1966 Apr;81(4):329–341. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. S., Paul T. O., Jampolsky A. Mangement of infantile esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976 Aug;82(2):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(76)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON D. A., ZEIDNER J., ZAGORSKI H. J., UHLANER J. E. A psychometric evaluation of ortho-rater and wall-chart tests. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 May;37(5):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(54)91222-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gansner J. Zur Häufigkeit der Schielamblyopie. Statistische Erhebungen an vorschulpflichtigen Kindern einer städtischen Bevölkerung. Ophthalmologica. 1968;155(3):234–244. doi: 10.1159/000305286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickstein M., Millodot M. Retinoscopy and eye size. Science. 1970 May 1;168(3931):605–606. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3931.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. G., Cohen M. M. Laser interferometry in the evaluation of potential macular function in the presence of opacities in the ocular media. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1971 May-Jun;75(3):629–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLT L. B. OFFICE PRESCHOOL VISUAL ACUITY TESTING. Eye Ear Nose Throat Mon. 1965 Aug;44:49–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartridge H., Owen H. B. TEST TYPES. Br J Ophthalmol. 1922 Dec;6(12):543–549. doi: 10.1136/bjo.6.12.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield E. M., Barrett C. D., Jr, Nudell R. J. Detroit Project 20/20. Sight Sav Rev. 1967 Winter;37(4):202–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield E. M. Progress in preschool vision screening. Sight Sav Rev. 1967 Winter;37(4):194–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht S., Mintz E. U. THE VISIBILITY OF SINGLE LINES AT VARIOUS ILLUMINATIONS AND THE RETINAL BASIS OF VISUAL RESOLUTION. J Gen Physiol. 1939 May 20;22(5):593–612. doi: 10.1085/jgp.22.5.593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht S., Shlaer S., Pirenne M. H. ENERGY, QUANTA, AND VISION. J Gen Physiol. 1942 Jul 20;25(6):819–840. doi: 10.1085/jgp.25.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton A. F., Stanley J. C. Pitfalls in testing children's vision by the Sheridan Gardiner single optotype method. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972 Feb;56(2):135–139. doi: 10.1136/bjo.56.2.135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Receptive fields and functional architecture of monkey striate cortex. J Physiol. 1968 Mar;195(1):215–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N. Stereoscopic vision in macaque monkey. Cells sensitive to binocular depth in area 18 of the macaque monkey cortex. Nature. 1970 Jan 3;225(5227):41–42. doi: 10.1038/225041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyams L., Safir A., Philpot J. Studies in refraction. II. Bias and accuracy of retinoscopy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1971 Jan;85(1):33–41. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1971.00990050035006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing M., Costenbader F. D., Parks M. M., Albert D. G. Early surgery for congenital esotropia. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 Jun;61(6):1419–1427. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)90480-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram R. M. Refraction as a basis for screening children for squint and amblyopia. Br J Ophthalmol. 1977 Jan;61(1):8–15. doi: 10.1136/bjo.61.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JONKERS G. H. The examination of the visual acuity of children. Ophthalmologica. 1958 Sep;136(3):140–144. doi: 10.1159/000303426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAIVONEN M., KOSKENOJA M. VISUAL SCREENING FOR CHILDREN AGED FOUR YEARS AND PRELIMINARY EXPERIENCE FROM ITS APPLICATION IN PRACTICE. (A PRELIMINARY REPORT). Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1963;41:785–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KITTREDGE E., CUNNINGHAM F. PRE-KINDERGARTEN VISION SCREENING IN YONKERS PUBLIC SCHOOLS. J Sch Health. 1965 Jun;25:278–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1746-1561.1965.tb01620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith C. G., Diamond Z., Stansfield A. Visual acuity testing in young children. Br J Ophthalmol. 1972 Nov;56(11):827–832. doi: 10.1136/bjo.56.11.827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. G., Chen K. F., Frenkel M. Subjective and objective visual acuity testing techniques. Arch Ophthalmol. 1976 Dec;94(12):2086–2091. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1976.03910040746009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler L., Stigmar G. Vision screening of four-year-old children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1973 Jan;62(1):17–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1973.tb08060.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. S., Glick E. B. Stereoscopic perception and Snellen visual acuity. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;78(4):722–724. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76312-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewkonia I. Objective assessment of visual acuity by induction of optokinetic nystagmus. Br J Ophthalmol. 1969 Sep;53(9):641–644. doi: 10.1136/bjo.53.9.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linksz A. AOS, : John Green, theand the Reasonable Notation of Visual Acuity Measurements. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1972;70:314–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linksz A. Visual acuity in the newborn with notes on some objective methods to determine visual acuity. Doc Ophthalmol. 1973 Feb 21;34(1):259–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00151813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann O. Vision of young children. Arch Ophthalmol. 1969 Jun;81(6):763–775. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1969.00990010765003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippmann O. Vision screening of young children. Am J Public Health. 1971 Aug;61(8):1586–1601. doi: 10.2105/ajph.61.8.1586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maffei L., Campbell F. W. Neurophysiological localization of the vertical and horizontal visual coordinates in man. Science. 1970 Jan 23;167(3917):386–387. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3917.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. J. Development of anisotropy in late childhood. Vision Res. 1977;17(6):703–710. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6989(77)80006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millodot M., Miller D., Jernigan M. E. Evaluation of an objective acuity device. Arch Ophthalmol. 1973 Dec;90(6):449–452. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1973.01000050449008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. E., Baker A. G. Stereoscopic aftereffects: evidence for disparity-specific neurones in the human visual system. Vision Res. 1973 Dec;13(12):2273–2288. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(73)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. E., Freeman R. D., Westheimer G. Effect of orientation on the modulation sensitivity for interference fringes on the retina. J Opt Soc Am. 1967 Feb;57(2):246–249. doi: 10.1364/josa.57.000246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDLOEW W. SQUINT--THE FREQUENCY OF ONSET AT DIFFERENT AGES, AND THE INCIDENCE OF SOME ASSOCIATED DEFECTS IN A SWEDISH POPULATION. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1964;42:1015–1037. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1964.tb03667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORDLOW W., JOACHIMSSON S. A screening test for visual acuity in four year old children. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1962;40:453–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1962.tb07816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikara T., Bishop P. O., Pettigrew J. D. Analysis of retinal correspondence by studying receptive fields of binocular single units in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(4):353–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00233184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGLE K. N. On the problem of an international nomenclature for designating visual acuity. Am J Ophthalmol. 1953 Jul;36(7 1):909–921. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(53)92172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OGLE K. N. Present status of our knowledge of stereoscopic vision. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Oct;60(4 Pt 2):755–774. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1958.00940080775019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
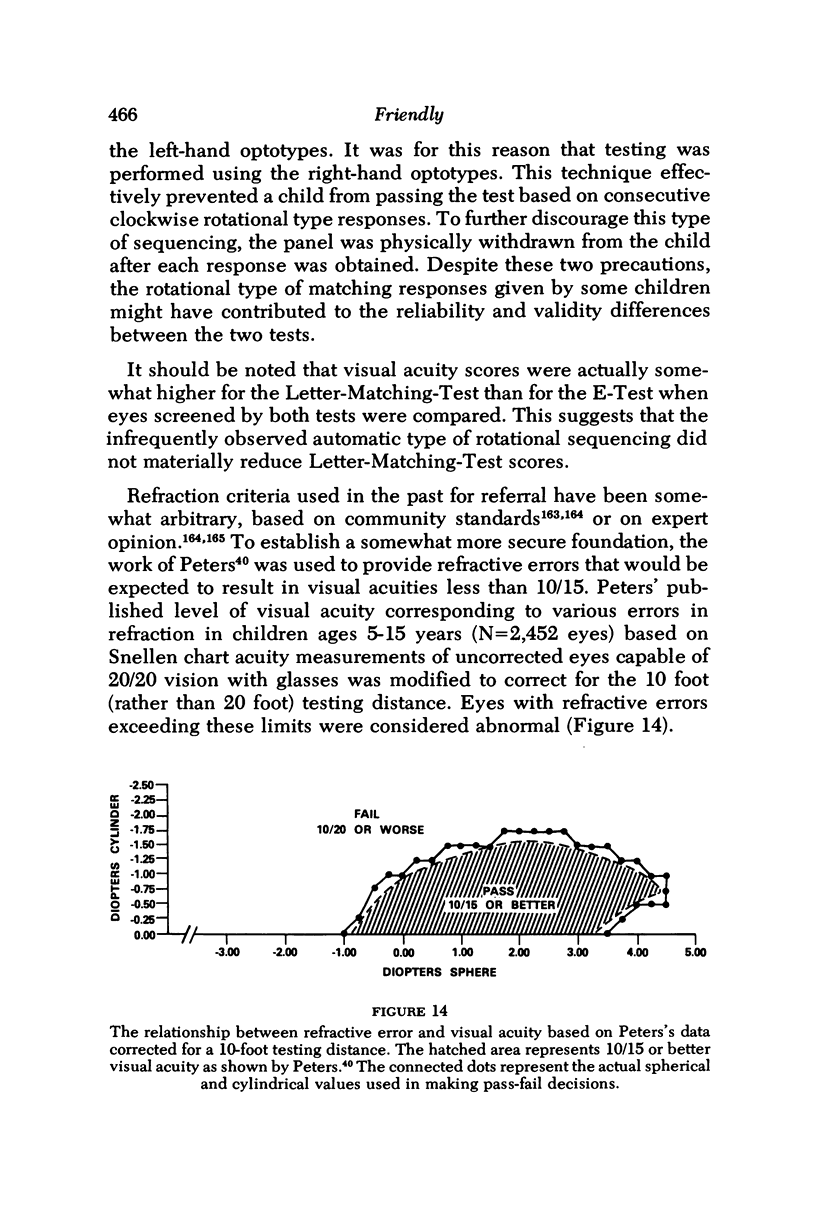
- PETERS H. B. The relationship between refractive error and visual acuity at three age levels. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom. 1961 Apr;38:194–198. doi: 10.1097/00006324-196104000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS H. B. The relationship between refractive error and visual acuity at three age levels. Am J Optom Arch Am Acad Optom. 1961 Apr;38:194–198. doi: 10.1097/00006324-196104000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks M. M., Friendly D. S. Treatment of eccentric fixation in children under four years of age. Am J Ophthalmol. 1966 Mar;61(3):395–399. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(66)91044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. M. The objective determination of vision and visual acuity. Br J Physiol Opt. 1966;23(2):107–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew J. D., Nikara T., Bishop P. O. Responses to moving slits by single units in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res. 1968;6(4):373–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00233185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINECKE R. D., COGAN D. G. Standardization of objective visual acuity measurements; opticokinetic nystagmus vs. Snellen acuity. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1958 Sep;60(3):418–421. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1958.00940080436010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDEL R. G., TEUBER H. L. DISCRIMINATION OF DIRECTION OF LINE IN CHILDREN. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1963 Oct;56:892–898. doi: 10.1037/h0046592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYCHENER R. O. Vision tests in infants and young children. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1958 Feb;:231–238. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)30629-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecke R. D., Simons K. A new stereoscopic test for amblyopia screening. Am J Ophthalmol. 1974 Oct;78(4):714–721. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76311-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards W. Stereopsis and stereoblindness. Exp Brain Res. 1970;10(4):380–388. doi: 10.1007/BF02324765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDLER J. A test of the significance of the difference between the means of correlated measures, based on a simplification of student's t. Br J Psychol. 1955 Aug;46(3):225–226. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1955.tb00542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTING B. H. Testing infants' vision; an apparatus for estimating the visual acuity of infants and young children. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 Nov;38(5):714–715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERIDAN M. D. Vision screening of very young or handicapped children. Br Med J. 1960 Aug 6;2(5196):453–456. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5196.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOAN L. L. Measurement of visual acuity; a critical review. AMA Arch Ophthalmol. 1951 Jun;45(6):704–725. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1951.01700010719013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOAN L. L. New test charts for the measurement of visual acuity at far and near distances. Am J Ophthalmol. 1959 Dec;48:807–813. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(59)90626-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANDARDS for referral of school children for an eye examination. Am J Ophthalmol. 1954 May;37(5):710–718. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(54)91224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUART J. A., BURIAN H. M. A study of separation difficulty. Its relationship to visual acuity in normal and amblyopic eyes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1962 Mar;53:471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND N. S. Visual discrimination of orientation by octopus: mirror images. Br J Psychol. 1960 Feb;51:9–18. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8295.1960.tb00719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safir A., Kulikowski C., Deuschle K. Automatic refraction: how it is done: some clinical results. Sight Sav Rev. 1973 Fall;43(3):137–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütte E., Groten H., Leymann J., Lizin F. Augenärztliche Reihenuntersuchungen im Kindergarten. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1976 Apr;168(4):584–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan M. D. The STYCAR graded-balls vision test. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1973 Aug;15(4):423–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1973.tb05062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol S., Dobson V. Pattern reversal visually evoked potentials in infants. Invest Ophthalmol. 1976 Jan;15(1):58–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokol S. Visually evoked potentials: theory, techniques and clinical applications. Surv Ophthalmol. 1976 Jul-Aug;21(1):18–44. doi: 10.1016/0039-6257(76)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. M. Congenital strabismus. The common sense approach. Arch Ophthalmol. 1967 Apr;77(4):478–484. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1967.00980020480010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter R. R., Phillips R. M., Shaffer K. Measurement of visual acuity of preschool children by their parents. Sight Sav Rev. 1966 Summer;36(2):80–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voipio H., Hyvarinen L. Objective measurement of visual acuity by arrestovisography. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966 Jun;75(6):799–802. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.00970050801017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Noorden G. K., Isaza A., Parks M. E. Surgical treatment of congenital esotropia. Trans Am Acad Ophthalmol Otolaryngol. 1972 Nov-Dec;76(6):1465–1478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN L. R., DILLMAN A. OBJECTIVE MEASUREMENT OF VISUAL ACUITY. USING OPTOKINETIC NYSTAGMUS AND ELECTRO-OCULOGRAPHY. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964 Jun;71:822–826. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1964.00970010838008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walraven J. Amblyopia screening with random-dot stereograms. Am J Ophthalmol. 1975 Nov;80(5):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(75)90286-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenheimer F. S. Home vision screening in the San Francisco Bay area. Sight Sav Rev. 1967 Fall;37(3):157–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youngson R. M. Anomaly in visual acuity testing in children. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975 Mar;59(3):168–170. doi: 10.1136/bjo.59.3.168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]