Abstract
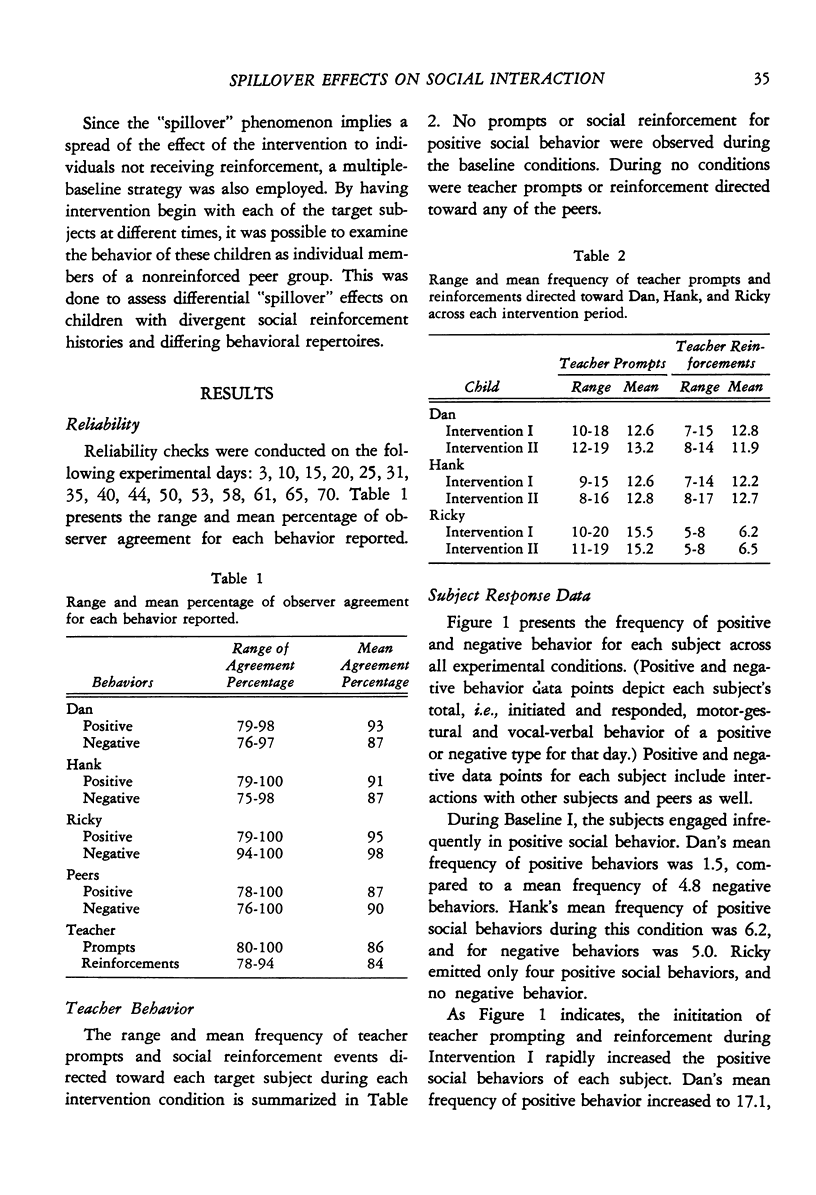
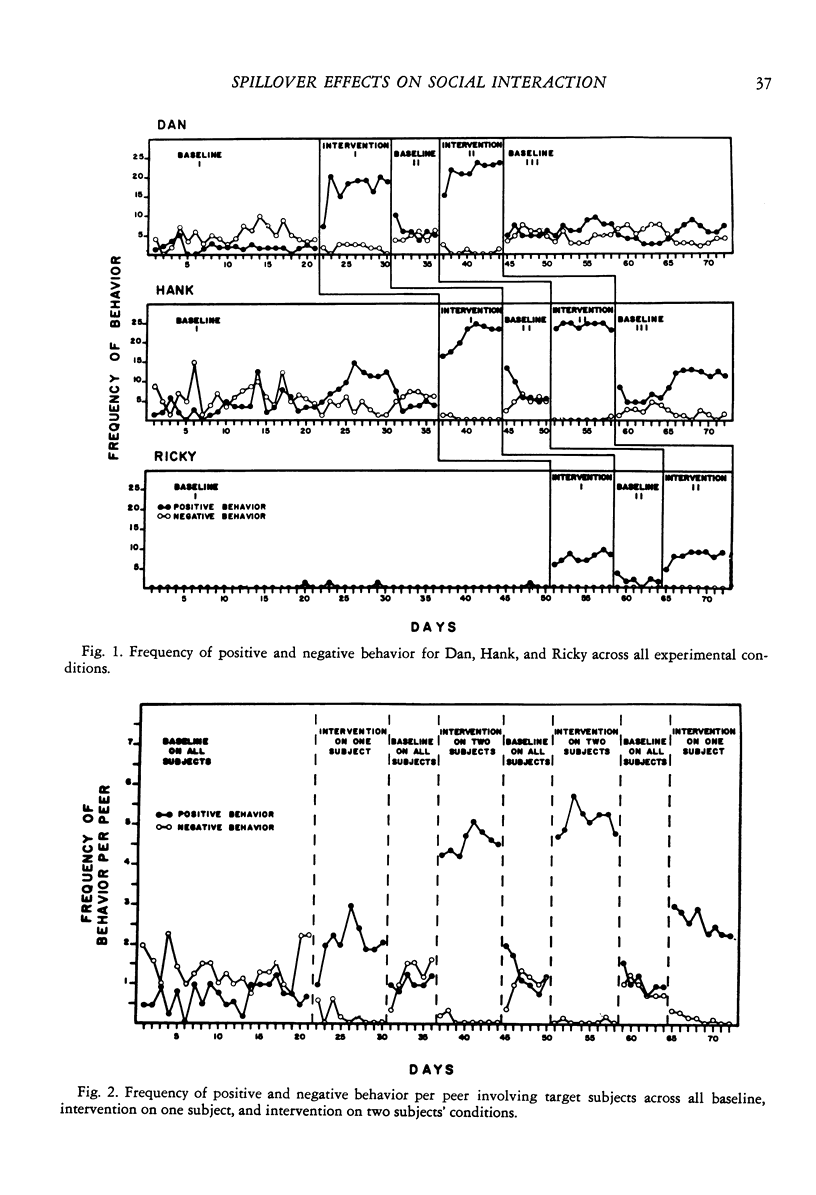
The effects of prompting and social reinforcement directed to target subjects on their social behavior and that of peers who never received prompting and reinforcement for positive social behavior, were examined. In a combined reversal and multiple-baseline design, three behaviorally handicapped preschool boys who exhibited divergent social behavior repertoires and varied histories with social reinforcement events were sequentially exposed to intervention conditions in order to investigate "spillover" of treatment effects. Prompting and reinforcement increased positive social behavior and decreased negative social behavior emitted by all target subjects. The results also demonstrated a "spillover" effect on two target subjects, who at various times were not under intervention, and on the peers as well. The findings suggest that: (a) the direct and indirect effects of intervention procedures may be enhanced by designing treatment based on the social repertoire and reinforcement histories of the subjects; and (b) the treatment "spillover" effect may be increased by applying procedures to two children at once, rather than at one at a time.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer D. M., Wolf M. M., Risley T. R. Some current dimensions of applied behavior analysis. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):91–97. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broden M., Bruce C., Mitchell M. A., Carter V., Hall R. V. Effects of teacher attention on attending behavior of two boys at adjacent desks. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Fall;3(3):199–203. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buell J. Collateral social development accompanying reinforcement of outdoor play in a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Summer;1(2):167–173. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charlesworth R., Hartup W. W. Positive social reinforecement in the nursery school peer group. Child Dev. 1967 Dec;38(4):993–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabman R. S., Lahey B. B. Feedback in classroom behavior modification: effects on the target and her classmates. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):591–598. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabman R., Spitalnik R., Spitalnik K. Sociometric and disruptive behavior as a function of four types of token reinforcement programs. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Spring;7(1):93–101. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia E., Guess D., Byrnes J. Development of syntax in a retarded girl using procedures of imitation, reinforcement, and modelling. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Summer;6(2):299–310. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. V., Lund D., Jackson D. Effects of teacher attention on study behavior. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):1–12. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. M., Reynolds N. J., Baer D. M., Brawley E. R., Harris F. R. Effect of contingent and non-contingent social reinforcement on the cooperative play of a preschool child. J Appl Behav Anal. 1968 Spring;1(1):73–76. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1968.1-73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartup W. W., Glazer J. A., Charlesworth R. Peer reinforcement and sociometric status. Child Dev. 1967 Dec;38(4):1017–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazdin A. E. The effect of vicarious reinforcement on attentive behavior in the classroom. J Appl Behav Anal. 1973 Spring;6(1):71–78. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1973.6-71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirby F. D., Toler H. C. Modification of preschool isolate behavior: a case study. J Appl Behav Anal. 1970 Winter;3(4):309–314. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1970.3-309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn M. The child as a determinant of his peers' approach to him. J Genet Psychol. 1966 Sep;109(1ST):91–100. doi: 10.1080/00221325.1966.10533683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL H. R., MCCANDLESS B. R. A study in prediction of social behavior of preschool children. Child Dev. 1957 Jun;28(2):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'connor R. D. Modification of social withdrawal through symbolic modeling. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Spring;2(1):15–22. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris S. G., Cairns R. B. An experimental and ethological analysis of social reinforcement with retarded children. Child Dev. 1972 Sep;43(3):717–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strain P. S., Timm M. A. An experimental analysis of social interaction between a behaviorally disordered preschool child and her classroom peers. J Appl Behav Anal. 1974 Winter;7(4):583–590. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1974.7-583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt P. R., Ulrich R. E., Hawkins R. P. An elementary student as a behavioral engineer. J Appl Behav Anal. 1969 Summer;2(2):85–92. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1969.2-85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


