Abstract
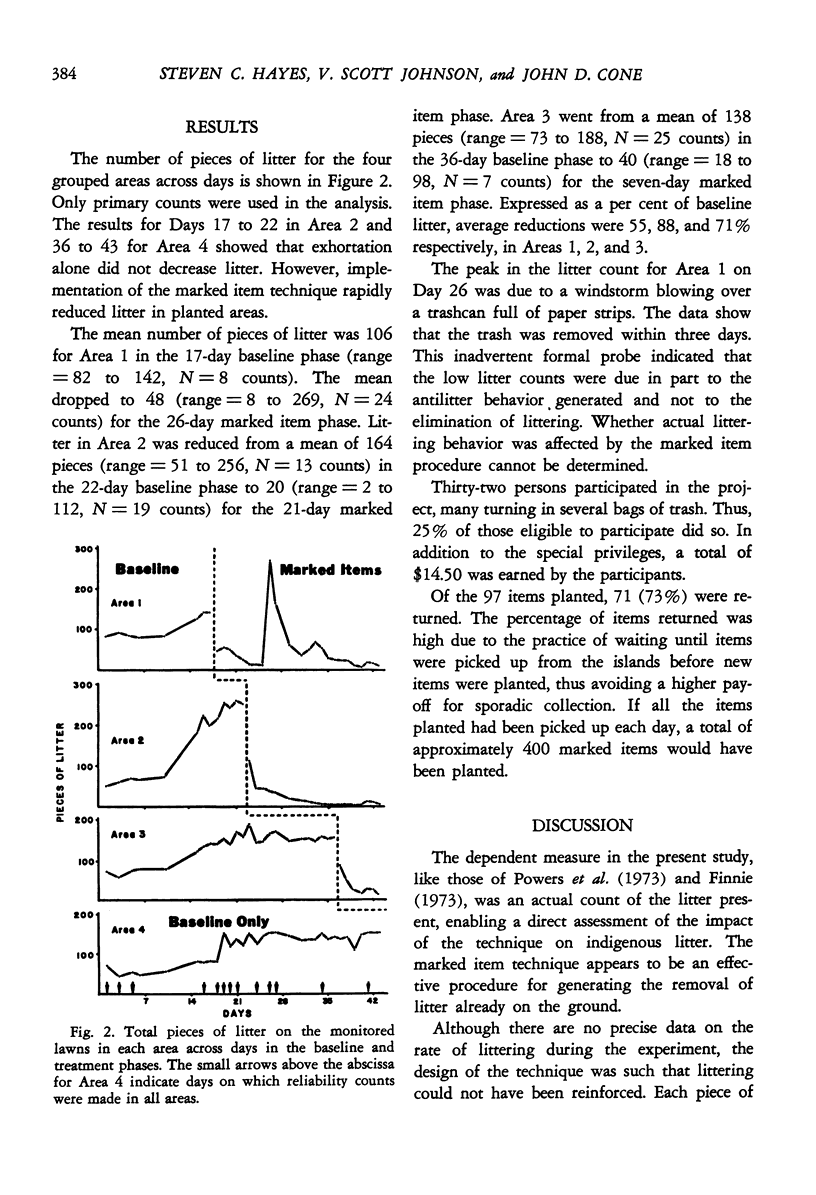
Unobtrusively marked items of litter were placed among existing trash on the grounds of a federal youth correctional facility. Inmates voluntarily collected trash and deposited it at a central location, where they were given money or special privileges for each piece of marked litter found. A multiple-baseline design with litter counts in three areas revealed successive reductions of 55%, 88%, and 71% after 17, 22, and 36 days of baseline, respectively. A fourth area served as a baseline-only control, and revealed no systematic changes. Advantages of the procedure over previously devised techniques were discussed and applications in other areas of pollution control suggested.
Keywords: anti-litter behavior, instructions, marked item technique, multiple baseline, prison setting, reinforcement, control of litter
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. L., Clark R. N., Hendee J. C. An experimental analysis of anti-litter procedures. J Appl Behav Anal. 1971 Summer;4(2):71–75. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1971.4-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman C., Risley T. R. Anti-litter procedures in an urban high-density area. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Fall;7(3):377–383. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. N., Burgess R. L., Hendee J. C. The development of anti-litter behavior in a forest campground. J Appl Behav Anal. 1972 Spring;5(1):1–5. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1972.5-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R. B., Osborne J. G., Anderson E. G. Positive reinforcement of litter removal in the natural environment. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Winter;6(4):579–586. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


