Abstract
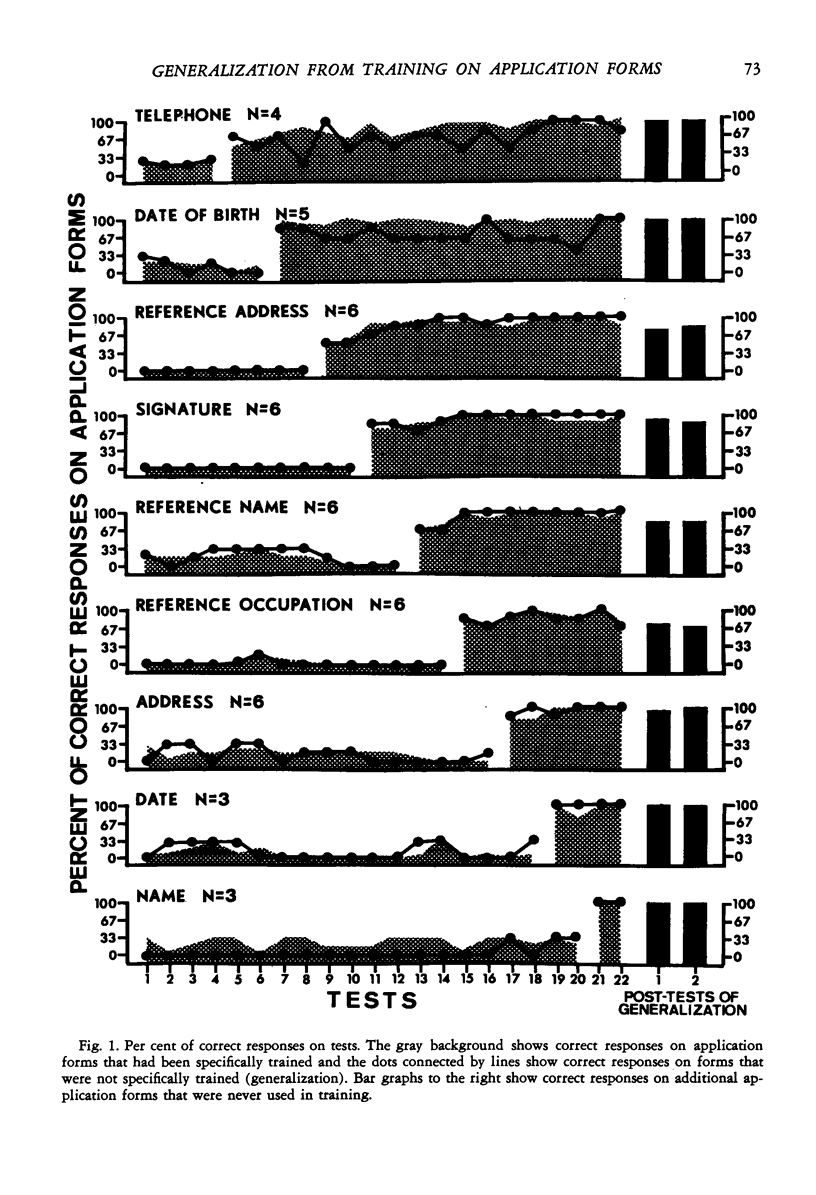
Little attention has been given to how formal classroom instruction can be adapted to teach youths everyday skills such as the correct writing of biographic information frequently requested in transactions like applying for a job or a social security number and cashing a check. In this study, six youths in a special education classroom were taught to complete job application forms with the date, their name, signature, address, telephone number, date of birth, and a reference's name, address, and occupation. Each youth was trained on one item of biographic information at a time, after which he was tested on four application forms, including one on which he had not been trained. The tests show that after an item had been taught, it was correctly used in completing application forms on which the youths had been trained and forms on which they had never been trained. The study demonstrates the feasibility of teaching community-living, vocation-related skills to special-education youths in a classroom setting.
Keywords: academic behavior, prevocational skills, disadvantaged children, education, generalization, job-finding skills, retardates, self-paced instruction, biographic information
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Born D. G., Gledhill S. M., Davis M. L. Examination performance in lecture-discussion and personalized instruction courses. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):33–43. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham T. A., Finfrock S. R., Breunig M. K., Bushell D. The use of programmed materials in the analysis of academic contingencies. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Summer;5(2):177–182. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brigham T. A., Graubard P. S., Stans A. Analysis of the effects of sequential reinforcement contingencies on aspects of composition. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Winter;5(4):421–429. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloney K. B., Hopkins B. L. The modification of sentence structure and its relationship to subjective judgements of creativity in writing. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Fall;6(3):425–433. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael J. S., Corey J. R. Contingency management in an introductory psychology course produces better learning. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):79–83. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


